Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hemostatic dressings for prehospital trauma care: strengths, problems and prospects
Sun Guo-fei, Liu Jian-heng, Zhang Li-cheng, Zhang Li-hai, Tang Pei-fu
- Department of Orthopaedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2017-12-18Online:2018-08-08Published:2018-08-08 -
Contact:Tang Pei-fu, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Sun Guo-fei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopaedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the General Project, No. CWS14CO66; the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. AWS14C003; the Major Sub-topics, No. 2016YFC1102005
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Guo-fei, Liu Jian-heng, Zhang Li-cheng, Zhang Li-hai, Tang Pei-fu. Hemostatic dressings for prehospital trauma care: strengths, problems and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0735.
share this article
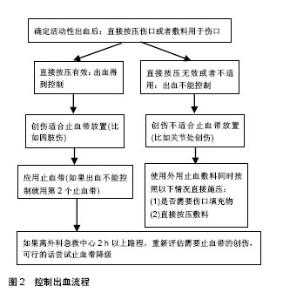
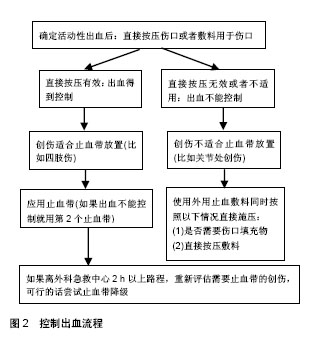
2.1 止血敷料的理想性质 动脉和静脉出血是两种不同的出血类型。在战场或紧急环境下由于创伤的严重性和复杂性,很难辨认出血是属于哪种类型出血,所以没必要区分止血剂是否为动脉或静脉止血,理想的止血剂应是对动静脉出血都起到很好的止血效果。 在2003年,美国陆军外科研究所的Pusateri 等[13,15,19,24]阐述了用于院前或战场上理想止血敷料的特征。总结为:能够在出血时2 min内止住大动脉和静脉出血;可即时使用,无需现场搅拌或使用前制备;使用简单,受伤者、同伴或医务兵经过最简单培训都可用;具有质轻且耐用的特性;在恶劣环境下至少有2年的保质期(在-10至55 ℃的范围都可用);使用安全,无组织损伤或感染的风险;是廉价的。除了由Pusateri等提到的标准,没有免疫原性并在手术时容易去除也是必不可少的[9,13,25-26]。目前简易爆炸装置是战场上创伤的主要来源之一,其可能导致伤口有不规则的深度和几何形状,因此,止血剂敷料的可塑性也是必不可少的[12,27]。 2.2 止血敷料的分类 止血敷料按照作用机制进行分类:①浓缩因子类:这类止血剂通过快速吸收血液中的水分进行止血,使红细胞和蛋白质成分浓缩,导致血凝块的形成、QuikClot、QuikClot ACS(高级凝血海绵)、TraumaDex、和自我扩张止血聚合物都是这类;②黏附剂:通过粘连组织并物理封闭创伤出血口,HemCon和Celox是这类的主要样品;③补充促凝因子类:主要通过释放促凝因子到创伤位置达到凝血效果,干纤维蛋白胶敷料(DFSD)是这类敷料[28-30]。此外还可按照成分进行分为矿物类,比如QuikClot Advanced和WoundStat,吸收水分,浓缩红细胞和凝血因子,但产生放热反应;壳聚糖类,比如HemCon ChitoFlex(HCF)和HemCon ChitoGauze(HCG),具有黏附于伤口作用;乙酰化葡萄糖胺类,比如mRDH,是使用乙酰化的聚-N-乙酰基葡糖胺作为有效成分,使血小板结合、凝血级联反应活化、红细胞聚集及局部血管收缩。 用于控制表皮伤口渗血的止血方法也可通过作用机制进行分类,主要是机械性方法(比如直接按压)、物理性方法(比如烧灼)和生理性方法(比如纤维蛋白、自身凝血酶、胶原蛋白和肾上腺素)[31]。美国食品和药物管理局将止血敷料作为第二类医疗器械[32]。目前有几种止血剂已获得美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)和CE的批准并用于创伤部位,这其中包括QuikClot,是在2002年第一个被FDA批准的外用止血剂,其后形成的QuikClot ACS+(2006年7月批准的,由同一家公司生产)、自我膨胀止血聚合物(SEHP)、HemCon、Celox、改性快速部署止血剂(MRDH)、WoundStat、combatgauze、FASTACT/SeraSeal和TraumaDex都获得批准。目前几种止血剂得到了开发,如QuikClot、QuikClot ACS+、HemCon、WoundStat和CombatGauze,已应用到实践中[13,33-35]。 