Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (24): 3773-3779.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0861
Seven joints ultrasonic score and superoxide dismutase measurement for assessing the activity of rheumatoid arthritis
Xu Jia1, Gao Song2, Mo Han-you1, Shi Yu-hong1
- 1Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, 2Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2018-01-04Online:2018-08-28Published:2018-08-28 -
Contact:Shi Yu-hong, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Rheumatism and Immunity, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xu Jia, Master, Lecturer, Department of Rheumatism and Immunity, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81460257; the Self-Financing Project of Health Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. Z2013518
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Jia1, Gao Song2, Mo Han-you1, Shi Yu-hong1. Seven joints ultrasonic score and superoxide dismutase measurement for assessing the activity of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3773-3779.
share this article
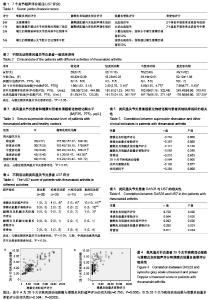
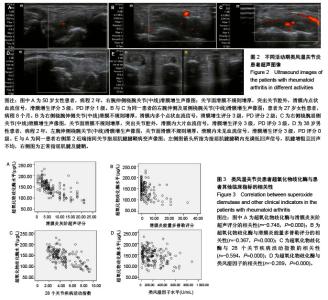
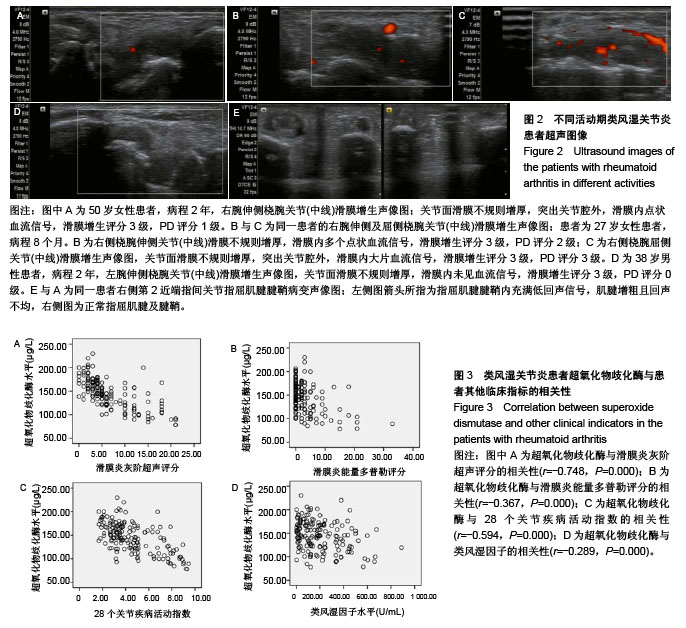
轻、中、重度活动期类风湿关节炎患者DAS28评分及血清类风湿因子水平高于稳定期类风湿关节炎患者(P < 0.05)。不同活动期类风湿关节炎患者血清抗环瓜氨酸多肽抗体接近(P > 0.05)。 2.2 血清超氧化物歧化酶水平 血样进行超氧化物歧化酶检测,检测方法按试剂盒说明书步骤执行。轻、中、重度活动期类风湿关节炎患者血清超氧化物歧化酶水平均低于稳定期患者和健康对照组(P < 0.05)。轻度活动期类风湿关节炎患者血清超氧化物歧化酶水平较中度活动期类风湿关节炎患者略有升高,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。健康对照者和稳定期类风湿关节炎患者血清超氧化物歧化酶水平接近(P > 0.05;表3)。 2.3 US7评分 重度活动期类风湿关节炎患者US7评分中滑膜炎灰阶超声、滑膜炎能量多普勒评分和腱鞘炎及肌腱炎灰阶超声评分高于稳定期患者(P < 0.05),且滑膜炎能量多普勒评分同时也高于轻、中度活动期患者(P < 0.05)。轻、中度活动期类风湿关节炎患者滑膜炎灰阶超声评分高于稳定期患者(P < 0.05)。不同活动期类风湿关节炎患者骨侵蚀评分接近(P > 0.05;表4,图2)。 2.4 类风湿关节炎患者超氧化物歧化酶与患者其他临床指标的相关性 类风湿关节炎患者超氧化物歧化酶水平与US7评分中滑膜炎灰阶超声评分、滑膜炎能量多普勒评分、"
| [1] Cruz ME, Manuela Gaspar M, Bárbara M, et al. Liposomal superoxide dismutases and their use in the treatment of experimental arthritis. Methods Enzymol. 2005;391:395-413.[2] Walther M, Harms H, Krenn V, et al. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(2):331-338.[3] Szkudlarek M, Court-Payen M, Jacobsen S, et al. Interobserver agreement in ultrasonography of the finger and toe joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(4):955-962.[4] Reiche BE, Ohrndorf S, Feist E, et al. Usefulness of power Doppler ultrasound for prediction of re-therapy with rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study of longstanding rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(2):204-216. [5] Ishibashi T, Sato B, Shibata S, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of infused molecular hydrogen in saline on rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;21(2):468-473. [6] Zhang G, Zhao MS, Xia RH, et al. Relationship between oxidative stress and depression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2012;44(2):199-203.[7] Wruck CJ, Fragoulis A, Gurzynski A, et al. Role of oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: insights from the Nrf2-knockout mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(5):844-850. [8] Naredo E, Rodríguez M, Campos C, et al. Validity, reproducibility, and responsiveness of a twelve-joint simplified power doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(4):515-522. [9] Backhaus M, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H, et al. Evaluation of a novel 7-joint ultrasound score in daily rheumatologic practice: a pilot project. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(9):1194-1201. [10] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(4):265-270.[11] Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492-509. [12] 曲世晶,叶华,贾汝琳,等.血清学阴性类风湿关节炎关节液中抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体?抗突变型瓜氨酸波形蛋白抗体的测定及临床意义[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(6):933-936.[13] Nash KM, Ahmed S. Nanomedicine in the ROS-mediated pathophysiology: Applications and clinical advances. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(8):2033-2040. [14] 李婷,包军,殷健,等.