Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 310-315.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of polymer interbody fusion cages
- Department of Spinal Surgery, Central Hospital of Shengli Oilfield, Dongying 257000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2017-08-02Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
About author:Wang Peng, Master, Department of Spinal Surgery, Central Hospital of Shengli Oilfield, Dongying 257000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Peng, Sun Gui-sen, Li Hong-qi, Guo Long-sheng, Lang Ming-lei, Liu Wen-jun, Fan Wei-qiang.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
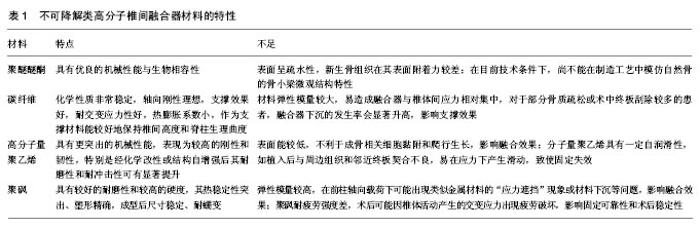
2.1 不可降解类高分子材料 见表1。 2.1.1 聚醚醚酮 聚醚醚酮是1977年首次合成的树脂型工程塑料,问世以来因其优良的机械特性和生物相容性,成为目前制造椎间融合器的最常用材料。聚醚醚酮是一种化学结构非常稳定的聚合物,电解质溶液浸泡及常规消毒灭菌(如高压蒸汽、碘剂、乙醇、紫外线、γ射线)条件下不分解。材料无毒性,经FDA认证后允许接触食品或人体组织,制成融合器应用于骨组织后,局部炎症反应轻,对神经组织刺激小[9]。作为一种热塑性材料,聚醚醚酮加工成型简易,可添加植骨孔加快融合速率,亦可附加螺钉钉道、防滑纹等结构设计,使其防止植入椎间后随椎体活动产生滑动,固定更牢靠[10]。生物力学实验表明,聚醚醚酮材料具有适宜的韧性与刚性,在交变应力条件下耐疲劳性亦远胜于目前常见的树脂型高分子材料,可在有效承载椎体前柱应力时产生轻微形变而有利于融合[11-12]。需要特别指出的是,与传统金属材料相比,聚醚醚酮具有与骨组织相似的弹性模量,使融合器与椎体终板骨皮质弹性模量匹配、应力载荷在融合器与邻近骨质间分配均匀,有效减少了应力遮挡引起的融合器周边骨质压缩、骨质吸收、假关节形成等术后并发症,提高了融合率[10]。 聚醚醚酮材料虽具有上述优良的机械性能与生物相容性,但由于其表面呈疏水性,新生骨组织在其表面附着力较差;在目前技术条件下,尚不能在制造工艺中模仿自然骨的骨小梁微观结构特性,致使融合手术后骨组织生长速度慢于传统自体植骨融合。为提高融合效率,可对聚醚醚酮材料进行仿生学加工成型,或将高纯度聚醚醚酮改性为复合材料,如加入碳纤维进行共混改性,或喷涂羟基磷灰石、等离子钛等进行表面改性,以提高融合器的机械性能和诱导成骨能力[13]。 2.1.2 碳纤维 碳纤维材料椎间融合器应用于脊柱外科已有20余年[14]。碳纤维从严格意义讲并非有机高分子材料,而是一种含碳量在95%以上(质量分数)的无机高分子材料。碳纤维的微观结构是一种类似于人造石墨的不规则层状结构,原子间靠共价键结合,层状结构间由范德华力联结,因此碳纤维的化学性质非常稳定,并具有与传统金属材料相似的力学特性:首先,碳纤维的轴向刚性理想,支撑效果好;其次,碳纤维的耐交变应力性好,热膨胀系数小,作为支撑材料能较好地保持椎间高度和脊柱生理曲度[15]。另外有研究证实,碳纤维与钛金属均具有较好的组织相容性,而碳纤维融合器术后融合器下沉并发症发生率较低[16]。正因如此,碳纤维可以加工成类似于钛金属网的管型融合器,也能像聚醚醚酮材料一样制成衬垫型融合器,并添加植骨孔等结构,植入骨粒后既能提供良好的骨传导性能,又有利于骨性融合。与传统金属材料相比,碳纤维材料的另一优势在于X射线透过性能好,且不干扰磁场的均匀性和射频的稳定性,因而在CT断层扫描、磁共振等骨科常用的影像学检查中不影响对融合器邻近骨组织的观察[17]。 虽然碳纤维轴向刚度可满足支撑需求,但材料弹性模量较大,易造成融合器与椎体间应力相对集中,对于部分骨质疏松或术中终板刮除较多的患者,融合器下沉的发生率会显著升高,影响支撑效果[18]。此外,纯碳纤维材料加工难度较大,无法注塑成型,只能通过减材制造法成型,在冲压、切削制件过程中,表面产生的细微毛刺将增加对局部组织的刺激性,可能引起白细胞聚集和炎性因子释放,造成局部疼痛;而表面处理工艺复杂,增加了制造成本,使单纯碳纤维材料的应用受到一定限制。因而目前各制造商多将碳纤维作为改性材料掺入其他材料(主要是部分抗压和抗折弯性能不佳的树脂材料)中,使后者的机械性能显著改善。 2.1.3 高分子量聚乙烯 高分子量聚乙烯是将乙烯单体高度聚合成相对分子质量大于100万后形成的聚烯烃类树脂材料。高分子量聚乙烯化学性质稳定,无毒性,在体内电解质浸泡条件下不易老化降解。高分子量聚乙烯较传统高密度聚乙烯具有更突出的机械性能,表现为较高的刚性和韧性,特别是经化学改性或结构自增强后其耐磨性和耐冲击性可有显著提升,近年来人工全髋、全膝关节置换中已广泛使用高分子量聚乙烯假体衬垫,经证实其临床效果满意。