2.3 常用止血敷料的结构组成与分析 QuikClot是一种合成的颗粒状矿物沸石,由硅氧化物、钠、铝、镁组成,还包括少量石英,含有1%水分,可快速吸附水分子[26]。QuikClot的主要止血机制是吸收水分子,浓缩血小板、红细胞和凝血因子来进一步促进血凝块形成,避免了物种间疾病传播和过敏反应,对凝血障碍者的止血效果 差[36]。但这个过程产生热量(是放热反应),是由于吸收血液中的水分后会放出大量的热,导致伤口炎症。根据从动物研究和病例报告获取的资料,由放热反应带来的热损伤和烧伤以及生物降解能力差是QuikClot面临的主要挑战[6,37-38]。因此,对QuikClot进行改良产生第二代产品,高级凝血海绵(QuikClot Advanced Clotting Sponge,ACS),是与QuikClot相同组分的较大颗粒的玻璃粉制做而成,包装成网袋,产生较小的放热反应。其他系列改良产品比如QuikClot Advanced Clotting Sponge +(ACS+),据称产生更少的热量[36-37]。QuikClo用不同铝硅酸盐矿物(即高岭土)制造出第三代产品QuikClotCombat Gauze (QCG)和QuikClot Combat Gauze XL (QCX),止血机制是激活内源性凝血途径,是促凝作用,具有独立的凝血功能,可用于具有凝血障碍的创伤者上[15,26]。 自膨胀止血聚合物(self expandinghaemostatic polymer,SEHP)是由吸水性材料形成的,由一个超吸水性聚合物和一个黏结剂组成,并包含在4×4聚合物密封袋。聚合物是粉末形状,一旦吸水并进行膨胀,可呈现各种形状填充于创伤处。自膨胀止血聚合物通过两种机制来控制出血:①机械性:当吸收血液水分时,自膨胀止血聚合物快速膨胀,直接对创伤区域产生填塞效果。由于膨胀的聚合物与创伤腔隙相吻合,压力以统一均匀的方式施压到所有出血点;②生化性:随着血液中水分的吸收,凝血因子和血小板浓缩,导致机体凝血级联反应的触发。该聚合物直接吸收水分子到内部基体中,不能通过挤压来排除水分子,与海绵吸水机制不同,无放热反应,经过了FDA/CE批准,需要进一步探讨与其他止血敷料的止血效果[39-40]。 TraumaDex是植物淀粉类,形式为多微孔多糖止血颗粒,可从天然植物马铃薯淀粉中提取,不含多肽或蛋白质,为无菌的白色粉末,具有良好的亲水性,能使血液快速脱水形成血凝块,阻止血液渗出,在体内可迅速降解、吸收,但局部组织有轻微炎症反应[41]。凝血机制为吸收水分,浓缩血小板和凝血因子,形成凝胶样基质增加凝固快[42]。类似止血敷料还有支链淀粉,又称胶淀粉,由几千个葡萄糖残基组成的多糖,具有优良的缓释、增稠、黏合、保水能力。该止血淀粉末质量轻、易携带、可用于不同伤口和可反复应用且不会影响之前的止血效果、无不良反应,有望用于战场上止血,不良反应有待进一步验证[26]。 Hemcon绷带是美国HemCon公司推出的以冻干壳聚糖为基质的止血带(HemCon Bandage),通过壳聚糖分子上质子化的胺基团吸引带负电荷的红细胞,吸附纤维蛋白原和血浆蛋白来起作用,能迅速止住大量出血,起组织黏附和机械封闭作用[27]。该绷带在美国陆军应用期间得到了发展[6,43]。壳聚糖,即聚氨基葡萄糖(碱性多糖,学名为(1,4)-2-氨基-2-脱氧-β-D-葡萄糖),是自然界中惟一的碱性多糖,具有抑菌、抗癌、降脂、增强免疫等多种生理功能,具有无毒无刺激、无免疫原性、无热源反应、不溶血、无致突变性及可自然降解、良好的组织相容性等特性,具有极大的医学应用价值,是迄今为止惟一被日本政府允许可宣传的机能性保健食 品[24]。其主要是从虾蟹壳中提取带正电的多糖,能吸引带负电的血细胞并促进血液凝固,具有黏性,能紧紧地黏附于创口,不依赖于自身传统的凝血途径[44]。壳聚糖的止血、抑菌、抗菌性、生物相容性、促进伤口愈合及易于形成凝胶的性质,赋予它用作止血材料的良好性能,柔韧性好,可供军队战斗时使用,甚至在极其恶劣的天气和地形亦可使用,它可使伤口形成结实的有黏附性的血块,然后转运伤员。止血方式依靠绷带紧紧缠绕伤口处组织来抑制流血,用这种绷带处理的伤口还可很好地阻止感染,用消毒水可使绷带轻易脱落。在使用该绷带时使其贴于出血处,而不是皮肤上,否则将不起到止血效果。实验表明在常规止血方法(压迫止血和使用止血纱布)失效的情况下,用HemCon Bandage能在2 min内止血,有优异的伤口组织修复性能。直至目前为止,HemCon已发运了超过13 000条绷带,在伊拉克和阿富汗被特种部队首先使用。 但HemCon绷带是坚硬的,难以放置在深或小的伤口,可用剪刀剪切,但仍很难应用。由于其硬度和形状,HemCon最好是用于有限区域的平面,即Hemcon的主要障碍是在恶劣条件下不能很好地发挥作用[6,39]。壳聚糖是从水生贝壳类动物得到的,对贝类过敏患者,在使用壳聚糖粉和绷带时会遇到过敏的问题,经过Waibel 等[45]临床试验研究,第一次证明海鲜贝壳类过敏者使用壳聚糖绷带未发生任何不良过敏反应。颗粒止血剂如QuikClot和WoundStat也存在一些问题,外科医生清洗伤口时,发现他们是很难去除的,而且在有风的环境下使用容易吹进救护人员的眼睛中。对此,建议使用某些止血产品的纱布型代替之。目前研究的几种新型止血纱布敷料是很有前途的,如CombatGauze、CeloxGauze、ChitoGauze。Littlejohn等[32]文献综述显示,战创纱布被证明在战场上是安全和有效的,美国食品和药物管理局批准新的壳聚糖基止血纱布CeloxGauze和ChitoGauze,它们在临床前试验中都表现出很好的止血效果,据报道在外部短期应用也是安全和有效的。活动性出血部位在开始时应用手直接按压来控制活动性出血,然后去除纱布敷料进行止血。最近美国创伤外科医师委员会提出了有关止血的循证指南,其提倡在院前创伤出血应同时使用止血带和止血剂。图2示用于偏远地区出血控制的原则[32]。"
