Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (33): 5268-5273.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0648
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on CXC chemokine receptor 4 expression and chemotaxis in bone marrow microenvironment
Wang Jin, Niu Ben, Ma Xiao-rong, Zhang Wang-gang
- Department of Hematology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2018-06-28Online:2018-11-28Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Zhang Wang-gang, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hematology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Jin, MD, Attending physician, Department of Hematology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, No. 2016JQ8032; the Special Fund for Talent Training in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, No. RC(XM)201307
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jin, Niu Ben, Ma Xiao-rong, Zhang Wang-gang. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on CXC chemokine receptor 4 expression and chemotaxis in bone marrow microenvironment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5268-5273.
share this article
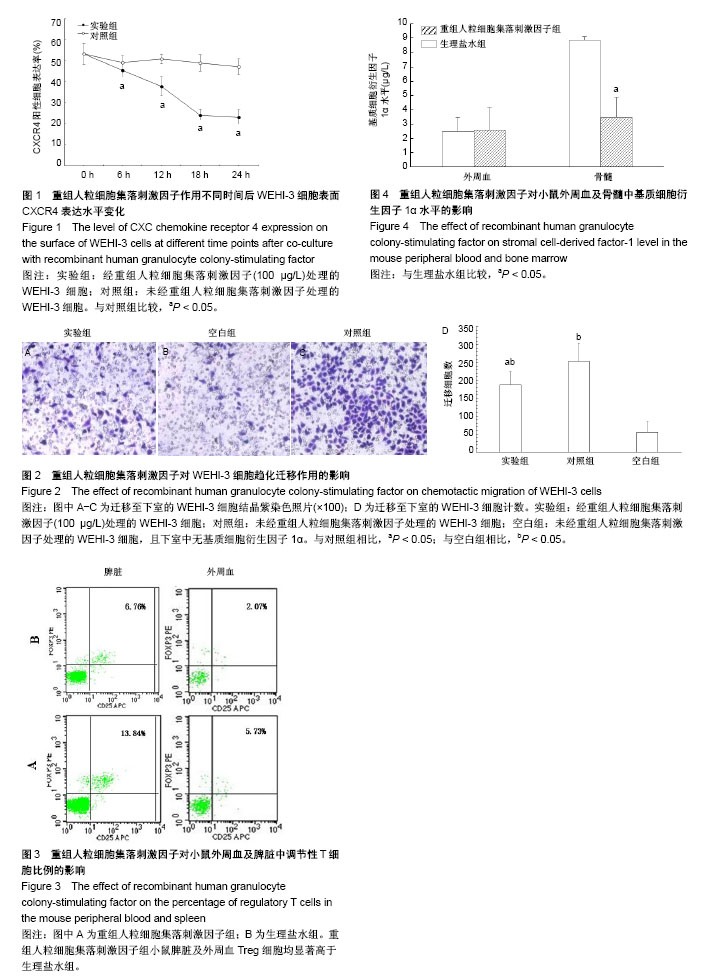
2.1 rhG-CSF对WEHI-3细胞表面CXCR4表达的影响 二者共同孵育6 h时,实验组WEHI-3细胞CXCR4的表达率为(45.27±3.27)%,对照组为(49.13±3.20)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。共同孵育12 h时,实验组WEHI-3细胞CXCR4的表达率为(37.82±4.51)%,对照组为(50.81±2.24)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。共同孵育18 h时,实验组WEHI-3细胞的CXCR4表达量为(24.11±2.90)%,而对照组为(48.83±3.85)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。共同孵育24 h时,实验组CXCR4的表达率为(23.10± 3.73)%,对照组为(47.04±3.81)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。对照组WEHI-3细胞培养前后CXCR4表达无明显变化(P > 0.05)。 如图1所示,当WEHI-3细胞与rhG-CSF共同孵育6,12,18,24 h时,与同时间点对照组相比,CXCR4的表达量均明显下降(P < 0.05)。随孵育时间的延长呈下降趋势,但是共同培养18 h与24 h相比二者CXCR4表达量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),CXCR4表达量基本稳定,不再明显下降。 2.2 rhG-CSF对WEHI-3细胞趋化能力的影响 对迁移至下室的WEHI-3细胞行结晶紫染色,如图2A-C所示,对照组未经rhG-CSF处理的WEHI-3细胞可在SDF-1α趋化因子的驱动下正常迁移至下室,空白组细胞在无SDF-1α作用下只有极少量细胞迁移至下室,而实验组经rhG-CSF处理后迁移至下室的WEHI-3细胞较对照组明显减少。 倒置显微镜下细胞计数结果如图2D所示,实验组WEHI-3细胞迁移至下室细胞数显著低于对照组,二者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),提示WEHI-3细胞与rhG-CSF共培养18 h后对SDF-1α趋化迁移能力显著下降(P < 0.05)。 2.3 rhG-CSF对小鼠外周血Treg细胞比例的影响 如图3所示,rhG-CSF组Balb/C小鼠经过rhG-CSF处理后,外周血CD4+CD25+FOXP3+细胞占CD4+细胞比例为(6.64±1.60)%,而生理盐水组小鼠外周血中CD4+CD25+FOXP3+细胞占CD4+细胞比例为(2.96±0.29)%。rhG-CSF组小鼠外周血Treg细胞比例显著高于生理盐水组(P < 0.05)。 rhG-CSF组小鼠经过rhG-CSF处理后,脾脏CD4+CD25+FOXP3+细胞占CD4+细胞比例为(14.21±0.86)%,而生理盐水组小鼠脾脏CD4+CD25+FOXP3+细胞占CD4+细胞比例为(6.28±1.13)%。rhG-CSF组小鼠脾脏Treg细胞比例显著高于生理盐水组(P < 0.05)。 2.4 rhG-CSF对小鼠骨髓SDF-1α水平的影响 如图4所示,rhG-CSF组小鼠骨髓腔冲洗液离心后,上清液中SDF-1α水平为(3.47±1.43) μg/L,而生理盐水组SDF-1α水平为(8.87±0.24) μg/L,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),rhG-CSF组较生理盐水组显著降低。而rhG-CSF组小鼠外周血血清SDF-1α水平与生理盐水组相比,二者间差异无显著性意义[rhG-CSF组(2.60±1.60) μg/L;生理盐水组(2.48±1.01) μg/L,P > 0.05],提示rhG-CSF处理可导致健康Balb/C小鼠骨髓中SDF-1α水平显著下降,而对外周血SDF-1α水平无明显影响。"
