Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (24): 3780-3785.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0818
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of volleyball exercise with bone mineral density in females at different ages
Luo Wei
- Department of Physical Education, Zhengzhou Chenggong University of Finance and Economics, Zhengzhou 451200, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2017-12-14 -
About author:Luo Wei, Master, Lecturer, Department of Physical Education, Zhengzhou Chenggong University of Finance and Economics, Zhengzhou 451200, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research & Development Program of Henan Province, No. 172102310163
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Wei. Correlation of volleyball exercise with bone mineral density in females at different ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3780-3785.
share this article
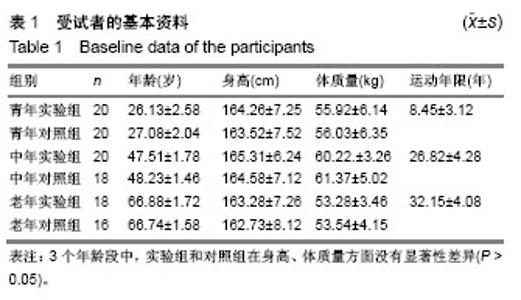
2.1 受试者数量分析 实验中112名受试者根据实验方案全部进行了相关部位的骨密度测定。通过SPSS 20.0数据统计软件对所得数据进行boxplot检验,发现1个奇异值,因此该受试者的数据被剔除。对于出现的极值进行了3次重复测定,发现数据可靠性强,取其平均值作为最终数据,因此实验有效受试者的数量为111名。 2.2 实验组和对照组受试者基线资料分析 由于人体的骨密度和身高体质量有显著的相关性[18-19],因此在实验前对不同年龄段受试者的实验组和对照组进行了独立样本的t 检验,结果发现3个年龄段中,实验组和对照组在身高、体质量方面差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),这就排除了身高体质量对骨密度的影响。见表1。"
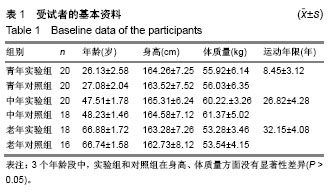
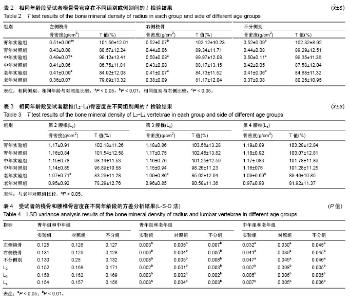
2.3 相同年龄段受试者桡骨骨密度的组间比较和侧别比较 见表2。通过对相同年龄段实验组和对照组受试者桡骨骨密度的均值比较发现,无论左侧、右侧还是不分侧别,实验组和对照组在各个年龄段差异均有显著性意义 (P 0.05),尤其是青年组右侧桡骨实验组与对照组差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。在进行相同组别的侧别比较时发现,除青年实验组外(P < 0.05),其他5组差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。< 2.4 相同年龄段受试者腰椎(L2-L4)骨密度的组间比较 见表3。通过对相同年龄段实验组和对照组受试者腰椎(L2-L4)骨密度进行均值比较后发现,青年阶段和中年阶段的L2、L3和L4的骨密度差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但是老年阶段实验组的L2、L3和L4的骨密度却高于对照组(P < 0.05)。 2.5 受试者相关部位骨密度的不同年龄段差异 见表4。通过对受试者的桡骨和腰椎(L2-L4)骨密度在不同年龄段间进行单方差分析后发现,青年组和中年组在各个观测指标上差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),青年组和老年组所有观测指标差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01),中年组和老年组差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),尤其是L2、L3和L4差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。"
| [1] 李力研.“世界3”与“人造动物园”-文明历程中的灵肉分裂与体育运动(上)[J].体育文化导刊,2004,12:14-15,17.[2] 中国健康促进基金会骨质疏松防治中国白皮书编委会.骨质疏松症中国白皮书[J].中国健康管理学杂志,2009,3(3):148-154.[3] Budhia S,Mikyas Y,Tang M,et al.Osteoporotic fractures: asystematic review of U.S.healthcare costs and resourceutilization.Pharmacoeconomics.2012;30(2):147-170.[4] Watts NB,GLOW investigators. Insights from the Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women( GLOW).Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(7):412-422.[5] El Hadidy el HM, Ghonaim M, El Gawad SSh, et al.Impact of severity,duration,and etiology of hyperthyroidism on bone turnover markers and bone mineral density in men. BMC Endocr Disord. 2011;11:15.[6] Turner AG,Anderson PH,Morris HA.Vitamin D and bone health.J Clin Lab Invest Suppl.2012;243(4):65-72.