Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2466-2474.doi: 10.12307/2026.642
Previous Articles Next Articles
Constructing a risk prediction nomogram model for cognitive impairment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage
Huang Fengqin, Hu Yalin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei
- Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-26Accepted:2025-06-30Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-08-28 -
Contact:罗兴梅,博士,主任医师,贵州医科大学附属医院,贵州省贵阳市 550000 -
About author:黄凤琴,女,1998年生,贵州省毕节市人,穿青族,贵州医科大学在读硕士,医师,主要从事老年神经方面的研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Regional Fund Cultivation Program for the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. gyfynsfc[2023]-46 (to LXM); Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. Qiankeheji-ZK[2024] General 225 (to LXM); Doctoral Research Foundation of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. gyfybsky-2023-28 (to LXM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Fengqin, Hu Yalin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei. Constructing a risk prediction nomogram model for cognitive impairment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2466-2474.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
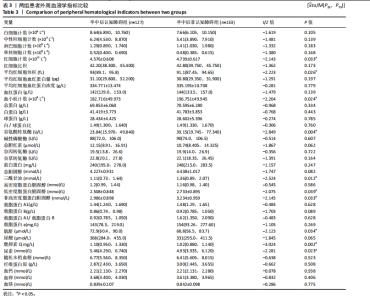
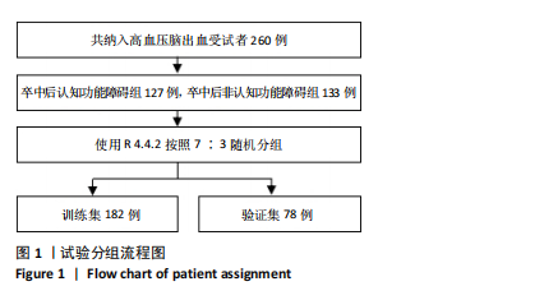
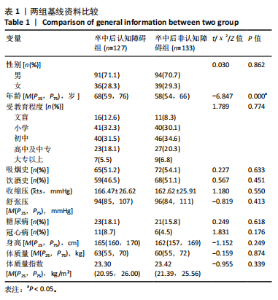
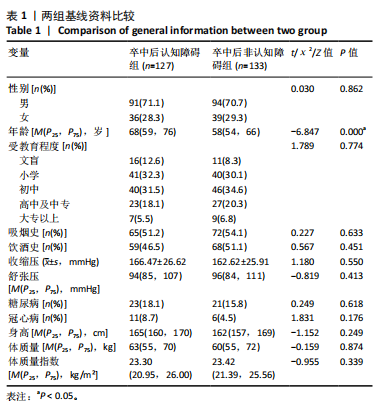
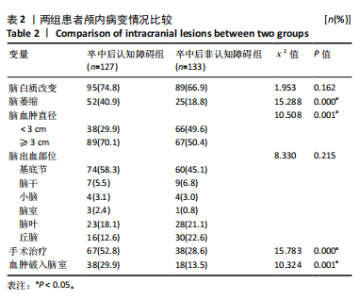
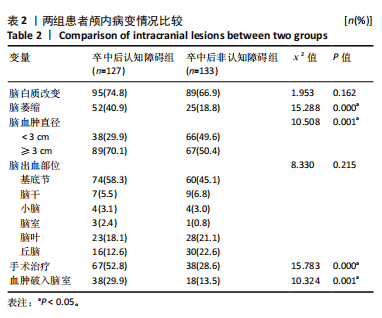
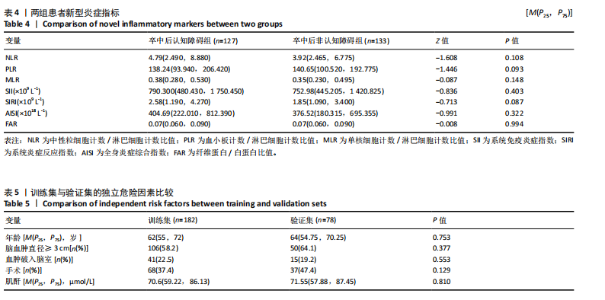
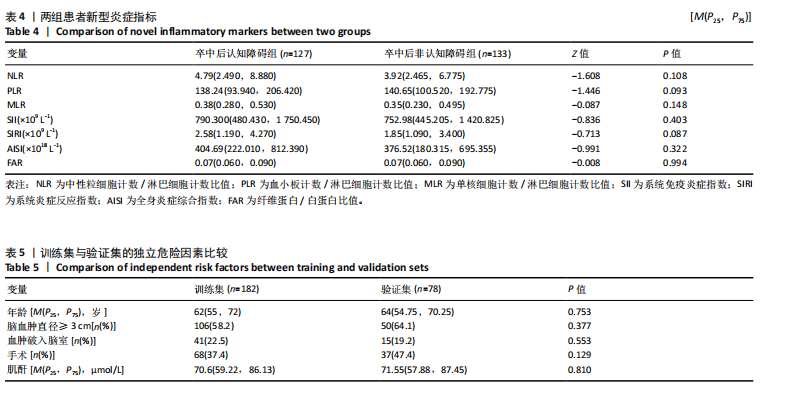
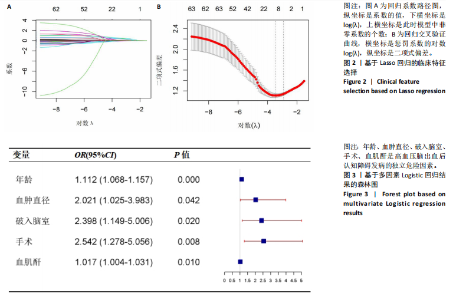
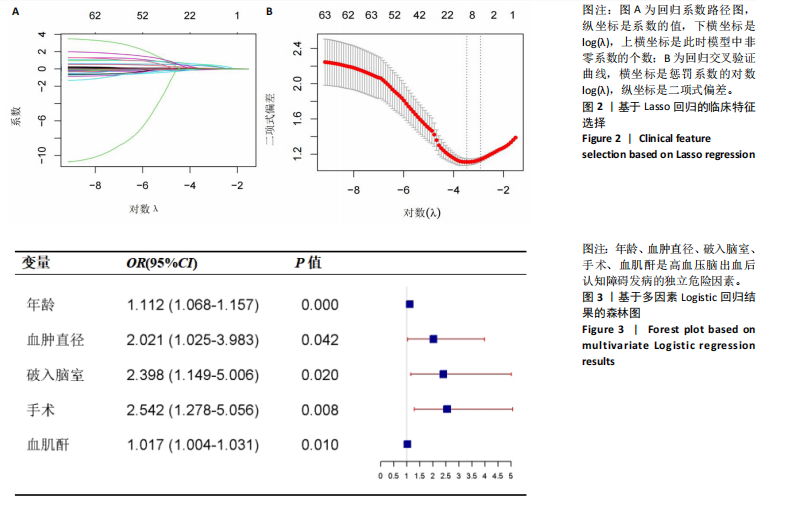
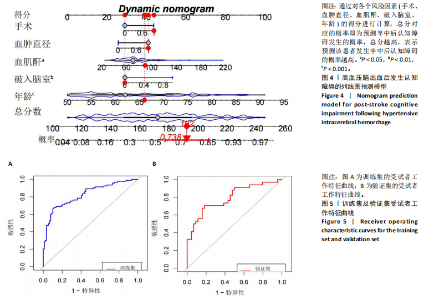
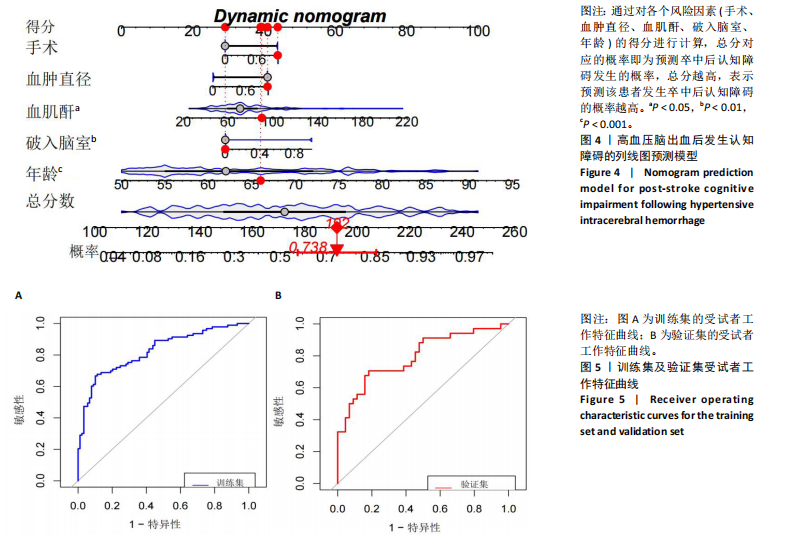
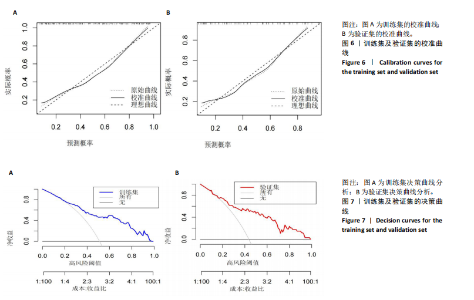
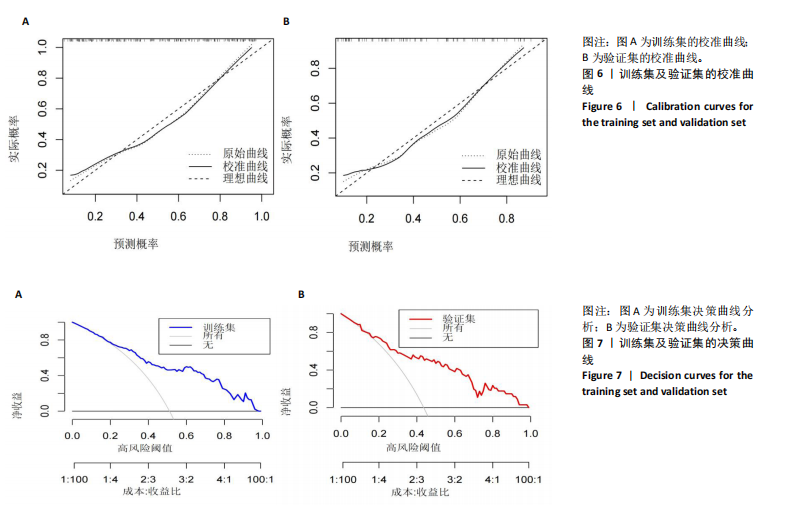
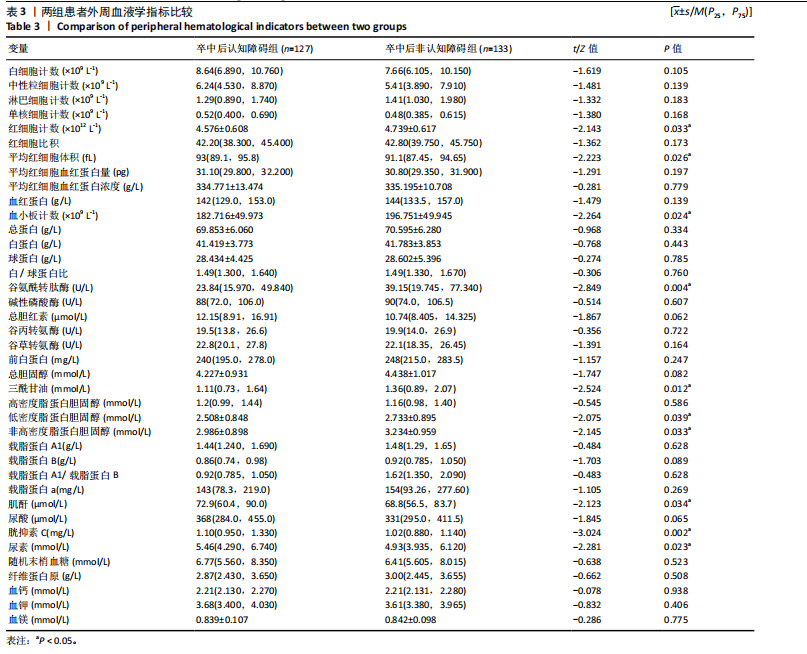
2.3.3 两组外周血液学指标比较 与卒中后非认知障碍组相比,卒中后认知障碍组患者红细胞计数、血小板计数、谷氨酰转肽酶、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平、非高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平低于卒中后非认知障碍组,而平均红细胞体积、肌酐、胱抑素C及尿素水平高于卒中后非认知障碍组(P < 0.05),白细胞计数、血糖、总胆红素等指标在两组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。 2.3.4 两组新型炎症指标比较 中性粒细胞计数/淋巴细胞计数比值(NLR)、血小板计数/淋巴细胞计数比值(PLR)、单核细胞计数/淋巴细胞计数比值(MLR)、系统免疫炎症指数(SII)、系统炎症反应指数(SIRI)、全身炎症综合指数(AISI)、纤维蛋白/白蛋白比值 (FAR)等指标在两组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表4。 