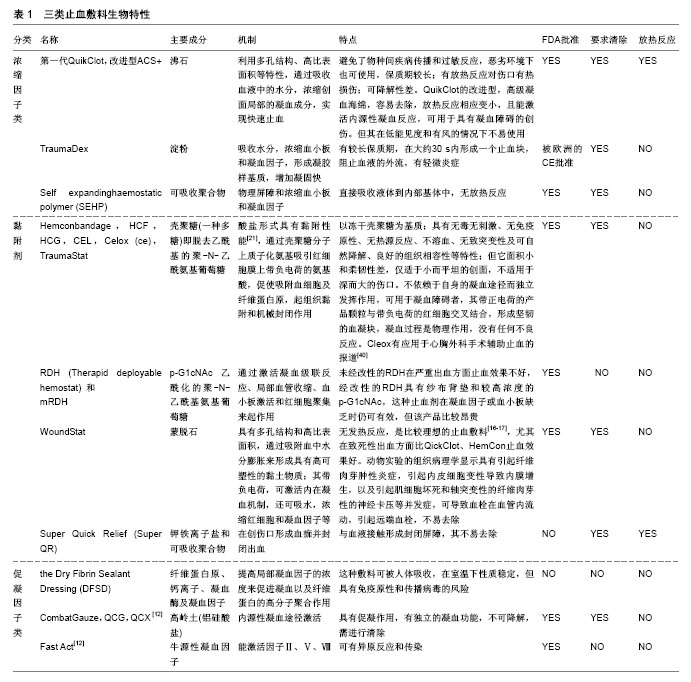
Celox的主要成分是壳聚糖颗粒,颗粒为珍珠色的,无毒无味的,其能通过吸附、脱水和与红细胞相结合来促使血凝块的形成。Celox的止血机制同HemCon Bandage,一旦直接接触血液,带正电的Celox将与带负电荷的红细胞结合,不依赖于身体的凝血机制进行止血,形成坚韧的血凝块,凝血过程是物理作用,没有任何不良反应。Celox对于那些接受抗血小板或抗凝药物的患者或是低温条件下都是有效的,不会在远离应用部位形成凝块。一旦凝块形成后,可通过清水或生理盐水冲洗伤口,移除Celox。该产品能以颗粒和绷带两种形式进行使用。Celox颗粒形态是一个轻量级的粉末,据报道将其用于临床上心胸外科辅助止血有很好的效果,但其在低能见度和有风的情况下不易使用[15,18,33,44]。 TraumaStat是一种新型的由二氧化硅、壳聚糖和聚乙烯合成的纱布般止血敷料。TraumaStat被证明优于HemCon敷料及纱布敷料,尤其是在控制活动性出血方面,有更好的止血效果及更少的止血失败率,同时还可减少失血。该敷料的一致性结构,使其与血液和凝血因子更好地接触并发生作用,形成牢固、更大的凝血 块[2,46]。 WoundStat由蒙脱石颗粒组成,可以认为此止血剂是利用蒙脱石颗粒来止血的,通过吸附血中水分、膨胀来形成具有高可塑性的黏土物质,其能黏附于组织和封闭出血部位。此外,水的吸收可以浓缩凝血因子和血细胞。另外重要的一点是,带负电荷的颗粒,可以激活内在的止血途径和加速凝血过程,对于致死性动脉出血有很好的止血效果[19-20,34,47-48]。WoundStat激活凝血途径可引起血管内皮损伤和血栓在管腔内流动,导致远端血栓形成[13]。虽然其止血效果好,满足理想止血敷料的特征,但动物实验的组织病理学显示具有引起纤维肉芽肿性炎症,引起内皮细胞变性导致内膜增生,以及引起肌细胞坏死和轴突变性的纤维肉芽性的神经卡压等并发症,因此使用时要考虑其安全性[47-48]。 超快速急救剂(Super QR)是由钾离子盐和可吸收聚合物组成的矿物性止血粉末(使用它后在创伤口形成血痂并封闭出血),将其完全去除干净是不可能的,因为它太紧密地结合组织。止血药中,包括HemCon、Celox和QuikClot ACS+,都是相对比较容易去除的[13,49]。 乙酰化葡萄糖胺类止血敷料,其代表为mRDH,是一种生物相容性材料,来自于海洋微藻,由聚-N-乙酰基氨基葡萄糖(即聚乙酰氨基葡萄糖,p-glcnac)纳米纤维材料组成,由Rapid Deployment Haemostat改性而 来[28,35,50]。从作用机制来看,mRDH是通过激活凝血级联反应、局部血管收缩、血小板激活和红细胞聚集来起作用的。值得注意的是,这种止血剂在凝血因子或血小板缺乏时仍可有效,因此可用于凝血障碍患者。据称在mRDH的应用中没有损伤作用的相关报道。尽管第一代快速止血剂在控制严重出血上是无效的,但已被证明改良型mRDH在动静脉出血和凝血功能障碍患者中是有效的。这种敷料是这些止血剂中最贵的,限制了其广泛应用[14-15,24,35,50]。 冻干纤维蛋白胶敷料(the dry fibrin sealant dressing,DFSD)即固态纤维蛋白密封敷料[35,51],是为了弥补液态纤维蛋白密封剂的不足而设计的,其更加柔软且具有弹性,能贴附在任何形状的伤口上,在 2.0-3.0 min内形成纤维蛋白凝块,达到止血目的,在减少失血量、提高存活率方面比液态更具优越性。DFSD是由高度纯化的人纤维蛋白原、钙离子、凝血酶及凝血因子组成,通过提高局部凝血因子的浓度来促进凝血。尽管现代净化技术几乎可消除病毒传播的风险,但DFSD具有潜在的免疫原性和传播病毒风险,这就是为什么DFSD并未取得FDA批准[26]。目前研究的基于壳聚糖的敷料,已在抗菌性能上得到改进[13,52]。DFSD作为基础药物评估于2003年由美国军队在阿富汗和伊拉克地区使用,但很快被FDA批准的QuikClot和HemCon产品所取代。虽然它还没有获得FDA批准,但仍然纳入这篇综述中,因为它一直是许多研究的主题,并在动物体内研究中有很好的止血效果[13]。 CombatGauze是一种混合了高岭土(高岭土是一种非金属矿产,是一种以高岭石族黏土矿物为主的黏土和黏土岩)的柔顺布料,通过激活内源性凝血途径来进行止血,其止血性能是来自于原材料(人造丝和聚酯混合物)、高岭土涂层和大的表面积作用,现被认为是战场上用于治疗危及生命出血的一线敷料[49]。高岭土是一种铝硅酸盐,无放热反应,动物止血模型显示其对动静脉、脾脏和肝脏出血具有很好的止血效果[29]。高岭土是不可生物降解的,在达到止血效果后必须清除[30]。 2.4 其他新型止血敷料 由硅酸盐纳米颗粒分散到明胶中组成具有剪切变稀性的复合水凝胶,具有可注射性、生物相容性、可降解性、生理稳定性及具有载体输送功能。因具有剪切变稀性,可在肝撕裂伤进行局部有效止血。