Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (27): 4410-4416.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0359
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fat embolism after arthroplasty
Li Teng-qi1, Sun Wei1, Wang Yun-ting2
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Clinical Medical College, Peking University, Beijing 100029, China; 2Health and Family Planning of Tibet Autonomous Region, Lasa 850000, Tibet Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2018-09-28Published:2018-09-28 -
Contact:Sun Wei, Chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Clinical Medical College, Peking University, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Li Teng-qi, Doctoral candidate, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Clinical Medical College, Peking University, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81372013 and 81672236
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Teng-qi, Sun Wei, Wang Yun-ting. Fat embolism after arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(27): 4410-4416.
share this article
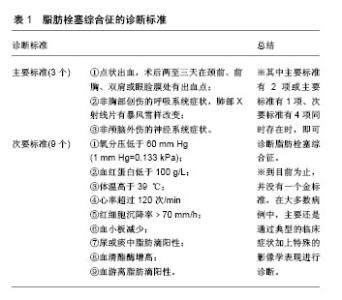
2.1 病因 脂肪栓塞综合征往往发生在创伤患者中,尤其是长骨或多处骨折后。除此之外,骨折手术中扩髓、骨盆骨折及关节置换都是其重要原因。还有长期类固醇摄入、静脉高营养状态、抽脂术以及骨髓移植等较少见的医源性因素。非医源性的原因更为少见,但也时有发生,比如镰刀细胞危象、胰腺炎、脂肪液化、肝脂肪变性、糖尿病、骨髓炎及骨肿瘤溶解等[4]。 2.2 发病机制 脂肪栓塞综合征主要影响毛细血管,尤其是静脉端的毛细血管。因此,肺脏成为其主要受累器官。此外,脂滴及乳糜微粒也可进入全身循环系统从而影响心脏、大脑、皮肤及视网膜等器官。引起这些全身症状的机制包括:①肺内的动静脉畸形;②被挤压变形的脂滴通过了肺毛细血管;③经未关闭的卵圆孔从而绕过了肺循环;④因肺内压突然上升导致关闭的卵圆孔再次开放[4]。Roberts等[7]在2013年报道了1例卵圆孔关闭不全的患者半髋关节术后出现脑脂肪栓塞,此患者并非受心肺复苏影响(心肺复苏过程中胸外压的增加有可能导致微脂肪栓子进入系统循环)。脂肪栓塞综合征的具体发病机制目前尚不清楚,根据文献报道,有两种机制得到较多认可[1,4,8]。一是机械机制,在骨折和关节手术中,由于髓内钉的置入,引起髓内压增加,最终导致脂滴进入脉管系统而引起的物理性阻塞。脂滴随静脉系统进入肺循环,阻塞肺毛细血管网,当其阻塞达80%肺毛细血管网时,会导致急性心功能不全。脂滴形成的肺栓子会引起肺灌注压上升,肺血管充血,导致右心负荷增加。随着呼吸增加,右心通过扩张增加心排出量,这也需要回心血量的增加,此时心电图会提示右心劳损。而心脏最易受低血容量影响,患者此时常死于急性右心衰竭[1-2,4,9-10]。另一种是生化机制,当肺内出现脂滴时,肺能够分泌脂肪酶,将脂肪分解为游离脂酸和甘油。游离脂酸可引起附近炎症反应,增加毛细血管的通透性,破坏肺泡结构及肺泡表面活性物质,对肺脏及毛细血管内皮直接造成毒性作用。另外,骨折和败血症也会引起体内激素水平的改变,从而导致循环系统中出现游离脂酸。从脂肪栓子到游离脂酸的转化一般需要24-48 h,因此脂肪栓塞综合征通常也发生于栓子入侵后的24- 72 h内[1-2,4,9]。 2.3 临床表现 脂肪栓塞综合征通常表现为多器官的功能紊乱,尤其是呼吸系统、中枢神经系统、心血管系统、皮肤和眼球。这些症状通常在发病12-72 h后出现。脂肪栓塞综合征可无任何临床症状,也可表现为短时间急性损伤的致命事件,甚至造成患者迅速死亡。亚临床脂肪栓塞综合征可发生于几乎所有的长骨骨折患者中,其主要表现为血压分压的降低,比较微小的血生化变化,并无特殊临床症状,比如呼吸困难等。临床上往往将其与一些术后症状混淆,例如疼痛、感觉不适、炎症反应、呼吸急促、心动过速以及发热等[1,4,9]。 呼吸系统的症状常是首发症状。多表现为血氧不足、呼吸急促及呼吸困难。甚至一些患者会直接发展为呼吸衰竭,需要立即行机械通气。如果没有持续的脂肪栓子或感染继续发生,肺功能往往会在第3天恢复。神经系统的症状一般于10-120 h后出现而且不同患者表现差异很大,从意识不清至癫痫。