2.4 预测模型变量的筛选 为减少变量间的多重共线性及过拟合问题,使用Lasso回归进行变量筛选,通过交叉验证选择最佳λ值(选取lambda.1se作为最佳λ值),见图2。 根据Lasso回归分析筛选出7个变量,包括年龄、血肿破入脑室、血肿直径、手术、脑出血位置、白细胞计数、肌酐值。将上述危险因素纳入多元logistic回归分析,结果显示:年龄(P=0.000)、血肿直径(P=0.042)、破入脑室(P=0.020)、手术(P=0.008)、血肌酐(P=0.010)是高血压脑出血后认知障碍发病的独立危险因素,见图3。 2.5 构建预测模型 基于R软件,按照7∶3随机将队列分为训练集和验证集,结果显示:训练集182例,验证集78例。比较训练集和验证集年龄、血肿直径、血肿破入脑室、手术、肌酐值5个危险因素,结果显示差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表5,将上述指标作为预测因子构建训练集风险预测的列线图模型,见图4。 2.6 预测模型的验证及应用 (1)区分度评价:训练集和验证集的列线图预测模型曲线下面积分别为0.826(95%CI 0.765-0.885)和0.795(95%CI 0.693-0.898),表示模型区分度较佳,见图5。 (2)校准度评价:经Hosmer-Lemeshow检验,训练集的χ2=12.710,P=0.122(P > 0.05);验证集的χ2=4.328,P=0.826(P > 0.05),表明预测模型的预测值和实际值无差异,说明该预测模型拟合优度好。"
| [1] TU WJ, WANG LD. China stroke surveillance report 2021. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):33. [2] AN SJ, KIM TJ, YOON BW. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Clinical Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update. J Stroke. 2017; 19(1):3-10. [3] FEIGIN VL, LAWES CM, BENNETT DA, et al. Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2(1):43-53. [4] SEIFFGE DJ, FANDLER-HÖFLER S, DU Y, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage - mechanisms, diagnosis and prospects for treatment and prevention. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024;20(12):708-723. [5] LEKOUBOU A, NGUYEN C, KWON M, et al. Post-stroke Everything. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023;23(11):785-800. [6] EL HUSSEINI N, KATZAN IL, ROST NS, et al. Cognitive Impairment After Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023;54(6):e272-e291. [7] 邓里娜,吴波.《中国脑出血诊治指南2019》更新要点及解读[J].心脑血管病防治,2021,21(1):13-17+34. [8] 汪凯,董强,郁金泰,等.卒中后认知障碍管理专家共识2021[J].中国卒中杂志,2021,16(4):376-389. [9] 曲艳吉,卓琳,詹思延.中国脑卒中后认知障碍流行病学特征的系统评价[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2013,15(12):1294-1301. [10] ROST NS, BRODTMANN A, PASE MP, et al. Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1252-1271. [11] ZHOU W, FENG H, TAO H, et al. Factors Influencing Poststroke Cognitive Dysfunction: Cross-Sectional Analysis. JMIR Form Res. 2024;8:e59572. [12] MA Y, HE X, YANG T, et al. Cognitive function in older adults with stroke: A latent profile analysis. Geriatr Nurs. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2024.10.053. [13] SPRINGER MV, CHEN B, WHITNEY RT, et al. Age differences in the change in cognition after stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024; 33(12):108087. [14] QUINN TJ, RICHARD E, TEUSCHL Y, et al. European Stroke Organisation and European Academy of Neurology joint guidelines on post-stroke cognitive impairment. Eur Stroke J. 2021;6(3):I-XXXVIII. [15] BRITO DV, NÓBREGA C. Making bridges between preclinical and clinical insights into age-related cognitive decline. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(8):2321-2322. [16] CHAU JPC, LO SHS, ZHAO J, et al. Apathy mediates the association between age and cognition after stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2024;46(21): 5038-5043. [17] PLUTA R, JABŁOŃSKI M, JANUSZEWSKI S, et al. Crosstalk between the aging intestinal microflora and the brain in ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:998049. [18] DONNELLAN C, WERRING D. Cognitive impairment before and after intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review. Neurol Sci. 2020; 41(3):509-527. [19] GU Y, WANG F, GONG L, et al. A nomogram incorporating red blood cell indices to predict post-stroke cognitive impairment in the intracerebral hemorrhage population. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:985386. [20] XIONG L, REIJMER YD, CHARIDIMOU A, et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage and cognitive impairment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(5):939-944. [21] ZHANG Z, GUO P, HUANG S, et al. Inhibiting Microglia-Derived NLRP3 Alleviates Subependymal Edema and Cognitive Dysfunction in Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus after Intracerebral Hemorrhage via AMPK/Beclin-1 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4177317. [22] LIU DZ, WALDAU B, ANDER BP, et al. Inhibition of Src family kinases improves cognitive function after intraventricular hemorrhage or intraventricular thrombin. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(7): 2359-2367. [23] JIANG C, ZOU X, ZHU R, et al. The correlation between accumulation of amyloid beta with enhanced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment after intraventricular hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2019; 131(1):54-63. [24] MAGID-BERNSTEIN J, GIRARD R, POLSTER S, et al. Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions. Circ Res. 2022;130(8):1204-1229. [25] DE OLIVEIRA MANOEL AL. Surgery for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):45. [26] IBRAHIM A, ARIFIANTO MR, AL FAUZI A. Minimally Invasive Neuroendoscopic Surgery for Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Review of the Rationale and Associated Complications. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2023;130:103-108. [27] MA Y, CHEN Y, YANG T, et al. Blood biomarkers for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024;33(8):107632. [28] OH YS, KIM JS, PARK JW, et al. Arterial stiffness and impaired renal function in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci. 2016;37(3): 451-457. [29] IGARASHI K, YOSHIDA M, WARAGAI M, et al. Evaluation of dementia by acrolein, amyloid-β and creatinine. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;450:56-63. [30] AURIEL E, KLIPER E, SHENHAR-TSARFATY S, et al. Renal Function, MRI Brain Changes and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment. Stroke. 2015; 46(suppl_1):A47. [31] AURIEL E, KLIPER E, SHENHAR-TSARFATY S, et al. Impaired renal function is associated with brain atrophy and poststroke cognitive decline. Neurology. 2016;86(21):1996-2005. [32] BALACHANDRAN VP, GONEN M, SMITH JJ, et al. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4): e173-e180. |
| [1] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [2] | Yang Peng, Xu Chenghan, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie, Li Lin, Shi Jinyu. A meta-analysis of risk factors for residual back pain after vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 731-739. |
| [3] | Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640. |
| [4] | Zhang Yuxin, Yu Cong, Zhang Cui, Ding Jianjun, Chen Yan. Differences in postural control ability between older adults with mild cognitive impairment and those with normal cognition under different single-task and dual-task conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1643-1649. |
| [5] | Wang Rongqiang, Yang Liu, Wu Xiangkun, Shang Lilin. Analysis of factors associated with prognosis of osteoporosis patients after hip arthroplasty and construction of Nomogram prediction model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7137-7142. |
