Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1152-1158.doi: 10.12307/2025.297
Previous Articles Next Articles
Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
Chen Yuning1, Jiang Ying1, Liao Xiangyu1, Chen Qiongjun1, Xiong Liang1, Liu Yue1, 2, Liu Tong1, 2
- 1The Fifth Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-11Accepted:2024-03-06Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-20 -
Contact:Liu Tong, MD, Associate chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, The Fifth Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China Co-corresponding author: Liu Yue, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The Fifth Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Yuning, Master candidate, The Fifth Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:The Special Research of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province, No. 20203001 (to LY); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (General Program), No. 2022A1515011676 (to LY); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Provincial-Enterprise Joint Fund), No. 2022A1515220012 (to LT); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82174482 (to LT); Central Finance Transfer Local Project, No. 602023057 (to LY and LT [project participants]); Guangdong Liu Yue Famous Chinese Medicine Workshop Construction Project, No. [2023]108 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
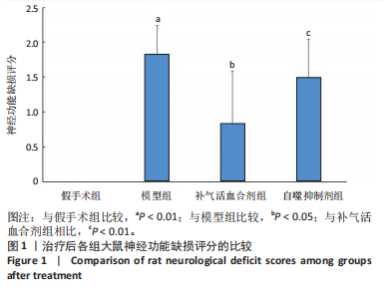
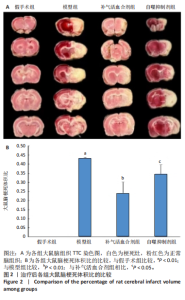
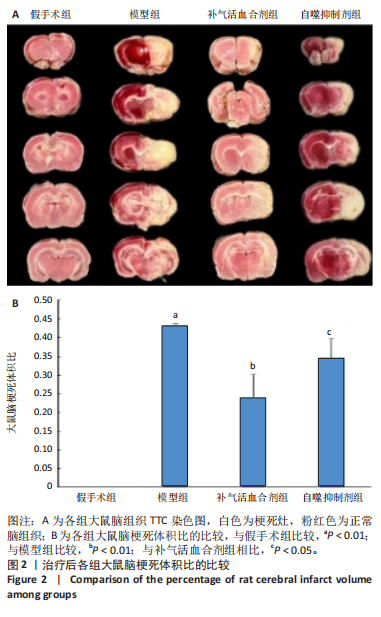
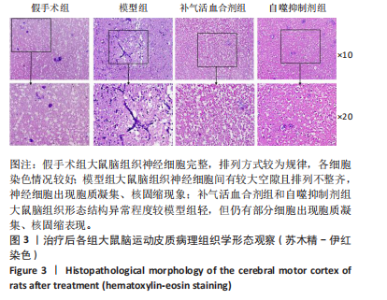
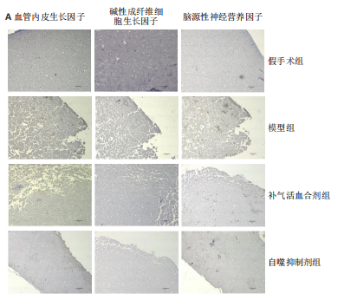
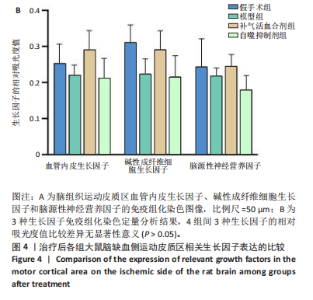
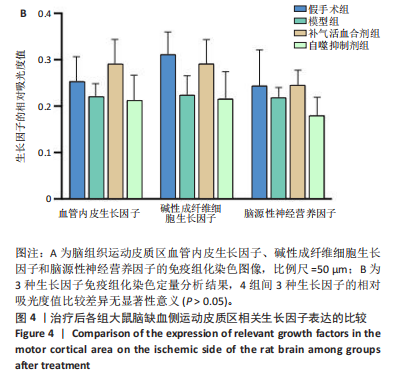
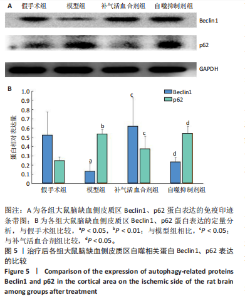
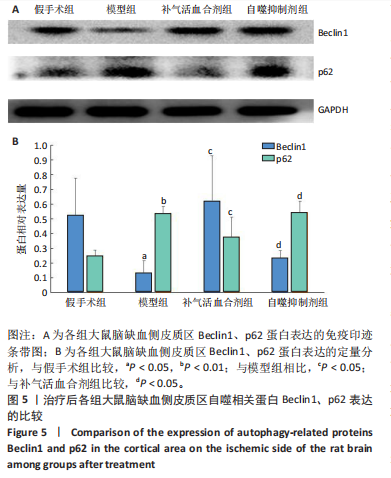
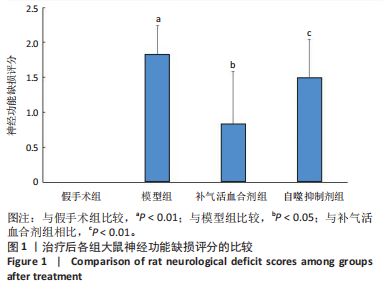
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验过程每组确保纳入10只大鼠,最终共纳入40只大鼠进行统计分析。 2.2 治疗后各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分的比较 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠神经功能缺损评分升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,补气活血合剂组大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低(P < 0.05);与补气活血合剂组比较,自噬抑制剂组大鼠神经功能缺损评分升高(P < 0.01),见图1。 2.3 治疗后各组大鼠脑梗死体积的比较 TTC染色结果显示,假手术组大鼠脑组织成正常红色,大体观察未见苍白梗死灶;模型组、补气活血合剂组、自噬抑制剂组大鼠脑组织右侧均可见大脑苍白梗死灶,见图2A。与假手术组相比,模型组大鼠脑梗死体积比显著增加(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,补气活血合剂组大鼠脑梗死体积比减少(P < 0.01);与补气活血合剂组相比,自噬抑制剂组大鼠脑梗死体积比增加(P < 0.05),见图2B。 2.4 治疗后各组大鼠脑组织形态观察结果 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,假手术组大鼠脑组织神经细胞完整,排列方式较为规律,各细胞染色情况较好;模型组大鼠脑组织神经细胞间有较大空隙且排列不整齐,神经细胞出现胞质凝集、核固缩现象;补气活血合剂组和自噬抑制剂组大鼠脑组织形态结构异常程度较模型组轻,但仍有部分细胞出现胞质凝集、核固缩表现,见图3。 2.5 治疗后各组大鼠脑缺血侧皮质区相关生长因子表达的比较 免疫组化染色结果显示,血管内皮生长因子多表达在神经元细胞、神经胶质细胞及毛细血管内皮,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子多表达在神经元细胞、神经胶质细胞,4组间3种生长因子的表达比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图4。 2.6 运动后各组大鼠脑缺血侧皮质区自噬相关蛋白Beclin1、p62的比较 Western blot检测结果显示,与假手术组相比,模型组Beclin1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,补气活血合剂组Beclin1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与补气活血合剂组相比,自噬抑制剂组Beclin1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),p62蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),见图5。"