止血机制是硅酸盐纳米颗粒具有高电荷,呈-39 mV的电势,能促进凝血因子聚合;而明胶是变性蛋白,具有两性,含有负电荷呈+10 mV的电势,具有吸水性能。两者形成的复合水凝胶能吸附血液成分,使血小板聚集,促进凝血[53]。 Self-assembling peptide(自组装多肽)是麻省理工学院和香港大学最近报道的一种自组装多肽止血材 料[54]。它可在15 s内止住伤口流血,该材料主要由缩氨酸多肽组成,特点施加到流血的伤口时,缩氨酸就会迅速聚集形成一种胶状体,以达到止血效果。缩氨酸胶体最终会分解为氨基酸,还可作为组织修复过程中的成分。该材料不会对周围细胞产生损伤,也不会引起免疫反应。甚至在储存3年后都能够产生疗效。此外,自组装多肽类纳米纤维屏障可分解成氨基酸、缩氨酸溶液,应用于潮湿的不可控制的环境,如事故、战场等,而且它也不含任何动物或人类添加剂(避免了生物污染源)。其止血机制肽的自组装行为。目前用于止血的自组装肽主要为离子互补型两亲肽,其具有规则的重复单位;带正电的氨基酸残基和带负电的氨基酸残基被不带电的疏水性残基分开,在生理环境下,自组装肽变成纳米纤维,进而形成三维水凝胶,是肽止血的关键。其独特之处: ①自组装肽止血并不依赖于机体凝血机制,血凝块是在材料应用1.0-2.0 min后才开始形成的;②没有观察到材料与伤口界面上血小板的聚集;③短肽溶液能够在组装前快速填充和适应不规则伤口,组装后的水凝胶尺寸也有利于贴合伤口;④自组装止血短肽单体通常含有带电氨基酸精氨酸和谷氨酸残基,使短肽自组装形成的纤维带电荷,带电荷的纤维可通过静电作用与创口很好地黏合;⑤凝胶动力学并不能作为判断止血效应的直接依据。其优点:①安全无毒性:无免疫原性;②高效、快速的止血功效:现已证明自组装肽能够在15 s 内对于脑、脊髓、皮肤、肝脏和股动脉创伤发挥显著的止血疗效;③易用性:该材料可在试管或在喷雾瓶中预混;它在室温有一个很长的保质期,而不需要冷藏,在恶劣的环境下(-80至60 ℃)仍有效;④成本:首先是可人工合成并可批量生产;⑤广泛适应性:作为液体制剂易于在各种出血创面、创口给药,能够顺应和填充不规则的空隙,覆盖暴露或磨损伤口组织,而不需要任何组织加压。自组装肽可组装长纤维,经超声处理后可组装成短纤维,一段时间后这些短肽再次组装为长纤维,且自组装纤维长度和水凝胶储能模量相关(P < 0.05)[55]。复合材料中RADA16-Ⅰ的浓度越高止血效果越佳,自组装纤维长度与动物模型的完全止血所需时间呈负相关[56]。自组装肽能够减少术中出血,且对神经组织有修复作用,在院前急救条件下有很重要的意义,其快速的止血、可视性及降解吸收性,使自组装肽成为具有很大潜力的止血敷料。 目前水凝胶止血敷料相对于其他敷料具有以下优点[57]:有益于维持创面湿润环境,避免了纱布常常与伤口粘在一起,不利于伤口愈合;水凝胶是透明的,有利于观察伤口愈合情况;水凝胶可递送药物,可抗感染并利于伤口愈合;水凝胶具有可塑性及优异的机械性能,并且无不良反应。Du等[58]报道一种多功能原位成型水凝胶,其由泊洛沙姆407和188及其他成分(氨基己酸、聚维酮碘、利多卡因和壳聚糖)组成,无炎症反应,可促进伤口修复与愈合,减少出血部位疼痛,止血效果好且具有抗菌性,具有良好的生物相容性。Komatsu等[59]报道的中性自组装肽水凝胶,无生物原性,非粘连且透明的,可经过高压灭菌法杀菌。为了避免疾病传染性,合成类止血敷料得到了很大发展,中科院合成了以聚乙二醇为原料的双网络水凝胶,负载抗生素,得到了止血性能和抗菌性良好的止血凝胶[60]。 上面所述的止血敷料各具特征,需要对它们进行评价与分析,Zhang等[61]通过对纳入3篇描述性文献和38篇比较文献的综述,证明纤维蛋白胶敷料、Celox和WoundStat这3种敷料比目前所报道的其他止血辅料具有更好的优势。Granville-Chapman等[13]也证明Celox和WoundStat能够有效止住在战场上因外伤引起的出血。经过对纳入的文献分析可知,目前止血敷料都有许多不良反应,将它们的作用机制、成分及不良反应进行汇总制成表1。 2.5 止血敷料的院内使用 累及内脏器官损伤的创伤经常发生,有的器官(如脾)可完全摘除,但大部分内脏(如肝脏)需要保存,严重的内脏损伤止血操作给创伤外科医生带来挑战。面对内脏器官损伤导致的出血,尤其比较脆弱的肝脏组织出血,不易采用纱布按压,而使用止血敷料可达到很好的止血效果[15,25]。目前,已有文献报道使用氨甲环酸等止血敷料能减少骨盆骨折失血性休克的死亡率[32]。 2.6 未来展望 当前外用止血敷料有许多缺陷,阻止了其更广泛的推广应用,未来需要进一步改进敷料性能。事实上,目前还没有发现理想的敷料,没有任何一个止血敷料在临床上表现出优越的性能,仍然需要继续优化止血敷料的成分和结构。此外,目前的止血敷料大多仅仅在发达国家使用,在战场和日常生活创伤中使用止血敷料可挽救生命,因此在发展中国家中也要更好地发展止血敷料。特别注意的是,上述止血敷料若使用不当,会导致止血失败,因此也要加强止血敷料的操作使用培训[15]。 "
