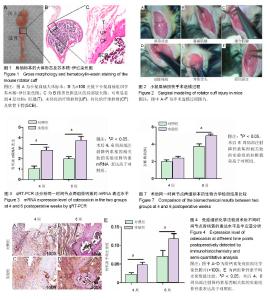
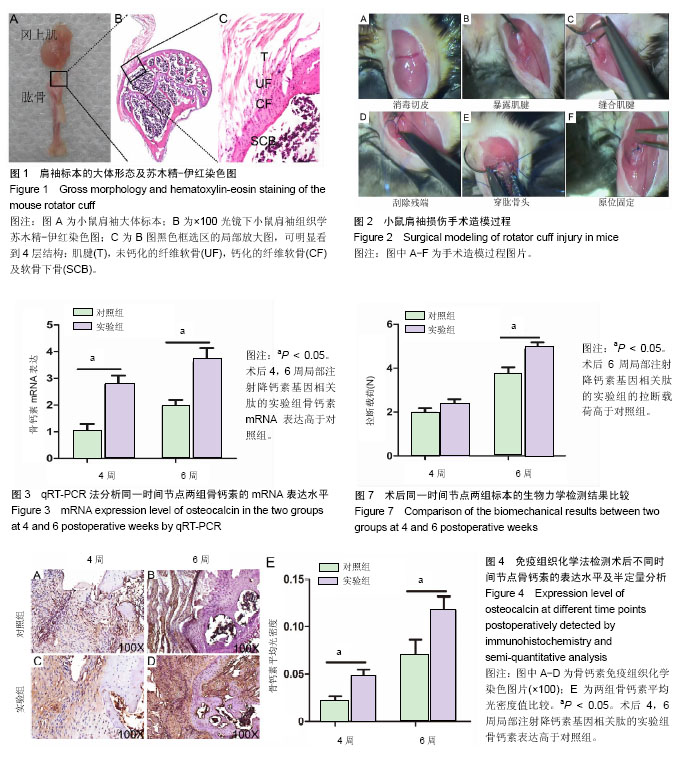
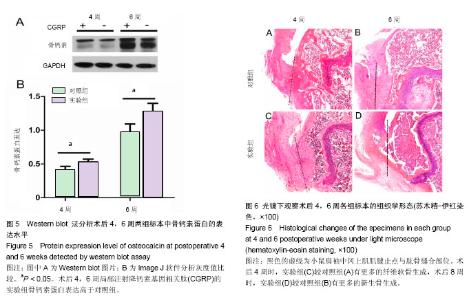
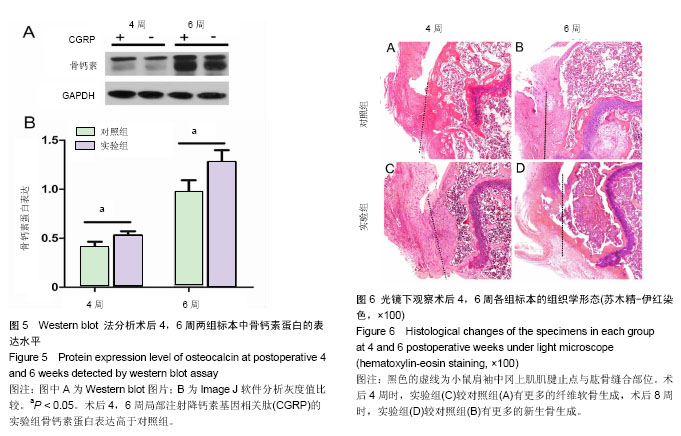
| [1] Lu H, Chen C, Qu J, et al. Initiation Timing of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation for Tendon-Bone Healing in a Rabbit Model. Am J Sports Med.2016; 44(10):2706-2715.[2] Wu Y, Dong Y, Jiang J, et al. Evaluation of the Bone-ligament and tendon insertions based on Raman spectrum and its PCA and CLS analysis. Sci Rep.2017;7: 38706.[3] Atesok K, Fu FH, Wolf MR, et al. Augmentation of tendon-to-bone healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(6): 513-521.[4] Lu H, Liu F, Chen H, et al. The effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on bone-tendon junction healing: Initiating after inflammation stage. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(10):1697-1706.[5] Mather RC 3rd, Koenig L,Acevedo D,et al. The societal and economic value of rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(22):1993-2000.[6] Lichtenberg S, Liem D, Magosch P, et al. Influence of tendon healing after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair on clinical outcome using single-row Mason-Allen suture technique: a prospective, MRI controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2006;14(11):1200-1206.[7] Galatz LM,Ball CM,Teefey SA,et al. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86-a(2): 219-224.[8] Deymier AC, An Y,Boyle JJ,et al. Micro-mechanical properties of the tendon-to-bone attachment. Acta Biomater. 2017;56: 25-35. [9] Leung KS, Chong WS, Chow DH, et al. A Comparative Study on the Biomechanical and Histological Properties of Bone-to-Bone, Bone-to-Tendon, and Tendon-to-Tendon Healing: An Achilles Tendon-Calcaneus Model in Goats. Am J Sports Med.2015;43(6):1413-1421.[10] Lu H, Hu J, Qin L, et al. Area, length and mineralization content of new bone at bone-tendon junction predict its repair quality. J Orthop Res, 2011, 29(5): 672-7.[11] Wei J, Karsenty G. An overview of the metabolic functions of osteocalcin. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.2015;16(2):93-98.[12] Serre CM, Farlay D, Delmas PD, et al. Evidence for a dense and intimate innervation of the bone tissue, including glutamate-containing fibers. Bone.1999;25(6): 623-629.[13] Zhai L, Sakurai T, Kamiyoshi A, et al. Endogenous calcitonin gene-related peptide suppresses ischemic brain injuries and progression of cognitive decline. J Hypertens. 2018;36(4): 876-891.[14] Niedzwiedzki T, Filipowska J. Bone remodeling in the context of cellular and systemic regulation: the role of osteocytes and the nervous system. J Mol Endocrinol.2015;55(2):R23-36.[15] Ackermann PW, Franklin SL, Dean BJ, et al. Neuronal pathways in tendon healing and tendinopathy--update. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).2014;19:1251-1278.[16] Zhou Y, Zhang H, Zhang G, et al. Calcitonin generelated peptide reduces Porphyromonas gingivalis LPSinduced TNFalpha release and apoptosis in osteoblasts. Mol Med Rep.2018;17(2): 3246-3254.[17] Da Silva MR,Linhares D,Vasconcelos DM, et al. Neuroimmune expression in hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2017;18(1):394.[18] Tang P, Duan C, Wang Z, et al. NPY and CGRP Inhibitor Influence on ERK Pathway and Macrophage Aggregation during Fracture Healing. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4): 1457-1467.