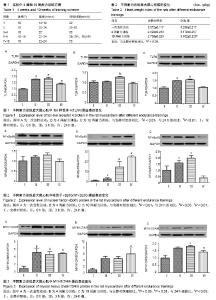
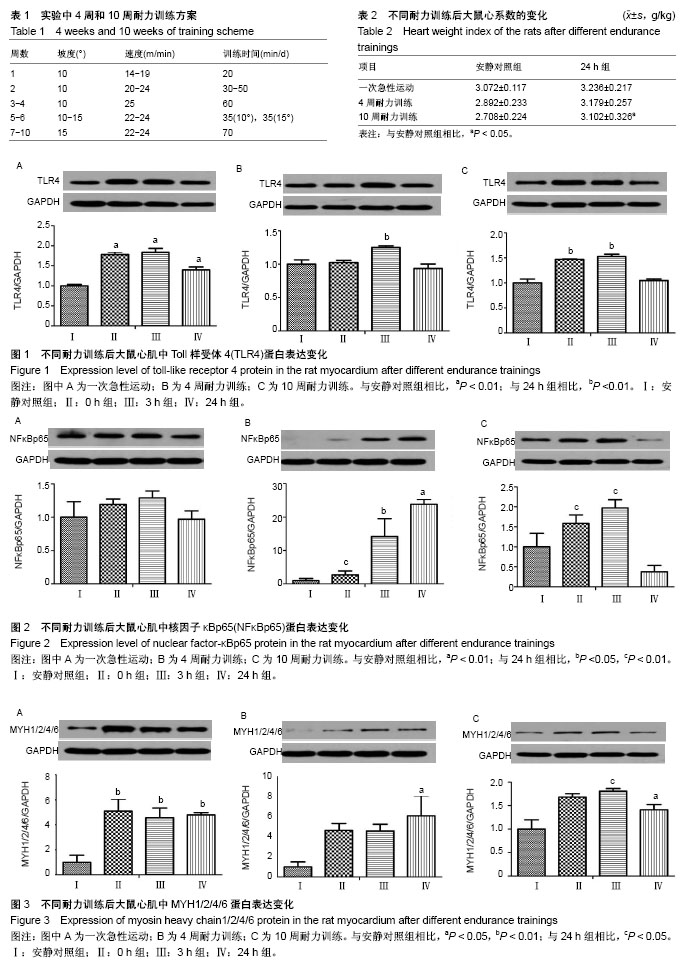
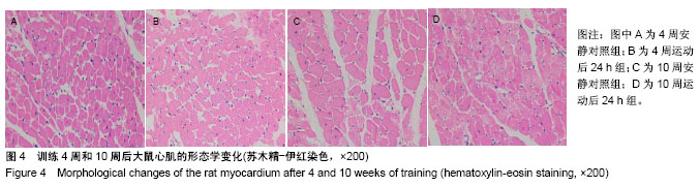
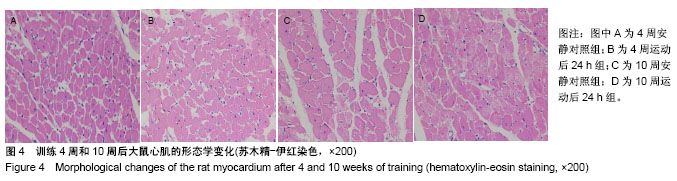
| [1] 唐朝枢,于严,樊贵,等.心肌缺血再灌注损伤时心肌心钠素和血管紧张素II的变化及其病理生理意义[J].心肺血管学报, 1990,9(4): 213-216.[2] 卢章,李凡,罗菲菲.血管紧张素-(1-7)对乳鼠心肌细胞缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].岭南急诊医学杂志,2015,20(1):3-4,10.[3] Wang J, Zhang Y, Guo LL, et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits the TLR4-NFκB-TNFα pathway and attenuates neonatal rat cardiomyocyte injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(10):775-779. [4] 康晓敏,吕宏娟,王霞,等.Toll样受体4(TLR4)在血管紧张素Ⅱ (AngII)致高血压小鼠心脏纤维化中的作用[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(10):1077-1081.[5] Li Y, Ha T, Gao X, et al. NF-kappaB activation is required for the development of cardiac hypertrophy in vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287(4):H1712-1720.[6] 倪菁.细胞内信号通路对心肌肥大调控作用的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2017,37(1):168-176.[7] 贝毅桦,肖俊杰.运动诱导心脏再生:治疗心血管疾病的新途径[J].上海大学学报(自然科学版),2016,22(3):293-301.[8] Zhao M, Zhou A, Xu L, et al. The role of TLR4-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in neuroinflammation in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 2014;269:93-101.[9] 孙善美,宋鲁成.TLR4与肿瘤细胞凋亡相关性的研究进展[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2016,21(7):661-664.[10] Ha T, Li Y, Hua F, et al. Reduced cardiac hypertrophy in toll-like receptor 4-deficient mice following pressure overload. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;68(2):224-234.[11] 牵欣,徐波.中等强度耐力运动对心脏局部AngII及AT1R表达的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(8):67-71.[12] 杨锐,王芬珍.在体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中NF-κBp65与AngII的关系[J].重庆医学,2014(15):1901-1903.[13] 蔡辉,郭郡浩,商玮,等.压力负荷增加大鼠模型心肌α-MHC和β-MHC mRNA的表达[J].医学研究学报, 2009,22(10): 1032-1035.[14] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.[15] 王蕴红,赵明华,梁蕾,等.耐力训练对大鼠心肌JAKs和SOCSs表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2):181-183,191.[16] 张丽琴,王蕴红,赵明华,等.运动对大鼠心肌FOS和HSP70表达的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2010,33(2):64-66,70.[17] 赵祎镭,李丹露.心肌肥厚模型建立方法的研究进展[J].中国药房, 2014,25(5):473-475.[18] Deguine J, Barton GM. MyD88: a central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:97.[19] 李维根,陈晓彤,高云秋,等.