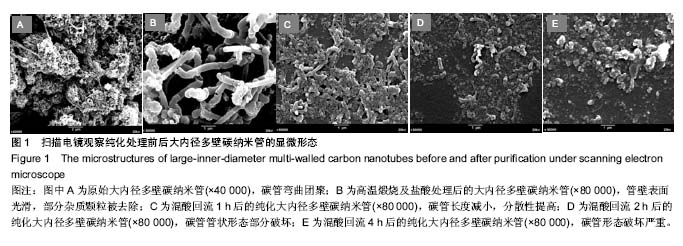
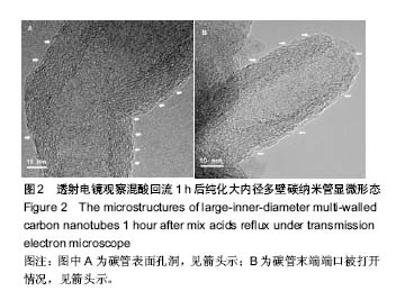
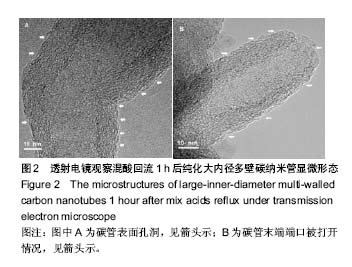
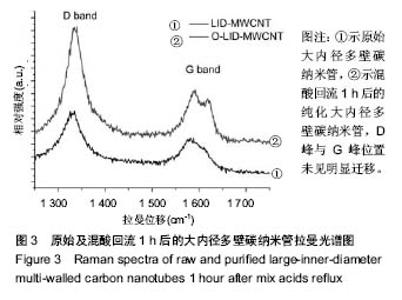
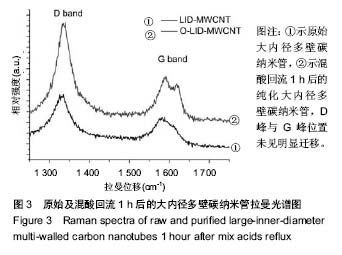
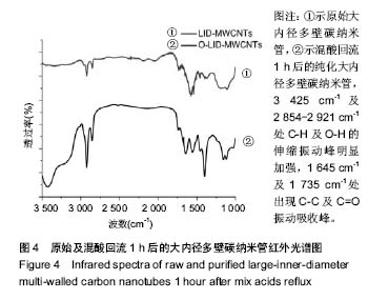
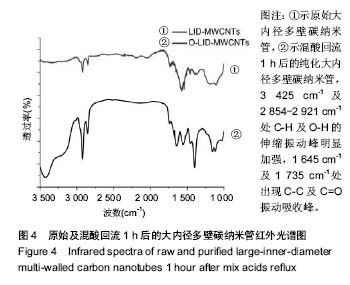
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 896-901.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0065
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of mixed acid reflux time on purification and biocompatibility of large-inner-diameter multi-walled carbon nanotubes
- 1Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan province, China
-
Received:2017-09-01Online:2018-02-28Published:2018-02-28 -
Contact:Sui Lei, Chief physician, Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
About author:Meng Ai, Master, Physician, Hospital of Stomatology, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:Tianjin Natural Science Foundation, No. 16JCZDJC32800
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Meng Ai, Wang Jian, Sui Lei. Effect of mixed acid reflux time on purification and biocompatibility of large-inner-diameter multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(6): 896-901.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
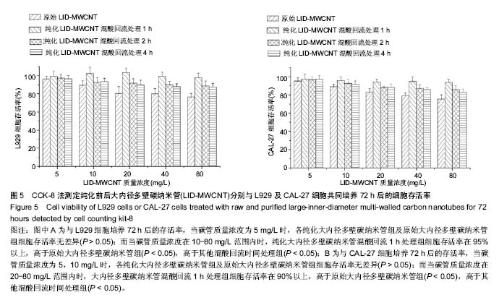
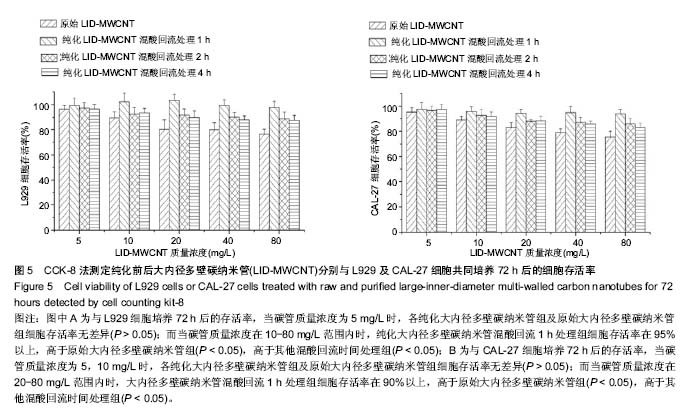
2.2 纯化LID-MWCNT的细胞相容性 细胞增殖实验结果显示,不同质量浓度原始LID-MWCNT分别培养L929及CAL-27细胞72 h后,细胞存活率均降低,表现出细胞毒性作用并呈一定的浓度依赖性。在相同碳管悬液质量浓度下,各纯化LID-MWCNT组细胞生存率高于原始LID-MWCNT组,其中混酸回流1 h组细胞生存率显著性高于其他混酸回流时间组。 L929细胞增殖实验结果显示,碳管质量浓度为5 mg/L 时,各纯化LID-MWCNT组及原始LID-MWCNT组间细胞存活率无差异(P > 0.05);当碳管质量浓度在10-80 mg/L范围内时,混酸回流1 h处理组细胞存活率在95%以上,高于原始LID-MWCNT组(P < 0.05),且高于其混酸回流时间组 (P < 0.05),表现出更好的生物相容性;在相同碳管质量浓度下,混酸回流2 h与4 h处理组间细胞存活率均无差异 (P > 0.05),见图5A。 CAL-27细胞增殖实验结果显示,碳管质量浓度为5, 10 mg/L时,各纯化LID-MWCNT组及原始LID-MWCNT组间细胞存活率无差异(P > 0.05);而当碳管质量浓度在20-80 mg/L范围内时,混酸回流1 h处理组细胞存活率在90%以上,高于原始LID-MWCNT组(P < 0.05),且高于其混酸回流时间组(P < 0.05),显示出更低的细胞毒性作用;在相同碳管质量浓度下,混酸回流2 h与4 h处理组间细胞存活率均无差异(P > 0.05),见图5B。 "
| [1]Sharkey JJ,Stranks SD,Huang J,et al.Engineering nanostructures by binding single molecules to single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano.2014;8(12):12748-12754. [2]Xu J,Xie Y,Zhang H,et al.Fabrication of PLGA/MWNTs composite electrospun fibrous scaffolds for improved myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2014;123: 907-915.[3]Uetani K,Ata S,Tomonoh S,et al.Elastomeric thermal interface materials with high through-plane thermal conductivity from carbon fiber fillersvertically aligned by electrostatic flocking. Adv Mater.2014;26(33):5857-5862.