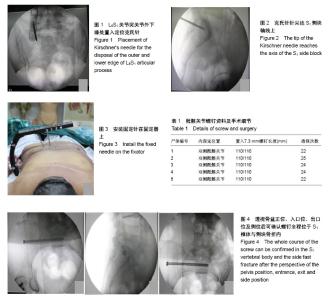
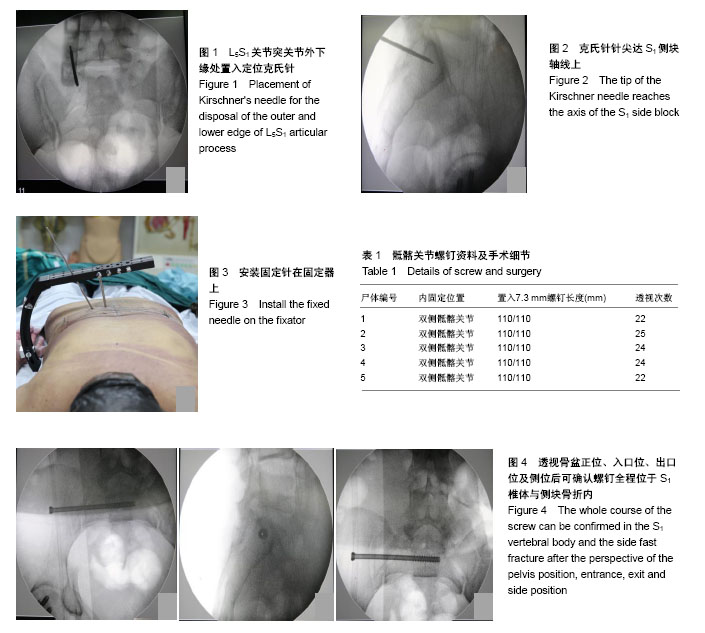
| [1] Zwingmann J, Sudkamp NP, Konig B, et al. Intra- and postoperative complications of navigated and conventional techniques in percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation after pelvic fractures: Results from the German Pelvic Trauma Registry. Injury. 2013;44(12):1765-1772.[2] Krishnan BH, Sharma Y, Magdum G. A retrospective analysis of percutaneous SI joint fixation in unstable pelvic fractures: Our experience in armed forces. Medical journal, Armed Forces India. 2016;72(3):231-235.[3] Sagi HC, Lindvall EM. Inadvertent intraforaminal iliosacral screw placement despite apparent appropriate positioning on intraoperative fluoroscopy. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2005;19(2):130-133. [4] Chen PH, Hsu WH, Li YY, et al. Outcome analysis of unstable posterior ring injury of the pelvis: comparison between percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation and conservative treatment. Biomed J. 2013;36:289-294.[5] Miller AN, Routt ML Jr. Variations in sacral morphology and implications for iliosacral screw fixation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(1):8-16.[6] Zwingmann J, Konrad G, Kotter E, et al. Computer-navigated iliosacral screw insertion reduces malposition rate and radiation exposure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(7): 1833-1838.[7] Takao M, Nishii T, Sakai T, et al. Iliosacral screw insertion using CT-3D-fluoroscopy matching navigation. Injury. 2014; 45(6):988-994.[8] Ziran BH, Wasan AD, Marks DM, et al. Fluoroscopic imaging guides of the posterior pelvis pertaining to iliosacral screw placement. J Trauma. 2007;62(2):347-356; discussion 356.[9] van den Bosch EW, van Zwienen CM, van Vugt AB. Fluoroscopic positioning of sacroiliac screws in 88 patients. J Trauma. 2002;53(1):44-48.[10] Tonetti J, van Overschelde J, Sadok B, et al. Percutaneous ilio-sacral screw insertion. fluoroscopic techniques. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(8):965-972. [11] Templeman D, Schmidt A, Freese J, et al. Proximity of iliosacral screws to neurovascular structures after internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(329):194-198.[12] Tonetti J, Carrat L, Blendea S, et al. Clinical results of percutaneous pelvic surgery. Computer assisted surgery using ultrasound compared to standard fluoroscopy. Comput Aided Surg. 2001;6(4):204-211.[13] Zwingmann J, Konrad G, Mehlhorn AT, et al. Percutaneous iliosacral screw insertion: malpositioning and revision rate of screws with regards to application technique (navigated vs. Conventional). J Trauma. 2010;69(6):1501-1506.[14] Stockle U, Konig B, Hofstetter R, et al. Navigation assisted by image conversion. An experimental study on pelvic screw fixation. Der Unfallchirurg. 2001;104(3):215-220.[15] Hinsche AF, Giannoudis PV, Smith RM. Fluoroscopy-based multiplanar image guidance for insertion of sacroiliac screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(395):135-144.[16] Smith HE, Yuan PS, Sasso R, et al. An evaluation of image-guided technologies in the placement of percutaneous iliosacral screws. Spine. 2006;31(2):234-238.[17] Conflitti JM, Graves ML, Chip Routt ML, Jr. Radiographic quantification and analysis of dysmorphic upper sacral osseous anatomy and associated iliosacral screw insertions. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(10):630-636.[18] Gardner MJ, Routt ML, Jr. Transiliac-transsacral screws for posterior pelvic stabilization. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(6): 378-384. |