Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2629-2640.doi: 10.12307/2026.617
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies
Jiang Kai1, Rong Yifa1, Jia Haifeng1, Li Hanzheng1, Lu Bowen1, Liang Xuezhen1, Li Gang2
- 1The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Micro-Orthopedics, The Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-01Accepted:2025-06-13Online:2026-04-08Published:2025-09-01 -
Contact:Li Gang, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Micro-Orthopedics, The Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jiang Kai, MS candidate, The First Clinical Medical College of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
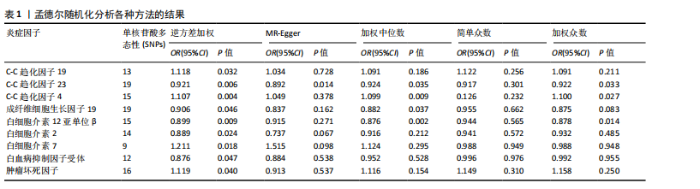
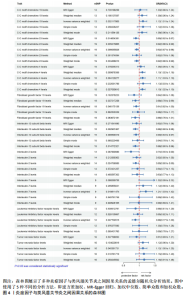
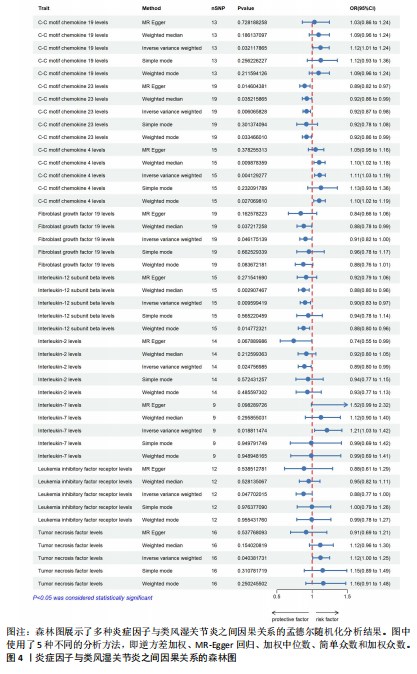
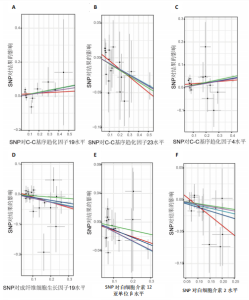
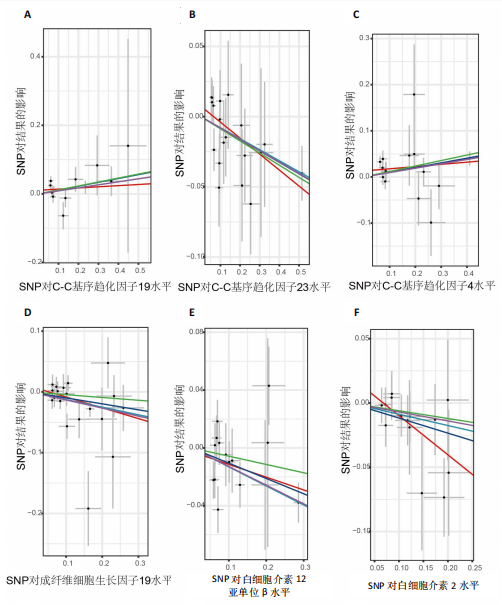
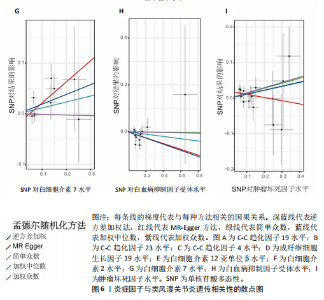
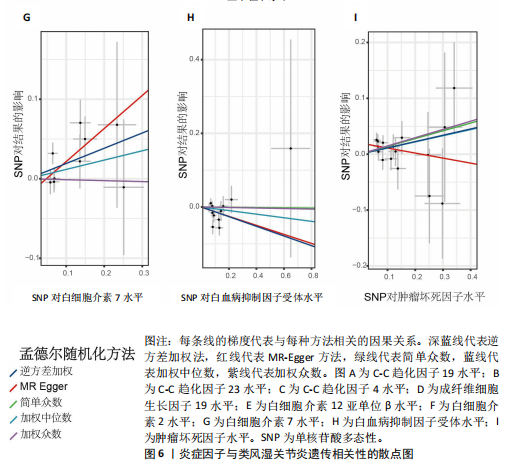
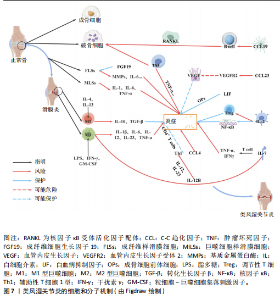
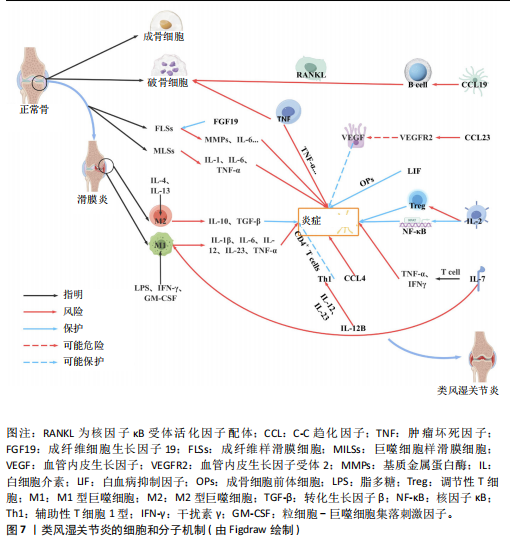
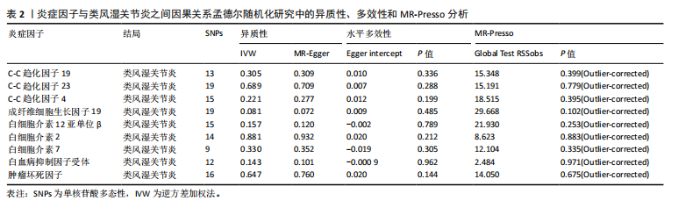
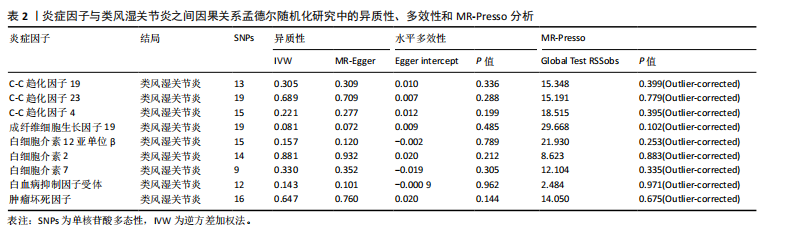
2.1 正向孟德尔随机化分析 通过正向孟德尔随机化分析,主要根据逆方差加权法筛选炎症因子,P值< 0.05。去除异质性和水平多效性的P值都要> 0.05,见表2。 研究结果显示,C-C趋化因子4、C-C趋化因子19、C-C趋化因子23、成纤维细胞生长因子19、白细胞介素12亚单位β、白细胞介素2、白细胞介素7、白血病抑制因子受体以及肿瘤坏死因子水平与类风湿关节炎疾病的发生风险密切相关(分别对应GCST90274765、GCST90274767、GCST90274770、GCST90274787、GCST90274798、GCST90274806、GCST90274816、GCST90274820、GCST90274839)。 研究发现91个炎症因子中的9个炎症因子与类风湿关节炎疾病存在显著阳性结果,其中C-C趋化因子23(OR=0.921,P=0.006)、成纤维细胞生长因子19(OR=0.906,P=0.046)、白细胞介素12亚单位β(OR=0.899,P=0.009)、白细胞介素2(OR=0.889,P=0.024)、白血病抑制因子受体(OR=0.876,P=0.047)对类风湿关节炎起保护作用,C-C趋化因子19(OR=1.118,P=0.032)、C-C趋化因子4(OR=1.107,P=0.004)、白细胞介素7(OR=1.211,P=0.018)、肿瘤坏死因子水平(OR=1.119,P=0.040)对类风湿关节炎起危险作用,见图4。 2.2 反向孟德尔随机化分析 通过反向孟德尔随机化分析,主要根据逆方差加权法筛选炎症因子,要求P值> 0.05,剔除反向阳性,发现9个炎症因子全部符合要求,见图5。"
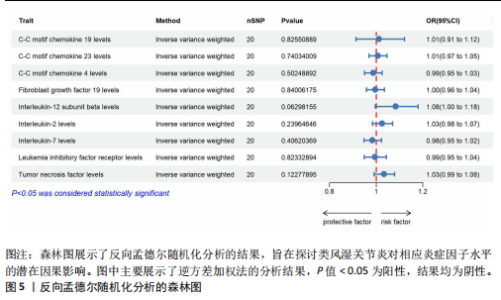
2.3 最终结果 在对91种炎症因子与类风湿关节炎关联性的分析中,采用了逆方差加权方法进行综合评估。最终结果显示,91种炎症因子中与类风湿关节炎疾病有显著阳性结果的是:C-C趋化因子23(OR=0.921,P=0.006)、成纤维细胞生长因子19(OR=0.906,P=0.046)、白细胞介素12亚单位β(OR=0.899,P=0.009)、白细胞介素2(OR=0.889,P=0.024)、白血病抑制因子受体 (OR=0.876,P=0.047)、C-C趋化因子19(OR=1.118,P=0.032)、C-C趋化因子4 (OR=1.107,P=0.004)、白细胞介素7(OR=1.211,P=0.018)、肿瘤坏死因子水平(OR=1.119,P=0.040)。见图6。"
| [1] NEUMANN E, FROMMER K, DILLER M, et al. [Rheumatoid arthritis]. Z Rheumatol, 2018;77(9):769-775. [2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016; 388(10055):2023-2038. [3] WU YY, LI XF, WU S, et al. Role of the S100 protein family in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):35. [4] ZHOU Q, LI T, FANG G, et al. Bioactive Molecules against Rheumatoid Arthritis by Suppressing Pyroptosis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(7):952. [5] KOLARZ G. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Acta Med Austriaca. 