Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (28): 4580-4586.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0300
Previous Articles Next Articles
Roles of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor and their precursors in nervous system
Dai Yun-fei1, Wang Tong-tong1, Ma Wei1, Yang Jin-wei1, 2, Wang Xian-bin1, Zhang Tong2, Su Ping3, Guo Jian-hui2, Li Li-yan1
- 1Institute for Neuroscience, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Second Department of General Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 3the First People’s Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2018-03-10 -
Contact:Li Li-yan, MD, Professor, Institute for Neuroscience, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China Corresponding author: Guo Jian-hui, Professor, Second Department of General Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China Corresponding author: Su Ping, Chief physician, the First People’s Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Dai Yun-fei, Master candidate, Institute for Neuroscience, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China Wang Tong-tong, Master, Institute for Neuroscience, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China Dai Yun-fei and Wang Tong-tong contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31560295; the Basic Applied Research of Yunnan Province (Combined Project of Kunming Medical University), No. 2015FB098; the Health Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province, No. 2014NS202
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Yun-fei1, Wang Tong-tong1, Ma Wei1, Yang Jin-wei1, 2, Wang Xian-bin1, Zhang Tong2, Su Ping3, Guo Jian-hui2, Li Li-yan1. Roles of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor and their precursors in nervous system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4580-4586.
share this article
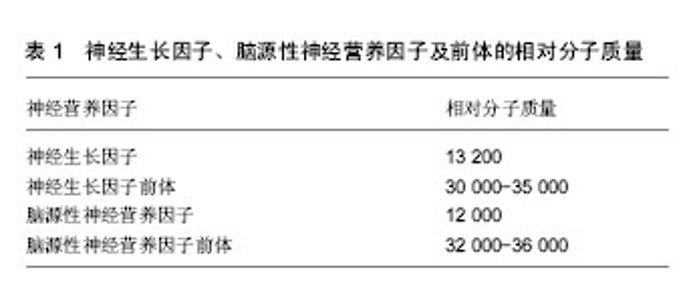
2.2 神经生长因子及前体 成熟的神经生长因子由118个氨基酸残基组成,相对分子质量约为13 200(表1),一级结构具有50%的相似性,主要来源于中枢神经系统、胎盘组织、唾液腺、前列腺、蛇毒腺以及脑内胆碱能神经元支配区。神经生长因子主要在海马和大脑皮质产生[10]。生理状态下,神经生长因子在脑内的含量由低到高依次为纹状体、小脑、基底前脑、嗅球、大脑皮质和海马[11]。研究发现神经生长因子在胚胎发育阶段可以维持神经元存活,促进神经元生长和发育,而在神经受损后能够阻止损伤神经元的死亡,同时可以促进神经元的分化[12]。神经生长因子在体内首先以前体形式合成,神经生长因子前体的相对分子质量为30 000-35 000(表1),其可通过多种蛋白酶的裂解作用合成成熟的神经生长因子[13]。近年来研究发现在神经生长因子的合成过程中,其前体表现出了与神经生长因子相反的生物学作用[12,14]。神经生长因子前体还是一种重要的凋亡因子,广泛分布于神经系统以及非神经系统的组织及细胞中[14],并且神经生长因子前体的前体区域有2个片段存在生物学活性[15]。"
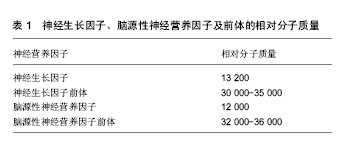
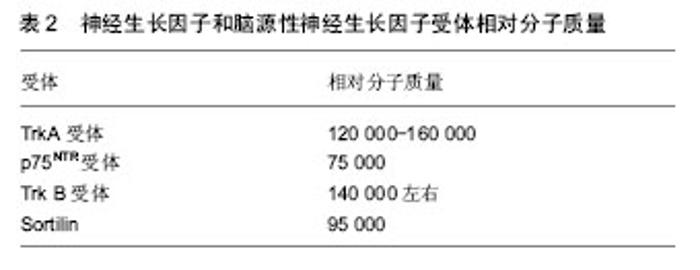
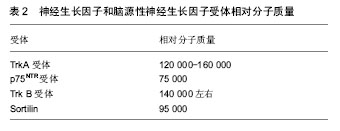
实验证实神经生长因子前体可以在中枢神经系统和外周神经系统等部位检测到,而神经生长因子作为成熟的蛋白在中枢神经系统和外周神经系统等部位检测到的量却很少,说明神经元和星形胶质细胞可以分泌神经生长因子前体,而不分泌成熟的神经生长因子[16]。研究发现神经生长因子前体在胞外的裂解主要是通过纤溶酶起作用[17],主要依赖基质金属蛋白酶3和7[18]。因此推测,细胞内合成的神经生长因子前体可以发挥促神经元存活的生物学功能,也可以在胞外继续存在并产生促细胞凋亡的生物学作用。 2.3 脑源性神经营养因子及前体 脑源性神经生长因子是由119个氨基酸组成的一类相对分子质量为12 000的分泌蛋白(表1),其含有3对二硫键,可在体内以二聚体形式存在[19]。脑源性神经生长因子主要分布在中枢神经系统,在海马和大脑皮质组织中含量最高。脑源性神经生长因子的表达水平在发育阶段中受到调控,在出生 15 d时表达量最高,而后逐渐降低至成体水平[20]。脑区兴奋性刺激可以提高大脑中脑源性神经生长因子mRNA的表达水平[21]。神经元的兴奋可以诱导脑源性神经生长因子在突起处聚集后释放进入到突出间隙[22]。 脑源性神经营养因子前体是成熟脑源性神经生长因子的前体形式,肽链长度为249个氨基酸,氨基酸序列第57和58位点是酶切的识别位点,相对分子质量为 32 000-36 000(表1)。早期研究认为脑源性神经生长因子的基因先转录翻译成脑源性神经营养因子前体,之后在高尔基体和内质网中被丝氨酸蛋白酶裂解,释放出具有生物活性的羧基端成为成熟的脑脑源性神经生长因子蛋白被分泌到胞外从而发挥生物学功能,脑源性神经营养因子前体作为中间物质不发挥生物学功能[23]。近来的研究认为脑源性神经营养因子前体不仅可以作为脑源性神经生长因子的前体形式存在,本身也可由神经元突触直接分泌到细胞外,发挥与脑源性神经生长因子不同的功能[24]。 在细胞外,脑源性神经营养因子前体可以在纤维蛋白溶酶原活化物[25]、丝氨酸蛋白纤溶酶[26]、金属蛋白酶的作用下裂解为成熟的脑源性神经生长因子[27]。胞外未裂解的脑源性神经营养因子前体可以被星形胶质细胞摄取,并在适当的时候释放,使脑源性神经营养因子前体能够循环利用[28]。