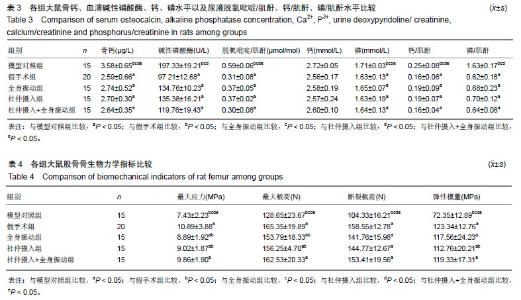
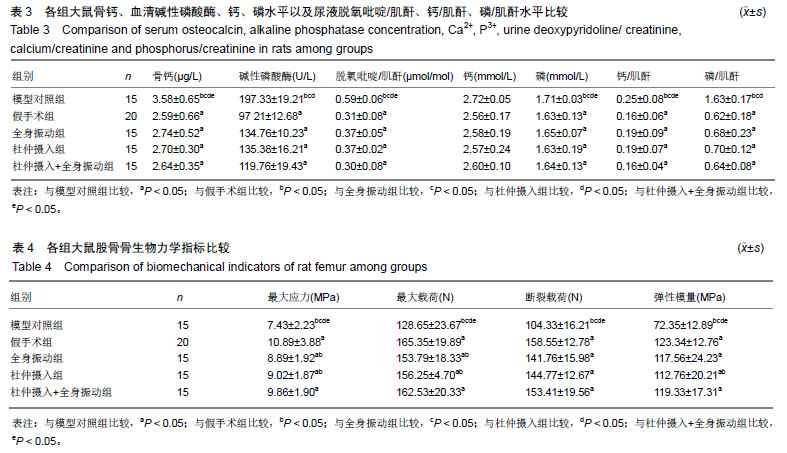
| [1]Cotts KG, Cifu AS. Treatment of osteoporosis. JAMA. 2018; 319 (10) :1040.[2]Cano A, Chedraui P, Goulis DG,et al. Calcium in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis: EMAS clinical guide. Maturitas. 2018;107(3):7-12.[3]Paci M,Burks S,Wang MY. Consensus guidelines for the treatment of osteoporosis. Neurosurgery. 2018;82(1):N6.[4]Shams-White MM,Chung M,Fu Z, et al. Animal versus plant protein and adult bone health: A systematic review and meta-analysis from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Plos One. 2018;13(2):e0192459.[5]Chen YM,Lee HC,Chen MT,et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone supplementation combined with Weight-Loading Whole-Body Vibration Training (WWBV) affects exercise performance and muscle glycogen storage in middle-aged C57BL/6 mice. Int J Med Sci. 2018; 15(6):564-573.[6]Yoon J,Kanamori A,Fujii K,et al. Evaluation of maslinic acid with whole-body vibration training in elderly women with knee osteoarthritis. Plos One. 2018;13(3):e0194572.[7]Siebert MJ,Böselt T,Greulich T,et al. Effects of a 6 week whole-body vibration training (WBVT) in stable COPD patients: a randomized clinical trial. Pneumologie. 2017; 71(S1) :PA2216.[8]Lynch JH. ACSM's Clinician profile. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2018; 17(5):141[9]卢其腾,农小连,吴家昌,等. 去势联合地塞米松建立大鼠骨质疏松模型的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(1):34-36.[10]Cheng ML,Gupta V. Premenopausal osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metabol Clin North. 2013;17(2):240-244.[11]Kenanidis E,Potoupnis ME,Kakoulidis P,et al.Management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis:clinical data in relation to disease demographics,bone mineral density and fracture risk. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015;14(7):1035-1053.[12]Seno T,Yamanoto A,Kukida Y,et al. Once-weekly teriparatide improves glucocorticoid - induced osteoporosis in patients with inadequate response to bisphosphonates. Springerplus. 2016;5(1):1056-1063.[13]Zhu L,Chen J,Zhang J,et al. Parathyroid hormone(PTH) induces autophagy to protect osteocyte cell survival from dexa-Nmethasone damage. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23(21): 4034-4040.[14]Tolba MF,El-Serafi AT,Omar HA. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects against glucocorticoid- induced osteopo-rosis in vivo:impact on oxidative stress and RANKL/OPG signals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;324(29):26-35.[15]李三华,陈全利,杨加强. 杜仲总黄酮对去卵巢大鼠骨组织代谢的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2018,38(7):3198-3200[16]骆瑶,陈兰英,官紫祎,等. 杜仲提取物对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢?骨密度及骨微结构的影响[J].中药材, 2016,39(11): 2624-2628.[17]Corina M,Vulpoi C,Branisteanu D. Relationship between bone mineral density, weight, and estrogen levels in pre and postmenopausal women. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2011; 116(4): 946-950.[18]Davison KS,Kendler DL,Ammann P,et al. Assessing fracturerisk and effects of osteoporosis drugs: bone mineral densityand beyond. Am J Med. 2009;122(11): 992-997.[19]Huang RP,Rubin CT,Mcleod KJ. Changes in postural muscle dynamics as a function of age. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999;54(8): 352-357.[20]巴洪冰,程亮.全身振动训练对老年女性骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(3):324-342.[21]朱再胜,章振林. 不同模式骨折风险评估工具在绝经后女性的应用和评估[J].中国全科医学,2014, 17(16): 1851-1854.[22]祁珊珊,王永吉,庞田田,等. 去卵巢大鼠骨?生殖系统组织病理学与形态计量学观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015, 21(7): 774-779. |