1988;15(5): 128-130. [6] LOTTENBURGER T, JUNKER P, HORSLEV-PETERSEN K. Diurnal Variation of Connective Tissue Metabolites in Early and Long-Standing Rheumatoid Arthritis and in Healthy Individuals. Scand J Rheumatol. 2011;40(2):88-94. [7] MORALES AJ. Study Design for the Evaluation of Treatment. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1996;14(2):111-118. [8] MURPHY SW. Longitudinal Studies 1: Determinants of Risk. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2249:83-101. [9] BOEHM FJ, ZHOU X. Statistical Methods for Mendelian Randomization in Genome-Wide Association Studies: A Review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:2338-2351. [10] BURGESS S, SMALL DS, THOMPSON SG. A Review of Instrumental Variable Estimators for Mendelian Randomization. Stat Methods Med Res. 2017;26(5):2333-2355. [11] LI J, TANG M, GAO X, et al. Mendelian Randomization Analyses Explore the Relationship between Cathepsins and Lung Cancer. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1019. [12] YUAN S, MICHAELSSON K, WAN Z, et al. Associations of Smoking and Alcohol and Coffee Intake with Fracture and Bone Mineral Density: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;105(6):582-588. [13] PENG H, WANG S, WANG M, et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolism. 2022; 133:155220. [14] ZHAO R, ZHANG YW, YAO JY, et al. Genetic Association between Interleukin-17 and Susceptibility to Rheumatoid Arthritis. BMC Med Genomics, 2023;16(1):277. [15] SMITH GD, EBRAHIM S. ‘Mendelian Randomization’: Can Genetic Epidemiology Contribute to Understanding Environmental Determinants of Disease? Int J Epidemiol. 2003;32(1):1-22. [16] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98. [17] CHEN Z, BOEHNKE M, WEN X, et al. Revisiting the Genome-Wide Significance Threshold for Common Variant GWAS. G3 (Bethesda). 2021;11(2):jkaa056. [18] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Avoiding Bias from Weak Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):755-764. [19] YAO X, HUANG J, ZHONG H, et al. Targeting Interleukin-6 in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases and Cancers. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141(2):125-139. [20] KUWABARA T, ISHIKAWA F, KONDO M, et al. The Role of IL-17 and Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3908061. [21] RODRIGUEZ-ELIAS AK, MALDONADO-MURILLO K, LOPEZ-MENDOZA LF, et al. Genetics and Genomics in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An Update. Gac Med Mex. 2016;152(2):218-227. [22] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. [23] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes: Key Effector Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255. [24] KERKMAN PF, ROMBOUTS Y, VAN DER VOORT EI, et al. Circulating Plasmablasts/Plasmacells as a Source of Anticitrullinated Protein Antibodies in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(7):1259-1263. [25] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [26] MOADAB