Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (12): 1877-1882.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0206
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effects of probiotics on the cell membrane in different tissues of rats after treadmill exercise
Mo Wei-bin1, 2, Zhou Yan3, Yang Yan-tao1
- 1Sport School of Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources, Ministry of Science and Technology of China, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Clinical Medicine, Shanghai General Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 201600, China
-
Received:2018-02-26Online:2018-04-28Published:2018-04-28 -
Contact:Zhou Yan, M.D., Pharmacist, Department of Clinical Medicine, Shanghai General Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 201600, China -
About author:Mo Wei-bin, Master, Senior experimentalist, Sport School of Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources, Ministry of Science and Technology of China, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 21562006 and 31060121; the “Teacher Growth” Project of China Education Development Foundation, No. EDF2016005; the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2018KY0090; the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of China, No. CMEMR2012-B04
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mo Wei-bin1, 2, Zhou Yan3, Yang Yan-tao1. Protective effects of probiotics on the cell membrane in different tissues of rats after treadmill exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(12): 1877-1882.
share this article
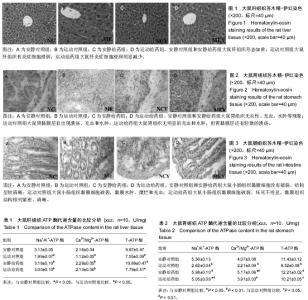
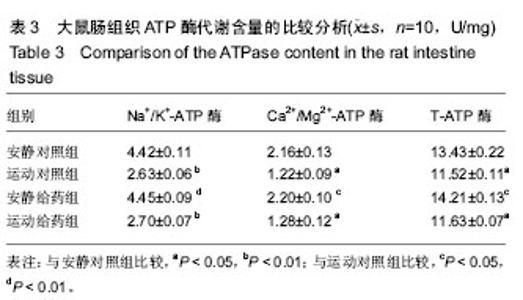
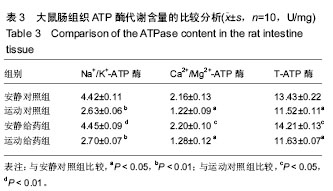
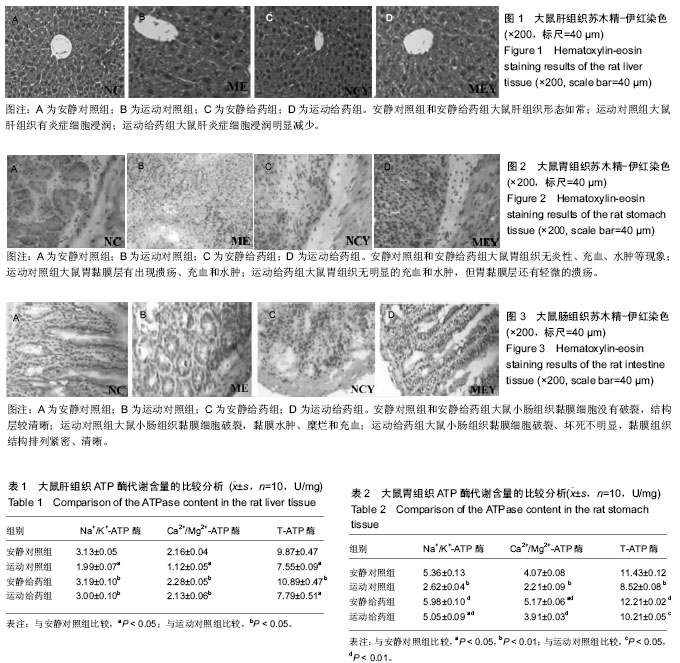
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠40只,分为4组,实验过程无脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 大鼠各组织的形态学变化比较 2.2.1 大鼠肝组织苏木精-伊红染色结果 安静对照组和安静给药组大鼠肝脏细胞索清楚、肝窦、中央静脉细胞形态排列规则和汇管区细胞形态如常。运动对照组大鼠肝小叶结构明显紊乱、肿胀、胞质内有大量的脂滴和有炎症细胞浸润。运动给药组大鼠肝细胞空泡数目明显减少,但胞浆内的脂滴和炎症细胞浸润明显减少,但汇管区血管冲血,仍有少量的炎症细胞浸润。见图1。 2.2.2 大鼠胃组织苏木精-伊红染色结果 光镜下观察发现,安静对照组和安静给药组大鼠胃组织细胞膜无发现破裂,胃黏膜连续性好,无炎性、无充血、水肿和糜烂等现象出现。运动对照组大鼠胃细胞膜层有大量的细胞破裂,胃黏膜层有出现溃疡、充血和水肿;运动给药组大鼠胃组织细胞膜层细胞破裂的比例明显减少,无明显的充血和水肿,但胃黏膜层还有轻微的溃疡。见图2。 2.2.3 大鼠肠组织苏木精-伊红染色结果 通过光镜下观察发现,安静对照组和安静给药组大鼠小肠组织黏膜细胞没有破裂,绒毛上皮细胞排列紧密,黏膜组织结构层较清晰。运动对照组大鼠小肠组织黏膜细胞破裂,黏膜水肿、糜烂和充血,纤维结构紊乱;运动给药组大鼠小肠组织黏膜细胞破裂、坏死不明显,黏膜组织结构排列紧密、清晰。见图3。 2.3 大鼠各组织ATP酶代谢含量的比较分析 见表1-3。 