作为一种热塑性树脂材料,其加工工艺相对简易,成型后在常温垂直、旋转等方向交变应力条件下,材料无明显蠕变,在制造椎间融合器方面有较大潜力[19]。 然而高分子量聚乙烯椎间融合器的应用并不及高分子量聚乙烯关节置换假体广泛。首先,作为一种疏水性、非极性聚合物,高分子量聚乙烯表面能较低,不利于成骨相关细胞黏附和爬行生长,影响融合效果[20];其次,高分子量聚乙烯具有一定自润滑性,如植入后与周边组织和邻近终板契合不良,易在应力下产生滑动,致使固定失效。制造符合临床要求的融合器需增加材料表面粗糙度和亲水性,其改进思路为表面处理工艺的进一步完善[21],近年来,高分子量聚乙烯表面纳米材料喷涂的研究即是此方面的有益探索。 2.1.4 聚砜 聚砜是一种性能优良的非晶型工程塑料,也是较早研究的骨替代材料之一[22]。在实验室研究中,聚砜的力学性能优异,表现为较好的耐磨性和较高的硬度,其热稳定性突出,塑形精确,成型后尺寸稳定、耐蠕变[23-24]。聚砜材料无毒性,符合FDA医药及食品接触材料检测标准,耐高温、耐蒸汽,经高压蒸汽灭菌 (205.8 kPa,132 ℃,10 min)后仍然能保持良好机械性能。对聚砜的生物相容性研究表明,聚砜植入体内后,与组织接触界面未见异常组织学改变,作为融合材料与骨组织接触后紧密结合,提示对骨性融合无明显影响[25]。 聚砜材料的缺陷在于其弹性模量较高,在前柱轴向载荷下可能出现类似金属材料的“应力遮挡”现象或材料下沉等问题,影响融合效果。此外,聚砜耐疲劳强度差,术后可能因椎体活动产生的交变应力出现疲劳破坏,影响固定可靠性和术后稳定性。将聚砜混掺羟基磷灰石后制成复合材料是在保持材料机械强度同时降低弹性模量的可靠途径,而适当的成型后处理可进一步减小材料的内应力,显著增加融合器的抗疲劳性能[26]。 此外,尚有多种不可降解高分子合成材料,因具有无毒无害的化学特性、良好的生物相容性和一定的机械强度而有潜力作为椎间融合器的制造材料,如聚四氟乙烯、聚氨酯、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯等,但均存在一定缺陷,例如:聚四氟乙烯材料表面能较低,材料-骨组织界面的新生骨组织难以附着;聚氨酯材料易老化的问题尚待解决;聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯脆性较大,冲击力较大时容易发生碎裂[27-29]。因此上述材料作为融合器代替自然骨组织支撑椎体前柱结构仍存在不足之处,临床上尚未见相关的成熟产品大规模应用。 "

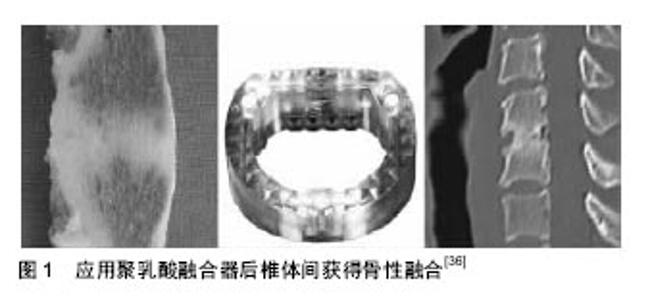
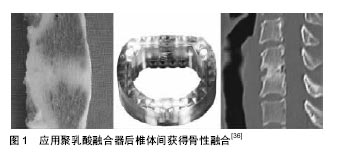
2.2 可降解类高分子材料 2.2.1 聚碳酸酯 聚碳酸酯是一类由含碳酸酯基单体聚合而成的高分子树脂型材料,热塑性好,成型简易的同时具有耐疲劳、耐蠕变的特性,材料的硬度和刚性高,可承受前柱系统的轴向载荷,与其他材料混掺改性后,能根据个体和部位差异制成符合各种机械性能要求的融合器。聚碳酸酯生物相容性好,降解过程温和缓慢,降解产物无毒,并可利用该特性加入抗生素或抗肿瘤等药物制成缓释载体,在局灶发挥治疗作用[30]。 聚碳酸酯材料本身虽无毒害作用,但在当前制造工艺下,聚合反应中需应用双酚A,聚合产物中亦可能含有微量双酚A,在降解时产生游离双酚A难以避免。毒理学研究证实双酚A具有致癌、致畸等潜在的生物毒性[31],故仍需对材料制造工艺继续优化。 2.2.2 α-多聚酸 α-多聚酸是目前制造融合器较常用的一类可降解高分子材料。研究较多的包括由α-乳酸为单体聚合制得的聚乳酸和以α-乙醇酸为单体聚合制得的聚乙醇酸。上述材料在体内电解质液浸泡环境中可逐步降解为单体形式,被细胞与组织吸收。然而动物实验发现聚乙醇酸降解速度过快,不但易造成术后固定强度丢失,还可引起椎间隙内α-乙醇酸浓度过高,导致局部无菌性炎症,刺激硬脊膜与神经根[32-33],当前技术条件下尚难以克服上述材料缺陷。与α-聚乙醇酸不同,α-聚乳酸具有手性结构,有多种异构单体,各种同分异构体的分子表面能和化学性质不同,因而通过对各种同分异构体含量比例进行调节,可聚合成降解速度各异的聚乳酸材料,并通过控制聚合程度制造不同力学特性的聚乳酸材料,因此目前各实验室与临床上多使用聚乳酸作为椎间融合器的制造材料。 聚乳酸材料亲水性好,具有良好的生物相容性,植入椎间隙后约8周后开始逐步降解,与生理条件下骨组织重构周期基本同步,因而其降解过程与骨性融合过程互相交叉重叠,新生骨组织可逐步取代聚乳酸支撑材料完成融合(图1)[34-36]。聚乳酸材料初步降解产物为乳酸,并可进一步经组织代谢转化为二氧化碳和水,安全无毒。但需要注意的是当患者存在营养不良、年老等不利于骨质融合的因素时,支撑强度过早丢失对前柱稳定性可能产生不良影响。 聚乳酸材料酸性降解产物引起局部pH值降低可能是影响融合的危险因素,除可引起骨基质溶解外,破骨细胞在酸性环境中亢进的骨吸收作用亦不可忽视[37-39]。需要指出的是,目前限制聚乳酸材料制品临床推广的主要技术难点在于其脆性较大,如术中需将融合器打入椎间隙,敲击过程中常出现融合器破裂。目前已制成聚乳酸混掺羟基磷灰石的复合材料,制成融合器后,材料机械性能优于自体髂骨[40],降解速度可控,降解后乳酸单体可被部分中和,更重要的是,羟基磷灰石直接提供成骨支架结构,利于新生骨细胞爬行进而促进融合,从而扩展了聚乳酸材料的应用范围。 2.2.3 氨基酸共聚物 氨基酸共聚物是由6-氨基己酸为主体骨架,加入甘氨酸、丙氨酸等氨基酸共同聚合而成的新型可降解高分子材料。