Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 3058-3065.doi: 10.12307/2026.662
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which andrographolide intervenes in insulin resistance in rats with gestational diabetes mellitus
Wang Peng, Lu Huan, Liu Haifeng, Li Feng
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Nuclear Industry 416 Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-07Accepted:2025-07-31Online:2026-04-28Published:2025-09-29 -
Contact:Liu Haifeng, MS, Associate chief physician, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Nuclear Industry 416 Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Peng, Attending physician, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Nuclear Industry 416 Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Chengdu Medical Research Project, No. 2018065 (to LF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Peng, Lu Huan, Liu Haifeng, Li Feng. Mechanism by which andrographolide intervenes in insulin resistance in rats with gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3058-3065.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
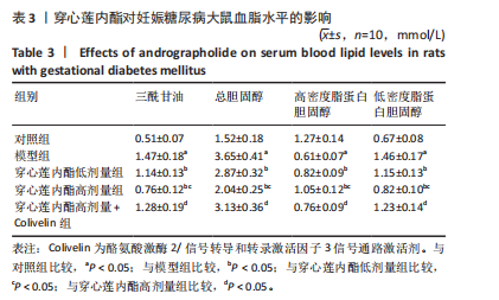
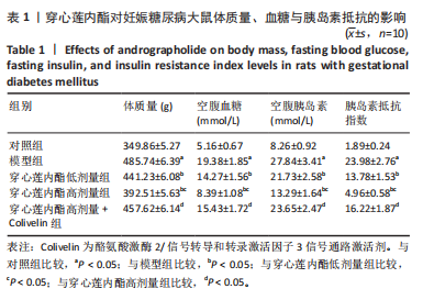
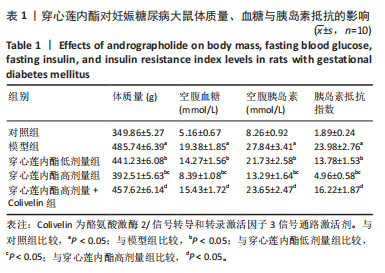
2.4 穿心莲内酯对妊娠糖尿病大鼠血脂水平的影响 模型组三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平均高于对照组(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平低于对照组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯低、高剂量组三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平均低于模型组(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平均高于模型组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量组三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平低于穿心莲内酯低剂量组(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平高于穿心莲内酯低剂量组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量+Colivelin组三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平高于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平低于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),见表3。"
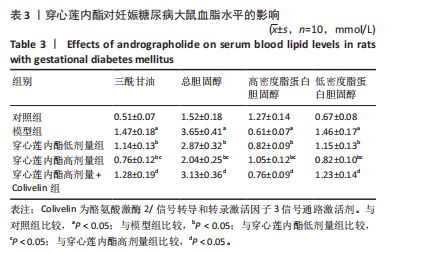
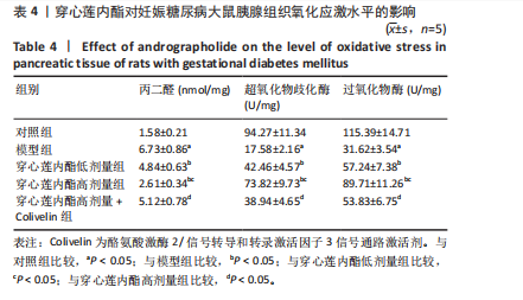
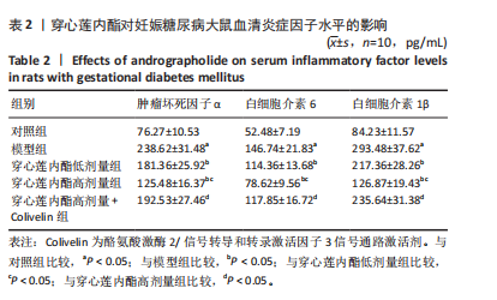
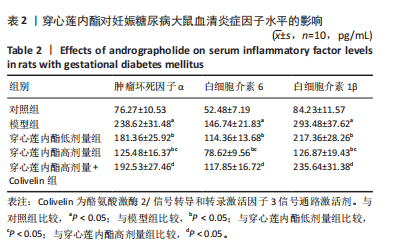
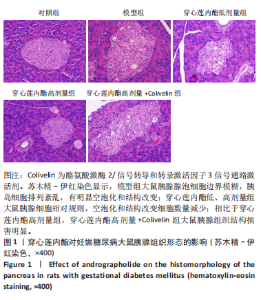
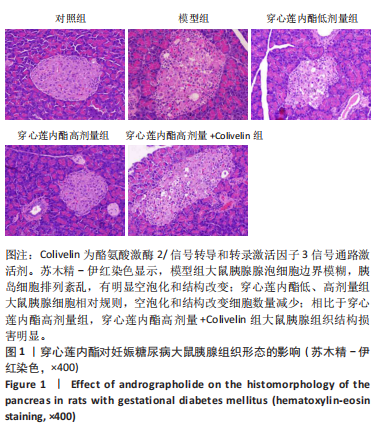
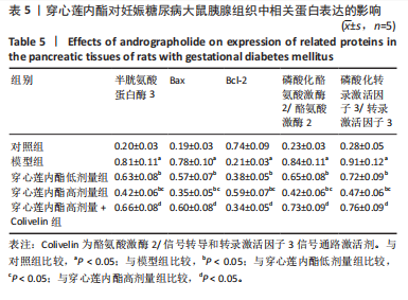
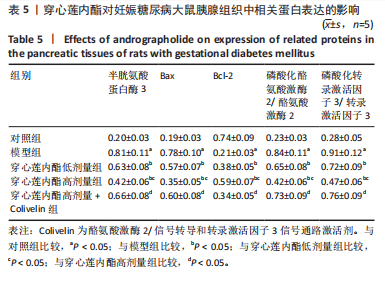
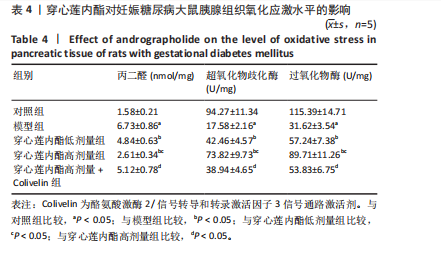
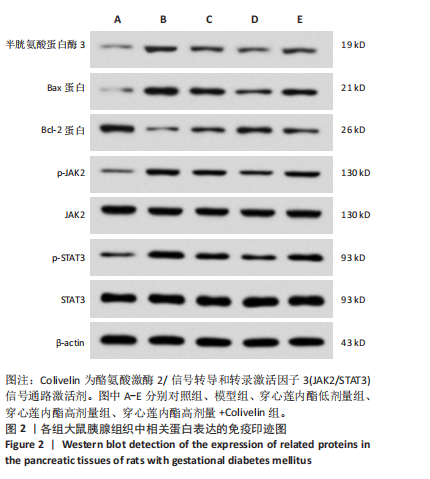
2.6 穿心莲内酯对妊娠糖尿病大鼠胰腺组织氧化应激水平的影响 模型组超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物氢酶活性均低于对照组(P < 0.05),丙二醛水平高于对照组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯低、高剂量组超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物氢酶活性均高于模型组(P < 0.05),丙二醛水平均低于模型组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量组超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物氢酶活性均高于穿心莲内酯低剂量组(P < 0.05),丙二醛水平低于穿心莲内酯低剂量组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量+Colivelin组大鼠胰腺组织超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物氢酶活性低于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),丙二醛水平高于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),见表4。 2.7 穿心莲内酯妊娠糖尿病大鼠胰腺组织中相关蛋白表达的影响 模型组Bax、半胱氨酸蛋白酶3、p-JAK2/JAK2、p-STAT3/STAT3蛋白表均高于对照组"
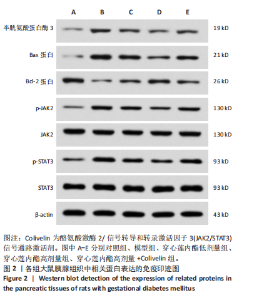
