Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (18): 2849-2854.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0703
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro antibacterial effect of benzalkonium chloride on five common oral pathogens
Dai Jing, Chen Yan-bin, Chen Shan, Ren Jing, Li Kun-man, Yang Jun-ying
- Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2017-11-02Online:2018-06-28Published:2018-06-28 -
Contact:Yang Jun-ying, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Dai Jing, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:A Transverse Issue: In Vitro Bacteriostasis Experiment of Benzalkonium Chloride on Common Pathogens of Oral Diseases, No. K0601161
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Jing, Chen Yan-bin, Chen Shan, Ren Jing, Li Kun-man, Yang Jun-ying . In vitro antibacterial effect of benzalkonium chloride on five common oral pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2849-2854.
share this article
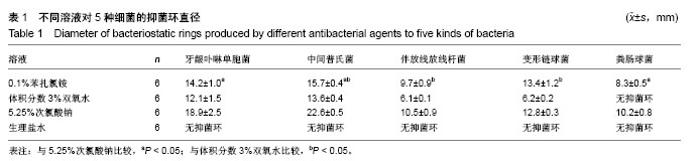
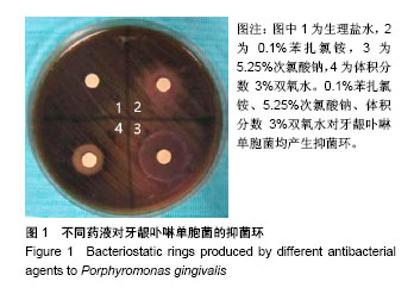
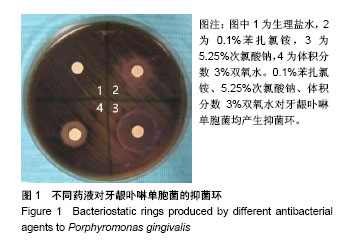
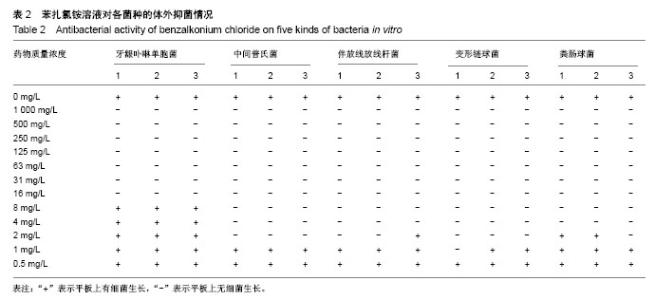
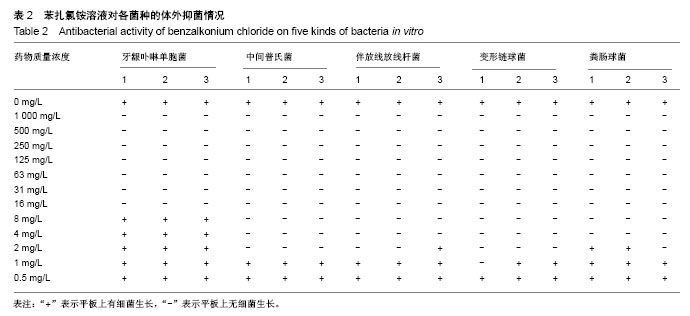
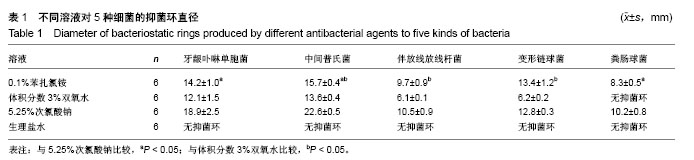
2.2 单因素方差分析结果 对牙龈卟啉单胞菌与中间普氏菌,0.1%苯扎氯铵表现出了较强的抑菌效果,抑菌环直径分别为(14.2±1.0),(15.7±0.4)mm,然而其抑菌效果均次于5.25%次氯酸钠(P < 0.05);0.1%苯扎氯铵对牙龈卟啉单胞菌的抑菌效果与体积分数3%双氧水比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);对中间普氏菌,0.1%苯扎氯铵优于体积分数3%双氧水(P < 0.05);0.1%苯扎氯铵对伴放线放线杆菌和变形链球菌的抑菌效果均优于体积分数3%双氧水(P < 0.05),与5.25%次氯酸钠比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),0.1%苯扎氯铵对两者抑菌环直径分别为(9.7±0.9),(13.4±1.2)mm;0.1%苯扎氯铵对粪肠球菌的抑菌环直径为(8.3±0.5)mm,抑菌效果优于体积分数3%双氧水(P < 0.05),较5.25%次氯酸钠差(P < 0.05),体积分数3%双氧水对粪肠球菌不产生抑菌环,见表1。"
| [1] Rajaram A,Kotrashetti VS,Somannavar PD,et al.Culture-based identification of pigmented Porphyromonas and Prevotella species in primary endodontic infections.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects.2016;10(3):136-141.[2] Pan C,Liu J,Wang H,et al.Porphyromonas gingivalis can invade periodontal ligament stem cells. BMC Microbiol.2017; 17(1):38.[3] Choi EY,Bae SH,Ha MH,et al. Genistein suppresses Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages and attenuates alveolar bone loss in ligature- induced periodontitis.Arch Oral Biol.2016;62:70-79.[4] Nomura R,Ogaya Y,Nakano K.Contribution of the Collagen- Binding Proteins of Streptococcus mutans to Bacterial Colonization of Inflamed Dental Pulp.PLoS One.2016;11(7):e0159613.[5] Stojanovi? N,Kruni? J,Popovi? B,et al.Prevalence of Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis in infected root canals and their susceptibility to endodontic treatment procedures: a molecular study .Srp Arh Celok Lek.2014;142(9-10):535-541.[6] Raja M,Ummer F,Dhivakar CP.Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans—a tooth killer J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(8):ZE13-16.[7] Priyank H,Pandey V,Bagul A,et al.Evaluation of 4% Sodium Hypochlorite in eliminating Enterococcus faecalis from the Root Canal when Used with Three Irrigation Methods: An in vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract.2017;18(3):214-217.[8] Kobayashi Y,Hayashi M,Yoshino F,et al.Bactericidal effect of hydroxyl radicals generated from a low concentration hydrogen peroxide with ultrasound in endodontic treatment.