| [6] | Wang Zhifeng, Yang Jiao, Xi Yujiang, Xu Shuangfeng, Shi Ting, Lan Junfeng, Hao Zhihui, He Pengfen, Yang Aiming, Pan Pan, Wang Jian. Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126. |
| [7] | Zhao Yuxin, Zhang Deqi, Bi Hongyan. Effect of different stimulation modalities of non-invasive brain stimulation on cognitive function in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5212-5223. |
| [8] | Dong Zhiwen, Yu Cong, Chen Yan, Ding Jianjun . Central nervous mechanisms underlying effects of cognitive impairment on dual-task stance: #br# functional near-infrared spectroscopy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3579-3587. |
| [9] | Qi Liuxin, Zhou Mian, Wang Xiangyu, Sun Wei, Wang Jiangna. Effect of support surface stability on balance in the elderly with mild cognitive impairment under different visual input conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3897-3902. |
| [10] | Li Zhipeng, Huan Dawei, Yuan Zhaofeng, Qiu Yue, Zhang Chao, Xia Tianwei, Shen Jirong. Risk factors of postoperative mortality of femoral neck fractures in elderly patients and construction of a nomogram predictive model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3361-3366. |
| [11] | Shi Jiao, Li Xingjie, Liu Qiqi, Liu Jun, Yuan Xu, Chen Shangjie. Effect of electronic moxibustion on the volume of hippocampal subregion in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3176-3181. |
| [12] | Deng Longfei, Zhang Yeting, Fu Yan. Aerobic exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and alleviates cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2209-2214. |
| [13] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [14] | Shen Lianwei, Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Risk factor analysis of metabolic syndrome and construction of a nomogram prediction model in middle-aged and elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 657-662. |
| [15] | Zhu Hongliu, Wang Wei. Correlation analysis of low back pain in middle-aged and elderly people in China and construction of a linear graph prediction mode [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4937-4942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||