主要包括兴奋、焦虑、烦躁、意识不清、瞻望以及昏迷。人们认为这些症状主要是大脑缺氧的直接后果,而不是脑栓塞。并且这些症状一般是一过性、可恢复的。Yao等[11]通过回顾性调查发现轻度的意识障碍主要由不完全脑栓塞引起,正是因为其临床症状不典型而常被忽视。当然也存在不可恢复的永久性损伤如失语症、双侧瞳孔不等大、失用症等。皮肤瘀点、瘀斑可能是脂肪栓塞综合征的最后症状,由红细胞从过度扩张的毛细血管溢出所形成,主要出现在上胸部及腋窝,一般发生于36 h内。经常作为脂肪栓塞综合征的诊断性体征,一般为自限性,1周之内就会消失。甚至在肤色较深的患者身上会被忽视[1,4]。 2.4 诊断 关于脂肪栓塞综合征的诊断目前一直存在争议,认可度较高的是Gurd and Wilson提出的脂肪栓塞综合征诊断标准,见表1,包含3个主要标准:①点状出血,术后两三天在颈前、前胸、双肩或眼睑膜处有出血点;②非胸部创伤的呼吸系统症状,肺部X射线片有暴风雪样改变;③非颅脑外伤的神经系统症状。9个次要标准:①血氧分压低于60 mm Hg(1 mm Hg= 0.133 kPa);②血红蛋白低于100 g/L;③体温高于 39 ℃;④心率超过120次/min;⑤红细胞沉降率 > 70 mm/h;⑥血小板减少;⑦尿或痰中脂肪滴阳性;⑧血清酯酶增高;⑨血游离脂肪滴阳性。其中主要标准有 2 项或主要标准有1项、次要标准有4项同时存在时,即可诊断脂肪栓塞综合征。也有学者认为应把心动过速、呼吸急促、发热、大脑受累及动脉血氧含量降低作为诊断标准。还有很多其他观点,不过都与上述标准大同小异。到目前为止,并没有一个金标准,在大多数病例中,主要还是通过典型的临床症状加上特殊的影像学表现进行诊断[12]。不过有学者专门针对脑脂肪栓塞的诊断标准进行了研究,Lee等[13-14]通过对2 000多例双膝关节置换患者的回顾性研究,对脑脂肪栓塞的诊断标准进行了补充和修改,即脑MRI有脑栓塞病灶+1主要标准+至少3个次要标准或者MRI有脑栓塞病灶+2主要标准+至少2个次要标准。另外,患者应没有可导致这些症状的基础性疾病。"

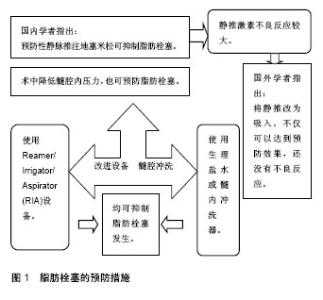
2.5 物理学检查 近些年很多学者对于脂肪栓塞综合征的各种物理学检查进行了颇多研究,其目的主要是探索在脂肪栓塞综合征发病过程中,是否可以通过物理学检查迅速发现,从而早期介入,阻止或延缓其发展。由于脂肪栓塞综合征累及呼吸系统和神经系统时会导致较重后果,所以在物理学检查中将着重对这两个系统进行阐述。 2.5.1 呼吸系统 胸部X射线:对于胸部不适的患者一般都会首选胸片,George等[4]通过回顾性研究提出,脂肪栓塞综合征最初时期胸片并无异常,但随着双侧肺脏的弥漫性绒毛状浸润(暴风雪样现象),尤其是肺底和外周,X射线检查可出现异常。这种典型的暴风雪样现象仅出现于30%-50%患者,这就可以与心源性肺水肿、肺挫伤、急性呼吸窘迫综合征及吸入性肺炎鉴别。而Newbigin 等[12]却认为,脂肪栓塞综合征患者胸片并无特征性,无法与肺水肿、肺挫伤及吸入性或感染性肺炎鉴别,只是在监测疾病进程中有一些作用。 胸部CT:关于胸部CT,脂肪栓塞综合征 典型的影像学表现主要是肺片状磨玻璃样阴影及肺实变。Newbigin等[15]甚至认为胸部CT尤其是高分辨率CT不仅可以提供诊断依据,还可以判定肺部不适的原因。肺片状磨玻璃样阴影主要体现在胸部CT上,可以看出受影响的肺部与正常肺部的明显间隔,主要表现为受累部位小叶缺损。这种位置上的分布可能反映了在栓子事件发生过程中由于肺部分栓塞而引起的肺灌注变化,栓塞部位呈低灌注状态。肺泡腔的实变则为脂肪栓塞综合征更为严重的情况,反映肺部更广泛的出血和水肿。很多关于脂肪栓塞综合征诊断文献中都突出强调了胸部CT在脂肪栓塞综合征诊断中的重要性,那么在脂肪栓塞综合征的整个动态进展中,CT上是否也会表现出动态变化呢?换句话说,影像学表现、症状出现的时间以及手术时间与临床病程及病情严重性是否存在关联。Newbigin等[15]通过临床回顾性研究发现,脂肪栓塞综合征在CT通常表现为肺磨玻璃影和肺实变,少数表现为小叶中心型结节。其中肺磨玻璃影的程度和肺实变的出现与疾病的严重性呈正相关,如果肺磨玻璃影超过肺野的75%或者有肺实变出现,暗示着疾病已经非常严重,需要进行积极的治疗。而前文中,在脂肪栓塞综合征临床表现中提到,并非所有脂肪栓塞综合征都有临床症状,有些甚至被认为是术后症状而被忽视。换句话说,患者可能在没有发现脂肪栓塞综合征的情况下已经痊愈[2]。对于无症状的脂肪栓塞综合征,在诊疗过程中,医生很少会对其进行CT等其他检查,从而也很难收集这类患者的影像学数据。不过Vigdorchik等[16]设计了一项前瞻性研究,收集了无症状的关节置换术后患者1年内的CT影像学数据,所得结果有些出人意料,下肢手术患者存在很高的血管栓塞并发症风险,如深静脉血栓和脂肪栓子。于是Vigdorchik[16]选择了20例全关节置换的患者(15例膝关节,5例髋关节),通过多排CT在术后早期进行扫描,多排CT对肺栓子探测的敏感性达90%-100%,特异性达86%-94%,甚至还可区分出血栓、脂肪栓子和骨水泥栓子。这些学者预测会从术后早期的CT中找到脂肪或骨髓栓子的证据,不过事实并非如此,他们没有发现任何肺栓子,无论是骨髓栓子、脂肪栓子、血栓甚至是微栓子都没有,这与之前的研究形成鲜明对比。尽管有事实证明栓子形成于关节置换术中,但是如果术后CT发现了栓子,那么可以认定为真正的术后并发症;但是如果没有发现,并且肺部症状确实在手术后发生,那么不能够简单地认为是脂肪或骨髓栓塞的结果。除传统CT外,CT肺动脉造影与双能量CT在临床上也用于肺脂肪栓塞的诊断中。