由表1可知,运动对照组大鼠肝组织Na+/K+-ATP酶、Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶和T-ATP酶含量均低于安静对照组(P < 0.05); 安静给药组大鼠肝组织Na+/K+-ATP酶、Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶和T-ATP酶含量均高于运动对照组(P < 0.05);运动给药组大鼠肝组织Na+/K+-ATP酶、Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶和T-ATP酶含量均高于运动对照组但低于安静对照组和安静给药组,其中运动给药组大鼠肝组织Na+/K+-ATP酶、Ca2+/Mg2+-TP酶与运动对照组比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),运动给药组大鼠肝组织T-ATP酶与安静对照比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 由表2可知,运动对照组、运动给药组大鼠胃组织Na+/K+-ATP酶含量均低于安静对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),安静给药组与运动给药组大鼠胃组织Na+/K+-ATP酶含量均高于运动对照组(P < 0.01);运动对照组大鼠胃组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量低于安静对照组(P < 0.01),安静给药组大鼠胃组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量高于安静对照组和运动对照组(P < 0.01);运动给药组大鼠胃组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组(P < 0.01);运动对照组大鼠胃组织T-ATP酶含量低于安静对照组(P < 0.01),安静给药组与运动给药组大鼠T-ATP酶含量均高于运动对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。 由表3可知,运动对照组和运动给药组大鼠肠组织Na+/K+-ATP酶含量低于安静对照组(P < 0.01),安静给药组大鼠肠组织Na+/K+-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组(P < 0.01),运动给药组大鼠Na+/K+-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组(P > 0.05);运动对照组和运动给药组大鼠肠组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量低于安静对照组(P < 0.05),安静给药组大鼠肠组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组(P < 0.05),运动给药组大鼠肠组织Ca2+/Mg2+-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组(P > 0.05);运动对照组和运动给药组大鼠肠组织T-ATP酶含量低于安静对照组(P < 0.05),安静给药组和运动给药组大鼠肠组织T-ATP酶含量高于运动对照组,其中安静给药组与运动对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Peters HPF, Vries WRD, Vanbergehenegouwen GP, etal. Potential benefits and hazards of physical activity and exercise on the gastrointestinal tract. Gut.2001;48(3):435-439.[2] 杨建昌,王军,陈乐琴,等. 过度训练对大鼠胃肠道组织形态及功能的影响[J].中国体育科技,2005,41(5):123-126.[3] Waterman JJ, Kapur R. Upper gastrointestinal issues in athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep.2012; 11(2):99.[4] 耿雪.以肠道菌群为靶点的运动性胃肠综合征干预研究进展[J].体育科研, 2017,38(3):78-83.[5] 王平.牛磺酸对一次性力竭运动大鼠肝组织氧化损伤的预防作用研究[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2008,34(10):66-68.[6] 袁海燕,胡亚哲. 不同强度有氧运动对大鼠肝细胞的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8311-8316.[7] Limasilva AE, Oliveira FR, Nakamura FY, et al.Effect of carbohydrate availability on time to exhaustion in exercise performed at two different intensities. Braz J Med Biol Res.2009;42(5):404-412.[8] FAO,WHO.Report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on evaluation of health and nutritional proper ties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria.Coraoba: Argentina, 2001.[9] Del PM, Morelli L, Strozzi GP, et al. Probiotics: from research to consumer. Dig Liver Dis. 2006;38 Suppl 2:S248-255.[10] Huang WC,Chen YM,Kan NW,et al.Hypolipidemic Effects and Safety of Lactobacillus Reuteri 263 in a Hamster Model of Hyperlipidemia. Nutrients.2015;7(5):3767.