研究表明,氨基酸共聚物具有与人体骨质相似的刚度与弹性模量,使融合术后的骨-材料界面发生微骨折和内固定物下沉的可能性降低,有利于骨的生成和改建,降低不融合率[41];氨基酸共聚物具有较好的亲水性和生物相容性,材料的力学特性和降解速率可通过调节各氨基酸组分进行个体化设计,降解产物呈中性至弱酸性,降低了骨溶解风险[42]。 另外,近年来尚有聚己内酯和一些多聚糖类等可降解高分子材料经证实可克服传统材料的诸多缺陷,有望用于制作融合器[43]。但与上述新材料相关的研究较少且多以动物实验和生物力学实验为主,动物实验虽有助于研究材料的毒性和生物相容性,但难以模拟人类正常站立情况下的椎体序列受力情况,无法评估材料力学特性在材料降解过程中的动态变化;常规生物力学实验虽能获得材料本身力学特性数据,但无法精确模拟体液浸泡、韧带附着等生物体内力学环境,对骨-材料接触界面成骨代谢情况等研究热点问题也存在局限。鉴于目前尚缺乏适当的研究模型与设计严密的临床试验,聚己内酯和多聚糖类可降解高分子材料在脊柱外科的应用前景尚不明朗,值得进一步关注并改进完善。 "
| [1]Zhao M,Li H,Liu X,et al.Response of Human Osteoblast to n-HA/PEEK--Quantitative Proteomic Study of Bio-effects of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite.Sci Rep.2016;6:22832.[2]Iwasaki K,Ikedo T,Hashikata H,et al.Autologous clavicle bone graft for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with titanium interbody cage.Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(5): 761-768.[3]van Jonbergen HP,Spruit M,Anderson PG,et al.Anterior cervical interbody fusion with a titanium box cage: early radiological assessment of fusion and subsidence.Spine J.2005;5(6):645-649.[4]Teunissen M,van der Veen AJ,Smit TH,et al.Effect of a titanium cage as a stand-alone device on biomechanical stability in the lumbosacral spine of canine cadavers.Vet J.2017;220:17-23.[5]董喆,奚廷斐.生物相容性材料作用机制研究进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2011,34(1):62-64.[6]Zhang HX,Xiao GY,Wang X,et al.Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of calcium phosphate composite scaffolds containing simvastatin-loaded PLGA microspheres for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(10): 3250-3258.[7]Meers CM,Verleye GB,Smeets D,et al.Fine grained osseointegrative coating improves biocompatibility of PEEK in heterotopic sheep model.Int J Spine Surg.2015;9:35.[8]Sekine C,Tsubata Y,Yamada T,et al.Recent progress of high performance polymer OLED and OPV materials for organic printed electronics.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2014;15(3): 034203.[9]Lemcke J,Al-Zain F,Meier U,et al Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Spacers for Anterior Cervical Fusion: A Retrospective Comparative Effectiveness Clinical Trial.Open Orthop J.2011; 5:348-353.[10]Grasso G,Giambartino F,Tomasello G,et al.Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with ROI-C peek cage: cervical alignment and patient outcomes.Eur Spine J.2014;23 Suppl 6:650-657.