(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达低于对照组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯低、高剂量组Bax、半胱氨酸蛋白酶3、p-JAK2/JAK2、p-STAT3/STAT3蛋白均低于模型组(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达均高于模型组(P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量组Bax、半胱氨酸蛋白酶3、p-JAK2/JAK2、p-STAT3/STAT3蛋白表达均低于穿心莲内酯低剂量组,Bcl-2蛋白表达高于穿心莲内酯低剂量组 (P < 0.05);穿心莲内酯高剂量+Colivelin组Bax、半胱氨酸蛋白酶3、p-JAK2/JAK2、p-STAT3/STAT3蛋白表达均高于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达低于穿心莲内酯高剂量组(P < 0.05),见图2,表5。"
| [1] LU W, HU C. Molecular biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus and postpartum diabetes. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(16):1940-1951. [2] PINTO S, CROCE L, CARLIER L, et al. Thyroid dysfunction during gestation and gestational diabetes mellitus: a complex relationship. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023;46(9):1737-1759. [3] UGWUDIKE B, KWOK M. Update on gestational diabetes and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2023;35(5):453-459. [4] POBLETE JA, OLMOS P. Obesity and Gestational Diabetes in Pregnant Care and Clinical Practice. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2021;19(2):154-164. [5] YAN Q, QIU D, LIU X, et al. The incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus among women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022;22(1):370-382. [6] MELAMED N, AVNON T, BARRETT J, et al. Gestational diabetes in twin pregnancies-a pathology requiring treatment or a benign physiological adaptation? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024;231(1):92-104.e4. [7] LU L, WAN B, SUN M. Mendelian randomization identifies age at menarche as an independent causal effect factor for gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(1):248-260. [8] PAULSEN CP, BANDAK E, EDEMANN-CALLESEN H, et al. The Effects of Exercise during Pregnancy on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Preeclampsia, and Spontaneous Abortion among Healthy Women-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(12):6069. [9] TSAKIRIDIS I, GIOULEKA S, MAMOPOULOS A, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: An Overview of National and International Guidelines. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2021;76(6):367-381. [10] LU Q, LI Y, YE D, et al. Longitudinal metabolomics integrated with machine learning identifies novel biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023;209(Pt 1):9-17. [11] ZENG B, WEI A, ZHOU Q, et al. Andrographolide: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytother Res. 2022;36(1):336-364. [12] ZHANG S, XIE X, ZHAO J, et al. Andrographolide and its Derivatives in Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Planta Med. 2025; 91(5):259-270. [13] NAIK RR, MUNIPALLY PK, NAGARAJU T. Andrographolide reorganise hyperglycaemia and distorted antioxidant profile in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2017; 10(1):26-38, [14] 武莉,冯吉波,王延茹,等.穿心莲内酯对胰岛素抵抗大鼠的影响及可能作用机制分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2024,5(3):1-13. [15] CHEN B, NING K, SUN ML, et al. Regulation and therapy, the role of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in OA: a systematic review. