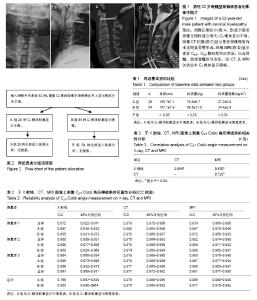
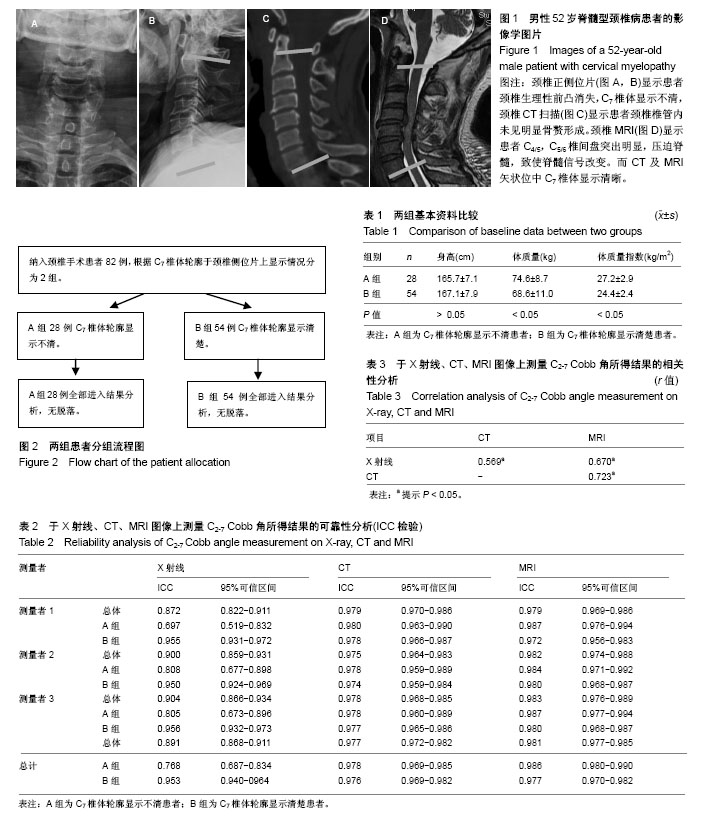
| [1] Miyazaki M, Hymanson HJ, Morishita Y, et al.Kinematic analysis of the relationship between sagittal alignment and disc degeneration in the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(23):E870-876.[2] 赵文奎,于淼,韦峰,等.无症状成人颈椎矢状位曲度分析及其与全脊柱矢状位参数的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(3): 231-238.[3] 王磊,王伟,张永兴,等.保留颈后方韧带复合体单开门椎管扩大成形术后其颈椎生理曲度及活动范围的中远期随访[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(3):222-226.[4] 林圣荣,周非非,孙宇,等.颈后路单开门椎管扩大椎板成形术后颈椎矢状面平衡的变化[J].中华医学杂志, 2014, 94(35): 2726-2730.[5] 鲍达,马远征,袁文,等.前路融合内固定方式对颈椎曲度的影响[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2004, 24(12):705-708.[6] 邓元,倪斌.颈椎矢状序列测量方法的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(7):655-659.[7] Jun HS, Chang IB, Song JH, et al.Is it possible to evaluate the parameters of cervical sagittal alignment on cervical computed tomographic scans? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39(10):E630-636.[8] 张明才,石印玉,王翔,等.颈椎生理曲度异常对颈椎病发病作用的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(10):746-749.[9] 白晓东,张韶峰,杨传铎,等.颈椎曲度异常的测量及其病因[J].中国临床康复, 2005,9(30):10-12.[10] Villavicencio AT, Babuska JM, Ashton A, et al.Prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical study evaluating the correlation of clinical outcomes and cervical sagittal alignment.Neurosurgery. 2011;68(5):1309-1316.[11] Park MS, Kelly MP, Lee DH, et al.Sagittal alignment as a predictor of clinical adjacent segment pathology requiring surgery after anterior cervical arthrodesis. Spine J. 2014;14(7): 1228-1234.[12] Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, et al.The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery.Neurosurgery. 2012;71(3):662-669.[13] Silber JS, Lipetz JS, Hayes VM, et al.Measurement variability in the assessment of sagittal alignment of the cervical spine: a comparison of the gore and cobb methods.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(4):301-305.[14] 蒋维利,申才良,董福龙,等.颈椎间盘突出程度与颈椎X线片相关指标测量值的相关性研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志, 2015,20(2): 112-117.[15] 王连雷,刘新宇,原所茂,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者颈椎矢状位曲度变化及影响因素分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2015, 33(6):712-716,720.[16] 张浩,周文超,陈元元,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症单开门椎管扩大成形术后颈椎矢状位参数变化与疗效的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016,26(3):206-210. |