但由于肺脂肪栓塞最初只是在外周血管中分散形成小脂滴,CT肺动脉造影很难探测到,所以其受到一定限制。而双能量CT可以使局部对比剂碘化,从而显示出肺灌注情况,在肺脂肪栓塞的诊断中敏感性更高。鉴于此,国内学者通过设计动物实验,将CT肺动脉造影与双能量CT两者进行对比,得出结论:双能量CT在肺动脉栓塞的诊断中敏感性与准确性都较CT肺动脉造影高[17]。 超声:超声心动图具有快速、无创、能够即时反映心室功能的优点。另外还能够很容易监测到任何来源的心腔内栓子。Saranteas等[18]通过对1例半髋关节置换术后患者突发脂肪栓塞综合征的诊疗回顾,再次强调了经胸壁超声心动图对骨科术后患者脂肪栓塞综合征诊断的重要性。这名患者在术后进入麻醉恢复室半小时后出现心动过缓(35 次/min)、低血压(85/45 mm Hg)以及血氧饱和度持续恶化。超声心动图显示:下腔静脉扩张 (2.2 cm),同时看到内部多个强回声的栓子通过下腔静脉进入右心房。患者很快失去意识,血压继续下降,进入抢救状态。此时再次复查超声心动图显示,右心室扩张,收缩功能减退,左心室明显受压,随后患者心率消失,很快死亡。Shine等[19]也通过经食道超声心动图,记录了在髋关节术假体植入时患者突发脂肪栓塞综合征,栓子经过下腔静脉阻塞右心房和三尖瓣的过程。鉴于对死亡患者的诊疗回顾,应该考虑骨科手术中将超声心动图作为术后一段时间内甚至术中的常规监测项目,从而能够及时发现栓子,早期介入,阻止或延缓病情发展。除了监测到栓子,区分出栓子的种类也非常重要,因为这直接影响下一步的治疗方案。Mitsuoka等[20]注意到,多普勒超声可以识别动脉中的栓子特征,评估栓子的位置和大小,从而为预防脑梗死提供指导。那么静脉中的栓子特征是否也可通过多普勒超声识别,从而为预防肺栓塞提供指导。Mitsuoka通过设计动物实验和人体实验发现,不同性质的栓子在彩色多普勒中反应的回声强度和频移这两个参数不同,这就为区分不同栓子提供了理论可能,他们最终发现,在动物体内根据回升强度和频移不同可以将栓子识别并区分出来,而人体试验中,由于术前抗凝治疗、术后穿弹力袜等措施的实行,监测到肺栓子患者较少。无法对栓子分类,不过根据频移参数,能够区分出患者是否存在肺栓子。 2.5.2 神经系统 MRI:对于脑脂肪栓塞,CT的诊断价值不高。有些脑部CT正常的患者在MRI中也可发现小的栓塞病灶。所以大多数学者认为MRI是诊断脑脂肪栓塞的最佳选择,甚至有人建议,关节或骨折术后的患者如果出现急性精神症状,即使脑部CT正常,也应再做脑部MRI,避免漏诊。脂肪栓塞综合征在脑部MRI的典型表现为:T2加权像上多发非融合的高信号小病灶,包括灰质和白质。病灶大小和数量与神经损伤的程度相关。这些病灶一般在症状出现后的4 h内显示出来,然后在数周至数月内逐渐消失。然而,在弥散加权像上,病灶可在症状出现后的1 h内被探测到,主要为多发的点状高信号小病灶。其主要体现了脂肪栓子引起急性脑血管阻塞时,脑细胞发生细胞毒性水肿后产生的病灶。Mustanoja等[21-24]通过病例回顾也提出在全膝关节置换术后出现脑脂肪栓塞时,急性期主要看DWI的点状高信号病灶,推测神经损伤程度时主要关注病灶的数量和大小。Shacklock 等[25]也通过病例回顾指出,对于脑脂肪栓塞,CT在诊断上没有MRI确切。所以对怀疑脑脂肪栓塞的患者,MRI是必不可少的。 2.6 治疗和预防 在脂肪栓塞综合征中,预防、早期发现和及时治疗非常关键。一旦脂肪栓塞综合征诊断成立,患者需立即转入ICU,有条件应该监测中心静脉压,因为中心静脉压可直接反映右心内压力以及肺动脉压状况,可及时指导治疗。白蛋白具有亲脂性,可抵消部分游离脂酸的毒性作用。多巴酚丁胺作为正性肌力药物也可用于脂肪栓塞综合征的治疗,效果较去甲肾上腺素更佳。大剂量的糖皮质激素抗炎,肝素抗凝也用于脂肪栓塞综合征患者的抢救。对于脂肪栓塞,一般溶栓效果较差。除药物外,呼吸支持也是必不可少的,持续面罩吸氧,密切监测血氧分压及氧饱和度,必要时可行机械通气呼气末正压给氧[4,26]。 关于脂肪栓塞综合征的治疗过程,多数文献报道都比较类似。总的原则是呼吸支持、循环支持、抗炎、抗凝、溶栓、强心等。不过作者认为,治疗只是最后一步,最关键的应该是预防,降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率,甚至避免其发生。前已述及,症状较轻的脂肪栓塞综合征一般无需特殊治疗,甚至不治自愈,而症状严重的患者往往来不及抢救。所以,无论是从术前的药物应用、脂肪栓塞综合征风险评估,到手术方式的选择、技术的改进,乃至术后预防性的医疗手段。综合整个诊疗过程,想方设法降低其发生率才是核心。糖皮质激素对脂肪栓塞综合征的治疗效果已得到认可,但能否降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率尚未确定。国内学者Jiang等[27]通过设计随机对照实验,在术中注入骨水泥前1 h静推地塞米松20 mg,对照组用生理盐水。并于术后4,8,24 h行外周静脉血脂肪滴计数及直径测量。得出结论,预防性使用地塞米松,能够有效降低周围血游离脂肪滴数量与直径,抑制脂肪栓塞的形成,减轻栓子对机体组织的损害,缓解呼吸困难、咳嗽、咳痰及高热谵妄等症状,在脂肪栓塞综合征综合防治中起着重要作用。但目前预防性静脉内使用激素受到很多限制,主要原因还是激素的全身不良反应较多,如果能降低甚至避免其不良反应,那么对于脂肪栓塞综合征的预防将会是非常有利的。国外学者Sen等[28]通过设计随机对照试验,对70例单纯骨折患者,实验组预防性使用吸入性环索奈德,根据Gurd标准和动脉血氧监测发现,对照组有更多患者出现脂肪栓塞综合征和低氧血症,两者之间的差别具有统计学意义,再次证明了激素对于预防脂肪栓塞综合征的作用,更重要的是,实验组中患者均未出现激素并发症及不良反应。