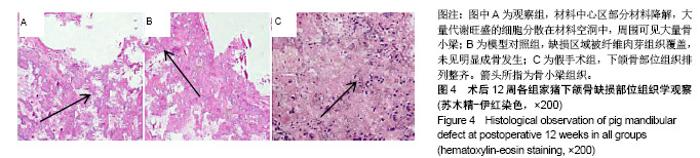
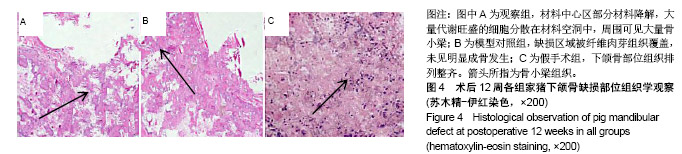
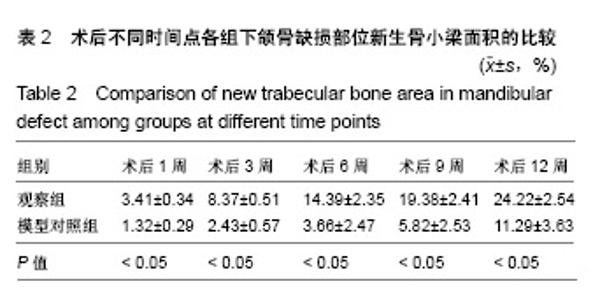
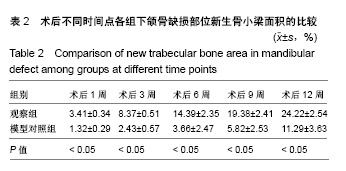
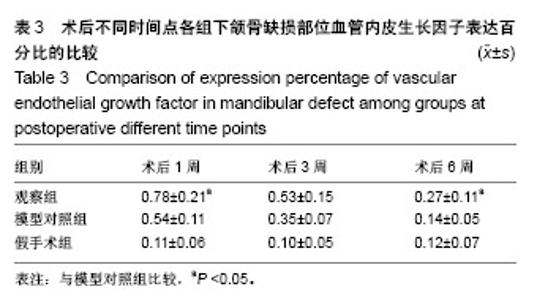
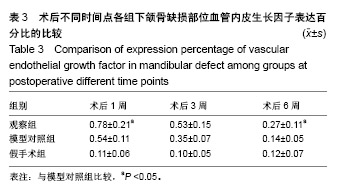
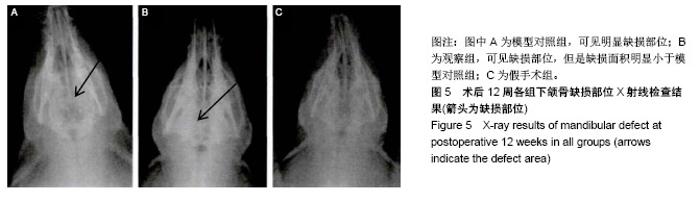
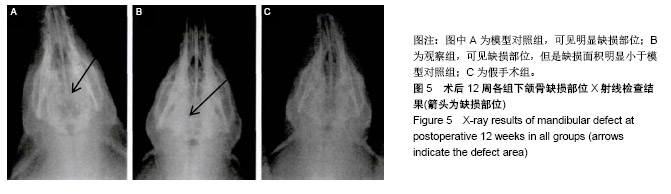
| [1]庄颖,陈希亮,李勇,等.魔芋葡甘聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原复合材料构建组织工程椎间盘纤维环支架[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(16):2412-2417.[2]许莹莹,王敬,韩尚志,等.载辛伐他汀/纳米羟基磷灰石胶原复合组织工程材料对家猪牙槽骨缺损的修复作用[J].山东医药, 2017,57(42):43-45.[3]Wang X,Wu X,Xing H,et al.Porous nano-hydroxyapatite/ collagen scaffolds loading insulin PLGA particles for restoration of critical size bone defect.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017; 9(13):11380-11391.[4]范田堂,陈景帝,刘小翠,等.Fe3O4-壳聚糖-胶原-纳米羟基磷灰石原位复合支架的仿生制备及表征[J].复合材料学报, 2017,34(11): 2593-2597.[5]李冬梅,刘新晖,李庆星.纳米级细胞型组织工程人工骨的构建:修复下颌骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(14):2146-2151.[6]He S,Lin KF,Sun Z,et al.Effects of Nano-hydroxyapatite/ Poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) Microsphere-Based Composite Scaffolds on Repair of Bone Defects: Evaluating the Role of Nano-hydroxyapatite Content.Artif Organs.2016; 40(7):E128-E135.[7]赵小妹,袁卫军.青少年期下颌骨缺损患者行Ⅱ期修复重建的观察与护理[J].上海护理,2017,17(1):56-58.[8]彭祥,王文军.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料在脊柱修复重建中的研究与应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(10):911-914.[9]Cao S,Li H,Li K,et al. In vitro mineralization of MC3T3‐E1 osteoblast‐like cells on collagen/nano‐hydroxyapatite scaffolds coated carbon/carbon composites.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(2):533-543.[10]高宁,刘颖蒙,付坤,等.折叠腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损后种植修复的疗效观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2018, 53(1):26.[11]Dau M,Kämmerer PW,Henkel KO,et al. Bone formation in mono cortical mandibular critical size defects after augmentation with two synthetic nanostructured and one xenogenous hydroxyapatite bone substitute - in vivo animal study.Clin Oral Implants Res.2016;27(5):597-603.[12]周莉,吴凤群,罗仲宽,等.多孔载药纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺/壳聚糖复合材料的制备与性能[J].化学研究与应用, 2017,29(1): 89-93.[13]王延伟,张雅琪,于翔,等.PHA/纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料的结晶性能和力学性能研究[J].塑料科技,2017,45(3):61-65.[14]Pripatnanont P,Praserttham P,Suttapreyasri S,et al.Bone Regeneration Potential of Biphasic Nanocalcium Phosphate with High Hydroxyapatite/Tricalcium Phosphate Ratios in Rabbit Calvarial Defects. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(2):294.[15]丁姗姗,禹怡君,刘超,等.超顺磁性支架材料修复兔下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].医学研究生学报,2017,30(3):251-256.[16]陈婷婷,崔海坡,宋成利,等.不同含量纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸复合材料的性能[J].机械工程材料,2017,41(8):40-43.[17]罗睿,王银龙.灰度比评价奥邦骨修复材料对下颌骨缺损修复的有效性[J].中国美容医学杂志,2018, 27(3):114-117.[18]车鸿泽,车彦海,卢晴,等.PLGA涂层处理的nHA-Mg多孔复合材料对兔颌骨缺损的修复作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017, 43(2):276-280.[19]Gravvanis A,Kakagia D,Katsikeris N,et al.Dermal Matrix for Intraoral Lining Following Composite Mandibular Defect Reconstruction With Chimeric Fibular Osseocutaneous Flap.J Craniofac Surg.2016;27(7):1711-1714.