| [1] Bewick MA, Lafrenie RM. Adhesion dependent signalling in the tumour microenvironment: the future of drug targetting. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(22):2833-2848. [2] Peled A, Tavor S. Role of CXCR4 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Theranostics. 2013;3(1):34-39. [3] Nervi B, Ramirez P, Rettig MP, et al. Chemosensitization of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100. Blood. 2009;113(24):6206-6214. [4] Zeng Z, Shi YX, Samudio IJ, et al. Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML. Blood. 2009;113(24): 6215-6224. [5] Kim HY, Lee SY, Kim DY, et al. Expression and functional roles of the chemokine receptor CXCR7 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood Res. 2015;50(4):218-226. [6] Sison EA, Rau RE, McIntyre E, et al. MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukaemia stem cell interactions with bone marrow stroma promote survival and therapeutic resistance that can be overcome with CXCR4 antagonism. Br J Haematol. 2013;160(6): 785-797. [7] 房丽君,涂怀军,李剑.MSC通过CXCL12/CXCR4轴介导CML细胞对TKI耐药的进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2015,23 (4):1221-1224.[8] Perkins S, Fleischman RA. Hematopoietic microenvironment. Origin, lineage, and transplantability of the stromal cells in long-term bone marrow cultures from chimeric mice. J Clin Invest. 1988;81(4):1072-1080. [9] Reiter J, Drummond S, Sammour I, et al. Stromal derived factor-1 mediates the lung regenerative effects of mesenchymal stem cells in a rodent model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Respir Res. 2017;18(1):137. [10] Shi H, Lu R, Wang S, et al. Effects of SDF-1/CXCR4 on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Inflammation. 2017;40(3):937-945. [11] Sharma M, Afrin F, Tripathi R, et al. Regulated expression of CXCR4 constitutive active mutants revealed the up-modulated chemotaxis and up-regulation of genes crucial for CXCR4 mediated homing and engraftment of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2013;9(1):19-27. [12] Zhang B, Liu N, Gu B, et al. Effect of high glucose on migration of BMSCs through inhibiting CXCR-4. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2014;23(6):646-650. [13] Wu J, Wu X, Liang W, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of chemokine receptor CXCR4 overexpression in patients with esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(4):3709-3715. [14] Han M, Lv S, Zhang Y, et al. The prognosis and clinicopathology of CXCR4 in gastric cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(5):4589-4597. [15] Lv S, Yang Y, Kwon S, et al. The association of CXCR4 expression with prognosis and clinicopathological indicators in colorectal carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis. Histopathology. 2014;64(5):701-712. [16] Möhle R, Schittenhelm M, Failenschmid C, et al. Functional response of leukaemic blasts to stromal cell-derived factor-1 correlates with preferential expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in acute myelomonocytic and lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000;110(3):563-572. [17] Tavor S, Petit I. Can inhibition of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis eradicate acute leukemia. