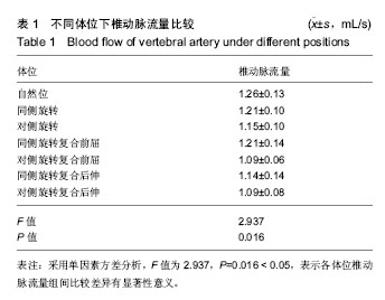
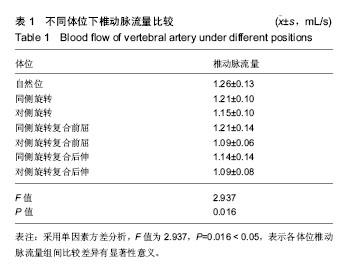
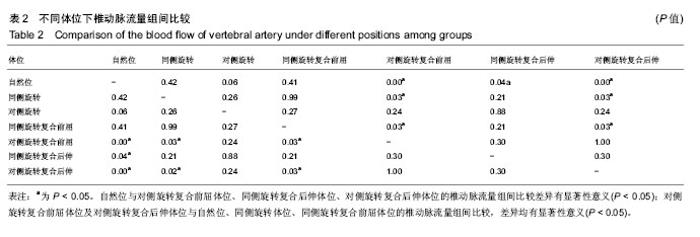
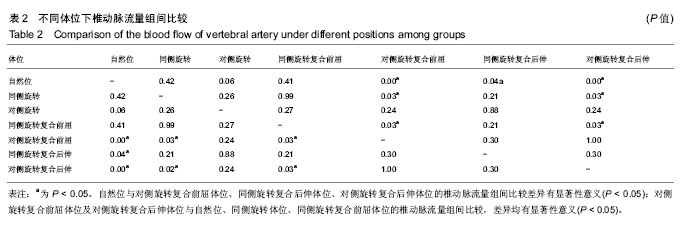
| [1] 戈晓华,邹艳秋,赵红.椎动脉血流失衡状态对椎基底动脉供血不足的影响作用[J].医学影像学杂志,1998,8(1):25-27. [2] 乔羽.颈部血管彩超对椎基底动脉供血不足病因的诊断意义[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2014,2(11):163-165.[3] 赵丽,孙玉山.颈部血管彩超对椎基底动脉供血不足病因诊断的价值[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(8):942-943.[4] 朱丹丹,张炽敏,李嘉.彩色多普勒超声对椎-基底动脉供血不足患者治疗前后椎动脉血流的对比研究[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2008,24(6):517-519.[5] 刘兵,戴玉景.旋转手法治疗椎动脉型颈椎病的应用解剖及流体力学研究[J].中国骨伤,2003,16(2):21-23.[6] 刘静,杨金有,洪洋.正常体位下人体椎动脉内血流动力学数值模拟分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2015,32(1):110-114.[7] 王辉昊,陈博,詹红生,等.流固耦合分析颈椎生理活动对椎动脉血流动力学的影响[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(6):511-516.[8] 廖穗祥,夏虹,昌耘冰,等.上颈椎三维有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(27):5269-5272.[9] 刘兵,戴玉景.旋转手法治疗椎动脉型颈椎病的应用解剖及流体力学研究[J].中国骨伤,2003,16(2):21-23.[10] 刘奎.有限旋转手法对椎动脉型颈椎病的相关骨性解剖学结构的研究[D].湖北中医学院,2007.[11] Maksymowych W, Mallon C, Richardson R, et al. Development and validation of a Simple tape-based measurement tool for recording cervical rotation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: comparison with agoniom-based approach.J Rheumatol. 2006;33(11):2242-2249.[12] Piper SL, Howarth SJ, Triano J, et al. Quantifying strain in the vertebral artery with simultaneous motion analysis of the head and neck: a preliminary investigation. Clin Biomech. 2014;29(10) :1099-1107.[13] 洪水棕,吴振坤,祝曙鸣.人体颈椎的力学实验研究[J].中国医学生物工程学报,1987,2(6):75-83.[14] 周兢,李自清,徐琳琳,等.彩色多普勒超声测量椎动脉血流量对后循环缺血的诊断价值[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(35):6949.[15] 朱立国,张清,高景华,等.旋转手法治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床疗效研究[J].中国骨伤,2005,18(8):489-490.[16] 朱立国,于杰,高景华,等.旋转手法治疗神经根型颈椎病对疼痛的VAS评分临床研究.[J].北京中医,2005,24(5):297-298.[17] 王乾,朱立国,高景华,等.旋提手法治疗神经根型颈椎病的疗效观察[J].中医正骨,2009,21(6):9-11.[18] 朱立国,冯敏山,毕方杉,等.颈椎旋转(提)手法的在体力学测量[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(8):673-676.[19] 朱立国,冯敏山,魏戌,等.个体因素对颈椎旋提手法操作影响的在体力学研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(9):14-17.[20] 冯敏山,朱立国,魏戌,等.颈椎旋提手法操作轨迹的动态捕捉研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(2):176-177.[21] Hurwita EL, Aker PD, Adams A, et al. Manipulation and mobilization of the cervical spine: a systematic review of literature. Spine. 1996;21:1746-1760. [22] Di Fabio RP. Manipulation of the cervical spine: risks and benefits. Phys Ther.1999;79:50-65.[23] Kapral MK, Bondy SJ. Cervical manipulation and risk of stroke. CMAJ. 2001;165(7):907-908.[24] Bertino RE, Talkad AV, DeSanto JR, et al. Chiropractic manipulation of the neck and cervical artery dissection. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(2):150-152.[25] 王辉昊,詹红生,张明才,等.手法治疗颈椎病意外事件分析与预防策略思考[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(9):730-735.[26] 贾杰,闻春艳,张文杰.转颈试验在彩色多普勒超声检测颅外段椎动脉诊断椎动脉型颈椎病的价值[J].中国实用诊断学, 2015,19(9):1544-1545.[27] Powell FC, Hanigan WC, Olivero WC, et al. A risk /benefit analysis of spinal manipulation therapy for relief of lumbar of cervical pain. Neurosurgery. 1993;33(1):73-79.[28] Machaly SA, Senna MK, Sadek AG. Vertigo is associated with advanced degenerative changes in patients with cervical spondylosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30(12):1527-1534.[29] Quesnele JJ, Triano JJ, Noseworthy MD, et al. Changes in vertebral artery blood flow following various head positions and cervical spine manipulation. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014;37(1) :22-31.[30] Thomas LC, McLeod LR, Osmotherly PG, et al. The effect of end-range cervical rotation on vertebral and internal carotid arterial blood flow and cerebral inflow: A sub analysis of an MRI study. Man Ther. 2015;20(3) :475-480. |