Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4067-4076.doi: 10.12307/2026.705
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism by which acupuncture regulates autophagy in a rat model of cerebral hemorrhage
Ji Dejiang, Zhang Xiaojing, Ye Gaxi
- Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yinchuan 750021, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-08-28Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-26 -
Contact:Ye Gaxi, MS, Attending physician, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yinchuan 750021, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Ji Dejiang, MS, Attending physician, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Ningxia Medical University Affiliated Autonomous Region Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yinchuan 750021, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Ningxia Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2023AAC03693 (to JDJ); 2023 Young Talent Cultivation Project of Ningxia Autonomous Region, No. [2024]6 (to JDJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Dejiang, Zhang Xiaojing, Ye Gaxi. Role and mechanism by which acupuncture regulates autophagy in a rat model of cerebral hemorrhage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4067-4076.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
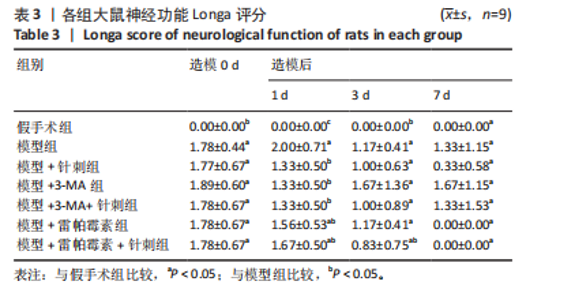
2.1 实验动物数量分析及行为学观察 实验购买75只SD大鼠,其中将63只SD大鼠随机分成7组,每组9只。多余大鼠同时进行脑出血模型制备以便及时补充死亡个体,在脑出血造模时有5只大鼠死亡。在大鼠苏醒后进行行为学观察,发现假手术组大鼠表现基本正常,各造模组有不同程度的偏瘫和运动障碍,大鼠表现为转圈、身体一侧倾斜,部分大鼠出现昏迷甚至无法行走的情况。针刺治疗后大鼠运动能力有所恢复,部分大鼠能够自主行走,针刺时间越久大鼠步态越正常。 2.2 大鼠神经功能Longa评分 Longa评分发现:假手术组无神经功能缺损现象,评分为0;模型组及其他各组在造模后出现神经功能缺损体征。与假手术组相比,模型组神经功能评分显著升高(P < 0.05),其中在造模后第1天评分最高;与模型组相比,模型+针刺组、模型+雷帕霉素组、模型+雷帕霉 素+针刺组在造模后第1天得分显著降低(P < 0.05),且随着针刺时间的增加,神经功能缺损得分降低,其中在针刺第7天时得分降低最明显;与模型组相比,模型+3-MA组在造模第3天和造模第7天神经功能损伤最严重(P < 0.05);模型+3-MA+针刺组神经缺损情况较模型+3-MA组情况减轻(P < 0.05)。大鼠造模结果见图1;Longa评分结果见表3。"
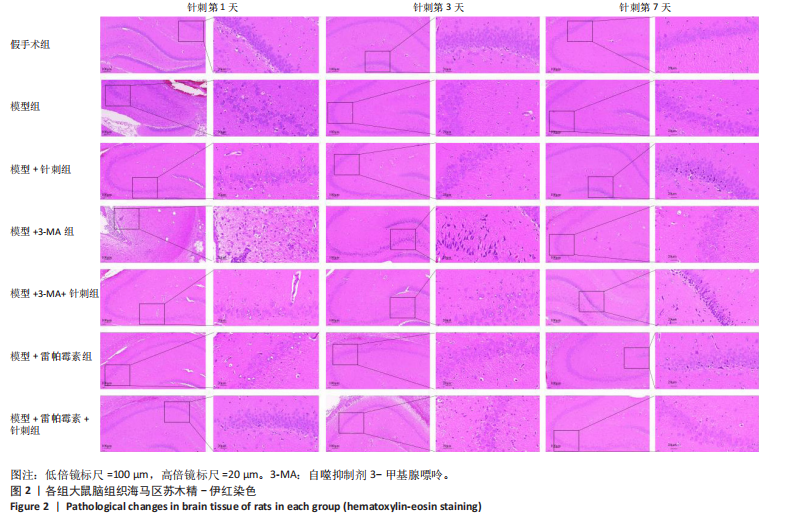
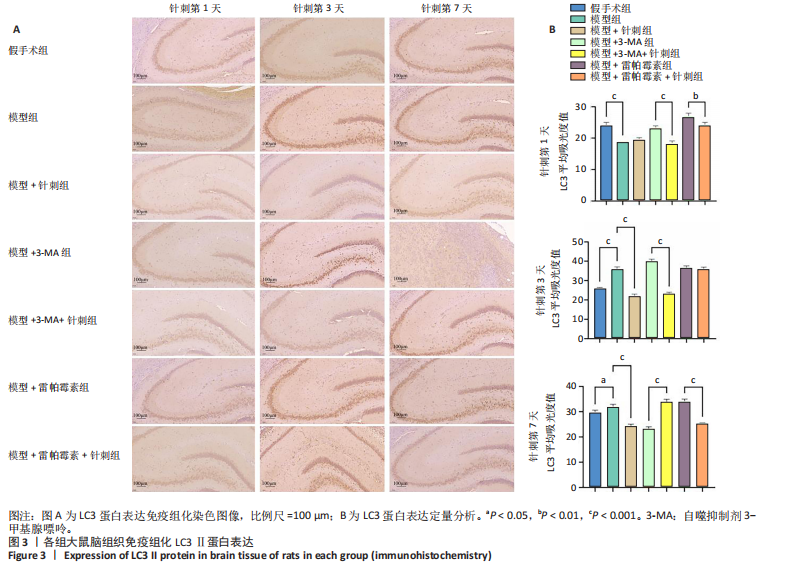
2.3 脑组织形态学观察 苏木精-伊红染色观察结果显示,假手术组脑组织各层结构清晰,细胞排列规则,未见炎症细胞及小胶质细胞浸润;模型组周围血管内皮肿胀且炎症细胞浸润,部分小胶质细胞增生;模型+针刺组在针刺第1天存在炎症细胞浸润,随着针刺时间增加炎症细胞浸润及细胞肿胀程度降低;模型+3-MA组炎症细胞浸润随时间增加,小胶质细胞游离增生明显,神经细胞萎缩排列杂乱;模型+ 3-MA+针刺组和模型+雷帕霉素组随着针刺时间增加,炎症细胞浸润逐渐减少,神经元细胞逐渐排列整齐;模型+雷帕霉素+针刺组在针刺前3 d有少量炎症细胞浸润及小胶质细胞游离,针刺第7天海马区未见炎症细胞,神经元细胞正常,排列规则,结果见图2。 2.4 免疫组化检测LC3蛋白表达 免疫组化观察结果发现:LC3在细胞质中表达。与假手术组相比,模型组LC3蛋白表达在针刺第1天显著降低(P < 0.05),在针刺第3天和第7天显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型"
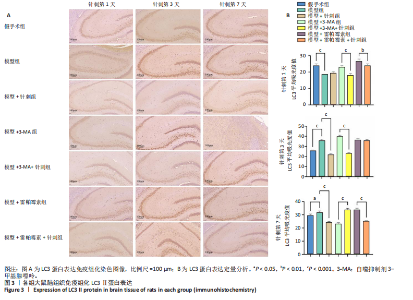
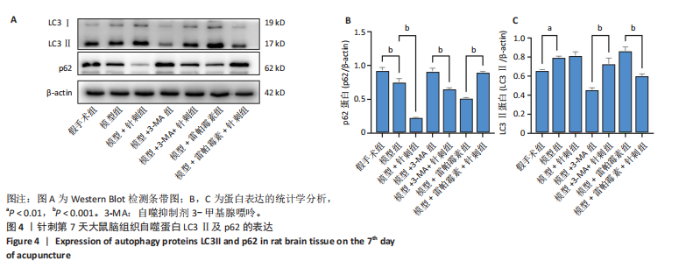
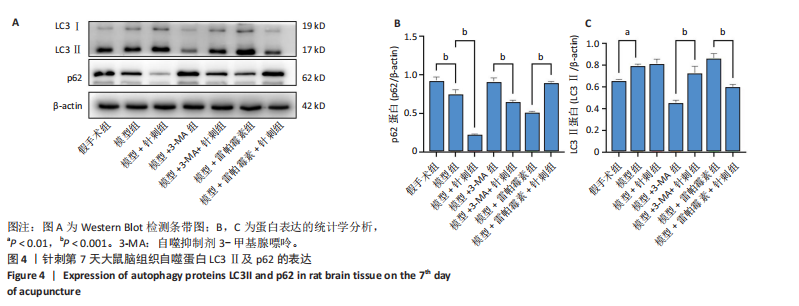
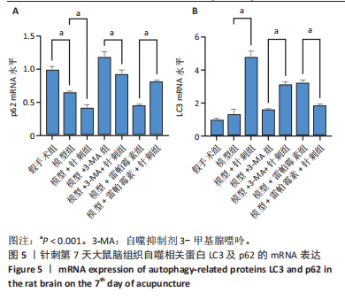
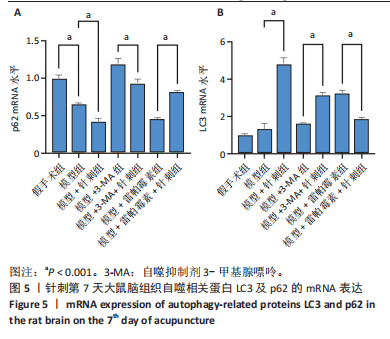