| [1] World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2020. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [2] LAVER KE, LANGE B, GEORGE S, et al. Virtual reality for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;11(11):CD008349. [3] YANG YR, CHEN YH, CHANG HC, et al. Effects of interactive visual feedback training on post-stroke pusher syndrome: a pilot randomized controlled study. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(10):987-993. [4] 刘悦,卢阳佳,邝伟川,等.中风复元口服液治疗气虚痰浊内阻型中风60例临床疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2012,14(12):18-20. [5] 周嘉澄,刘悦,林延.中风复元汤治疗脑梗死恢复期60例总结[J].湖南中医杂志,2009,25(5):14+91. [6] ZHAO L, DING LD, XIA ZH, et al. A Network-Based Approach to Investigate the Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Huangqi-Chuanxiong and Sanleng-Ezhu Herb Pairs in the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:844186. [7] DU X, AMIN N, XU L, et al. Pharmacological intervention of curcumin via the NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1249644. [8] LONG J, GU C, ZHANG Q, et al. Extracellular vesicles from medicated plasma of Buyang Huanwu decoction-preconditioned neural stem cells accelerate neurological recovery following ischemic stroke. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1096329. [9] LONG EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1): 84-91. [10] 黄柳,贾妍,郭炳彦,等. RhoA激酶信号通路介导的自噬障碍在2型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化中的作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2019,11(12):1446-1450. [11] SPORNS PB, FULLERTON HJ, LEE S, et al. Current treatment for childhood arterial ischaemic stroke. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021; 5(11):825-836. [12] AJOOLABADY A, WANG S, KROEMER G, et al. Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;225:107848. [13] LEES KR, BLUHMKI E, VON KUMMER R, et al. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHET trials. Lancet. 2010; 375(9727):1695-1703. [14] PEÑA ID, BORLONGAN C, SHEN G, et al. Strategies to Extend Thrombolytic Time Window for Ischemic Stroke Treatment: An Unmet Clinical Need. J Stroke. 2017;19(1):50-60. [15] NITZSCHE A, POITTEVIN M, BENARAB A, et al. Endothelial S1P1 Signaling Counteracts Infarct Expansion in Ischemic Stroke. Circ Res. 2021;128(3):363-382. [16] TAO T, LIU M, CHEN M, et al. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Challenges and prospective. Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 216:107695. [17] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022; 42(1):259-305. [18] JIANG HJ, HUANG XL, XIAN B, et al. Chinese herbal injection for cardio-cerebrovascular disease: Overview and challenges. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1038906. [19] DUAN H, ZHANG Q, LIU J, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell, the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;168:105599. [20] 陈少茹,李智勇.中风复元合剂中芍药苷和橙皮苷的含量测定[J].今日药学,2020,30(1):15-18. [21] 刘通,廖翔宇,陈玉宁,等.补气活血合剂对脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠血清外泌体及Nestin, GFAP蛋白表达的影响[J].中医康复,2024, 1(2):8-13. [22] FU C, ZHANG X, LU Y, et al. Geniposide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation via autophagy in BV-2 microglial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106547. [23] WU C, YANG M, LIU R, et al. Nicotine Reduces Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Response to Escherichia coli K1 Infection by Inhibiting Autophagy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:484. [24] HOU K, XU D, LI F, et al. The progress of neuronal autophagy in cerebral ischemia stroke: Mechanisms, roles and research methods. J Neurol Sci. 2019;400:72-82. [25] WU S, YIN Y, DU L. FUS aggregation following ischemic stroke favors brain astrocyte activation through inducing excessive autophagy. Exp Neurol. 