抗环瓜氨酸多肽抗体在类风湿关节炎诊断中的价值[J].中华内科杂志,2011,50(2):99-101.[15] Haye Salinas MJ, Retamozo S, Vetorazzi L, et al. Anticitrulin antibody and the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicina (B Aires). 2013;73(1):21-25.[16] Stamp LK, Khalilova I, Tarr JM, et al. Myeloperoxidase and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(10):1796-1803. [17] Hitchon CA, El-Gabalawy HS. Oxidation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(6):265-278. [18] Ryu H, Chung Y. Regulation of IL-17 in atherosclerosis and related autoimmunity. Cytokine. 2015;74(2):219-227.[19] Abdollahzad H, Aghdashi MA, Asghari Jafarabadi M, et al. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Inflammatory Cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Med Res. 2015; 46(7):527-533. [20] Onodera Y, Teramura T, Takehara T, et al. Reactive oxygen species induce Cox-2 expression via TAK1 activation in synovial fibroblast cells. FEBS Open Bio. 2015;5:492-501.[21] 余菲,徐亮.血清SOD活性和胱抑素浓度在类风湿关节炎并发早期肾损伤中的意义[J].皖南医学院学报,2015,34(5):427-429.[22] Wang JG, Xu WD, Zhai WT, et al. Disorders in angiogenesis and redox pathways are main factors contributing to the progression of rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative proteomics study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(4):993-1004.[23] Kasama T, Kobayashi K, Sekine F, et al. Follow-up study of lipid peroxides, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in the synovial membrane, serum and liver of young and old mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Life Sci. 1988;43(23):1887-1896.[24] Veselinovic M, Barudzic N, Vuletic M, et al. Oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis patients: relationship to diseases activity. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;391(1-2):225-232.[25] 李拾林,吕国荣,胡麦果等.超声评分法评价类风湿关节炎的意义[J].中国超声医学杂志,2014,30(6):266-269. [26] Strunk J, Strube K, Rumbaur C, et al. Interobserver agreement in two- and three-dimensional power Doppler sonographic assessment of synovial vascularity during anti-inflammatory treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ultraschall Med. 2007;28(4):409-415.[27] Girardelli M, Bianco AM, Marcuzzi A, et al. A comparative analysis of serologic parameters and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: reply to Mishra and colleagues. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(9):2445-2446. [28] Filippin LI, Vercelino R, Marroni NP, et al. Redox signalling and the inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152(3):415-422. [29] Di Minno MN, Ambrosino P, Lupoli R, et al. Clinical assessment of endothelial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of literature studies. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(10): 835-842.[30] Dougados M, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Ferlet JF, et al. The ability of synovitis to predict structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study between clinical examination and ultrasound. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(5):665-671. [31] Herz B, Albrecht A, Englbrecht M, et al. Osteitis and synovitis, but not bone erosion, is associated with proteoglycan loss and microstructure damage in the cartilage of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1101-1106. [32] Hammer HB, Kvien TK. Comparisons of 7- to 78-joint ultrasonography scores: all different joint combinations show equal response to adalimumab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(3):R78. [33] 郑洁,张文静,邱少东,等.改良的7关节半定量超声对类风湿关节炎治疗前后的评价[J].中国超声医学杂志,2016,32(2):170-172.[34] Ceponis A, Onishi M, Bluestein HG, et al. Utility of the ultrasound examination of the hand and wrist joints in the management of established rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(2):236-244. [35] Szkudlarek M, Klarlund M, Narvestad E, et al. Ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography and clinical examination. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(2):R52. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||