| [1] Morrison CA.The prehospital treatment of the bleeding patient--dare to dream.J Surg Res.2013;180 (2):246-147.[2] Sambasivan CN,Cho SD,Zink KA,et al.A highly porous silica and chitosan-based hemostatic dressing is superior in controlling hemorrhage in a severe groin injury model in swine.Am J Surg. 2009; 197(5): 576-580.[3] Khoshmohabat H,Paydar S,Kazemi HM,et al.Overview of agents used for emergency hemostasis.Trauma Mon.2016;21(1):e26023.[4] Lier H,Krep H,Schroeder S,et al.Prospective randomized multicenter trial of fibrin sealant versus thrombin-soaked gelatin sponge for suture- or needle-hole bleeding from polytetrafluoroethylene femoral artery grafts.J Vasc Surg.2003;38(4):766-771.[5] Taylor LM Jr,Mueller-Velten G,Koslow A,et al.Prospective randomized multicenter trial of fibrin sealant versus thrombin-soaked gelatin sponge for suture-or needle-hole bleeding from polytetrafluoroethylene femoral artery grafts.J Vas Surg.2003;38(4):766-771.[6] Dai C,Liu C,Wei J,et al.Molecular imprinted macroporous chitosan coated mesoporous silica xerogels for hemorrhage control. Biomaterials. 2010;31(30):7620-7630.[7] Rothwell SW,Fudge JM,Chen WK,et al.Addition of a propyl gallate-based procoagulant to a fibrin bandage improves hemostatic performance in a swine arterial bleeding model.Thromb Res. 2002;108 (5-6):335-340.[8] Gruen RL,Brohi K,Schreiber M,et al. Haemorrhage control in severely injured patients.Lancet. 2012;380(9847):1099-1108.[9] Bilgili H,Kosar A,Kurt M,et al.Hemostatic efficacy of ankaferd blood stopper in a swine bleeding model.Med Princ Pract. 2009;18(3): 165-169.[10] Mannucci PM.Hemostatic drugs.N Engl J Med. 1998;339(4):245-253.[11] Rossaint R,Cerny V,Coats TJ,et al.Key issues in advanced bleeding care in trauma.Shock.2006;26 (4):322-331.[12] Kelly JF,Ritenour AE,McLaughlin DF,et al.Injury severity and causes of death from operation iraqi freedom and operation enduring freedom: 2003-2004 versus 2006.J Trauma. 2008;64(2 Suppl):S21-26.[13] Granville-Chapman J,Jacobs N,Midwinter MJ.Pre-hospital haemostatic dressings: A systematic review. Injury. 2011;42(5):447-459.[14] Vournakis JN,Demcheva M,Whitson AB,et al.The rdh bandage: Hemostasis and survival in a lethal aortotomy hemorrhage model.J Surg Res.2003;113(1):1-5.[15] Smith AH,Laird C,Porter K,et al.Haemostatic dressings in prehospital care.Emerg Med J.2013;30(10):784-789.[16] Mabry RL,Holcomb JB,Baker AM,et al.United states army rangers in somalia: An analysis of combat casualties on an urban battlefield.J Trauma.2000;49(3): 515-528.