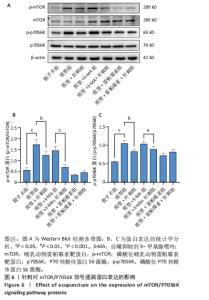
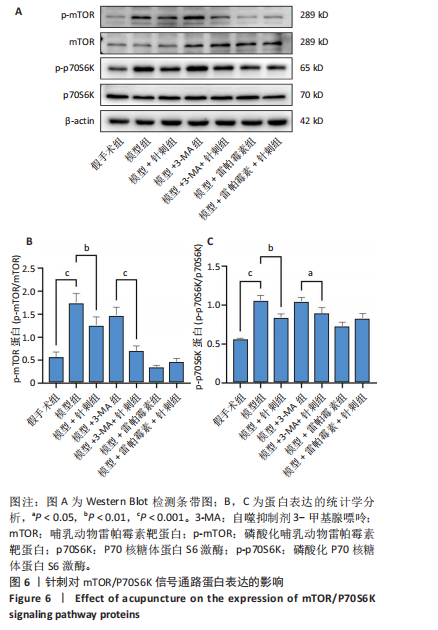
组相比,模型+针刺组LC3蛋白表达在针刺后第1天差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),在针刺第3天和第7天显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+3-MA组相比,模型+3-MA+针刺组LC3蛋白表达在针刺第1天和第3天表达显著降低(P < 0.05),在针刺第7天表达显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型+雷帕霉素组比较,模型+雷帕霉素+针刺组LC3蛋白表达在针刺第1天和第7天表达显著降低(P < 0.05),在第3天差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图3。 2.5 Western Blot检测自噬关键蛋白LC3Ⅱ、p62的表达 结果发现:针刺第7天与假手术组相比,模型组LC3蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,模型+针刺组LC3蛋白表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),p62蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+3-MA组相比,模型+3-MA+针刺组LC3蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+雷帕霉素组相比,模型+雷帕霉素+针刺组LC3蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),结果见图4。 2.6 RT-qPCR检测自噬蛋白LC3及p62的mRNA表达 结果显示:针刺第7天与假手术组比较,模型组LC3 mRNA表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),p62 mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,模型+针刺组LC3 mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05)、p62 mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+3-MA组相比,模型+3-MA+针刺组LC3 mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05),p62 mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+雷帕霉素组相比,模型+雷帕霉素+针刺组LC3 mRNA表达显著降低(P < 0.05),p62 mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05),结果见图5。 2.7 Western Blot检测mTOR/p70S6K通路的相关蛋白表达 结果显示,与假手术组相比,模型组p-mTOR和p-p70S6K表达显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,模型+针刺组p-mTOR和p-p70S6K表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+3-MA组相比,模型+3-MA+针刺组p-mTOR和p-p70S6K显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型+雷帕霉素组相比,模型+雷帕霉素+针刺组p-mTOR和p-p70S6K表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),结果见图6。"
| [1] LEE TH. Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2025;15(1): 1-8. [2] STERENSTEIN A, GARG R. The impact of sex on epidemiology, management, and outcome of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (sICH). J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024;33(7):107755. [3] GARCIA JH, WAGNER S, LIU KF, et al. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke. 1995;26(4):627-634. [4] DUPRÉ N, DRIEU A, JOUTEL A. Pathophysiology of cerebral small vessel disease: a journey through recent discoveries. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(10):e172841. [5] LI Q, YAKHKIND A, ALEXANDROV AW, et al.Code ICH: A Call to Action. Stroke. 2024;55(2):494-505. [6] LU P, CAO Z, GU H, et al. Association of sex and age with in-hospital mortality and complications of patients with intracerebral hemorrhage: A study from the Chinese Stroke Center Alliance. Brain Behav. 