Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1565-1572.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0717
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cytobiological effect of micro-arc oxidation coating on 3D-printed titanium alloy scaffold
- 1Analytical & Testing Center, Research Center for Nano Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, Sichuan Province, China; 2National Laboratory for Materials Science, Shenyang Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province , China
-
Received:2017-11-14Online:2018-04-08Published:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Zuo Yi, Researcher, Analytical & Testing Center, Research Center for Nano Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Jiong-jiong, Master candidate, Analytical & Testing Center, Research Center for Nano Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National 863 Project of China, No. 2015AA033702
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jiong-jiong, Zou Qin, Hu Fu,Chen Jie, Li Ji-dong, Li Shu-jun, Hao Yu-lin, Li Yu-bao, Zuo Yi. Cytobiological effect of micro-arc oxidation coating on 3D-printed titanium alloy scaffold[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1565-1572.
share this article
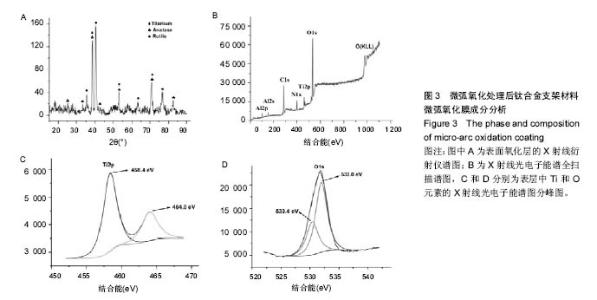
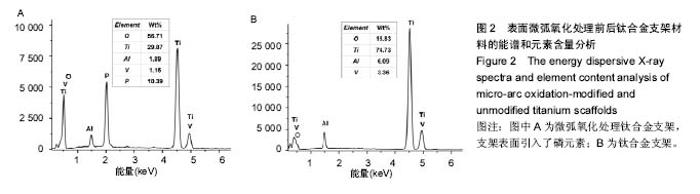
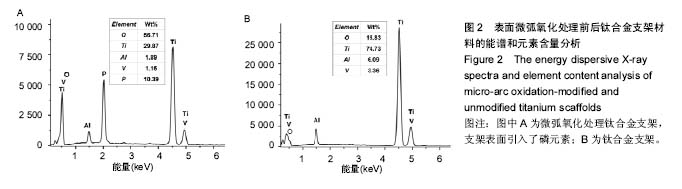
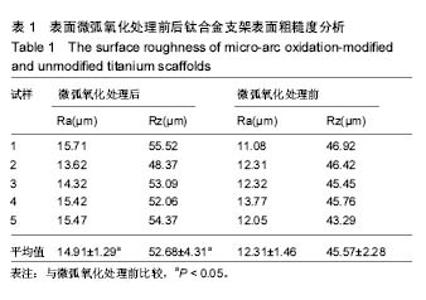
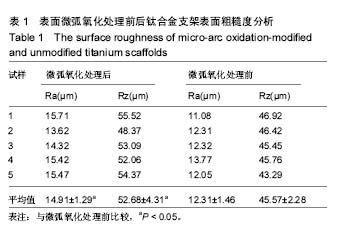
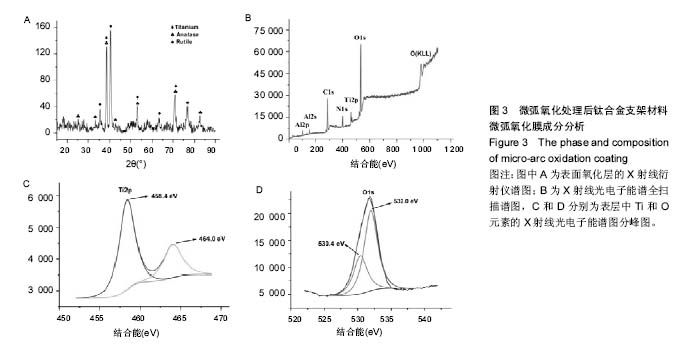
2.3 表面微弧氧化膜成分分析 由X射线衍射图谱(图3A)中可看出,氧化膜层主要由锐钛矿型TiO2构成,有少量的金红石型TiO2,钛衍射峰由基体材料产生。不同于能谱,在X射线衍射谱中未观察到含磷的结晶衍射峰,可能磷化合物以非晶形式存在于涂层中。 X射线光电子能谱图(图3B)观察元素时,在533.2 eV处检测到极强的O1s峰,在459.8 eV处检测到Ti2p峰。Al2p与Al2s峰分别在103.5 eV、155.0 eV处。未检测到钒元素,是由于在表面氧化膜层含量过低的原因,而检测到的C1s和N1s峰则是受到空气中成分的影响所致。 X射线光电子能谱图谱中(图3C)钛在Ti 2p3/2和 Ti 2p1/2两处有双峰,高能量的Ti 2p1/2的峰在464.0 eV处,而低能量的Ti 2p3/2的峰在458.4 eV处,均为Ti-O键的峰。O1s结合能(图3D)集中在530.4 eV和532.0 eV处。"
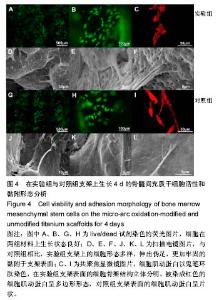
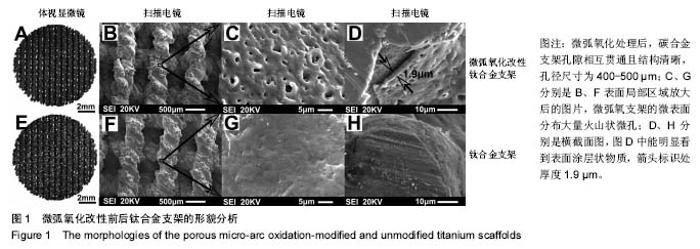
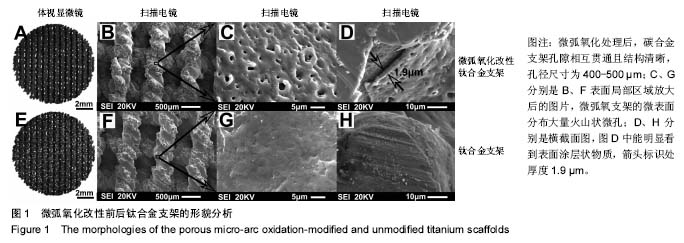
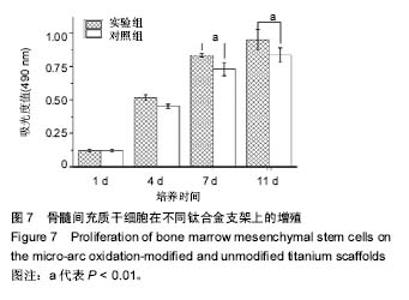
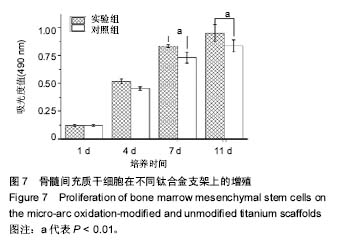
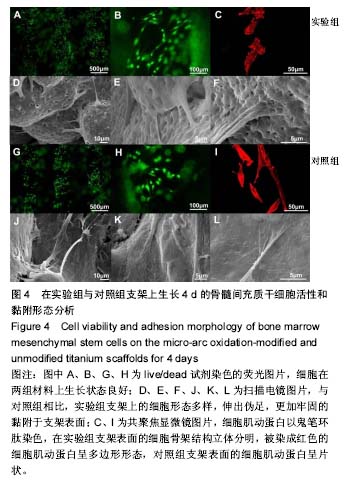
