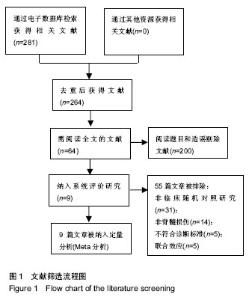
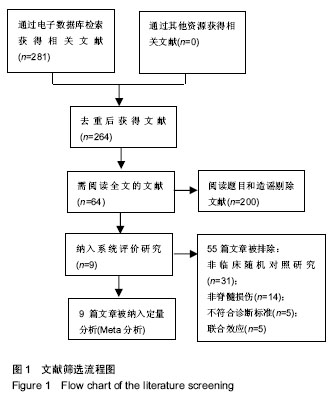
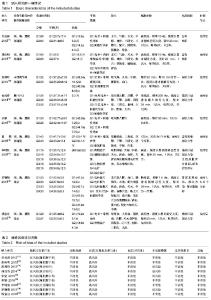
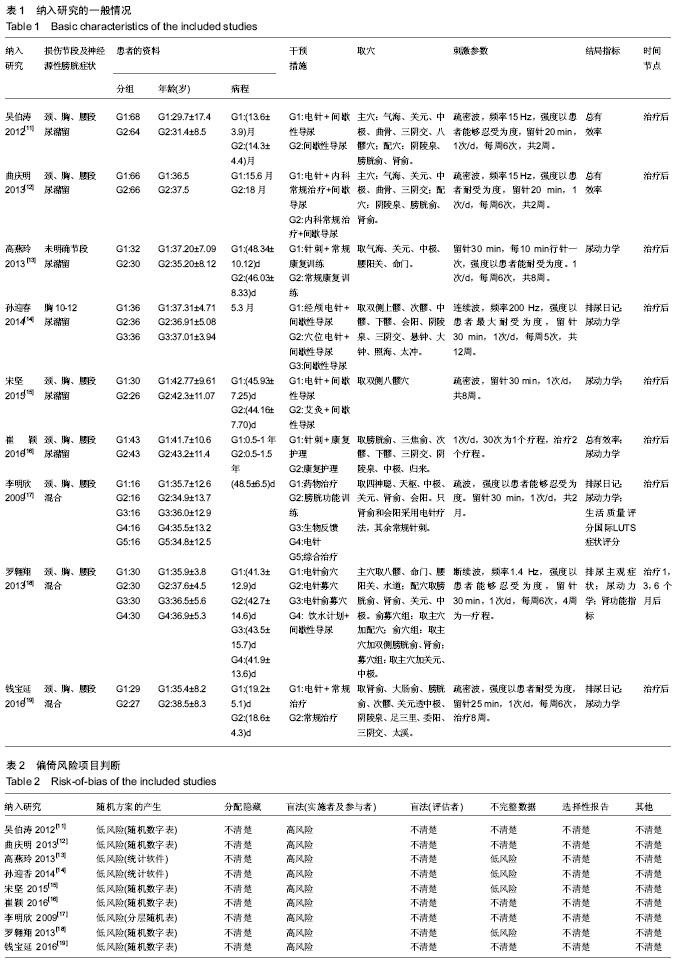
| [1] van den Berg ME, Castellote JM, Mahillo-Fernandez I, et al. Incidence of spinal cord injury worldwide: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology. 2010; 34(3):184-192.[2] 杨枭雄,于前进,秦江,等.脊髓损伤住院患者1027例流行病学分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(5):301-305.[3] 钮晟佳.苏州市脊髓损伤患者流行病学分析及相关因素研究[D].苏州大学,2016.[4] 侯春林.脊髓损伤后膀胱功能重建[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2009,1(1):4-6.[5] 王琰,范建中,王俊,等.脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的康复与治疗[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2009,31(4):197-200.[6] Dahlberg A, Perttilä I, Wuokko E, et al. Bladder management in persons with spinal cord lesion. Spinal Cord. 2004;42(12): 694-698.[7] 谢斌,岳雨珊,朱毅,等.阴部神经电刺激干预脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱:功能重建的文献研究[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(46): 7498-7502.[8] 朱森林,赵健乐,李晨琦,等. 电钉中髎穴治疗脊髓损伤后逼尿肌无力型神经源性膀胱36例[J]. 中国针灸, 2015,35(9):905-906.[9] Higgins JPT, Green S, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley. 2008:187–241.[10] Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta- analyses. BMJ. 2003, 327: 557-560.[11] 吴伯涛,李娟娟.电针联合间歇导尿治疗脊髓损伤后尿潴留68例[J].中医研究,2012, 25(11):68-70.[12] 曲庆明.电针督脉结合间歇导尿治疗外伤性脊髓损伤[J].中国保健营养, 2013,23(12):517-517.[13] 高燕玲,程熙,夏敏.针刺任督二脉经穴对不完全性脊髓损伤后尿潴留的影响[J].中医药通报, 2013, 12(4):46-47.[14] 孙迎春,李建军,程先宽,等.不同部位电针刺激对脊髓损伤逼尿肌无反射型神经源性膀胱逼尿肌压力的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2014, 20(8):734-737.