2023; 13(1):e2846. [7] 浦怡婷, 冯瑶婷, 吕鹤群, 等. 针灸治疗脑出血的机制研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2025,27(1):195-201. [8] 史波. 脑出血的治疗及预防知识[J].人人健康,2025(5):28-29. [9] LEHMANN H. Acupuncture in ancient China: how important was it really? J Integr Med. 2013;11(1).:45-53. [10] KONG Y, LI S, ZHANG M, et al. Acupuncture Ameliorates Neuronal Cell Death, Inflammation, and Ferroptosis and Downregulated miR-23a-3p After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rats. J Mol Neurosci. 2021; 71(9):1863-1875. [11] 王慧, 雷寿清, 杜小正, 等.“脑肠同调”法针刺治疗急性脑梗死及对IL-17、hs-CRP和TMAO水平的影响[J].中国针灸,2022, 42(8):853-856. [12] 陈秋欣, 孔莹, 于婷婷, 等. 针刺“百会”透“曲鬓”穴对急性脑出血大鼠血肿及CD36、HO-1表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志, 2021,37(8):59-63. [13] LI HQ, LI JH, LIU AJ, et al. GV20-based acupuncture for animal models of acute intracerebral haemorrhage: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2014;32(6):495-502. [14] 张宇豪. 基于海马突触传递效能和可塑性探讨电针改善血管性痴呆学习记忆功能的作用机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2020. [15] KLIONSKY DJ, PETRONI G, AMARAVADI RK, et al. Autophagy in major human diseases. Embo J. 2021;40(19):e108863. [16] 刘汇真, 张旖旎, 陈雨萌, 等. 安寐丹通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路调控细胞自噬改善睡眠剥夺小鼠学习记忆水平[J/OL]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 1-10[2025-04-14]. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20250609. [17] 汝少国, 朱增光, 崔鹏飞. 细胞自噬与应激反应[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2022,52(7):1-13. [18] LIU S, YAO S, YANG H, et al. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(10):648. [19] AJOOLABADY A, WANG S, KROEMER G, et al. Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;225:107848. [20] 姚嘉永,邹伟. 针刺治疗脑出血机制的研究进展[J]. 2022,47(1):88-94. [21] 黄琳,粟胜勇. 基于JAK/STAT信号通路探讨针刺治疗脑出血机制研究进展[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2024,31(2):186-190. [22] 陈秋欣, 孔莹, 于婷婷,等. 针刺对脑出血大鼠血红素氧化酶1及炎性因子表达的影响[J]. 康复学报,2021,31(5):408-414. [23] LIU C, GAO W, ZHAO L, et al. Progesterone attenuates neurological deficits and exerts a protective effect on damaged axons via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR-dependent pathway in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(6):2574-2589. [24] CHEN YN, ZHENG X, CHEN HL, et al. Stereotaxic atlas of the infant rat brain at postnatal days 7-13. Front Neuroanat. 2022;12:16:968320. [25] FANG J, SONG F, CHANG C, et al. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Models and Behavioral Tests in Rodents. Neuroscience. 2023;513:1-13. [26] 杨贝贝.针康法调控脂质过氧化抑制铁死亡对脑缺血大鼠的神经保护作用机制研究[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2023. [27] 董雯雯.