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2014;54:161-165.[9] Sahebjam AM,Moradi HJ,Khoshhal M,et al.Clinical Effect of Periodontal Pocket Irrigation with H2O2.Avicenna J Dent Res.2011;3(1):53-59.[10] Rashed HT.Evaluation of the effect of hydrogen peroxide as a mouthwash in comparison with chlorhexidine in chronic periodontitis patients: A clinical study.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent.2016;6(3):206-212.[11] Oguz Ahmet S,Mutluay MM,Seyfioglu Polat Z.Addition of benzalkonium chloride to self-adhesive resin-cements: some clinically relevant properties.Acta Odontol Scand.2014;72(8): 831-838.[12] Passariello C,Sannino G,Petti S.Intensity and duration of in-vitro antibacterial activity of different adhesives used in orthodontics.Eur J Oral Sci.2014;122(2):154-160.[13] Xu SY,Bian RL,Chen X.Methodology of Pharmacological Experiment.3rd. Beijing: People Hygiene Press, 2002:1657-1660.[14] Pataky L, Iványi I, Grigár A, et al. Antimicrobial efficacy of various root canal preparation techniques: an in vitro comparative study. J Endod,.2002;28(8):603-605.[15] Carrotte P. 21st century endodontics: part 3. Int Dent J. 2005; 55(4):247-253.[16] Pawar R,Alqaied A,Safavi K,et al.Influence of an apical negative pressure irrigation system on bacterial elimination during endodontic therapy: a prospective randomized clinical study.J Endod. 2012;38:1177-1181.[17] 樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[18] Fernandez y Mostajo M,van der Reijden WA,Buijs MJ,et al.Effect of an oxygenating agent on oral bacteria in vitro and on dental plaque composition in healthy young adults.Front Cell Infect Microbiol.2014;4:95.[19] Jhingta P,Bhardwaj A,Sharma D,et al.Effect of hydrogen peroxide mouthwash as an adjunct to chlorhexidine on stains and plaque.J Indian Soc Periodontol.2013;17(4):449-453.[20] 史宗道.口腔临床药物学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:154-155.[21] Al-Ali M,Sathorn C,Parashos P.Root canal debridement efficacy of different final irrigation protocols.Int Endod J.2012;45(10): 898-906.[22] Metzger Z,Basrani B,Goodis HE.Instruments, materials,and devices. In:Hargreaves KM, Cohen S, Berman LH, eds.Pathways of the Pulp(10th ed).St.Louis: Mosby Elsevia (USA),2011:223-282.[23] Vajrabhaya LO,Sangalungkarn V,Srisatjaluk R,et al.Hypochlorite solution for root canal irrigation that lacks a chlorinated odor.Eur J Dent.2017;11(2):221-225. [24] Urano H,Fukuzaki S.The mode of action of sodium hypochlorite in the cleaing process.Biocontrol Sci.2005;10(1/2):21-29.[25] Fukuzaki S.Mechanisms of actions of sodium hypochlorite in cleaning and disinfection processes.Biocontrol Sci.2006;11(4):147-157.[26] Del Carpio-Perochena A,Bramante CM,de Andrade FB,et al.Antibacterial and dissolution ability of sodium hypochlorite in different pHs on multi-species biofilms.Clin Oral Investig.2015;19(8):2067-2073.[27] Ragnarsson KT,Rechenberg DK,Attin T,et al.Available chlorine consumption from NaOCl solutions passively placed in instrumented human root canals.Int Endod J.2015;48(5):435-440.[28] Gernhardt CR,Eppendorf K,Kozlowski A,et al.Toxicity of concentrated sodium hypochlorite used as an endodontic irrigant.Int Endod J.2004;37(4):272-280.[29] Pozarowska D,Pozarowski P.Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) induces apoptosis or necrosis, but has no major influence on the cell cycle of Jurkat cells.Folia Histochem Cytobiol.2011;49(2):225-230.