[20]李元,吴迪,王天珏,等.磷酸钙复合材料构建模式对颌骨缺损修复效率的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017, 33(3):297-301.[21]张广德,靳霞,李荣亮,等.BMP-9/EPO双基因共转染ADSCs复合nHAC/PLA支架修复兔下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2017,15(3):202-208.[22]Shao H,Sun M,Zhang F,et al.Custom Repair of Mandibular Bone Defects with 3D Printed Bioceramic Scaffolds.J Dent Res.2018;97(1):22034517734846.[23]王希乾,彭立伟,王永功.快速原型技术在下颌骨缺损重建中的临床应用[J].河南医学研究,2016,25(10):1784-1785.[24]Shen SY,Yu Y,Zhang WB,et al.Angle-to-Angle Mandibular Defect Reconstruction With Fibula Flap by Using a Mandibular Fixation Device and Surgical Navigation.J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(6):1486.[25]孙莲莲,王志兴.同步辐射显微断层成像监测口腔骨植入材料置入体内后的生物相容性及定量分析:随机对照动物实验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):952-956.[26]陈贵征,孙玥,刘显,等.负载BMP-2的形状记忆支架修复兔下颌骨缺损的研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2017, 27(1):19-24.[27]Bucci T,Nocini PF. Functional Reconstruction of Nonsegmental Mandibular Defect With Fresh Frozen Bone Graft and Delayed Implants Placement. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(3):810.[28]Cruz-Neves S,Ribeiro N,Graça I,et al.Behavior of prostate cancer cells in a nanohydroxyapatite/collagen bone scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A.2017;105(7):2035-2046.[29]郭佳丽,韩颖超,徐磊,等.纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料作为污水处理吸附剂的研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2016,35(8):2466-2475.[30]Meimandiparizi A,Oryan A,Gholipour H.Healing potential of nanohydroxyapatite, gelatin and fibrin-platelet glue combination as tissue engineered scaffolds in radial bone defects of rats. Connect Tissue Res.2017;(2):1.[31]罗有福,高金鉴,高浩然,等.负载重组人骨形态发生蛋白2的α型半水硫酸钙/纳米羟基磷灰石复合植骨材料的成骨性能研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(4):348-353.[32]吕春堂,张庆福.计算机辅助设计和3D打印技术与下颌骨缺损的个体化重建[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2017, 27(1):1-7.[33]Salgado CL,Grenho L,Fernandes MH,et al.Biodegradation, biocompatibility, and osteoconduction evaluation of collagen-nanohydroxyapatite cryogels for bone tissue regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(1):55-68.[34]王彦夫,王程越,王绍刚,等.两种配比纳米羟基磷灰石复合胶原材料对犬拔牙窝骨缺损修复效果的比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2016,51(2):98-103.[35]Jing Z,Wu Y,Su W,et al.Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Collagen/Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Improve Bone Tissue Formation In Vitro and In Vivo.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(9): 2075-2087.[36]廖锋,刘士博,刘瑶,等.重组人骨保护素抑制破骨细胞及促进羟磷灰石修复去势大鼠下颌骨缺损的研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018,36(4):26-30.[37]李祥,冯辰栋,王林,等.3D打印多孔钛/壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架的制备与体外生物相容性研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016, 18(1):6-10.[38]Ginjupalli K,Averineni RK,Shavi GV,et al.Biodegradable composite scaffolds of poly(lactic‐co‐glycolic acid) 85:15 and nano-hydroxyapatite with acidic microclimate controlling additive. Polym Compos.2017;38(6):1175-1182.[39]赵志明,舒衡生,刘玉民,等.Ilizarov技术联合负压封闭引流治疗小腿中部大段骨合并软组织缺损效果观察[J].山东医药, 2016, 56(32):64-66.[40]冀晓媛,蔡银,谢安,等.基于纳米压痕法的羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸复合材料力学性能表征[J].复合材料学报,2018,35(3):553-563. |