自噬在小鼠脑出血后脑损伤中的作用及机制研究[D]. 苏州:苏州大学,2014. [28] SUN D, WANG W, WANG X, et al. bFGF plays a neuroprotective role by suppressing excessive autophagy and apoptosis after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):172. [29] KRAFFT PR, MCBRIDE DW, LEKIC T, et al. Correlation between subacute sensorimotor deficits and brain edema in two mouse models of intracerebral hemorrhage. Behav Brain Res. 2014;264:151-160. [30] GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators.Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820. [31] GROSS BA, JANKOWITZ BT, FRIEDLANDER RM. Cerebral Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage: A Review. JAMA. 2019;321(13):1295-1303. [32] 郑惠文.丁苯酞对大鼠脑出血后mTOR/P70S6K通路影响及机制研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2022. [33] 韩佳炜, 王淑华, 李桂平, 等.大鼠脑出血动物模型的制作技巧[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2018,21(7):707-711. [34] 王嘉, 苗明三, 和时博. 脑出血动物模型的中西医临床病证特点分析[J].中药药理与临床,2025,41(2):84-89. [35] 金红. 脑出血方治疗脑出血的临床疗效分析及基于PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路的自噬调控机制研究[D].长春:长春中医药大学,2024. [36] 李士超. 针刺联合康复理疗治疗脑出血的效果分析[J].中外医药研究,2024,3(34):81-83. [37] 李佳玲, 樊冰心, 张富文.《普济方•针灸门》目病选穴规律探析[J]. 中医眼耳鼻喉杂志,2024,14(2):87-90. [38] 康琳玲, 彭拥军, 邓小嫚.《普济方》针灸治疗中风选穴规律分析[J]. 江苏中医药,2023,55(2):66-69. [39] 席梦含, 王路, 张微, 等.针刺调节神经元程序性细胞死亡的机制研究进展[J].重庆医科大学学报,2024,49(4):362-369. [40] 郑雪霞, 林远茂, 陈银燕, 等.基于细胞自噬探讨针刺调控治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2025,27(10):103-108 [41] 杨金亮, 于大兴, 齐文升. 电针对呼吸机相关性膈肌功能障碍大鼠自噬小体及相关因子LC3、P62表达水平的影响[J]. 环球中医药, 2025;18(9):1741-1746. [42] XUE LX, CHEN SF, XUE SX, et al. LncRNA TUG1 compromised neuronal mitophagy in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting sirtuin 1. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022;38(6):1121-1136. [43] COLMAN RJ, ANDERSON RM, JOHNSON SC, et al. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science. 2009; 325(5937):201-204. [44] 翟淑娟, 潘景, 孙春意, 等. p62、OPTN在宫颈癌中的表达及其与HPV的相关性[J].昆明医科大学学报,2019,40(4):82-85. [45] 王宇, 代一宁, 郭孝静, 等.基于自噬探讨针刺改善缺血性脑卒中的机制研究进展[J]. 针刺研究,2025,50(2):204-209. [46] 王茸, 许军峰. 小胶质细胞与缺血性脑卒中的关系及针刺干预研究进展[J]. 针刺研究,2024,49(12):1319-1324. [47] ZHAO X AND WANG L. mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway promotes fibrillin-1 expression in AKI-to-CKD transition post CA/CPR. Cell Signal. 2025;128:111624. [48] SALAH TM, RABIE MA, EL SAYED NS. Renoprotective effect of berberine in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury: Role of Klotho and the AMPK/mtor/ULK1/Beclin-1 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2025;196:115179. [49] WANG Y, LIU Z, SHU S, et al.AMPK/mTOR Signaling in Autophagy Regulation During Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Front Physiol. 