Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (31): 5009-5014.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0365
Previous Articles Next Articles
Computed tomography for the detection of distal radioulnar joint instability fracture: normal variation and reliability of four scoring systems
Wang Xin
- Department of Radiology, Hainan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Haikou 570203, Hainan Province, China
-
Online:2018-11-08Published:2018-11-08 -
Contact:Wang Xin, Department of Radiology, Hainan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Haikou 570203, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Wang Xin, Attending physician, Department of Radiology, Hainan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Haikou 570203, Hainan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xin. Computed tomography for the detection of distal radioulnar joint instability fracture: normal variation and reliability of four scoring systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(31): 5009-5014.
share this article
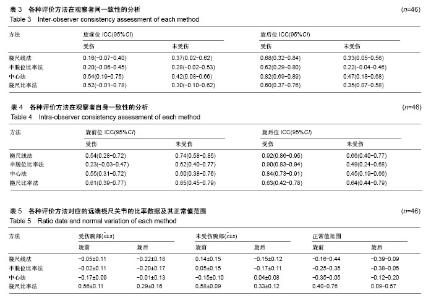
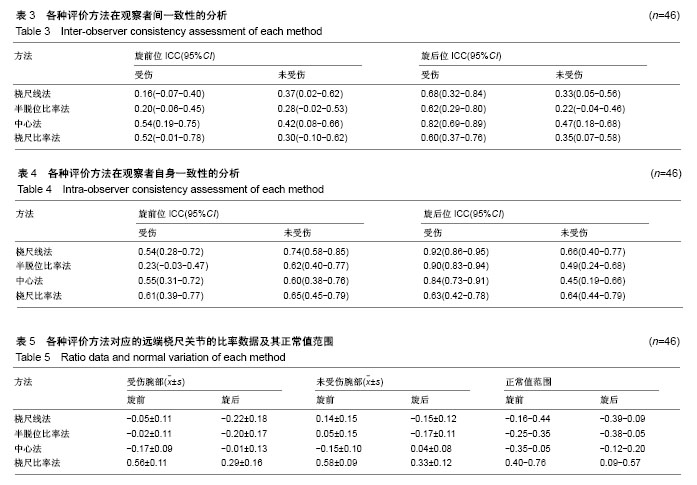
2.1 患者一般资料 研究对象的一般情况见表1。试验干预流程图见图5。伤侧腕部的前臂旋前及旋后角度间无统计学差异,健侧腕部的前臂旋前及旋后角度间亦无统计学差异(P伤侧=0.13,P健侧=0.84)。对于伤侧腕部,疼痛患者与非疼痛患者在旋前及旋后活动度(指伤侧角度/健侧角度)上无统计学差异(P旋前=0.78,P旋后=0.06)。 2.2 各种方法的一致性分析结果 结合观察者间一致性及观察者自身一致性,中心法具有最佳的可信度(ICC分别为0.73及0.82),见表2。当考虑腕部位置时,中心法无论在旋前位(ICC=0.47,95%CI:0.16-0.67)还是在旋后位(ICC=0.72,95%CI:0.58-0.81)仍均具有最佳的观察者间一致性。当考虑腕部位置时,桡尺线法在旋前位(ICC=0.67,95%CI:0.53-0.77)及旋后位(ICC=0.82,95%CI:0.74- 0.88)具有最佳的观察者自身一致性。此外,所有旋后位置上的ICCs均高于旋前位,提示旋后位置上诊断的一致性更高。 在单独分析观察者间一致性时,此4种方法ICCs及95%CI结果,见表3。结果可见中心法在旋后位上,对伤侧腕部的检测拥有完美可靠性(ICC=0.82),明显高于健侧腕部。 在单独分析观察者自身一致性时,4种方法ICCs及95%CI结果,见表4。结果可见半脱位比率法在旋后位上,对伤侧腕部的检测拥有完美可靠性(ICC=0.92),明显优于健侧腕部。 2.3 各种方法对应的远端桡尺关节正常值范围 4种方法测量所得的比率数据(CD/AB及AD/AB)及其正常值范围见表5。"

| [1] Rehman FU, Ajmal M. Effect of malunited fractured distal end of radius on the morphometric parameters of distal radioulnar joint. JMS. 2016; 32(3):124-128. [2] Wijffels MME, Keizer J, Buijze GA, et al. Ulnar styloid process nonunion and outcome in patients with a distal radius fracture: a meta-analysis of comparative clinical trials. Injury. 2014;45(12): 1889-1895. [3] Sammer DM, Shah HM, Shauver MJ, et al. The effect of ulnar styloid fractures on patient-rated outcomes after volar locking plating of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg. 2009;34(9):1595-1602. [4] Lindau T, Adlercreutz C, Aspenberg P. Peripheral tears of the triangular fibrocartilage complex cause distal radioulnar joint instability after distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg. 2000;25(3):464-468.[5] Lindau T, Hagberg L, Adlercreutz C, et al. Distal radioulnar instability is an independent worsening factor in distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;376(376):229. [6] Wijffels M, Ring D. The influence of non-union of the ulnar styloid on pain, wrist function and instability after distal radius fracture. J Hand Microsurg. 2011;3(1):11-14.[7] Krämer S, Meyer H, O'Loughlin PF, et al. The incidence of ulnocarpal complaints after distal radial fracture in relation to the fracture of the ulnar styloid. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013;38(7):710-717.[8] Dy C J, Jang E, Meyers K, et al. The impact of coronal alignment on distal radioulnar stability following distal radius fracture : not a clinical study. J Hand Surg. 2013;38(10):e7-e8.[9] Kitamura T, Moritomo H, Arimitsu S, et al. The biomechanical effect of the distal interosseous membrane on distal radioulnar joint stability: a preliminary anatomic study. J Hand Surg. 2011;36(10): 1626-1630.[10] Sung KB, Song HS. A comparison of ulnar shortening osteotomy alone versus combined arthroscopic triangular fibrocartilage complex debridement and ulnar shortening osteotomy for ulnar impaction syndrome. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(3):184-190.