2.5 接触角分析 实验组和对照组表面接触角结果分别为(76.57±2.37)°和(68.02±5.39)°。结果表明,接触角虽有小幅度增大,仍低于90°,钛合金支架在表面微弧氧化处理后仍可称之为亲水性材料。接触角在10°-80°之间的表面属于中等润湿表面,细胞在中等润湿的材料表面黏附能力相对较强[25]。与文献[26]中钛合金平板表面微弧氧化后出现接触角下降不同,此次实验三维支架表面微弧氧化后的接触角增加。原因可能是相对于平板结构,支架的大孔占比远高于微孔,液滴更易从光滑表面的未改性支架进入大孔实现浸润,表现为接触角比改性支架的更小。 2.6 细胞活性测试和形态学分析 细胞接种培养4 d以后,在两种材料的荧光图片上(图4A,B,G,H),均能看到明亮的绿色,反映出细胞较强的生命活力,说明细胞在材料上生长状态良好,几乎看不到红色荧光响应,可能因支架孔隙相对细胞较大,黏附性差的凋亡细胞在染色冲洗时从支架上脱落流失。细胞在支架材料上分布较为均匀。 真核细胞细胞质中错综复杂的纤维网构成细胞骨架,细胞的黏附状态与细胞骨架纤维紧密相关。研究中的钛合金支架多孔结构尺寸为400-500 μm,远大于细胞直径,微弧氧化处理后支架表面形成了直径为0.5-5 μm的微孔,这些微米和亚微米尺寸的多孔结构对细胞超微结构产生更为显著的影响。在实验组支架表面,细胞骨架结构立体分明,被染成红色的细胞肌动蛋白呈多边形形态(图4C)。在未对照组支架表面的细胞,肌动蛋白呈片状荧光响应(图4I)。 由扫描电镜图片可看到,在实验组支架材料表面黏附的细胞伸展成细长形或多角形不一,丝状伪足结构明显,细胞伸展状态良好,形态多样化(图4D-F)。不同于对照组支架上的细胞形态(图4J-L),在实验组支架上的细胞有更多板状伪足且部分伪足直接锚进表面微孔内,与材料黏附更加牢固。"
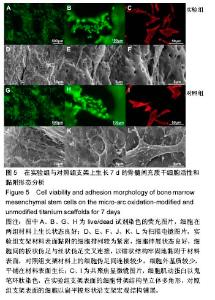
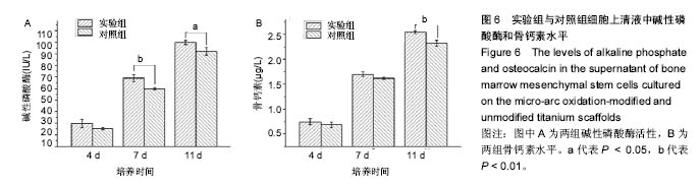
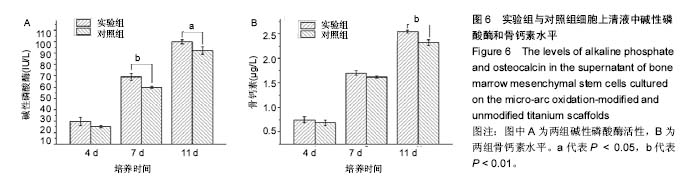
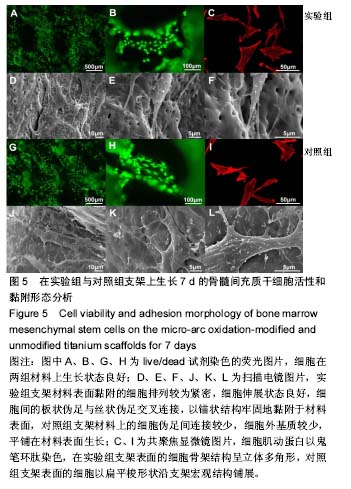
细胞接种培养7 d以后,细胞数目明显增多。在两种材料的荧光图片上,较密集地布满代表细胞活性良好的绿色(图5A,B,G,H),说明材料具有较好的细胞相容性。 在实验组支架表面,被染成红色的蛋白微丝呈网状结构,由微丝组成的骨架结构呈立体多角形(图5C)。而对照组支架表面的细胞以扁平梭形状沿支架宏观结构铺展,肌动蛋白红色响应较强(图5I)。由此可见,细胞骨架的结构和铺展状态等超微结构与支架微表面粗糙度有关。当细胞黏附于较粗糙的表面时,通过伪足可锚接于微弧氧化表面的沟和孔洞,无需排列良好的肌动蛋白网架。而在未改性支架的光滑表面上黏附时,细胞需伸展出肌动蛋白纤维,才能将自己稳定于材料的表面,因此观察到在未改性支架表面的肌动蛋白粗大清晰(红色荧光响应更强)。此时,由于应力纤维的强力伸展,细胞被施加一定张力,表现为未改性支架表面扁平伸展的细胞骨架结构。 由扫描电镜图片可看到,在实验组支架材料表面黏附的细胞排列较为紧密,开始出现细胞间的重叠,细胞伸展状态良好,支架表面细胞突出材料表面较为明显,胞浆饱满,细胞间的板状伪足与丝状伪足交叉连接,以锚状结构牢固地黏附于材料表面(图5D-F);对照组支架材料上的细胞伪足间的连接较少,细胞外基质较少,平铺在材料表面生长(图5J-L)。 李玉梅等[27]以微弧氧化处理的纯钛圆片进行相关研究也表明,微弧氧化改性钛表面黏附的细胞形状较不规则,无一定的方向性,而未处理的圆片微表面相对光滑,成骨细胞易被牵伸,并沿材料的二维平面伸展。由此可见,无论基材是三维支架还是二维平面体,微表面的粗糙度才是细胞黏附的关键。相对于未改性支架的光滑微表面黏附的细胞,微弧氧化改性后形成的粗糙微表面,不仅更适于细胞黏附,还利于细胞以三维立体状态生长增殖,细胞超微结构形态表现更好。"
| [1]Uchida M,Oyane A,Kim HM,et al.Biomimetic coating of laminin–apatite composite on titanium metal and its excellent cell-adhesive properties. Adv Mater.2004;37(13):1071-1074.[2]Smith CJ,Derguti F,Hernandez Nava EH, et al.Dimensional accuracy of electron beam melting (EBM) additive manufacture with regard to weight optimized truss structures.J Mater Process Tech.2016;229: 128-138.[3]Jia Z,Li M,Xiu P,et al.A novel cytocompatible, hierarchical porous Ti6Al4V scaffold with immobilized silver nanoparticles.Mater Lett. 2015;157:143-146.[4]Parthasarathy J,Starly B,Raman S,et al.Mechanical evaluation of porous titanium (Ti6Al4V) structures with electron beam melting(EBM).J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010;3:249-259.