这也为如何安全使用激素指出了方向。另外,髓内压升高也是诱发脂肪栓塞综合征的重要因素。扩髓及插入髓内钉或初次髋关节置换时髓内压可分别升高至 760 mm Hg及1 000 mm Hg,导致髓腔内脂肪、骨髓组织甚至骨屑进入血液循环。那么从理论上看,如果能降低髓内压,就可以降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率。传统的钻孔和髓内钉植入会导致髓内压升高,致使骨髓和脂肪进入循环。而钻孔器/灌注器/抽吸器(Reamer/ Irrigator/Aspirator RIA)等设备据说可以在钻孔过程中降低髓内压,见图1。Miller等[29]通设计及动物实验,得出结论,与传统钻孔和置入髓内钉技术相比,使用钻孔器/灌注器/抽吸器设备钻孔可明显降低脑脂肪栓塞事件的发生率。既然髓腔内容物入血可引起脂肪栓塞综合征,那么在术中如果将髓腔内容物移除,理论上也能降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率。Zhao等[30]通过设计对照实验,在全膝关节置换术中,用生理盐水冲洗髓腔,通过经食道超声心动观测脂肪栓子,得出结论:在全膝关节置换术中,使用髓腔生理盐水冲洗移除髓腔内容物可使脂肪栓子的数量和大小都明显降低,从而降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率。此外,Baig等[31]也报道了一种简易的髓内冲洗设备,在置入髓内钉之前,尽可能移除髓腔内物质,从而尽量避免脂肪栓塞综合征发生。 目前,半髋关节置换主要存在骨水泥加固型与非骨水泥型2种术式,而骨水泥加固型应用更多,因为有荟萃分析证实,骨水泥加固型术后疼痛较轻,关节灵活度更佳。那么这两种术式对术后脂肪栓塞综合征发生有无影响?有文献指出,在骨水泥置入的过程中有可能引起脂肪栓子入血,导致严重并发症甚至死亡。Kowalski 等[32]通过动物实验研究双侧骨水泥型假体置入与单侧置入对心肺功能的影响,实验最终发现,双侧骨水泥型组肺内脂肪栓子明显更多,约25%的肺血管床都被脂肪阻塞。那么非骨水泥型术式是否会降低脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率?Yli-Kyyny等[33]也通过对200多例患者的回顾性研究证实,非骨水泥型围手术期的骨折概率更高,但心血管事件发生的概率较低,早期死亡率也较低。之后Yli-Kyyny[34]又通过对25 000多例股骨颈骨折行半髋关节手术的患者进行回顾性分析,总结出非骨水泥型术后第1天的死亡率较低,但1周后的死亡率两者并无明显差别,而且术后3个月内,非骨水泥型术式的翻修率和机械并发症更多。 近年来,在全膝关节置换术中使用计算机辅助导航使得下肢与假体组件的对线更佳,不过这种更好的对线系统还没展示出更好的临床预后。与传统全膝关节置换术髓内定位相比,计算机辅助导航技术在脂肪栓塞综合征的预防上好像并没有什么优势。O’Connor等[35-36]通过前瞻性随机对照研究发现,计算机辅助导航对脂肪栓子的形成过程、数量和大小并无任何影响。即使从理论上讲能够抑制脂肪栓子,其效果也无任何临床意义。Malhotra等[37]同样也注意到了这个问题,传统的全膝关节置换术式会使髓腔内压增高,从而导致脂肪栓子形成,而计算机辅助导航不需要使用髓内棒,因而不会增加髓内压,可能会抑制脂肪栓塞综合征发生。Malhotra等[37]也设计了随机对照实验,将两种不同术式进行了对比,最终发现,在传统全膝关节置换术中,通过经食道超声心动监测看到血中栓子量确实更多一些,不过之后的数据分析却发现这种区别没有临床意义。除了计算机辅助导航,还有一种新颖的全膝关节置换技术:Patient specific instrument(PSI),即“个性化”的全膝关节置换术,其可通过患膝的3D成像,制作出针对该患者的截骨工具(包括股骨与胫骨),从而使截骨尽可能减少,创伤更小。而且这种微型截骨工具不进入髓腔,无论是术中出血量还是术后脂肪栓塞综合征的发生率都会降低。不过Predescu等[38]通过研究发现,Patient specific instrument(PSI)与传统全膝关节置换术在手术时间、术后力线以及术后活动度上并无明显差别,暂时只能作为一种替代疗法,需要更多的试验去验证。 "
| [1] Yeo SH, Chang HW, Sohn SI, et al. Pulmonary and cerebral fat embolism syndrome after total knee replacement. J Clin Med Res. 2013;5(3):239-242.[2] Volpin G, Gorski A, Shtarker H, et al. Fat embolism syndrome following injuries and limb fractures. Harefuah. 2010;149(5): 304-308, 335.[3] Sakashita M, Sakashita S, Sakata A, et al. An autopsy case of non-traumatic fat embolism syndrome. Pathol Int. 2017;67(9): 477-482.[4] George J, George R, Dixit R, et al. Fat embolism syndrome. Lung India. 2013;30(1):47-53.