[17] Navein J,Coupland R,Dunn R.The tourniquet controversy.J Trauma. 2003;54(5 Suppl):S219-220.[18] Pozza M,Millner RW.Celox (chitosan) for haemostasis in massive traumatic bleeding: Experience in afghanistan.Eur J Emerg Med. 2011;18(1):31-33.[19] Carraway JW,Kent D,Young K,et al.Comparison of a new mineral based hemostatic agent to a commercially available granular zeolite agent for hemostasis in a swine model of lethal extremity arterial hemorrhage.Resuscitation. 2008;78(2):230-235.[20] Ward KR,Tiba MH,Holbert WH,et al.Comparison of a new hemostatic agent to current combat hemostatic agents in a swine model of lethal extremity arterial hemorrhage.J Trauma.2007;63(2):276-283.[21] Yucel N,Lefering R,Maegele M,et al.Polytrauma Study Group of the German Trauma Society. Trauma associated severe hemorrhage (tash)-score: Probability of mass transfusion as surrogate for life threatening hemorrhage after multiple trauma.J Trauma. 2006; 60(6):1228-1236.[22] Brohi K,Singh J,Heron M,et al.Acute traumatic coagulopathy.J Trauma.2003;54(6):1127-1130.[23] Davenport R,Manson J,De'Ath H,et al.Functional definition and characterization of acute traumatic coagulopathy.Crit Care Med.2011; 39(12):2652-2658.[24] Pusateri AE,McCarthy SJ,Gregory KW,et al.Effect of a chitosan-based hemostatic dressing on blood loss and survival in a model of severe venous hemorrhage and hepatic injury in swine.J Trauma. 2003;54(1): 177-182.[25] Clay JG,Zierold D,Grayson K,et al.Dextran polymer hemostatic dressing improves survival in liver injury model.J Surg Res. 2009; 155(1):89-93.[26] Kilbourne M,Keledjian K,Hess JR,et al.Hemostatic efficacy of modified amylopectin powder in a lethal porcine model of extremity arterial injury.Ann Emerg Med.2009;53(6):804-810.[27] Pusateri AE,Holcomb JB,Kheirabadi BS,et al.Making sense of the preclinical literature on advanced hemostatic products.J Trauma. 2006; 60(3):674-682.[28] Robinson K.Controlling bleeding in the field: Hemostatic powders and dressings debut in the prehospital setting.J Emerg Nurs. 2004;30(2): 160-161.[29] Lawton G,Granville-Chapman J,Parker PJ.Novel haemostatic dressings.J R Army Med Corps., 2009;155(4):309-314.[30] Bennett BL,Littlejohn L.Review of new topical hemostatic dressings for combat casualty care.Mil Med. 2014;179(5):497-514.