[5]Li SJ,Murr LE,Cheng XY,et al.Compression fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V mesh arrays fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater.2012;60(3):793-802. [6]刘邦定,郭征,郝玉琳,等.多孔钛合金不同孔径大小对新骨长入的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(9):1601-1604. [7]Cremasco A,Messias AD,Esposito AR,et al.Effects of alloying elements on the cytotoxic response of titanium alloys.Mater Sci Eng C. 2011;31(5):833-839. [8]Su Y,Li K,Zhang L,et al.Ca-P bioactive coating prepared by combining microwave-hydrothermal and supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying methods.Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;72:371-377.[9]?erban VA,Ro?u RA,Bucur AI,et al.Deposition of titanium nitride layers by electric arc–reactive plasma spraying method. Appl Surf Sci. 2013; 265:245-249.[10]Laha T,Agarwal A,Mckechnie T,et al.Synthesis and characterization of plasma spray formed carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum composite. Mat Sci Eng A. 2004;381(1): 249-258.[11]Zhang W,Liu W,Liu Y,et al.Tribological behaviors of single and dual sol–gel ceramic films on Ti6Al4V.Ceram Int. 2009;35(4): 1513-1520.[12]Wang XX,Hayakawa S,Tsuru K,et al.Bioactive titania-gel layers formed by chemical treatment of Ti substrate with a H2O2/HCl solution. Biomaterials.2002;23(5):1353-1357.[13]Catauro M,Bollino F,Giovanardi R,et al.Modification of Ti6Al4V implant surfaces by biocompatible TiO2/PCL hybrid layers prepared via sol-gel dip coating: structural characterization, mechanical and corrosion behavior.Mater Sci Eng C.2016;74:501-507.[14]Yan Y,Sun J,Han Y,et al.Microstructure and bioactivity of Ca, P and Sr doped TiO2 coating formed on porous titanium by micro-arc oxidation. Surf Coat Tech.2010;205:1702-1713.[15]Wu J,Liu R,Wang B,et al.Preparation and characterization of carburized layer on pure aluminum by plasma electrolysis. Surf Coat Tech.2015;269:119-124. [16]Durdu S,Ömer Faruk Deniz,Kutbay I,et al.Characterization and formation of hydroxyapatite on Ti6Al4V coated by plasma electrolytic oxidation.J Alloys Compounds.2013;551(5):422-429.