[5] Chowdhary V, Mehta V, Bajaj T, et al. Rare imaging of a known entity: fat embolism seen on CT in lower extremity vein after trauma. Radiol Case Rep. 2017;12(3):488-490.[6] Jarmer J, Ampanozi G, Thali MJ, et al. Role of survival time and injury severity in fatal pulmonary fat embolism. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2017;38(1):74-77.[7] Roberts ST, Nicholson DJ, Oakley PW. Cerebral fat embolism following hip hemiarthroplasty in the absence of a patent foramen ovale with almost complete resolution. Hip Int. 2014; 24(3):306-309.[8] Bach AG, Schramm D, Surov A. Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolisms. Radiologe. 2017;57(3):217-230.[9] Michel AS, Coolen J, Verschakelen J, et al. Pulmonary fat embolism. JBR-BTR. 2013;96(5): 319.[10] Ong SCL, Balasingam V. Characteristic imaging findings in pulmonary fat embolism syndrome (FES). BMJ Case Rep. 2017.[11] Yao LB, Wang FA, Yang JA. Mental and behavioral abnormalities after arthroplasty and incomplete cerebral fat embolism. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(2):168-170.[12] Newbigin K, Souza CA, Torres C, et al. Fat embolism syndrome: State-of-the-art review focused on pulmonary imaging findings. Respir Med. 2016;113:93-100.[13] Lee SC, Yoon JY, Nam CH, et al. Cerebral fat embolism syndrome after simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a case series. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3):409-414.[14] Godoy DA, Di Napoli M, Rabinstein AA. Cerebral Fat Embolism: Recognition, Complications, and Prognosis. Neurocrit Care. 2017.[15] Newbigin K, Souza CA, Armstrong M, et al. Fat embolism syndrome: Do the CT findings correlate with clinical course and severity of symptoms? A clinical-radiological study. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(2):422-427.[16] Vigdorchik JM, Riesgo AM, Lincoln D, et al. Pulmonary findings on computed tomography in asymptomatic total joint arthroplasty patients. J Knee Surg. 2016;29(6):478-481.[17] Tang CX, Zhou CS, Zhao YE, et al. Detection of pulmonary fat embolism with dual-energy CT: an experimental study in rabbits. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(4):1377-1385.[18] Saranteas T, Kostopanagiotou G, Panou F. Focused assessed transthoracic echocardiography for the diagnosis of fat embolism in an orthopedic patient with hip hemiarthroplasty. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2014;28(4): e40-1.