Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (33): 5286-5291.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0662
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hepatic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by additional growth factors inhibits chronic liver fibrosis
Xiang Jun-xi1, 2, Liu Peng2, Yang Li-fei2, Su Jing-bo2, Zhang Xu-feng1, 2, Liu Xue-min1, 2, Lü Yi1, 2
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; 2National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Precision Surgery and Regenerative Medicine, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2018-07-11Online:2018-11-28Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Lü Yi, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Precision Surgery and Regenerative Medicine, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Xiang Jun-xi, MD, Assistant researcher, Attending physician, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Precision Surgery and Regenerative Medicine, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81501608; Key Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Plan of Shaanxi Province, No. 2014KCT-24
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiang Jun-xi, Liu Peng, Yang Li-fei, Su Jing-bo, Zhang Xu-feng, Liu Xue-min, Lü Yi. Hepatic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by additional growth factors inhibits chronic liver fibrosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5286-5291.
share this article
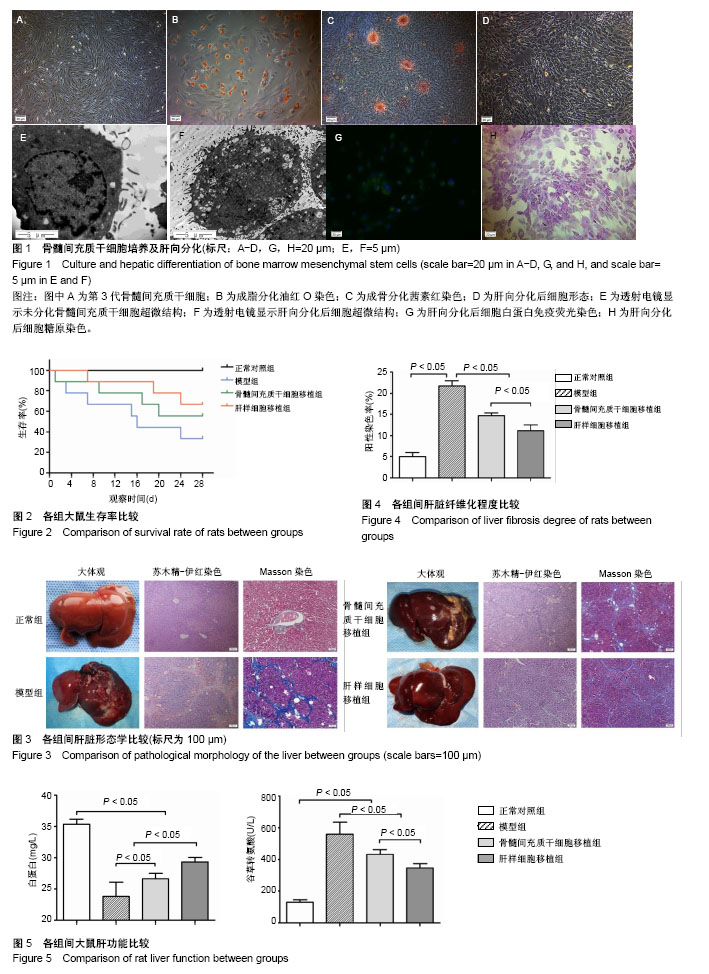
2.1 大鼠BMSCs培养、鉴定及诱导肝向分化 BMSCs传代至第3代时,绝大多数细胞呈均一的小梭形,细胞呈“鱼群状”生长,见图1A。流式细胞术检测结果显示,细胞均一高表达CD29、CD44、CD90,其阳性率分别为(96.6±2.8)%,(84.3±11.1)%,(88.9±8.4)%,而CD34、CD45则明显呈低表达,分别为(1.5±1.3)%,(6.1±2.8)%,符合BMSCs表面标记物的表达特征[22]。油红O染色及茜素红染色显示,经诱导分化后胞浆内可见密集的红染脂滴、致密的红色矿化结节形成,证实所获BMSCs具有成脂及成骨分化潜能(图1B,C)。 经肝向诱导分化至第21天,BMSCs即呈现出类似肝细胞的立方形,呈铺路石样分布并密集排列(图1D),透射电镜下可见细胞核浆比下降,而胞浆内可见多种成熟的细胞器结构及特异的黑色糖原颗粒(图1E,F)。免疫荧光显示,细胞表达肝脏特异性合成蛋白—白蛋白(图1G),糖原染色结果显示胞浆内可见紫红色糖原颗粒(图1H)。 2.2 生存率比较 在造模及接受细胞移植后的观察期内,正常对照组大鼠未发生死亡,观察期内存活率为100%。移植后观察,模型组大鼠存活率最低,至第4周末时仅为33.3%,BMSCs移植组次之,为55.6%,肝样细胞移植组生存率较高,为66.7%,见图2。 2.3 肝脏形态学分析 移植后第4周处死存活的所有大鼠并取肝脏组织行大体观察及组织学评价,见图3。大体观察可见,正常对照组大鼠肝脏形态及质地正常、表面光滑、色泽均一、边缘锐利。模型组、BMSCs移植组、肝样细胞移植组大鼠肝脏则呈现出不同程度色泽晦暗、质地明显变硬且不均,以模型组最为显著,而肝样细胞移植组程度最轻。 对各组大鼠肝脏进行苏木精-伊红染色及Masson染色,结果显示:正常对照组大鼠肝脏细胞形态正常,排列紧密有序,肝小叶形态清楚、规则,汇管区及中央静脉结构清楚。模型组肝脏内可见大量胶原纤维不规则增生,假小叶形成,肝细胞出现点片状坏死,肝内炎性细胞大量浸润。与模型组相比,BMSCs移植组、肝样细胞移植组大鼠肝脏纤维化程度均有不同程度的改善,胶原纤维增生及假小叶形成依次减少,肝细胞坏死数量降低。对Masson染色照片进行累积吸光度测量,以分析并比较各组肝脏内胶原纤维增生程度,见图4。正常组肝脏阳性染色率为(4.99±0.58)%,低于其余3组;模型组阳性率为(21.73±7.56)%,高于2个细胞移植组;BMSCs移植组阳性率为(14.69±0.37)%,亦高于肝样细胞移植组(11.14±0.82)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 大鼠肝功能比较 移植后4周收集各组存活大鼠的血清进行肝功能检测及比较,见图5。模型组大鼠血清白蛋白水平低于正常组[(23.8±2.3) mg/L,(35.4±0.9) mg/L],而模型组谷草转氨酶水平则高于正常组[(559.8±44.4) U/L,(129.1±4.8) U/L]。BMSCs移植组白蛋白、谷草转氨酶水平[(26.7±0.8) mg/L,(432.0±14.0) U/L],与模型组比较有一定程度的改善,肝样细胞移植组的肝功能改善程度更大[(29.4±0.7) mg/L,(347.0±11.3) U/L],优于BMSCs移植组(P < 0.05),但与正常对照组相比仍有较大差距。"