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):67-75. [16] GU Y, YU S, GU W, et al . M2 macrophage infusion ameliorates diabetic glomerulopathyvia the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in db/db mice. Ren Fail. 2024;46(2):2378210-2378221. [17] LI CD, ZHAO JY, CHEN JL, et al. Mechanism of the JAK2/STAT3-CAV-1-NR2B signaling pathway in painful diabetic neuropathy. Endocrine. 2019;64(1):55-66. [18] 魏小敏,王丽丽,刘海霞,等.丹参素通过STAT3/JAK2/SOCS1信号通路在妊娠期糖尿病干预中的作用机制研究[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2023,52(5):508-512. [19] LI T, WANG W, LI S, et al. Lusianthridin Exerts Streptozotocin-Induced Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Female Rats via Alteration of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J Oleo Sci. 2023;72(8):775-785. [20] WONG TS, MOHAMED TAP F, et al. Dual actions of gallic acid and andrographolide trigger AdipoR1 to stimulate insulin secretion in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model. J Tradit Complement Med. 2022;13(1):11-19. [21] WANG X, YANG B, LI Y, et al. AKR1C1 alleviates LPS induced ALI in mice by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(6):833-845. [22] SINGH S, YADAV M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus among Pregnant Women Delivering in a Tertiary Care Hospital: A Descriptive Cross-sectional Study. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2022;60(247):229-233. [23] DINESEN S, EL-FAITAROUNI A, FRISK NLS, et al. Circulating microRNA as Biomarkers for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6186-6197. [24] WU W, REN J, WANG J, et al. Metalloestrogens exposure and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: Evidence emerging from the systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Res. 2024;248(3):118321-118632. [25] ANA Y, PRAFULLA S, DEEPA R, et al. Emerging and Public Health Challenges Existing in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes in Pregnancy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(3):513-530. [26] WANG S, CUI Z, YANG H. Interactions between host and gut microbiota in gestational diabetes mellitus and their impacts on offspring. BMC Microbiol. 2024;24(1):161-170. [27] QIN Y, BILY D, AGUIRRE M, et al. Understanding PPARγ and Its Agonists on Trophoblast Differentiation and Invasion: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia. Nutrients. 2023;15(11):2459-2471. [28] LI Z, BECK R, DURNWALD C, et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Perinatal Complications. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2024;26(11):787-796. [29] ZAKARIA H, ABUSANANA S, MUSSA BM, et al. The Role of Lifestyle Interventions in the Prevention and Treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(2):287-298. [30] TRANIDOU A, TSAKIRIDIS I, APOSTOLOPOULOU A, et al. Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Based on Maternal Variables and Pregnancy Biomarkers. Nutrients. 2023;16(1):120-131. [31] ELEFTHERIOU D, ATHANASIADOU KI, SIFNAIOS E, et al. Sleep disorders during pregnancy: an underestimated risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocrine. 2024;83(1):41-50. [32] 孙跃先,王九妹,崔新刚,等.穿心莲内酯调节HMGB1/RAGE信号通路对糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠坐骨神经功能损伤的影响[J].