[19] Shine TS, Feinglass NG, Leone BJ, et al. Transesophageal echocardiography for detection of propagating, massive emboli during prosthetic hip fracture surgery. Iowa Orthop J. 2010;30:211-214.[20] Mitsuoka A, Inoue Y, Kume H, et al. Discrimination of types of venous emboli using Doppler ultrasound. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010;24(6):721-727.[21] Mustanoja S, Sundararajan S, Strbian D. Unconscious patient after elective bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Stroke. 2014; 45(3):e38-39.[22] Lützen N, Niesen WD, Kalbhenn J, et al. Teaching neuroimages: cerebral fat embolism after cemented hip replacement. Clin Neuroradiol. 2016;26(2):249-250.[23] Kokatnur L, Rudrappa M, Khasawneh KR. Cerebral fat embolism: Use of MR spectroscopy for accurate diagnosis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015;18(2):252-255.[24] Carmona R, Tuan A, Hughes TH, et al. Cerebral fat embolism syndrome following revision of right total hip arthroplasty. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014. pii: bcr2014204955.[25] Shacklock E, Gemmell A, Hollister N. Neurological effects of fat embolism syndrome: A case report. J Intensive Care Soc. 2017;18(4):339-341.[26] Chang RN, Kim JH, Lee H, et al. Cerebral fat embolism after bilateral total knee replacement arthroplasty -A case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010;59 Suppl:S207-210.[27] Jiang J, Wang H, Wang Y. Clinical study on effect of dexamethasone in preventing fat embolism syndrome after cemented hip arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24(8):913-916.[28] Sen RK, Prakash S, Tripathy SK, et al. Inhalational Ciclesonide found beneficial in prevention of fat embolism syndrome and improvement of hypoxia in isolated skeletal trauma victims. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017;43(3): 313-318.[29] Miller AN, Deal D, Green J, et al. Use of the reamer/irrigator/aspirator decreases carotid and cranial embolic events in a canine model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98(8): 658-664.[30] Zhao J, Zhang J, Ji X, et al. Does intramedullary canal irrigation reduce fat emboli? A randomized clinical trial with transesophageal echocardiography. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(3):451-455.[31] Baig MN, Curtin W. A simple and easy intramedullary lavage method to prevent embolism during and after reamed long bone nailing. Cureus. 