[11] Chen YM, Wei L, Chiu YS, et al. Lactobacillus plantarumTWK10 Supplementation Improves Exercise Performance and Increases Muscle Mass in Mice. Nutrients.2016;8(4):205.[12] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures.J Appl Physiol.1979;47(6):1278-1283.[13] 莫伟彬,邱晓玲,李国峰. 罗汉果甜苷对训练大鼠骨骼肌PGC-lα mRNA及蛋白表达的影响[J]. 现代预防医学,2017,44(1): 131-134.[14] Uronis JM,Arthur JC, Keku T, et al.Gut Microbial Diversity is Reduced by the Probiotic VSL#3 and Correlates with Decreased TNBS-Induced Colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Jan;17(1):289-297. [15] 张明明,方田,张静,等.益生菌制剂治疗肝硬化的meta分析[J].胃肠病学, 2014,19(1):25-31.[16] Bull-Otterson L, Feng W, Kirpich I, et al. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. Plos One. 2013;8(1):1-10.[17] Akama F,Nishino R,Makino S,et al.The effect of probiotics on gastric mucosal permeability in humans administered with aspirin.Scand J Gastroenterol.2011;46(7-8):831-836.[18] Jensen H, Grimmer S, Naterstad K, et al. In vitro testing of commercial and potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012; 153(1-2):216-222. [19] Schwartz M, Regueiro M. Prevention and Treatment of Postoperative Crohn’s Disease Recurrence: An Update for a New Decade. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13(1):95-100[20] Barbara G,Zecchi L,Barbaro R,et al.Mucosal permeability and immune activation as potential therapeutic targets of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46 Suppl:S52-55. [21] Korge P, Camphell KB. The importance of ATPase microenvionment in muscle fatigue: a hypothesis. Int J Sport Med.1995;16(3): 172.[22] 樊凯芳,唐迎雪,曹淑霞.三化汤对脑缺血-再灌注老龄大鼠胃肠组织Na+-K+-ATP酶活性及Ca2+-ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2009, 20(6):1367-1368.[23] Bachmann O,Juric M,Seidler U,et al. Basolateral ion transporters involved in colonic epithelial electrolyte absorption, anion secretion and cellular homeostasis.Acta Physiologica. 2011, 201(1):33.[24] 彭艳, 易受乡, 林亚平,等. 艾灸对脾虚大鼠空肠组织ATP含量和ATP酶活性的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2013, 23(1):8-13.[25] Li L,Feng R,Xu Q,et al.Expression of the β3 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase is increased in gastric cancer and regulates gastric cancer cell progression and prognosis via the PI3/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.2017;8(48):84285-84299.[26] Dunker DJ.Role of K-ATP channels in coronary vasodilation during exercise.Criculation.1993;88(3): 1250.[27] Mc Kenna MJ, Schmidt TA, Hargreaves M. Sprint training increases human skeletal muscle Na+/K+-ATPase concentration and improves K+ regulation. J ApplPhysiol.1993;75:173.