[7] Frost HM.Skeletal structure adapations to mechanical usage(SATMU):1.Redefining Wolff law:the bone modeline problem.Anat Rec.1990;226(4):403-413.[8] 赵桂增,程瑞换,介崇崇,等.太极拳运动对中老年人轻度抑郁症影响的研究[J]. 中国疗养医学,2015,24(5):452-454.[9] Polymeris A,Michalakis K,Sarantopoulou V.Secondary underlying mechanisms.Endocr Regul.2013;47(3):137-148.[10] Gómez C A,Ara I,González-Agüero A,et al.Effects of Training on Bone Mass in older Adults:a Systematic Review.Sports Med.2012;42(4): 25-301.[11] 王春燕,何成奇.骨质疏松症治疗中的运动疗法[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(37):6657-6663.[12] 李雯.当代排球:全民健身与娱乐[J].体育文化导刊,2015,11: 42-45.[13] 周强,丁世聪.日本妈妈排球运动的发展及其启示[J].体育文化导刊,2012,1:28-32. [14] 安珍,程静,王文志,等.峰值骨量与骨质疏松症[J].现代康复, 2001,5(2):14-17[15] Yusuke I,Kazutaka M,Koichi K.Analysis Of Trunk Muscle Activity In The S-ide Medicine-Ball Throw. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(8):2231-2240.[16] 范尧.核心力量训练过程中排球运动员跳发球速度与成功率变化规律及其提升机制[J].成都体育学院学报,2016,42(3):83-89.[17] 叶美婷,黄抒佳,王保兵,等.骨密度测量部位选择分析[J].中国辐射卫生,2012,21(1):90-91.[18] 黄陈恕,吴景全,朱艳琳.重庆地区中老年男性骨质疏松症患者骨密度与年龄、身高、体质量、体质量指数关系研究[J].四川医学,2016,37(7):717-720. [19] 毛未贤,张萌萌,马倩倩,等 长春地区女性骨密度与年龄、绝经年限、体重指数的相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,22(9): 1083-1086.[20] 文思敏.全身垂直振动对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨组织微结构和强度的影响[D].北京:首都体育学院,2014.[21] 谭雄进,王前,郑磊,等.不同年龄尾吊鼠负重骨骨代谢及力学性能变化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2003,9(1):6-8.[22] 李红娟,王正珍,严翊.体力活动与骨健康[J].北京体育大学学报,2012,35(8):37-42.[23] 李在军,邹晓丽.羽毛球运动对女大学生骨密度的影响[J].当代体育科技,2012,2(34):12-14. [24] 袁曦,朱李,王高,等.跑步和羽毛球运动对女大学生骨密度和相关血清指标影响的对比研究[J].国际检验医学杂志,2017,38(15): 2091-2093.[25] 钱芊.大学生田径运动员和普通大学生不同部位骨密度的均值比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32):5097-5102.[26] 金绪忠,吴纪饶.健美操运动对男大学生骨密度和骨代谢的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2011,32(7):814-815.[27] 张颖,赵克勇.健美操运动对女大学生骨密度影响的实验研究[J].保健医学研究与实践,2011,8(4):16-19.[28] 梁芝栋.大学生篮球运动员和普系学生的指长比差异[J].体育科技文献通报,2016,24(5):82-83.[29] 梁芝栋.人类指(趾)长比与运动能力关系研究的现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(29):4383-4388.[30] 梁芝栋.大学生篮球运动员和普系学生的指长比均值比较[J].体育学刊,2017,24(2):135-139.[31] 席磊.健身操和瑜伽交替练习对女大学生体成分、骨密度及心肺功能等的影响研究[D].曲阜:曲阜师范大学,2011.[32] 陈玉群.武术套路运动对青年期女性骨密度和骨代谢的影响[J].南京体育学院学报:自然科学版,2013,12(1):26-29.[33] 尹海滨.武术桩功练习对老年人骨密度和骨代谢生化标志物的影响[J].2013,19(5):479-481.[34] 刘武. 武术运动对青春后期女性骨密度以及基本体质指标的影响[J].2008,34(11):78-80.[35] 张丽,王美月.武术套路运动对女大学生骨密度和基本体质指标的影响[J].体育科技文献通报,2008,16(12):91-92. [36] 葛男,宋相勳,宋信穎.12周篮球运动训练对肥胖男大学生身体成分和骨骼密度影响的研究[J].曲阜师范大学学报,2014,40(3): 92-97.[37] 陈志斌,邓小林.太极拳和篮球运动对老年人骨代谢影响的比较[J].体育学刊,2002,5(11):31-32.[38] 姚鑫,罗琳,洪邦辉,等.太极拳运动对老年男性骨质疏松患者锻炼情绪及骨密度和生理指标的影响[J].贵州师范大学学报:自然科学版,2016,34(3):32-36.[39] 赵立君,李凤丽,陈琼,等.篮球专业和非篮球专业男性大学生身体不同部位骨密度对比分析[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2007, 33(6): 1077-1079. [40] 杨浩然.乒乓球运动对跟骨骨密度的影响[J].湖北体育科技,2008,7(6):692-693. [41] 成磊,雷云,胡燕,等.八段锦锻炼对社区围绝经期女性骨密度影响[J].中外医学研究,2017,15(1):135-137.[42] 郭梁,邹亮畴.网球运动对男性青少年骨密度的影响[J].吉林体育学院学报,2010,7(2):282,300.[43] 袁春华,陈佩杰,陈敏雄.男性青少年骨密度与下肢跳跃能力的关系及运动训练对其影响[J].体育学刊,2004,11( 6):39-41.