在细胞内,高尔基体内的内源性枯草杆菌蛋白酶可以将脑源性神经营养因子前体裂解成脑源性神经生长因子;在未成熟的分泌颗粒中可以通过蛋白前体转化酶的作用生成脑源性神经生长因子[29]。 通过使用特异性的脑源性神经营养因子前体的前体结构域抗体研究发现,脑源性神经营养因子前体广泛存在于中枢神经系统包括脊髓背角、三叉神经核、孤束核、杏仁核、海马、下丘脑和大脑皮质等[30]。通过对大鼠的各年龄段研究发现老龄大鼠的海马中大量聚集脑源性神经营养因子前体[31]。除中枢神经系统外,大鼠外周组织的浅表神经末梢、人的唾液和成年海鲈的肝脏、肾脏以及肌肉上也有脑源性神经营养因子前体的分布[32]。 2.4 神经生长因子和脑源性神经生长因子的受体 神经生长因子通过与细胞膜表面的受体结合而发挥作用,根据神经生长因子表面糖蛋白与细胞膜上凝集素结合能力的不同,其受体可被分为高亲和力受体Trk A和低亲和力受体p75NTR[33]。其中p75NTR由于能以相同的亲和力与所有的神经营养素结合,而被称为神经营养素受体[34]。这2种受体分别与神经生长因子相互作用,调控不同的信号通路,对神经元的存活、生长、分化和功能都有重要的调控作用[35]。当Trk A与p75NTR共表达时,p75NTR能够增加Trk A受体对神经生长因子的结合力,从而促进神经突起的生长和存活,也能提升其后的信号传导速 度[36];但是,如果神经生长因子仅与p75NTR结合,则会诱导细胞凋亡[37]。p75也能提高Trk A识别并增强与神经生长因子结合的特异性。如当成纤维细胞中p75和Trk A同时表达时,Trk A只能与神经生长因子结合从而自动磷酸化;而只表达Trk A时,神经生长因子、神经营养因子Ⅲ、神经营养因子Ⅳ、神经营养因子V均能导致Trk A的自动磷酸化[38]。 脑源性神经生长因子的受体有p75NTR和TrkB,其前体的受体有p75NTR、TrkB和sortilin[39]。其中,p75NTR为脑源性神经生长因子的低亲和力受体[40],TrkB为脑源性神经生长因子的高亲和力受体,脑源性神经生长因子通过与高亲和受体TrkB结合发挥促进中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的神经元与胶质细胞的分化和存活、髓鞘形成、神经元迁移和轴突伸缩,以及保护损伤后的神经元等生物学作用[41]。而sortilin是最近发现的vps10p-D (vacuolar protein sorting 10 domain)受体家族成员。 2.4.1 TrkA受体 TrkA受体含有790个氨基酸且相对分子质量为120 000-160 000(表2),是由原癌基因Trk编码的酪氨酸蛋白激酶家族成员,有3个亚型,分别是TrkA、TrkB和TrkC。神经营养因子可分别与其特异结合,其中神经生长因子可优先结合TrkA,脑源性神经生长因子和神经营养因子Ⅳ优先结合TrkB,神经营养因子Ⅲ优先结合TrkC[42]。Trk A是神经生长因子的特异性高亲和力受体,也是其功能性受体,神经生长因子只有与Trk A结合才能发挥出大多数生物学功能。Trk A的分子组成可以分为3个部分:细胞外结构域、跨膜结构域和胞内区。细胞外结构域具有识别并结合神经生长因子的功能;跨膜区和近膜结构域则负责信号的转导和活化;胞内区是Trk A的催化部位,也是Trk A发挥作用的关键部位[43]。神经生长因子与Trk A受体结合主要是通过免疫球蛋白C2结构域,通过跨膜结构域的帮助,在胞内酪氨酸激酶的磷酸化作用下启动并介导下游信号转导通路[44]。"
| [1] Xu ZQ, Li J, Deng J, et al. Effects of proBDNF on cell proliferation and differentiation in hippocampal dentate gyrus in Alzheimer' disease rat model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(19):1353-1356.[2] 薛小燕,郭小华,李敏,等.神经营养因子研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(12):3463-3466.[3] 郭雨霁,李盛芳.神经营养因子家族及其受体的研究进展[J].神经解剖学杂志,2001,17(3):288-294.[4] Ascano M, Bodmer D, Kuruvilla R. Endocytic trafficking of neurotrophins in neural development. Trends Cell Biol. 2012; 22(5):266-273.[5] Shakhbazau A, Martinez JA, Xu QG, et al. Evidence for a systemic regulation of neurotrophin synthesis in response to peripheral nerve injury. J Neurochem. 2012;122(3): 501-511. [6] Hempstead BL. Dissecting the diverse actions of pro- and mature neurotrophins. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006;3(1):19-24.[7] Barde YA, Edgar D, Thoenen H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982; 1(5):549-553.[8] Mandel AL, Ozdener H, Utermohlen V. Identification of pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 2009;54(7):689-695. [9] 张露,崔晓燕,李俊敏,等.糖氧剥夺对海马神经元中成熟脑源性神营养因子及其前体蛋白和突触素的影响[J].中国实用医刊,2016, 43(19):5-8.[10] Salehi A, Delcroix JD, Swaab DF. Alzheimer's disease and NGF signaling. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2004;111(3):323-345.[11] 周莉,李小刚.神经生长因子在脑缺血后的变化及治疗展望[J].西南军医,2011,13(6):1094-1096.[12] Zhou FQ, Zhou J, Dedhar S, et al. NGF-induced axon growth is mediated by localized inactivation of GSK-3beta and functions of the microtubule plus end binding protein APC. Neuron. 2004;42(6):897-912.[13] Bierl MA, Jones EE, Crutcher KA, et al. 'Mature' nerve growth factor is a minor species in most peripheral tissues. Neurosci Lett. 2005;380(1-2):133-137. [14] Song W, Volosin M, Cragnolini AB, et al. ProNGF induces PTEN via p75NTR to suppress Trk-mediated survival signaling in brain neurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30(46): 15608-15615. [15] Dicou E, Pflug B, Magazin M, et al. Two peptides derived from the nerve growth factor precursor are biologically active. J Cell Biol. 1997;136(2):389-398.