[19] Lui PP, Chan LS, Fu SC, et al. Expression of sensory neuropeptides in tendon is associated with failed healing and activity-related tendon pain in collagenase-induced tendon injury. Am J Sports Med.2010;38(4):757-764.[20] Zhang Y, Xu J, Ruan YC, et al. Implant-derived magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med. 2016;22(10): 1160-1169.[21] Chen J, Ma G, Liu W, et al. The influence of the sensory neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2016 Sep 13. [Epub ahead of print][22] Bell R, Taub P, Cagle P, et al. Development of a mouse model of supraspinatus tendon insertion site healing. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(1):25-32.[23] Depres-Tremblay G, Chevrier A, Snow M, et al. Rotator cuff repair: a review of surgical techniques, animal models, and new technologies under development. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(12): 2078-2085.[24] Lebaschi A, Deng XH, Zong J, et al. Animal models for rotator cuff repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016;1383(1): 43-57.[25] Wang IE, Shan J, Choi R, et al. Role of osteoblast-fibroblast interactions in the formation of the ligament-to-bone interface. J Orthop Res.2007;25(12):1609-1620.[26] Spalazzi JP, Dagher E, Doty SB, et al. In vivo evaluation of a multiphased scaffold designed for orthopaedic interface tissue engineering and soft tissue-to-bone integration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;86(1):1-12.[27] Guo L, Qu J, Zheng C, et al. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Decellularized Fibrocartilage "Book" Scaffold for Use in Tissue Engineering. PLoS One. 2015;10(12): e0144240.[28] Aonuma H, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, et al. Low serum levels of undercarboxylated osteocalcin in postmenopausal osteoporotic women receiving an inhibitor of bone resorption. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009;218(3):201-205.[29] Li J, Zhang H, Chao Y, et al. An overview of osteocalcin progress. J Bone Mineral Metabolism. 2016;34(4):367.[30] Ackermann PW, Ahmed M, Kreicbergs A. Early nerve regeneration after achilles tendon rupture--a prerequisite for healing? A study in the rat. J Orthop Res.2002;20(4): 849-856.[31] Hong HS, Lee J, Lee E, et al. A new role of substance P as an injury-inducible messenger for mobilization of CD29(+) stromal-like cells. Nat Med.2009;15(4):425-435.[32] Liang W, Li L, Cui X, et al. Enhanced proliferation and differentiation effects of a CGRP- and Sr-enriched calcium phosphate cement on bone mesenchymal stem cells. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater.2016;14(4):e431-e440.[33] Deng T, Yang L, Zheng Z, et al. Calcitonin generelated peptide induces IL6 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages mediated by mmu_circRNA_007893. Mol Med Rep.2017; 16(6): 9367-9374.[34] Duan JX, Zhou Y, Zhou AY, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide exerts anti-inflammatory property through regulating murine macrophages polarization in vitro. Mol Immunol.2017; 91: 105-113.[35] Lu H, Qin L, Cheung W, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerated bone-tendon junction healing through regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and cartilage formation. Ultrasound Med Biol.2008;34(8):1248-1260.[36] Kashem SW, Riedl MS, Yao C, et al. Nociceptive Sensory Fibers Drive Interleukin-23 Production from CD301b+ Dermal Dendritic Cells and Drive Protective Cutaneous Immunity. Immunity.2015;43(3):515-526. |