[11]Kulkarni AG,Hee HT,Wong HK.Solis cage(PEEK) for anterior cervical fusion: preliminary radiological results with emphasis on fusion and subsidence.Spine J.2007;7(2):205-209.[12]Baidya KP,Ramakrishna S,Rahman M,et al.Quantitative radiographic analysis of fiber reinforced polymer composites.J Biomater Appl.2001;15(3):279-289.[13]Fan JP,Tsui CP,Tang CY,et al.Influence of interphase layer on the overall elasto-plastic behaviors of HA/PEEK biocomposite.Biomaterials.2004;25(23):5363-5373.[14]Heary RF,Parvathreddy NK,Qayumi ZS,et al.Suitability of carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone cages for use as anterior struts following corpectomy.J Neurosurg Spine.2016; 25(2):248-255.[15]Hermansen A,Hedlund R,Vavruch L,et al.A comparison between the carbon fiber cage and the cloward procedure in cervical spine surgery: a ten- to thirteen-year follow-up of a prospective randomized study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(12):919-925.[16]宋成哲,金红旭.碳纤维椎间融合器与钛网椎间融合器修复腰椎退行性变:生物相容性比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(12):1909-1913.[17]Yoo M,Kim WH,Hyun SJ,et al.Comparison between Two Different Cervical Interbody Fusion Cages in One Level Stand-alone ACDF: Carbon Fiber Composite Frame Cage Versus Polyetheretherketone Cage. Korean J Spine.2014; 11(3):127-135.[18]Sardar Z,Jarzem P.Failure of a carbon fiber-reinforced polymer implant used for transforaminal lumbar interbodyfusion.Global Spine J.2013;3(4):253-256.[19]Nohara H,Kanaya F.Biomechanical study of adjacent intervertebral motion after lumbar spinal fusion and flexible stabilization using polyethylene-terephthalate bands.J Spinal Disord Tech.2004; 17(3):215-219. [20]Raimondo T,Puckett S,Webster TJ.Greater osteoblast and endothelial cell adhesion on nanostructured polyethylene and titanium.Int J Nanomedicine.2010;5:647-652.[21]Poulsson AH,Mitchell SA,Davidson MR,et al.Attachment of human primary osteoblast cells to modified polyethylene surfaces.Langmuir.2009;25(6):3718-3727.[22]Mokkapati VRSS,Koseoglu-Imer DY,Yilmaz-Deveci N,et al.Membrane properties and anti-bacterial/anti-biofouling activity of polysulfone-graphene oxide composite membranes phase inversed in graphene oxide non-solvent.RSC Adv. 2017;7(8):4378-4386.[23]Szymonowicz M,Rybak Z,Fraczek-Szczypta A,et al. Haemocompatibility and cytotoxic studies of non-metallic composite materials modified with magnetic nano and microparticles.Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2015;17(3):49-58.[24]Bilgen B,Chu D,Stefani R,et al.Design of a biaxial mechanical loading bioreactor for tissue engineering.J Vis Exp. 2013; 25(74):e50387.[25]Migacz K,Chiopek J,Morawska-Chochoi A,et al.Gradient composite materials for artificial intervertebral discs.Acta Bioeng Biomech.2014;16(3):3-12.[26]Wang M,Yue CY,Chua B. Production and evaluation of hydroxyapatite reinforced polysulfone for tissue replacement.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2001;12(9):821-826.[27]McKeown AD,Beattie RF,Murrell GA,et al.Biomechanical comparison of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) and PTFE interpositional patches and direct tendon-to-bone repair for massive rotator cuff tears in an ovine model.Shoulder Elbow.2016;8(1):22-31.[28]Pokharel P,Lee SH,Lee DS.Thermal, Mechanical, and Electrical Properties of GrapheneNanoplatelet/Graphene Oxide/ Polyurethane Hybrid Nanocomposite.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2015; 15(1):211-214.[29]Bharti A,Saroj UK,Kumar V,et al.A simple method for fashioning an antibiotic impregnated cemented rod for intramedullary placement in infected non-union of long bones.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016;7(Suppl 2):171-176.[30]Liao J,Zhang L,Zuo Y,et al. Development of nanohydroxyapatite/polycarbonate composite for bone repair.J Biomater Appl.2009;24(1):31-45.[31]Hoekstra EJ,Simoneau C.Release of bisphenol A from polycarbonate: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013;53(4): 386-402.[32]Suzuki H,Araki K,Matsui T,et al.Value of a novel PGA-collagen tube on recurrent laryngeal nerve regeneration in a rat model.Laryngoscope.2016;126(7):E233-239.[33]Singh M,Singh RK,Passi D,et al.Management of pediatric mandibular fractures using bioresorbable plating system - Efficacy, stability, and clinical outcomes: Our experiences and literature review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res.2016;6(2): 101-106.[34]Smit TH,Engels TA,Wuisman PI,et al.Time-dependent mechanical strength of 70/30 Poly(L, DL-lactide): shedding light on the premature failure of degradable spinal cages. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(1):14-18. [35]Engels TA,Sontjens SH,Smit TH,et al.Time-dependent failure of amorphous polylactides in static loading conditions.