中国药房,2024,35(5):572-577. [33] XU W, WANG H, SUN Q, et al. TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD axis-mediated inflammation and pyroptosis of islet β-cells is involved in cigarette smoke-induced hyperglycemia, which is alleviated by Andrographolide. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(3):1415-1428. [34] 亢丽娟, 董海平,宋艳艳.栀子苷调节HMGB1-RAGE信号通路对妊娠期糖尿病大鼠胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].解剖学研究,2024,46(2): 176-182,190 [35] KANG DH, KIM MJ, MOHAMED EA, et al. Regulation of uterus and placenta remodeling under high estradiol levels in gestational diabetes mellitus models†. Biol Reprod. 2023;109(2):215-226. [36] LUDOWICI E. Assessing Knowledge on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Child Health. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2023;82(10):227-231. [37] JI J, WU P, LI G, et al. The associations of ferritin, serum lipid and plasma glucose levels across pregnancy in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and newborn birth weight. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023; 23(1):478-489. [38] LIU Y, HOCHER JG, MA S, et al. Pre-pregnancy LDL/HDL and total Cholesterol/HDL ratios are strong predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus in women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024;22(1):155-167. [39] YE YX, WANG Y, WU P, et al. Blood Cell Parameters From Early to Middle Pregnancy and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;108(12):e1702-e1711. [40] SAUCEDO R, ORTEGA-CAMARILLO C, FERREIRA-HERMOSILLO A, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(10):1812-1820. [41] JOSHI NP, MADIWALE SD, SUNDRANI DP, et al. Fatty acids, inflammation and angiogenesis in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Biochimie. 2023;212(1):31-40. [42] SAUCEDO R, ORTEGA-CAMARILLO C, FERREIRA-HERMOSILLO A, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(10):1812-1824. [43] JĞŞÖÖERDOAN F, ENKAL E, ZER F, et al. Oxidative stress in maternal milk and cord blood in gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective study. Sao Paulo Med J. 2022;140(3):390-397. [44] ZHAO Z, WU Q, XU Y, et al. Groenlandicine enhances cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma cells through the BAX/Bcl-2/Caspase-9/Caspase-3 pathway. J Bone Oncol. 2024;48(2): 100631-100642. [45] WANG S, MA L, JI J, et al. Resistant Dextrin Protects Rats Against Streptozotocin Induced Gestational Diabetes Mellitus via Alteration of TLR4/MyD88/NF-B Signaling Pathway. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024;30(12):65-71. [46] LI Y, HU Q, WANG B. Effects of Apelin on the fibrosis of retinal tissues and Müller cells in diabetes retinopathy through the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway. Autoimmunity. 2023;56(1):2259129. [47] SUN M, ZHAO X, LI X, et al. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorates Liver Injury in Db/Db Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Inflammation Through the Nrf2 and JAK2/STAT3 Signalling Pathways. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16(3):4805-4819. [48] SUN M, ZHAO X, LI X, et al. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorates Liver Injury in Db/Db Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Inflammation Through the Nrf2 and JAK2/STAT3 Signalling Pathways. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16(2):4805-4819. [49] HU X, DUAN T, WU Z, et al. Puerarin Inhibits the PERK-eIF2[Formula: see text]-ATF4-CHOP Pathway through Inactivating JAK2/STAT3 Signal in Pancreatic beta-Cells. Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(7):1723-1738. |