大鼠极量运动后心肌血管紧张素Ⅱ的变化[J].中国运动医学杂志,1994,13(1):11-12,63-64.[20] 季丽萍,李平,冯照军.补肾益气中药对运动大鼠心脏内分泌影响[J].中国公共卫生,2010,26(12):1548-1550.[21] 陈雷.高强度游泳训练后AngII介导小鼠心肌细胞损伤中TLR4信号通路的作用[J].北京体育大学学报,2016,39(12):56-61.[22] Cristi-Montero C, Sánchez-Collado P, Veneroso C, et al. Effect of an acute exercise bout on Toll-like receptor 4 and inflammatory mechanisms in rat heart. Rev Med Chil. 2012; 140(10):1282-1288.[23] 王晓晨,吉爱国.NF-κB信号通路与炎症反应[J].生理科学进展, 2014,45(1):68-71.[24] 刘新育,顾剑民,薛松.NF-κB与心肌缺血再灌注损伤的研究现状及展望[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2016,32(1):55-58.[25] 尹雨芳,林强,曹建民,等.壳寡糖抗运动疲劳及对运动性免疫抑制的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2016(4):146-149.[26] 马继政,孙飙,吕远远.IGF-PI3K-Akt信号通路在生理性心肌肥大中的作用研究进展[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 6(3):6-10.[27] 温宝驹.PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号在运动性心肌肥大中的作用研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2013.[28] 李跃华,哈团柱,陈琪,等. NF-κB参与Akt信号途径激活诱导的心肌肥大[J].中国病理生理杂志,2005,21(3):484-488.[29] Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY, et al. Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(22):18934-18940.[30] 王蕴红,吴剑,陈一月,等.心肌信号通路激活水平的训练差异[C].中国生理学会运动生理学专业委员会会议暨"运动与血管保护"学术研讨会,西安,2015:6-7. [31] Jiang DS, Luo YX, Zhang R, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 protects against cardiac hypertrophy by targeting myocardin. Hypertension. 2014;63(1):119-127.[32] Jiang DS, Bian ZY, Zhang Y, et al. Role of interferon regulatory factor 4 in the regulation of pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension. 2013;61(6):1193-1202.[33] Wang J, Guo X, Dhalla NS. Modification of myosin protein and gene expression in failing hearts due to myocardial infarction by enalapril or losartan. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004; 1690(2):177-184.[34] 张丽娜,张天良,金国琴.巴戟天对D-半乳糖致衰老大鼠心肌细胞肌球蛋白和肌动蛋白基因表达的影响[J].中国老年学, 2011, 31(24):4836-4838.[35] 刘旭东,周里.间歇低氧训练对SD大鼠心肌肌球蛋白重链表达的影响[J].山东体育学院学报,2010,26(7):42-45.[36] Shave R, Ross P, Low D, et al. Cardiac troponin I is released following high-intensity short-duration exercise in healthy humans. Int J Cardiol. 2010;145(2):337-339.[37] 刘璐,施孟,刘祥梅.醋制泥鳅对游泳训练并力竭小鼠心肌HGF和MHC基因表达的影响[J].山西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 29(1):62-67.[38] 刘璐,刘祥梅,谭军,等.小鼠心肌MHC和TM1基因表达的运动训练实验研究[J].体育科学研究,2015,19(6):47-52. |