[31] Kratz A,Danon A.Controlling bleeding from superficial wounds by the use of topical alpha adrenoreceptor agonists spray. A randomized, masked, controlled study.Injury. 2004;35(11):1096-1101.[32] Littlejohn L,Bennett BL,Drew B.Application of current hemorrhage control techniques for backcountry care: Part two, hemostatic dressings and other adjuncts.Wilderness Environ Med.2015;26 (2):246-254.[33] Devlin JJ,Kircher S,Kozen BG,et al.Comparison of chitoflex(r), celox, and quikclot(r) in control of hemorrhage.J Emerg Med. 2011;41(3): 237-245.[34] Clay JG,Grayson JK,Zierold D.Comparative testing of new hemostatic agents in a swine model of extremity arterial and venous hemorrhage. Mil Med.2010;175(4):280-284.[35] Valeri CR,Vournakis JN.Mrdh bandage for surgery and trauma: Data summary and comparative review, J Trauma. 2011;71(2 Suppl 1): S162-166.[36] Rhee P,Brown C,Martin M,et al.Quikclot use in trauma for hemorrhage control: Case series of 103 documented uses.J Trauma. 2008;64(4): 1093-1099.[37] Arnaud F,Tomori T,Carr W,et al.Exothermic reaction in zeolite hemostatic dressings: Quikclot acs and acs+.Ann Biomed Eng. 2008;36(10):1708-1713.[38] Wright JK,Kalns J,Wolf EA,et al.Thermal injury resulting from application of a granular mineral hemostatic agent.J Trauma. 2004; 57(2):224-230.[39] Velmahos GC,Tabbara M,Spaniolas K,et al.Self-expanding hemostatic polymer for control of exsanguinating extremity bleeding.J Trauma. 2009;66(4):984-988.[40] Sambasivan CN,Schreiber MA.Emerging therapies in traumatic hemorrhage control.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009;15(6):560-568.[41] 史跃,杜宝堂,何远清,等.多微孔多聚糖止血粉应用于软组织创伤性出血[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3): 406-411.[42] Gegel B,Burgert J,Cooley B,et al.The effects of bleedarrest, celox, and traumadex on hemorrhage control in a porcine model.J Surg Res. 2010;164(1):e125-129.[43] Malmquist JP,Clemens SC,Oien HJ,et al.Hemostasis of oral surgery wounds with the hemcon dental dressing.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(6):1177-1183.[44] Millner RW,Lockhart AS,Bird H,et al.A new hemostatic agent: Initial life-saving experience with celox (chitosan) in cardiothoracic surgery. Ann Thorac Surg.2009;87(2):e13-14.[45] Waibel KH,Haney B,Moore M,et al.Safety of chitosan bandages in shellfish allergic patients.Mil Med. 2011;176(10):1153-1156.