2020;11:619730. [50] ZHANG H, LANG W, LIU X, et al. Procyanidin A1 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via regulating AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K-mediated autophagy. J Physiol Biochem. 2022;78(1):213-227. [51] WANG K, TANG J, FAN S, et al. ABBV-744 induces autophagy in gastric cancer cells by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6k and MAPK signaling pathways. Neoplasia. 2023;45:100936. |
| [1] | Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [2] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [3] | Liu Kexin, , Hao Kaimin, Zhuang Wenyue, , Li Zhengyi. Autophagy-related gene expression in pulmonary fibrosis models: bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1129-1138. |
| [4] | Hu Jing, Zhu Ling, Xie Juan, Kong Deying, Liu Doudou. Autophagy regulates early embryonic development in mice via affecting H3K4me3 modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [5] | Zheng Wen, Zhu Dongsheng, Wang Xiaodong. Secreted modular calcium binding protein regulates autophagy in the acetabular cartilage of rats with developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4618-4626. |
| [6] | Yang Chong, Wu Yuci, Yang Han, Wang Meiting, Liu Lei. Promoting effect of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on the reconstruction of damaged neurological function in rats with cerebral infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4347-4356. |
| [7] | Huang Lei, Wang Xianghong, Zhang Xianxu, Li Shicheng, Luo Zhiqiang. Mechanism and therapeutic potential of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 in regulating non-infectious spinal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3971-3982. |
| [8] | Pan Li, Zhu Zhou, Yan Zhaobo, Zhang Ning, Yang Zhihong, Xiong Jiaojiao, Yang Xiaofang. Moxibustion improves endothelial function in atherosclerotic mice by regulating fatty acid oxidation through mediating mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2764-2773. |
| [9] | Huang Fengqin, Hu Yalin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei. Constructing a risk prediction nomogram model for cognitive impairment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2466-2474. |
| [10] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [11] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [12] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [13] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [14] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [15] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||