2017;9(8):e1609.[32] Kowalski S, Bell D, Pilkey B. From the journal archives: Pulmonary marrow embolism: lessons learned from a canine model simulating dual component cemented arthroplasty. Can J Anaesth. 2014;61(9):876-880.[33] Yli-Kyyny T, Ojanperä J, Venesmaa P, et al. Perioperative complications after cemented or uncemented hemiarthroplasty in hip fracture patients. Scand J Surg. 2013; 102(2):124-128.[34] Yli-Kyyny T. Cemented or uncemented hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of femoral neck fractures? Acta Orthop. 2014; 85(1):49-53. [35] O'Connor MI, Brodersen MP, Feinglass NG, et al. Fat emboli in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study of computer-assisted navigation vs standard surgical technique. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(7):1034-1040.[36] Venkatesan M, Mahadevan D, Ashford RU. Computer-assisted navigation in knee arthroplasty: a critical appraisal. J Knee Surg. 2013;26(5):357-361.[37] Malhotra R, Singla A, Lekha C, et al. A prospective randomized study to compare systemic emboli using the computer-assisted and conventional techniques of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(11): 889-894.[38] Predescu V, Prescura C, Olaru R, et al. Patient specific instrumentation versus conventional knee arthroplasty: comparative study. Int Orthop. 2017;41(7):1361-1367. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [3] | Shu Wenbo, Chen Mengchi, Li Hua, Huang Liqian, Huang Binbin, Zhang Wenhai, Wu Yachen, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Liu Peng. Correlation between body fat distribution and characteristics of daily physical activity in college students [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1277-1283. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [10] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [12] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [13] | Xie Zhifeng, Liu Qing, Liu Bing, Zhang Tao, Li Kun, Zhang Chunqiu, Sun Yanfang. Biomechanical characteristics of the lumbar disc after fatigue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 339-343. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [15] | Jiang Xiaoyan, Zhu Haifei, Lin Haiqi, Lin Wentao. Cold therapy promotes self-limited recovery of delayed-onset muscle soreness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3609-3613. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||