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(1):89-97.[36]Smit TH,Engels TA,Sontjens SH,et al.Time-dependent failure in load-bearing polymers: a potential hazard in structural applications of polylactides.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010; 21(3):871-878.[37]Jiya T,Smit T,Deddens J,et al.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using nonresorbable poly-ether-ether-ketone versus resorbablepoly-L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide fusion devices: a prospective, randomized study to assess fusion and clinical outcome.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(3):233-237.[38]Wuisman PI,Krijnen MR,Helder MN,et al. Bioabsorbableinterbody cages in a sheep cervical spine fusion model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2005;30(17):2005-2006.[39]Kandziora F,Pflugmacher R,Scholz M,et al. Bioabsorbableinterbody cages in a sheep cervical spine fusion model.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(17):1845-1855.[40]胡孔和,靳安民,吴广森,等.生物活性颈椎椎间融合器的三维运动稳定性实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(48): 9406-9409.[41]Duan H,Yang H,Xiong Y,et al.Effects of mechanical loading on the degradability and mechanical properties of the nanocalcium-deficient hydroxyapatite-multi(amino acid) copolymer composite membrane tube for guided bone regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine.2013;8:2801-2807.[42]王孝军,李鸿,张刚,等.多元氨基酸共聚物的合成及性能表征[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2011,27(3):13-15.[43]Ergun A,Chung R,Ward D,et al.Unitary bioresorbable cage/core bone graft substitutes for spinal arthrodesis coextruded from polycaprolactonebiocomposites.Ann Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):1073-1087.[44]Koller H,Fierlbeck J,Auffarth A,et al.Impact of constrained dual-screw anchorage on holding strength and the resistance to cyclic loading in anterior spinal deformity surgery: a comparative biomechanical study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(6):E390-398.[45]Peters T,Chinthakunta SR,Hussain M,et al.Pedicle Screw Configuration for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Treatment: Short versus Long Posterior Fixation Constructs with and without Anterior Column Augmentation.Asian Spine J. 2014;8(1):35-43. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||