[4]Yamada K,Kim CT,Kim JH,et al.Single walled carbon nanotube- based junction biosensor for detection of Escherichia coli.PLoS One.2014;9(9):e105767.[5]刘俊希,张杰,张宇,等.复合叶酸-碳纳米管-紫杉醇的司盘-聚乙二醇超声对比剂微泡的制备[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(2):260-267.[6]Lodhi N,Mehra NK,Jain NK.Development and characterization of dexamethasone mesylate anchored on multi walled carbon nanotubes.J Drug Target.2013;21(1):67-76.[7]Aminzadeh Z,Jamalan M,Chupani L,et al.In vitro reprotoxicity of carboxyl-functionalised single- and multi-walled carbon nanotubes on human spermatozoa.Andrologia. 2016. doi: 10.1111/and.12741. [Epub ahead of print][8]Joddar B,Garcia E,Casas A,et al.Development of functionalized multi-walled carbon-nanotube-based alginate hydrogels for enabling biomimetic technologies.Sci Rep.2016;6:32456.[9]Wu Z,Mitra S.Microwave induced reactive base wash for the removal of oxidation debris from carboxylated carbon nanotubes.Carbon N Y.2015;1(88):233-238.[10]Darne C,Terzetti F,Coulais C,et al.Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of panel of single- and multiwalled carbon nanotubes: in vitro effects on normal Syrian hamster embryo and immortalized v79 hamster lung cells.J Toxicol. 2014;2014:872195.[11]Rodrigues BV,Leite NC,Cavalcanti BD,et al.Graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes as nanofeatured scaffolds for the assisted deposition of nanohydroxyapatite: characterization and biological evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;13(11):2569-2585.[12]Gorham JM,Osborn WA,Woodcock JW,et al.Detecting Carbon in Carbon: Exploiting Differential Charging to Obtain Information on the Chemical Identity and Spatial Location of Carbon Nanotube Aggregates in Composites by Imaging X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy.Carbon N Y. 2016;96:1208-1216. [13]Matson ML,Villa CH,Ananta JS,et al.Encapsulation of α-Particle-Emitting 225Ac3+ Ions Within Carbon Nanotubes.J Nucl Med.2015;56(6):897-900. [14]Agustina E,Goak J,Lee S,et al.Simple and Precise Quantification of Iron Catalyst Content in Carbon Nanotubes Using UV/Visible Spectroscopy. ChemistryOpen. 2015;4(5):613-619.[15]Bo?ena C,Patryk O,Ewa WA,et al.Water treatment by H2O2and/or UV affects carbon nanotube (CNT) properties and fate in water and tannic acid solution.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015;22(24):20198-20206. [16]Suri A,Coleman KS.The superiority of air oxidation over liquid-phase oxidative treatment in the purification of carbon nanotubes.Carbon.2011;49(9):3031-3038.