[17]Wang Y,Yu H, Chen C,et al.Review of the biocompatibility of micro-arc oxidation coated titanium alloys.Mater Design. 2015;85:640-652.[18]刘帅.钛合金材料表面阳极氧化和微弧氧化改性涂层的构建及生物学研究[D].第四军医大学,2014.[19]Lim YW,Kwon SY,Sun DH,et al.Enhanced cell integration to titanium alloy by surface treatment with micro-arc oxidation: A pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2009;467(9):2251-2258. [20]Zhu X,Chen J,Scheideler L,et al.Cellular reactions of osteoblasts to micron- and submicron-scale porous structures of titanium surfaces. Cells Tissues Organs.2004;178(1):13-22.[21]Yu SC,Park SN,Suh H.Adipose tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells attached to injectable PLGA spheres. Biomaterials. 2005; 26(29):5855-5863.[22]卢宁,赵龙凤,李红,等.应用全骨髓贴壁法获取高纯度大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2010,41(3): 277-280.[23]Qiao LP,Lou J,Zhang SF,et al.The entrance mechanism of calcium and phosphorus elements into micro-arc oxidation coatings developed on Ti6Al4V alloy.Surf Coat Tech.2015; 285:187-196.[24]Zhang RF,Qiao LP,Qu B,et al.Biocompatibility of micro-arc oxidation coatings developed on Ti6Al4V alloy in a solution containing organic phosphate.Mater Lett.2015;153(9):77-80.[25]方丽茹,翁文剑,沈鸽,等.骨组织工程支架及生物材料研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2003,20(1):148-152.[26]Tsai MT,Chang YY,Huang HL,et al.Micro-arc oxidation treatment enhanced the biological performance of human osteosarcoma cell line and human skin fibroblasts cultured on titanium–zirconium films. Surf Coat Tech.2016;303:268-276.[27]李玉梅,查年保,马威,等. 微弧氧化处理对钛表面MC3T3-E1细胞生物学行为的影响[J].上海口腔医学, 2015,24(5):551-556.[28]Huang Y,Wang Y,Ning C,et al.Hydroxyapatite coatings produced on commercially pure titanium by micro-arc oxidation.Biomed Mater. 2007;2(3):196-201.[29]Cheng XY,Li SJ,Murr LE,et al.Compression deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with cellular structures fabricated by electron beam melting.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;16(2):153-162.[30]Li XK,Yuan CF,Wang JL,et al.The treatment effect of porous titanium alloy rod on the early stage talar osteonecrosis of sheep.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58459.[31]吴穗丹,王焱,张辉,等.钛表面微弧氧化涂层的细胞生物活性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(47):8169-8174.