[11] Garcia-Elias M. CHAPTER 28-management of soft tissue contractures around the distal radioulnar joint. Principles Practice Wrist Surg. 2010; 11(3):327-334. [12] Lee SK, Lee JW, Choy WS. Volar stabilization of the distal fadioulnar joint for chronic instability using the pronator quadratus. Ann Plastic Surg. 2014;76(4):27-57. [13] Calfee RP, Wilson JM, Wong AHW. Variations in the anatomic relations of the posterior interosseous nerve associated with proximal forearm trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(1):81-90.[14] Kim JK, Koh YD, Do NH. Should an ulnar styloid fracture be fixed following volar plate fixation of a distal radial fracture? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):1. [15] Jupiter JB. Commentary: the effect of ulnar styloid fractures on patient-rated outcomes after volar locking plating of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg. 2009;34(9):1603-1604. [16] Sachs C, Lehnhardt M, Daigeler A. Das chronisch dezentrierte und instabile distale Radioulnargelenk. Trauma Und Berufskrankheit. 2014;16(4):237-244.[17] Katayama T, Ono H, Suzuki D, et al. Distribution of primary osteoarthritis in the ulnar aspect of the wrist and the factors that are correlated with ulnar wrist osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42(9):1253-1258. [18] Lee SK, Song YD, Choy WS. Correlation between dorsovolar translation and rotation of the radius on the distal radioulnar joint during supination and pronation of forearm. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2015;81(3):511. [19] Henmi S, Yonenobu K, Akita S, et al. Diagnosis of distal radioulnar joint subluxation in patients with rheumatoid wrist by computed tomography. Modern Rheumatol. 2007;17(4):279-282.[20] Lee SK, Song YD, Choy WS. Correlation between dorsovolar translation and rotation of the radius on the distal radioulnar joint during supination and pronation of forearm. Acta Orthop Belgica. 2015; 81(3):511. [21] O’Malley MP, Rodner C, Ritting A, et al. Investigation of triaxial stress state in retained austenite during quenching of a low alloy steel by In situ X-ray diffraction. Adv Mate Res. 2014;996(9):525-531.[22] Lo IK, Macdermid JC, Bennett JD, et al. The radioulnar ratio: a new method of quantifying distal radioulnar joint subluxation. J Hand Surg. 2001;26(2):236-243. [23] Heiss-Dunlop W, Couzens GB, Peters SE, et al. Comparison of plain X-rays and computed tomography for assessing distal radioulnar joint inclination. J Hand Surg. 2014;39(12):2417-2423.[24] Henmi S, Yonenobu K, Akita S, et al. Diagnosis of distal radioulnar joint subluxation in patients with rheumatoid wrist by computed tomography. Modern Rheumatol. 2007;17(4):279-282.[25] Park MJ, Kim JP. Reliability and normal values of various computed tomography methods for quantifying distal radioulnar joint translation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(1):145-153.[26] 王亦璁.骨折治疗的微创术式[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(3):190-192.[27] Laoutliev B, Havsteen I, Bech BH, et al. Interobserver agreement in fusion status assessment after instrumental desis of the lower lumbar spine using 64-slice multidetector computed tomography: impact of observer experience. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(10):2085-2090.[28] Johan AP, van Kollenburg AC, Vrahas MS, et al. Diagnosis of union of distal tibia fractures: a ccuracy and interobserver reliability. Injury. 2013;44(8):1073-1075.[29] Shieh G. Sample size requirements for the design of reliability studies: precision consideration. Behav Res Methods. 2014;46(3):808-822.[30] Hess F, Farshad M, Sutter R, et al. A novel technique for detecting instability of the distal radioulnar joint in complete triangular fibrocartilage complex lesions. Jnl Wrist Surg. 2012;1(2):153-158.[31] Kim JP, Park MJ. Assessment of distal radioulnar joint instability after distal radius fracture: comparison of computed tomography and clinical examination results. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(9):1486-1492. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||