[28] Sudar E, Velebit J, Gluvic Z, et al. Hypothetical mechanism of sodium pump regulation by estradiol under primary hypertension. J Theor Biol. 2008;251(4):584-592.[29] 黄丽萍,彭淑红,张甦,等.热性中药对大鼠肝脏能量代谢相关因子的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2010, 35(11):1470-1473.[30] 邓启烈,陈梅,莫伟彬,等.罗汉果叶黄酮及游泳训练对力竭大鼠股四头肌组织ATP酶代谢的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013, 19(5):181-185.[31] 吕亚青,曲林林,江海涛,等.他克莫司对小鼠肠黏膜屏障功能的损伤作用及分子机制[J].山东医药,2015, 55(45):11-13.[32] 彭艳,彭芬,易受乡,等.艾灸对脾虚大鼠小肠运动吸收功能及ATP含量的影响[J].中国针灸,2012, 32(3):246-250.[33] 刘艳环,刘克敏,马国栋.12周跑台训练对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏肝细胞癌下调的线粒体转运蛋白表达的改变及其对线粒体功能的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(1):12-15.[34] 衣雪洁.力竭性游泳对大鼠胃组织丙二醛、游离巯基和ATP含量的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志, 1999(2):131-133.[35] 勇入琳,曲怡,李欣欣,等.电针“足三里”对脾气虚大鼠空肠组织胃生长激素释放激素/环磷酸腺苷/蛋白激酶A表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2016, 41(6):497-501.[36] 刘秉文,陈俊杰.医学分子生物学[M].北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2000: 139.[37] Tsakiris S,Michelakakis H,Schulpis KH.Erythrocyte membrane acetylcholinesterase, Na+, K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities in patients with classical galactosaemia. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94(9): 1223-1226.[38] 黄海定,巫莉萍,邓时贵.大黄对肺卫失宣大鼠肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞超微结构及肺组织 Na+- K +- ATP 酶活力的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2011, 17(8): 190.[39] Hu F, Hui Z, Wei W, et al. Hypotonic stress promotes ATP release, reactive oxygen species production and cell proliferation via TRPV4 activation in rheumatoid arthritis rat synovial fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;486(1):108-115.[40] Korge P,Camphell KB.The importance of ATPase microenvionment in muscle fatigue: a hypothesis[J]. Int J Sport Med.1995;16(3): 172.[41] 郭婕,赵海霞,颜燕,等.硫磺熏蒸山药对大鼠肝组织抗氧化能力及 ATP 酶活性的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2010, 16(11): 152.[42] 许思毛,上官若男,彭峰林,等. 运动预处理对大负荷跑台运动引起的大鼠心肌损伤干预作用及其机制探讨[J].体育科学,2012, 32(7):45-52.[43] 何思淼,麻新远,衣雪洁.力竭游泳对大鼠肠组织MDA、Free-SH、ATP含量及Na+-K+-ATPase活性的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2011, 37(6): 71-73.[44] 张超, 姜军, 孙念绪,等.严重腹腔感染时大鼠胃黏膜血流量和Na+-K+- ATP酶活性变化对胃黏膜电位差的影响[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2004, 19(3):172-174.[45] 滕培颍,赵瑞芝,徐福平,等.附子半夏汤对阳虚模型大鼠不同脏器能量代谢的影响[J].新中医, 2017(2):4-6.[46] 吴严冰.白藜芦醇对力竭运动小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2015(19):3117-3122.[47] 黎健民.黄精多糖对力竭训练小鼠肝组织损伤的保护作用[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2016, 35(5):1036-1041. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||