[15] 宋坚.艾灸与电针结合间歇性导尿对神经源性膀胱的疗效对比[J].内蒙古中医药,2015, 34(8):115-116.[16] 崔颖,郭宝.针灸联合康复护理促进脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱恢复[J].长春中医药大学学报, 2016, 32(3):550-551.[17] 李明欣,郑国玲,朱士文,等. 综合治疗脊髓损伤患者神经源性膀胱的临床研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2009,31(9): 625-627.[18] 罗翱翔,由天辉,童钟.电针俞募穴治疗脊髓损伤神经源性膀胱的效果[J].广东医学,2013,34(24):3805-3808.[19] 钱宝延,蔡西国,马玉娟,等.电针俞募穴治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的临床观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016, 31(1):50-53.[20] 赵烨.电针治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱临床疗效的系统评价[D].天津中医药大学, 2015:16-42.[21] Wang J, Zhai Y, Wu J, et al. Acupuncture for chronic urinary retention due to spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016(4):1-9.[22] 王佳.针刺治疗脊髓损伤导致的慢性尿潴留的系统评价和Meta分析[D]. 中国中医科学院,2016:34-53.[23] 廖利民,吴娟,鞠彦合,等.脊髓损伤患者泌尿系管理与临床康复指南[J].中国康复理论与实践,2013,19(4): 301-317.[24] 李建军,杨明亮,杨德刚,等.“创伤性脊柱脊髓损伤评估、治疗与康复”专家共识[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2017, 23(3): 274-287.[25] 苏志维,付莉,郑华斌,等. 基于数据挖掘探析古代针灸对肠道运动的双向调节作用[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(06): 2202-2206.[26] 钟峰,杜俊毅,罗容,等.电针大肠俞募配穴对功能性肠病双向调节作用的临床观察[J].中医临床研究,2016,8(19):39-42.[27] 邓桂珠.电针内关、间使对恐惧情绪状态心率及心率变异性的影响[D].南方医科大学,2015.[28] 彭秀娟,梁琪,张永臣,等.针灸治疗尿潴留常用腧穴文献研究[J].中医杂志,2013,54(23):2046-2048.[29] 章薇,谭志高,曹卷舒,等.基于数据挖掘技术探析古代针灸治疗尿失禁的用穴规律[J].中国针灸,2015,35(12):1299-1303.[30] 王俊华.电针关元穴对脊髓损伤后尿潴留大鼠逼尿肌的影响及机制研究[D].湖北中医学院,2009.[31] 李忠仁. 实验针灸学.北京:中国中医药出版社,2003: 229-230.[32] 刘丛丛.电针次髎/中髎穴兴奋逼尿肌效应及其传入和传出神经调控机制[D].中国中医科学院,2014. |