[30] Wessels S,Ingmer H.Modes of action of three disinfectant active substances: a review.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.2013;67(3):456-467.[31] Jaramillo DE,Arriola A,Safavi K,et al. Decreased bacterial adherence and biofilm growth on surfaces coated with a solution of benzalkonium chloride.J Endod.2012;38(6):821-825.[32] da Costa LF,Amaral CD,Barbirato DD,et al.Chlorhexidine mouthwash as an adjunct to mechanical therapy in chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis.J Am Dent Assoc. 2017;148(5): 308-318.[33] Lamont T.Lower concentration of chlorhexidine and cetyl-pyridinium chloride mouthwash demonstrates some efficacy.Evid Based Dent.2012;13(2):52-53.[34] Tarbox BB,Conroy BP,Malicky ES,et al. Benzalkonium chloride. A potential disinfecting irrigation solution for orthopaedic wounds].Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(346):255-261.[35] Liebert MA.Final report on the safety assessment of benzalkonium chloride. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1989;8:589625. [36] Scannapieco FA.The oralmicrobiome: its role in health and in oral and systemic infections.Clin Microbiol Newsl. 2013;35(20): 163-169.[37] Larsen T, Fiehn NE. Dental biofilm infections - an update. APMIS. 2017;125(4):376-384.[38] [Awadalla HI, Ragab MH, Bassuoni MW, et al. A pilot study of the role of green tea use on oral health. Int J Dent Hygiene. 2011;9(2): 110-116.[39] George DE, Shetty R, Shetty PJ, et al . An In vitro Study to Compare the Effect of Different Types of Tea with Chlorhexidine on Streptococcusmutans.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(9): ZC05-ZC07.[40] Preshaw PM,Alba AL,Herrera D,et al.Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship.Diabetologia.2012;55(1):21-31.[41] Feng X, Zhu L, Xu L, et al. Distribution of 8 periodontal microorganisms in family members of Chinese patients with aggressive periodontitis.Arch Oral Biol.2015;60(3):400-407.[42] Akincibay H, Orsal SO, Sengün D, et al. Systemic administration of doxycycline versus metronidazole plus amoxicillin in the treatment of localized aggressive periodontitis: a clinical and microbiologic study.Quintessence Int.2008;39(2):e33-39.[43] Burgess DK, Huang H, Harrison P, et al. Non-Surgical Therapy Reduces Presence of JP2 Clone in Localized Aggressive Periodontitis.J Periodontol.2017;88(12):1263-1270.[44] Lima SM,Sousa MG,Freire Mde S,et al.Immune Response Profile against Persistent Endodontic Pathogens Candida albicans and Enterococcus faecalis In Vitro.J Endod.2015;41(7):1061-1065.[45] Cheng X,Chen B,Qiu J,et al.Bactericidal effect of Er:YAG laser combined with sodium hypochlorite irrigation against Enterococcus faecalis deep inside dentinal tubules in experimentally infected root canals.J Med Microbiol. 2016;65(2): 176-187.[46] Hiremath GS,Kulkarni RD,Naik BD.Evaluation of minimal inhibitory concentration of two new materials using tube dilution method: An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent.2015;18(2):159-162. [47] 邢飞鹏,孙立洲,王欣梅.苯扎氯铵溶液根管冲洗液抗菌效果研究[J].医药论坛杂志,2011,32(12):168-169.[48] Baron A,Lindsey K,Sidow SJ,et al.Effect of a Benzalkonium Chloride Surfactant-Sodium Hypochlorite Combination on Elimination of Enterococcus faecalis.J Endod. 2016;42(1): 145-149. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||