[17]Cui X,Wan B,Yu Y,et al.Length effects on the dynamic process of cellular uptake and exocytosis of single-walled carbon nanotubes in murine macrophage cells.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):1518. [18]Haniu H,Saito N,Matsuda Y,et al.Biological responses according to the shape and size of carbon nanotubes in BEAS-2B and MESO-1 cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:1979-1990.[19]Ha HK,Kim JW,Lee MR,et al.Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of β-Lactoglobulin Nanoparticles: The Effects of Particle Size and Surface Charge.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci.2015;28(3):420-427.[20][20] Braun EI,Draper R,Pantano P.Enriched surface acidity for surfactant-free suspensions of carboxylated carbon nanotubes purified by centrifugation.Anal Chem Res. 2016;8:26-33. [21]Fahrenholtz CD,Hadimani M,King SB,et al.Targeting breast cancer with sugar-coated carbon nanotubes.Nanomedicine(Lond). 2015;10(16):2481-2497.[22]Luo X,Matranga C,Tan S,et al.Carbon nanotube nanoreservior for controlled release of anti-in?ammatory dexamethasone. Biomaterials.2011;32(26):6316-6323.[23]Sobhani Z,Dinarvand R,Atyabi F,et al.Increased paclitaxel cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines using a novel functionalized carbon nanotube.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:705-719.[24]Morsy M,Helal M,El-Okr M,et al.Preparation, purification and characterization of high purity multi-wall carbon nanotube. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014;132:594-598.[25]Kim H,Kwak SY,Park JH,et al.Homogeneous Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes on Surface-Modified Bulk Titanium Substrates by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16(1): 903-909.[26]Ren J,Shen S,Wang D,et al.The targeted delivery of anticancer drugs to brain glioma by PEGylated oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified with angiopep-2.Biomaterials.2012;33(11): 3324-3333.[27]Chiu WM,Chang YA.Chemical modification of multiwalled carbon nanotube with the liquid phase method.J Appl Polym Sci. 2008; 107(3):1655-1660.[28]Araujo R,Marques MF,Jonas R,et al.Influence of Chemical Treatment on the Morphology and Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2016;16(1):1174-1180.[29]Wen S,Liu H,Cai H,et al.Targeted and pH-responsive delivery of doxorubicin to cancer cells using multifunctional dendrimer-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes.Adv Healthc Mater. 2013;2(9):1267-1276. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||