| [1] Bataller R, Gao B. Liver fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35(2):146-156. [2] Sakhuja P. Pathology of alcoholic liver disease, can it be differentiated from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(44): 16474-16479. [3] Pimpin L, Cortez-Pinto H, Negro F, et al. Burden of liver disease in Europe: Epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J Hepatol. 2018 May 17. doi:10.1016/j. jhep.2018.05.011. [Epub ahead of print][4] Ju S, Teng GJ, Lu H, et al. In vivo differentiation of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes for cell therapy to repair damaged liver. Invest Radiol. 2010;45(10):625-633. [5] Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, et al. Stem cell therapy for liver disease: parameters governing the success of using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):2111-2121. [6] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6(2):230-247. [7] Gonzaga VF, Wenceslau CV, Lisboa GS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Benefits Observed in Bone Marrow Failure and Acquired Aplastic Anemia. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:8076529. [8] Zhou Y, Tsai TL, Li WJ. Strategies to retain properties of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ex vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1409(1):3-17. [9] Lee MK, Lin SP, HuangFu WC, et al. Endothelial-derived extracellular matrix ameliorate the stemness deprivation during ex vivo expansion of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0184111. [10] Barrachina L, Remacha AR, Romero A, et al. Differentiation of equine bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells increases the expression of immunogenic genes. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018; 200:1-6. [11] Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284. [12] Krampera M, Pasini A, Pizzolo G, et al. Regenerative and immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6(4):435-441. [13] Fu X, Jiang B, Zheng B, et al. Heterogenic transplantation of bone marrow-derived rhesus macaque mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mouse. Peer J. 2018;6: e4336. [14] Jang YO, Kim SH, Cho MY, et al. Synergistic effects of simvastatin and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):264-271. [15] Obermajer N, Popp FC, Johnson CL, et al. Rationale and prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2014;19(1):60-64. [16] Russo FP, Alison MR, Bigger BW, et al. The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(6):1807-1821. [17] Di Bonzo LV, Ferrero I, Cravanzola C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as a two-edged sword in hepatic regenerative medicine: engraftment and hepatocyte differentiation versus profibrogenic potential. Gut. 2008;57(2):223-231. [18] Shiba Y, Fernandes S, Zhu WZ, et al. Human ES-cell-derived cardiomyocytes electrically couple and suppress arrhythmias in injured hearts. Nature. 2012;489(7415):322-325. [19] 孙晓晖,王颜刚.干细胞移植定向分化为胰岛β细胞治疗糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(1):165-168.[20] Jongkamonwiwat N, Noisa P. Biomedical and clinical promises of human pluripotent stem cells for neurological disorders. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:656531. [21] Xiang J, Zheng X, Zhu X, et al. Optimization of the protocols for in vitro culture and induction of hepatic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015;35(8):1090-1096. [22] Xiang J, Zheng X, Liu P, et al. Decellularized spleen matrix for reengineering functional hepatic-like tissue based on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Organogenesis. 