[16] Yano H, Torkin R, Martin LA, et al. Proneurotrophin-3 is a neuronal apoptotic ligand: evidence for retrograde-directed cell killing. J Neurosci. 2009;29(47):14790-14802. [17] Pang PT, Teng HK, Zaitsev E, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science. 2004;306(5695):487-491.[18] Ethell IM, Ethell DW. Matrix metalloproteinases in brain development and remodeling: synaptic functions and targets. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(13):2813-2823.[19] Mowla SJ, Farhadi HF, Pareek S, et al. Biosynthesis and post-translational processing of the precursor to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276 (16):12660-12666. [20] Ivanova T, Beyer C. Pre- and postnatal expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA/protein and tyrosine protein kinase receptor B mRNA in the mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2001;307(1):21-24.[21] Zafra F, Lindholm D, Castrén E, et al. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1992;12(12):4793-4799.[22] Lu B. BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn Mem. 2003;10(2):86-98.[23] Mandel AL, Ozdener H, Utermohlen V. Identification of pro- and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 2009;54(7):689-695. [24] Pang PT, Teng HK, Zaitsev E, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF by tPA/plasmin is essential for long-term hippocampal plasticity. Science. 2004;306(5695):487-491.[25] Nagappan G, Zaitsev E, Senatorov VV Jr, et al. Control of extracellular cleavage of ProBDNF by high frequency neuronal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(4): 1267-1272.[26] Gray K, Ellis V. Activation of pro-BDNF by the pericellular serine protease plasmin. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(6):907-910.[27] Keifer J, Sabirzhanov BE, Zheng Z, et al. Cleavage of proBDNF to BDNF by a tolloid-like metalloproteinase is required for acquisition of in vitro eyeblink classical conditioning. J Neurosci. 2009;29(47):14956-14964. [28] Bergami M, Santi S, Formaggio E, et al. Uptake and recycling of pro-BDNF for transmitter-induced secretion by cortical astrocytes. J Cell Biol. 2008;183(2):213-221. [29] Seidah NG, Mowla SJ, Hamelin J, et al. Mammalian subtilisin/kexin isozyme SKI-1: A widely expressed proprotein convertase with a unique cleavage specificity and cellular localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96(4):1321-1326.[30] Zhou XF, Song XY, Zhong JH, et al. Distribution and localization of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor-like immunoreactivity in the peripheral and central nervous system of the adult rat. J Neurochem. 2004;91(3):704-715.[31] Perovic M, Tesic V, Mladenovic Djordjevic A, et al. BDNF transcripts, proBDNF and proNGF, in the cortex and hippocampus throughout the life span of the rat. Age (Dordr). 2013;35(6):2057-2070. [32] Tognoli C, Rossi F, Di Cola F, et al. Acute stress alters transcript expression pattern and reduces processing of proBDNF to mature BDNF in Dicentrarchus labrax. BMC Neurosci. 2010;11:4. [33] Cui X, Chen L, Ren Y, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury repair strategies. Biosci Trends. 2013;7(5):202-208.[34] Hondermarck H. Neurotrophins and their receptors in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012;23(6):357-365. [35] Schecterson LC, Bothwell M. Neurotrophin receptors: Old friends with new partners. Dev Neurobiol. 