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010;20(3):178-185. [18] Passaro D, Quang CT, Ghysdael J. Microenvironmental cues for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia development. Immunol Rev. 2016;271(1):156-172. [19] Triplett TA, Cardenas KT, Lancaster JN, et al. Endogenous dendritic cells from the tumor microenvironment support T-ALL growth via IGF1R activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(8):E1016-1025. [20] Ten Hacken E, Burger JA. Microenvironment interactions and B-cell receptor signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863(3):401-413. [21] Poznansky MC, Olszak IT, Foxall R, et al. Active movement of T cells away from a chemokine. Nat Med. 2000;6(5):543-548. [22] Kim HK, De La Luz Sierra M, Williams CK, et al. G-CSF down-regulation of CXCR4 expression identified as a mechanism for mobilization of myeloid cells. Blood. 2006;108(3):812-820. [23] Zhang WG, Wang FX, Chen YX, et al. Combination chemotherapy with low-dose cytarabine, homoharringtonine, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor priming in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2008;83(3): 185-188. [24] 吉宇莹,张王刚,陈银霞,等.GHA预激方案治疗急性单核细胞白血病的机制及临床研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2010,18(1):213-218.[25] Sison EA, Brown P. The bone marrow microenvironment and leukemia: biology and therapeutic targeting. Expert Rev Hematol. 2011;4(3):271-283. [26] Delgado MB, Clark-Lewis I, Loetscher P, et al. Rapid inactivation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 by cathepsin G associated with lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31(3):699-707. [27] De La Luz Sierra M, Gasperini P, McCormick PJ, et al. Transcription factor Gfi-1 induced by G-CSF is a negative regulator of CXCR4 in myeloid cells. Blood. 2007;110(7): 2276-2285. [28] Strauss L, Bergmann C, Szczepanski M, et al. A unique subset of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells secreting interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(15 Pt 1): 4345-4354. [29] Zou W. Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(4):295-307. [30] Zou L, Barnett B, Safah H, et al. Bone marrow is a reservoir for CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells that traffic through CXCL12/CXCR4 signals. Cancer Res. 2004;64(22):8451-8455. [31] Vela-Ojeda J, García-Ruiz Esparza MA, Reyes-Maldonado E, et al. Peripheral blood mobilization of different lymphocyte and dendritic cell subsets with the use of intermediate doses of G-CSF in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol. 2006;85(5):308-314. [32] Matsushita N, Pilon-Thomas SA, Martin LM, et al. Comparative methodologies of regulatory T cell depletion in a murine melanoma model. J Immunol Methods. 2008;333(1-2):167-179. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||