2016;12(3):128-142. [23] He H, Liu X, Peng L, et al. Promotion of hepatic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on decellularized cell-deposited extracellular matrix. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:406871. [24] Jiang WC, Cheng YH, Yen MH, et al. Cryo-chemical decellularization of the whole liver for mesenchymal stem cells-based functional hepatic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3607-3617. [25] Ji R, Zhang N, You N, et al. The differentiation of MSCs into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a liver biomatrix scaffold and their transplantation into liver-fibrotic mice. Biomaterials. 2012;33(35):8995-9008. [26] Lee EJ, Hwang I, Lee JY, et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Improves the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via RAD51. Mol Ther. 2018;26(3):845-859. [27] Matsuda T, Takami T, Sasaki R, et al. A canine liver fibrosis model to develop a therapy for liver cirrhosis using cultured bone marrow- derived cells. Hepatol Commun. 2017;1(7):691-703. [28] Xu TB, Li L, Luo XD, et al. BMSCs protect against liver injury via suppressing hepatocyte apoptosis and activating TGF-β1/Bax singling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:1395-1402. [29] Kemp KC, Hows J, Donaldson C. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(11):1531-1544. [30] Aurich H, Sgodda M, Kaltwasser P, et al. Hepatocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue in vitro promotes hepatic integration in vivo. Gut. 2009;58(4):570-581. [31] Baghaei K, Hashemi SM, Tokhanbigli S, et al. Isolation, differentiation, and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2017;10(3):208-213. [32] Ma J, He Y, Liu X, et al. A novel electrospun-aligned nanoyarn/three-dimensional porous nanofibrous hybrid scaffold for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 1553-1567. [33] Salah RA, Mohamed IK, El-Badri N. Development of decellularized amniotic membrane as a bioscaffold for bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: ultrastructural study. J Mol Histol. 2018; 49(3):289-301. [34] Guerrero J, Oliveira H, Aid R, et al. Influence of the three-dimensional culture of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells within a macroporous polysaccharides scaffold on Pannexin 1 and Pannexin 3. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4):e1936-e1949. [35] Soto-Gutierrez A, Zhang L, Medberry C, et al. A whole-organ regenerative medicine approach for liver replacement. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(6):677-686. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [6] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [7] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [8] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [9] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [10] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [14] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [15] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||