2010;70(5): 332-338. [36] Skaper SD. The neurotrophin family of neurotrophic factors: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;846:1-12. [37] Aloe L. Rita Levi-Montalcini and the discovery of NGF, the first nerve cell growth factor. Arch Ital Biol. 2011;149(2):175-181. [38] Matusica D, Skeldal S, Sykes AM, et al. An intracellular domain fragment of the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR)) enhances tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) receptor function. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(16):11144-11154. [39] Petrie CN, Smithson LJ, Crotty AM, et al. Overexpression of nerve growth factor by murine smooth muscle cells: role of the p75 neurotrophin receptor on sympathetic and sensory sprouting. J Comp Neurol. 2013;521(11):2621-2643. [40] 彭凤玲,莫中成,郑翔,等.神经生长因子及其受体相关信号传导通路的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(31):6190-6193.[41] Matsumoto T, Rauskolb S, Polack M, et al. Biosynthesis and processing of endogenous BDNF: CNS neurons store and secrete BDNF, not pro-BDNF. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(2): 131-133. [42] He XL, Garcia KC. Structure of nerve growth factor complexed with the shared neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 2004;304(5672):870-875.[43] Gargano N, Levi A, Alema S. Modulation of nerve growth factor internalization by direct interaction between p75 and TrkA receptors. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50(1):1-12.[44] Vega CJ, Peterson DA. Stem cell proliferative history in tissue revealed by temporal halogenated thymidine analog discrimination. Nat Methods. 2005;2(3):167-169.[45] Strohmaier C, Carter BD, Urfer R, et al. A splice variant of the neurotrophin receptor trkB with increased specificity for brain-derived neurotrophic factor. EMBO J. 1996;15(13): 3332-3337.[46] Meloni M, Caporali A, Graiani G, et al. Nerve growth factor promotes cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2010;106(7):1275-1284. [47] Vicario A, Kisiswa L, Tann JY, et al. Neuron-type-specific signaling by the p75NTR death receptor is regulated by differential proteolytic cleavage. J Cell Sci. 2015;128(8): 1507-1517.[48] Xu G, He J, Guo H, et al. Activin A prevents neuron-like PC12 cell apoptosis after oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(11):1016-1024. [49] Huang CS, Zhou J, Feng AK, et al. Nerve growth factor signaling in caveolae-like domains at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(51):36707-36714.[50] Iacaruso MF, Galli S, Martí M, et al. Structural model for p75(NTR)-TrkA intracellular domain interaction: a combined FRET and bioinformatics study. J Mol Biol. 2011;414(5): 681-698. [51] 路露,陈美婉,罗焕敏.神经营养因子受体的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(1):126-131.[52] 卞雷斯,刘振国,王文安.神经营养因子受体Trk小分子激动剂研究进展[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2006,14(11):865-869.[53] Bachis A, Rabin SJ, Del Fiacco M, et al. Gangliosides prevent excitotoxicity through activation of TrkB receptor. Neurotox Res. 2002;4(3):225-234.[54] Nakamura K, Namekata K, Harada C, et al. Intracellular sortilin expression pattern regulates proNGF-induced naturally occurring cell death during development. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(8):1552-1554.[55] Sarret P, Krzywkowski P, Segal L, et al. Distribution of NTS3 receptor/sortilin mRNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2003;461(4):483-505.[56] 姜万梅,苗文哲,柳鹏,等.神经生长因子(NGF)对周围神经损伤的再生及恢复作用(综述)[J].伤残医学杂志,2003(4):74-76.