F, KHORRAMDELAZAD H, ABBASIFARD M. Role of CCL2/CCR2 Axis in the Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Latest Evidence and Therapeutic Approaches. Life Sci. 2021;269:119034. [27] HAN KY, KIM CW, LEE TH, et al. CCL23 Up-Regulates Expression of KDR/Flk-1 and Potentiates VEGF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Human Endothelial Cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;382(1):124-128. [28] ARRUDA-SILVA F, BIANCHETTO-AGUILERA F, GASPERINI S, et al. Human Neutrophils Produce CCL23 in Response to Various TLR-Agonists and TNFalpha. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:176. [29] CHEN H, LI J, PI C, et al. FGF19 Induces the Cell Cycle Arrest at G2-Phase in Chondrocytes. Cell Death Discov. 2023; 9(1):250. [30] KUROSE A, YOSHIDA W, YOSHIDA M, et al. Effects of Paclitaxel on Cultured Synovial Cells from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cytometry. 2001;44(4):349-354. [31] GUO A, LI K, XIAO Q. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 Alleviates Palmitic Acid-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress via the AMPK/PGC-1alpha Pathway in Skeletal Muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(4):1069-1076. [32] QUINONEZ-FLORES CM, LOPEZ-LOEZA SM, PACHECO-TENA C, et al. Stability of Housekeeping Genes in Inflamed Joints of Spontaneous and Collagen-Induced Arthritis in DBA/1 Mice. Inflamm Res. 2021; 70(5):619-632. [33] FUKUDA K, MIURA Y, MAEDA T, et al. Interleukin-12B is Upregulated by Decoy Receptor 3 in Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(4): 3647-3652. [34] WANG MJ, XU XL, MI YY, et al. Association of IL12B Gene Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Arch Med Res. 2016;47(2):126-133. [35] NGIOW SF, TENG MW, SMYTH MJ. A Balance of Interleukin-12 and -23 in Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(11):548-555. [36] WATFORD WT, HISSONG BD, BREAM JH, et al. Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the Immunoregulatory Roles of STAT4. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:139-156. [37] HUNTER CA. New IL-12-Family Members: IL-23 and IL-27, Cytokines with Divergent Functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(7): 521-531. [38] SINIGAGLIA F, D’AMBROSIO D, PANINA-BORDIGNON P, et al. Regulation of the IL-12/IL-12R Axis: A Critical Step in T-Helper Cell Differentiation and Effector Function. Immunol Rev. 1999;170:65-72. [39] POPE RM, SHAHRARA S. Possible Roles of IL-12-Family Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(4):252-256. [40] YUAN N, YU G, LIU D, et al. An Emerging Role of Interleukin-23 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019; 41(2):185-191. [41] ZHANG SX, WANG J, WANG CH, et al. Low-Dose IL-2 Therapy Limits the Reduction in Absolute Numbers of Circulating Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13: 1759720X211011370. [42] LI N, LI X, SU R, et al. Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Altered Gut Microbiota and Ameliorated Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:1365-1379. [43] SUN H, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Low Dose IL-2 Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis in Collagen-Induced Arthritis via JNK-Dependent Pathway. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2020;8(4):727-735. [44] KOSMACZEWSKA A, CISZAK L, SWIERKOT J, et al. Exogenous IL-2 Controls the Balance in Th1, Th17, and Treg Cell Distribution in Patients with Progressive Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with TNF-Alpha Inhibitors. Inflammation. 2015;38(2):765-774. [45] MITRA S, LEONARD WJ. Biology of IL-2 and Its Therapeutic Modulation: Mechanisms and Strategies. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;103(4):643-655. [46] ZHANG SX, CHEN HR, WANG J, et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Short-Term and Low-Dose IL-2 Combined with Tocilizumab to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1359041. [47] ZHANG C, LIU J, WANG J, et al. The Emerging Role of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in Cancer and Therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;221:107754. [48] WANG J, CHANG CY, YANG X, et al. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor, a Double-Edged Sword with Therapeutic Implications in Human Diseases. Mol Ther. 2023;31(2):331-343. [49] DECHANET J, TAUPIN JL, CHOMARAT P, et al. Interleukin-4 but Not Interleukin-10 Inhibits the Production of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor by Rheumatoid Synovium and Synoviocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24(12):3222-3228. [50] RODAN SB, WESOLOWSKI G, HILTON DJ, et al. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Binds with High Affinity to Preosteoblastic RCT-1 Cells and Potentiates the Retinoic Acid Induction of Alkaline Phosphatase. Endocrinology. 1990;127(4):1602-1608. [51] NICOLA NA, BABON JJ. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2015;26(5):533-544. [52] LEE J, PARK C, KIM HJ, et al. Stimulation of Osteoclast Migration and Bone Resorption by C-C Chemokine Ligands 19 and 21. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(7):e358. [53] BRUHL H, MACK M, NIEDERMEIER M, et al. Functional Expression of the Chemokine Receptor CCR7 on Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(12):1771-1774. [54] GUO X, XU T, ZHENG J, et al. Accumulation of Synovial Fluid CD19+CD24hiCD27+ B Cells Was Associated with Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14386. [55] SHI LJ, LI JH, HU FL, et al. [Clinical Significance of Serum C-C Chemokine Ligand 19 Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;48(1):667-671. [56] CHANG TT, LIN LY, CHEN C, et al. CCL4 Contributes to Aging-Related Angiogenic Insufficiency through Activating Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Inflammation. Angiogenesis. 