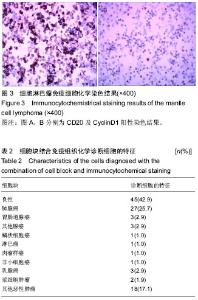
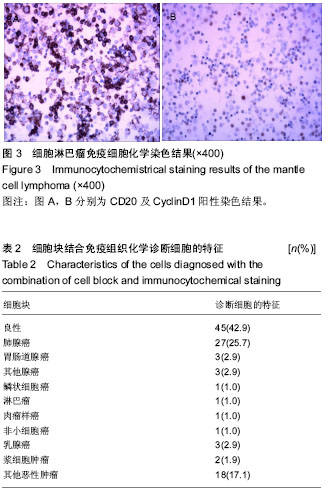
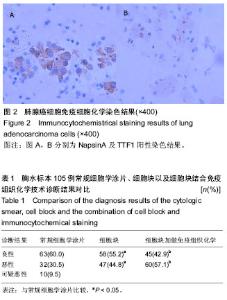
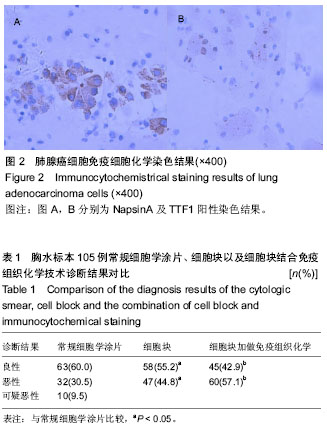
| [1] 董强刚,刘刚,黎飒,等.肺腺癌组织EGFR外显子19基因突变的实时定量PCR检测[J].肿瘤,2006,26(7):596-601.[2] 隋燕霞,柳雨,蒋娜,等.142例恶性胸水细胞蜡块的免疫组织化学检测及分子病理检测[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 2017,33(3): 292.[3] 阎红琳,袁静萍,刘琳,等.细胞蜡块结合免疫细胞化学在浆膜腔积液病理诊断中的应用[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2016,32(12): 1414-1417.[4] 杨新,王秋实,李艳青,等.细胞蜡块结合免疫组织化学有效提高胸水细胞学阳性检出率的临床研究[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2014, 22(12):2894-2897.[5] 权春姬,金仁顺.细胞蜡块结合免疫组织化学在小细胞癌诊断中应用价值[J].临床肺杂志,2017,22(6):1009-1011.[6] 张琪,薛庆亮.良恶性胸腔积液诊断的临床进展[J].临床肺科杂志, 2017,22(11):2101-2105. [7] Ugurluoglu C, Kurtipek E, Unlu Y, et al. Importance of the cell block technique in diagnosing patients with non-small cell carcinoma accompanied by pleural effusion. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP. 2015;16(7):3057-3060.[8] Turner BM, Cagle PT, Sainz IM, et al. Napsin a, a new marker for lung adenocarcinoma, is complementary and more sensitive and specific than thyroid transcription factor 1 in the differential diagnosis of primary pulmonary carcinoma: evaluation of 1674 cases by tissue microarray. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(2):163-171.[9] 周小鸽.淋巴瘤病理诊断中的抗体选择[J].诊断病理学杂志, 2010,17(1):4-6.[10] Werling RW, Yaziji H, Bacchi CE, et al. CDX2, a highly sensitive and specific marker of adenocarcinomas of intestinal origin: an immunohistochemical survey of 476 primary and metastatic carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27(3):303-310.[11] Fetsch PA, Abati A. Immunocytochemistry in effusion cytology: a contemporary review. Cancer. 2001;93(5):293-308.[12] Cheng F, Wang Q, Zhong D. Value of Cell Block in the Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion. Zhongguo Feiai Zazhi. 2015;18(10):652-655.[13] Satouchi M, Tanaka H, Yoshioka H. Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor gene T790M mutation in cytology samples using the cobas® EGFR mutation test. Lung Cancer. 2017;111:190-194. [14] Wang W, Tang Y, Li J, et al. Detection of ALK rearrangements in malignant pleural effusion cell blocks from patients with advanced non-smallcell lung cancer: a comparison of Ventana immunohistochemistry and fluorescencein situ hybridization. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015;123(2):117-122. [15] Billon P, Bryant EE, Joseph SA, et al. CRISPR-Mediated Base Editing Enables Efficient Disruption of Eukaryotic Genes through Induction of STOP Codons. Mol Cell. 2017;67(6): 1068-1079.[16] Paolillo C, Mu Z, Rossi G, et al. Detection of Activating Estrogen Receptor Gene (ESR1) Mutations in Single Circulating Tumor Cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(20): 6086-6093. [17] Haque F, Varlet P, Puntonet J, et al. Evaluation of a novel antibody to define histone 3.3 G34R mutant brain tumours. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017;5(1):45. [18] Willems H, Jacobs A, Hadiwikarta WW, et al. Thermodynamic framework to assess low abundance DNA mutation detection by hybridization. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0177384. [19] Wang W, Yuan Y, Zheng H, et al. A Pilot Study of Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Alpha- and Beta-Thalassemia with Target Capture Sequencing of Cell-Free Fetal DNA in Maternal Blood. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2017;21(7): 433-439. [20] Janku F, Zhang S, Waters J, et al. Development and Validation of an Ultradeep Next-Generation Sequencing Assay for Testing of Plasma Cell-Free DNA from Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(18):5648-5656. [21] Fricke F, Lee J, Michalak M, et al. TGFBR2-dependent alterations of exosomal cargo and functions in DNA mismatch repair-deficient HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):14.[22] Spira A, Yurgelun MB, Alexandrov L, et al. Precancer Atlas to Drive Precision Prevention Trials. Cancer Res. 2017;77(7): 1510-1541. [23] Kasahara N, Kenmotsu H, Serizawa M, et al. Plasma epidermal growth factor receptor mutation testing with a chip-based digital PCR system in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2017;106:138-144. [24] Breveglieri G, Travan A, D'Aversa E, et al. Postnatal and non-invasive prenatal detection of β-thalassemia mutations based on Taqman genotyping assays. PLoS One. 2017;12(2): e0172756. |