[44] 徐锋鹏,胡敏,黄俊豪,等.不同类型运动对骨密度影响的研究进展[J].上海体育学院学报,2017,41(1):55-60.[45] 阿英嘎.不同项目选项课班大学生跟骨骨密度的比较研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2004,19(4):99-100.[46] 梁文会,周玲,宋平,等.不同人群骨密度与体重和肌肉功能相关性分析[J].现代预防医学,2004,31(2):194-195.[47] 徐世民,刘鹏.太极对预防绝经后女性骨密度的荟萃分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(10):932-936.[48] 李颖,姜媛媛,宋宏伟.老年有氧健身操对绝经女性骨密度的影响[J].辽宁师范大学学报(自然科学版),2006,29(4):502-504.[49] 汪浩,蓝国彬.加强抗阻力锻炼对绝经女性骨密度的影响[J].山东体育学院学报,2008,24(5):35-37.[50] 刘建宇,向家俊,魏星临,等.广场舞对绝经后妇女骨密度、血清雌激素及平衡能力的影响[J].中国体育科技,2014,50(2):78-82.[51] 王娟,王正珍,李勇勤,等.ACSM 2015年世界健身趋势调查报告及对我国全民健身活动的启示[J].北京体育大学学报,2015, 38(1):51-56.[52] 林若崴,林立.大学生跟骨骨密度与跑步能力关系的研究-以北京体育大学非体育专业大学生为例[J].闽江学院学报,2017,16(2): 90-97.[53] 虞定海,王会儒,谢业雷,等.太极健骨操练习对绝经期女性骨密度的影响[J].上海体育学院学报,2014,38(6):100-104.[54] 高凤霞,张晓颖,李卫民,等.北京市平谷地区围绝经期妇女健康现状及认知状况调查[J].生殖医学杂志,2014,23(7):552-556.[55] 乔玉成.Cochrane 评价:绝经后妇女骨质疏松运动干预效果的比较[J].中国体育科技,2010,46 (6):121-128.[56] 周勇.运动锻炼防治绝经女性腰椎L2-4骨质疏松的作用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(1):72-74.[57] 王文志,杨定焯,全婷,等.体重对青年人骨矿含量和骨密度的影响[J].现代预防医学,2009,36(18):3590-3591.[58] 黄何平,宁亮生,温志宏.跟骨骨密度及骨强度与运动的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,200812(46): 9134-9137.[59] 董宏,孟良,王荣辉.体育锻炼对中老年人群骨密度影响的meta 分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2016,39(3): 58-65,87.[60] 李萍,孙平辉,孙茹.长期运动训练对男大学生身体各部位骨密度的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2005,31(4): 634-635.、[61] 谢欣池,谢玉萍.网球运动对中年肥胖女性身体成分的影响研究[J].当代体育科技,2012,2(16):12-13.[62] 魏亚茹,赵文艳,杜唯,等.黑龙江省体育院校大学生运动专项与骨密度的相关性研究[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2011,29(5): 119-122.[63] 王晓燕,马冠生,张倩,等.青春期男生全身骨量与体成分相关分析研究[J].中国热带医学,2007,26(4):67-69.[64] 孙晓.长期排球训练对男大学生身体不同部位骨密度的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2006,25(5):54-56.[65] 罗冬林,邹亮畴,范毅方,等.排球运动对男性青年骨量与身体成分的影响[J].广州体育学院学报,2009,29(6):72-74.[66] 朱欢,李荣娟,李峰,等.长期气排球运动对绝经后妇女骨密度的影响[J].湖北师范学院学报:自然科学版,2016,36(1):50-53.[67] 沈华.不同形式的健身运动和体成分对中老年女性骨密度的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2008,34(12):71-74.[68] Calbet JA, DiazHerrera P, Rodriguez LP.High bone mineral density in male elite professional volleyball player. Osteoporeslnt.1999;10:468-474.[69] Duchera G,Courteixa D,Mêmeb S,et al.Bone geometry in response to long-term tennis playing and its relationship with muscle volume:A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study in tennis players.Bone.2005;37:457-466.[70] 张京鲁,盖凌,刘淑敏,等.女子足球运动员与无运动训练女大学生腰椎、股骨颈骨密度比较[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2): 167-169.[71] 谢志丹.体育舞蹈运动对女大学生骨密度和身体成分的影响[D].西安:西安体育学院,2013.[72] 汪六六,沈彤,游丽琴,等.成人骨密度随年龄变化趋势分析[J].中国公共卫生,2001,17(2):157. [73] 张健,赵斐,张勇.雌激素、运动与绝经后骨质疏松症[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2009,28(3):67-69, 73. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Fan Jiabing, Zhang Junmei. Morphological measurement and analysis of the mandible in adult females with different vertical skeletal types [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1177-1183. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||