2024;27(3):475-499. [57] SUCUR A, JAJIC Z, ARTUKOVIC M, et al. Chemokine Signals Are Crucial for Enhanced Homing and Differentiation of Circulating Osteoclast Progenitor Cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):142. [58] ZHANG L, YU M, DENG J, et al. Chemokine Signaling Pathway Involved in CCL2 Expression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(4):1134-1142. [59] AHMAD R, KOCHUMON S, CHANDY B, et al. TNF-α Drives the CCL4 Expression in Human Monocytic Cells: Involvement of the SAPK/JNK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):908-921. [60] PICKENS SR, CHAMBERLAIN ND, VOLIN MV, et al. Characterization of Interleukin-7 and Interleukin-7 Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):2884-2893. [61] CHURCHMAN SM, PONCHEL F. Interleukin-7 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(6):753-759. [62] TORALDO G, ROGGIA C, QIAN WP, et al. IL-7 Induces Bone Loss In Vivo by Induction of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha from T Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(1):125-130. [63] VAN ROON JA, GLAUDEMANNS KA, BIJLSMA JW, et al. Interleukin 7 Stimulates Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha and Th1 Cytokine Production in Joints of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(2):113-119. [64] MEYER A, PARMAR PJ, SHAHRARA S. Significance of IL-7 and IL-7R in RA and Autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2022; 21(7):103120. [65] HARTGRING SA, VAN ROON JA, WENTING-VAN WM, et al. Elevated Expression of Interleukin-7 Receptor in Inflamed Joints Mediates Interleukin-7-Induced Immune Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(9):2595-2605. [66] CAI L, XU H, ZHANG H, et al. Blockade of IL-7Ralpha Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis via Inhibiting Th1 Cell Differentiation and CD4+ T Cell Migration. Mol Immunol. 2016;79:83-91. [67] XU H, CAI L, LI Z, et al. Dual Effect of IL-7/IL-7R Signalling on the Osteoimmunological System: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunology. 2021;164(1):161-172. [68] PETROVIC-RACKOV L, PEJNOVIC N. Clinical Significance of IL-18, IL-15, IL-12 and TNF-Alpha Measurement in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(4):448-452. [69] INAM IM, AMJAD S, ALAM SM, et al. Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha as a Competent Biomarker for Evaluation of Disease Activity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cureus. 2021;13(5):e15314. [70] AKATSUKA H, OKUBO M, ISHIDA H, et al. Synovial Mononuclear Cells Consist with T Cells Which Produce High Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. Microbiol Immunol. 