[57] Ledesma MD, Da Silva JS, Crassaerts K, et al. Brain plasmin enhances APP alpha-cleavage and Abeta degradation and is reduced in Alzheimer's disease brains. EMBO Rep. 2000;1(6): 530-535.[58] Fahnestock M, Michalski B, Xu B, et al. The precursor pro-nerve growth factor is the predominant form of nerve growth factor in brain and is increased in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001;18(2):210-220.[59] Harrington AW, Leiner B, Blechschmitt C, et al. Secreted proNGF is a pathophysiological death-inducing ligand after adult CNS injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(16): 6226-6230.[60] Lee R, Kermani P, Teng KK, et al. Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science. 2001;294(5548): 1945-1948.[61] Jansen P, Giehl K, Nyengaard JR, et al. Roles for the pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin in neuronal development, aging and brain injury. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(11):1449-1457.[62] Nykjaer A, Lee R, Teng KK, et al. Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature. 2004;427(6977): 843-848.[63] Masoudi R, Ioannou MS, Coughlin MD, et al. Biological activity of nerve growth factor precursor is dependent upon relative levels of its receptors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(27): 18424-18433.[64] 周健,孙克华.神经损伤后的再生与神经营养因子[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2006,11(1):36-38.[65] Yang JW, Ru J, Ma W, et al. BDNF promotes the growth of human neurons through crosstalk with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via GSK-3β. Neuropeptides. 2015;54: 35-46.[66] Tashima R, Mikuriya S, Tomiyama D, et al. Bone marrow-derived cells in the population of spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23701.[67] Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24: 677-736.[68] [68] Koshimizu H, Hazama S, Hara T, et al. Distinct signaling pathways of precursor BDNF and mature BDNF in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2010;473(3): 229-232.[69] [Taylor AR, Gifondorwa DJ, Robinson MB, et al. Motoneuron programmed cell death in response to proBDNF. Dev Neurobiol. 2012;72(5):699-712.[70] Fan YJ, Wu LL, Li HY, et al. Differential effects of pro-BDNF on sensory neurons after sciatic nerve transection in neonatal rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(9):2380-2390.[71] Gibon J, Buckley SM1, Unsain N1, et al. proBDNF and p75NTR Control Excitability and Persistent Firing of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons. J Neurosci. 2015;35(26):9741-9753.[72] Yang M, Lim Y, Li X, et al. Precursor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF) forms a complex with Huntingtin-associated protein-1 (HAP1) and sortilin that modulates proBDNF trafficking, degradation, and processing. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(18):16272-16284. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Luo Xuanxiang, Jing Li, Pan Bin, Feng Hu. Effect of mecobalamine combined with mouse nerve growth factor on nerve function recovery after cervical spondylotic myelopathy surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 719-722. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Xie Yang, Lü Zhiyu, Zhang Shujiang, Long Ting, Li Zuoxiao. Effects of recombinant adeno-associated virus mediated nerve growth factor gene transfection on oligodendrocyte apoptosis and myelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3678-3683. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||