| [1] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [2] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [3] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [4] | Chen Chunlan, Ye Meiyi, Pan Yuwei, Yuan Jia, Zhou Pengjun. Immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5031-5040. |
| [5] | Zhu Peng, Li Yingyu, Lu Xiaoqian, Wu Qiong. Anti-obesity effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 in naturally aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2536-2543. |
| [6] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [7] | Hu Lingli, Li Na, Li Jingyang, Zhang Eryun, Chen Yu, Gu Ying. Role of non-coding RNA and exosomes in pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus and their early diagnostic value [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5070-5077. |
| [8] | Liang Fei. Effects of cumulative and continuous exercise of different intensities on intestinal mucosal permeability in insulin-resistant mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4332-4339. |
| [9] | Liu Gang, Zeng Jie, Zhao Yalin, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhang Yaqi, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Shujin Jiannao Prescription alleviates inflammation in the cerebral cortex of rats with hypoxic-ischemic cerebral palsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3674-3679. |
| [10] | Guo Xiangying, Peng Zifu, He Yimin, Fang Hongbo, Jiang Ning. MiRNA-122 contributes to the effect of exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 272-279. |
| [11] | Liu Renfan, Lyu Liting, Wu Yi, Wang Lu. Effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition and glucose metabolism in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2274-2281. |
| [12] | Zhang Yan, He Ruibo, Wang Qingbo, Pi Yihua, Lu Chunmin, Xu Chuanyi, Ma Gang, Peng Peng. Effects of aerobic exercises with different load volumes on inflammatory response and insulin signaling pathway of skeletal muscle in obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1237-1244. |
| [13] | Ding Lili, Hu Mingzhi, Wu Zhihui, Sun Xiaolin, Wang Yongfu. Therapeutic effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-1-5p in MRL/lpr lupus mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1492-1500. |
| [14] | Sun Ying, Xiang Guangda, Xu Xiaoli. Effects of myeloid-derived growth factor on ventricular remodeling in aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5020-5025. |
| [15] | Deng Xiaohui, Zhang Zengzeng, Zhang Zhihua, Zhu Lingyan. Mechanism and application prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes gene-modified microRNA in the treatment of diabetic foot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5076-5084. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||