1997;41(4):367-370. [71] HAWORTH C, BRENNAN FM, CHANTRY D, et al. Expression of Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Regulation by Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1991;21(10):2575-2579. [72] CHOPIN F, GARNERO P, LE HENANFF A, et al. Long-Term Effects of Infliximab on Bone and Cartilage Turnover Markers in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(3):353-357. [73] GINTING AR, HIDAYAT R, SUMARIYONO S, et al. Role of Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-Alpha) in Bone Loss of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Rheumatol. 2020;2020:9149762. [74] OKAZAKI H, LIN Q, NISHIKAWA K, et al. TNFalpha but Not IL-17 Is Critical in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Spontaneously Occurring in a Unique FcgammaRIIB-Deficient Mouse Model. Mod Rheumatol. 2014;24(6):931-938. [75] FENG X. Regulatory Roles and Molecular Signaling of TNF Family Members in Osteoclasts. Gene. 2005;350(1):1-13. [76] MABILLEAU G, PASCARETTI-GRIZON F, BASLE MF, et al. Depth and Volume of Resorption Induced by Osteoclasts Generated in the Presence of RANKL, TNF-Alpha/IL-1 or LIGHT. Cytokine. 2012;57(2):294-299. [77] WU Y, YANG Y, WANG L, et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium on Osteoclasts: TNF-Alpha/NF-kappaB Inflammatory Signal Pathway-Mediated Mechanism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1109296. [78] ADAMI G, ORSOLINI G, ADAMI S, et al. Effects of TNF Inhibitors on Parathyroid Hormone and Wnt Signaling Antagonists in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;99(4):360-364. [79] POLLARD LC, CHOY EH, GONZALEZ J, et al. Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis Reflects Pain, Not Disease Activity. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(7):885-889. |
| [1] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [2] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [5] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [6] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [7] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [8] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [9] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [10] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [11] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles regulate expression of inflammatory factors in M1 macrophages and affect fibroblast co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [12] | Shalayiding · Aierxiding, Gao Jian, Alimujiang · Abudourousuli, Kutiluke · Shoukeer, Aikebaierjiang · Aisaiti, Gulimire · Yilihamu, Jiang Kan, Aikeremujiang · Muheremu. Mechanisms by which macrophage polarization regulates bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2484-2490. |
| [13] | Du Yanli, , Wang Yi, , Wang Zhenyu, Wang Xuanhui, , Li Xinye, , Xiong Xifeng, Miao Haixiong, . The role of p53 in musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514. |
| [14] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [15] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||