[32]Zhao Z,Chen X,Chen A,et al.Synthesis of bioactive ceramic on the titanium substrate by micro-arc oxidation.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90(2):438-445.[33]Teng FY,Ko CL,Kuo HN,et al.A comparison of epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts in dental implant titanium topographies. Bioinorg Chem Appl.2012;2012(4):687291.[34]Krupa D,Baszkiewicz J,Zdunek J,et al. Effect of plasma electrolytic oxidation in the solutions containing Ca, P, Si, Na on the properties of titanium.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2012;100: 2156-2166.[35]Zhou R,Wei D,Feng W,et al.Bioactive coating with hierarchical double porous structure on titanium surface formed by two-step micro-arc oxidation treatment.Surf Coat Tech.2014;252(9):148-156.[36]Erfanifar E,Aliofkhazraei M,Nabavi HF,et al.Growth kinetics and morphology of microarc oxidation coating on titanium. Surf Coat Tech. 2017;315:567-576. [37]St-Pierre JP,Gauthier M,Lefebvre LP,et al.Three-dimensional growth of differentiating MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts on porous titanium scaffolds. Biomaterials.2005;26(35):7319-7328.[38]Benoit DS,Schwartz MP,Durney AR,et al.Small functional groups for controlled differentiation of hydrogel-encapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells.Nat Mater.2008;7(10): 816-823.[39]郭宝刚,梁军,陈建敏,等.氧化时间对Ti6Al4V微弧氧化膜结构与性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报,2005,15(6):981-986.[40]Curran JA,Clyne TW.Porosity in plasma electrolytic oxide coatings. Acta Mater.2006; 54(7):1985-1993.[41]Chen HT,Hsiao CH,Long HY,et al.Micro-arc oxidation of β-titanium alloy: structural characterization and osteoblast compatibility.Surf Coat Tech.2009;204(6):1126-1131.[42]Kunzler TP,Huwiler C,Drobek T,et al.Systematic study of osteoblast response to nanotopography by means of nanoparticle-density gradients.Biomaterials.2007;28(33): 5000-5006.[43]Mizokami A,Kawakubo-yasukochi T,Hirata M.Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions.Biochem Pharmacol.2017;132:1-8.[44]赵煜,李冰雁,杜莉,等.磁性附着体模拟静磁场对成骨细胞分化功能的影响[J].中华口腔医学研究,2011,05(2):151-155.[45]丁思阳,夏露,陈宁,等.微弧氧化纯钛表面对成骨细胞蛋白合成功能的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2012,28(2):125-128. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||