[46] Arnaud F,Teranishi K,Okada T,et al.Comparison of combat gauze and traumastat in two severe groin injury models.J Surg Res. 2011;169(1): 92-98.[47] Gerlach T,Grayson JK,Pichakron KO,et al.Preliminary study of the effects of smectite granules (woundstat) on vascular repair and wound healing in a swine survival model.J Trauma. 2010;69(5):1203-1209.[48] Kheirabadi BS,Mace JE,Terrazas IB,et al.Safety evaluation of new hemostatic agents, smectite granules, and kaolin-coated gauze in a vascular injury wound model in swine.J Trauma. 2010;68(2): 269-278.[49] Kheirabadi BS,Scherer MR,Estep JS,et al.Determination of efficacy of new hemostatic dressings in a model of extremity arterial hemorrhage in swine.J Trauma.2009;67(3):450-459.[50] King DR,Schreiber MA.The mrdh bandage provides effective hemostasis in trauma and surgical hemorrhage.J Trauma. 2011;71 (2Suppl 1):S167-170.[51] 张平,肖南,张治纲,等.战创伤止血敷料的现状及展望[J].创伤外科杂志, 2009,(4):378-380.[52] Ong SY,Wu J, Moochhala SM,et al.Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials. 2008;29(32):4323-4332.[53] Gaharwar AK,Avery RK,Assmann A,et al.Shear-thinning nanocomposite hydrogels for the treatment of hemorrhage. Acs Nano. 2014;8(10):9833-9842.[54] Hsu BB,Conway W,Tschabrunn CM,et al.Clotting mimicry from robust hemostatic bandages based on self-assembling peptides.Acs Nano. 2015;9(9):9394-9406.[55] 李佳楠,钟小忠,王婷.短肽rada16-1自组装纤维长度与止血关系研究[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(5):76-80.[56] 甘慧,孟志云,吴卓娜,等.自组装肽的止血应用[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2015,23(3):903-909.[57] 陈向标.水凝胶医用敷料的研究概况[J].轻纺工业与技术, 2011,40(1):66-68.[58] Du L,Tong L,Jin Y,et al.A multifunctional in situ-forming hydrogel for wound healing.Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(6):904-910.[59] Komatsu S,Nagai Y,Naruse K,et al.The neutral self-assembling peptide hydrogel spg-178 as a topical hemostatic agent.PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102778.[60] Bu Y,Zhang L,Liu J,et al.Synthesis and properties of hemostatic and bacteria-responsive in situ hydrogels for emergency treatment in critical situations.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(20): 12674-23683.[61] Zhang YJ,Gao B,Liu XW.Topical and effective hemostatic medicines in the battlefield. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):10-19. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||