2022;355:114144. [26] LI H, PENG D, ZHANG SJ, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes neurogenesis via sirtuin 1/autophagy pathway in a cerebral ischemia model. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(5):791. [27] HE Q, LIU Q, CHEN Y, et al. Long-Zhi Decoction Medicated Serum Promotes Angiogenesis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Based on Autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018: 6857398. doi: 10.1155/2018/6857398. [28] ZHANG W, HAN L, WEN Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2912. [29] LU WH, SHI YX, MA ZL, et al. Proper autophagy is indispensable for angiogenesis during chick embryo development. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15(13):1742-1754. [30] TUWAR MN, CHEN WH, CHIWAYA AM, et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Translocator Protein (TSPO) as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(13):2298. [31] MARTINELLI S, ANDERZHANOVA EA, BAJAJ T, et al. Stress-primed secretory autophagy promotes extracellular BDNF maturation by enhancing MMP9 secretion. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4643. [32] LAN W, LI Z, LI YH, et al. Acupuncture combined with exercise training at different time points on nerve repair of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its effects on the expressions of Nestin, bFGF and EGF. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(1):38-45. [33] ZHANG R, XIE L, WU F, et al. ALG-bFGF Hydrogel Inhibiting Autophagy Contributes to Protection of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity viaPI3K/Akt/FOXO1/KLF4 Pathway After SCI. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:828896. |
| [1] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [2] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [3] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [4] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [5] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [6] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [7] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [8] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [9] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [10] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [11] | Zhou Lina, , Li Yun, , Liu Xixia, . Effects of different concentrations of hypertonic glucose in the repair of tendon injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6885-6892. |
| [12] | Tang Haoxu, Liang Yingjie, Li Ce, Ding Penglin, Qian Minlong, Yuan Lingli. Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6821-6827. |
| [13] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [14] | Liu Tong, , Huang Zhibin, Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, . Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene in neurological function, p-Akt and serum exosome expression in a rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6180-6186. |
| [15] | Tian Yong, Zhou Qing, Luo Chuanquan, Hu Hongmei, Ma Changlin, Yang Lei, Wei Lin. Emodin promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in septic model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5572-5578. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||