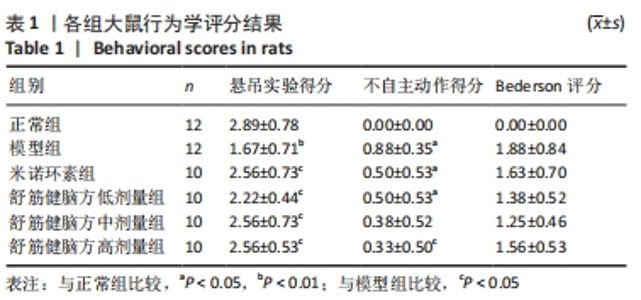
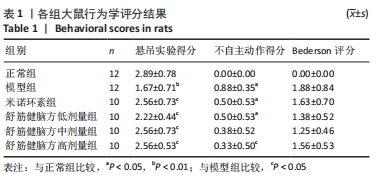
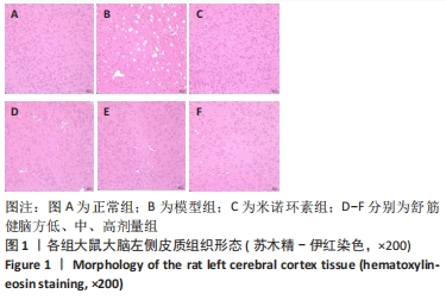
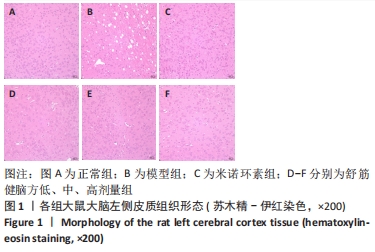
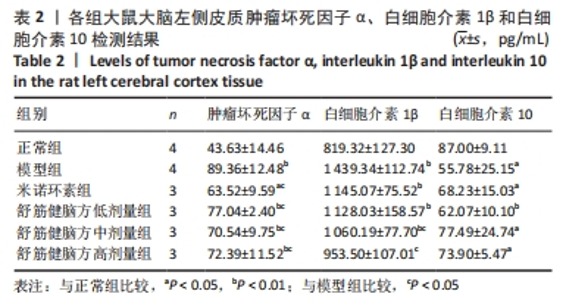
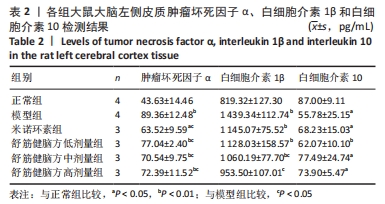
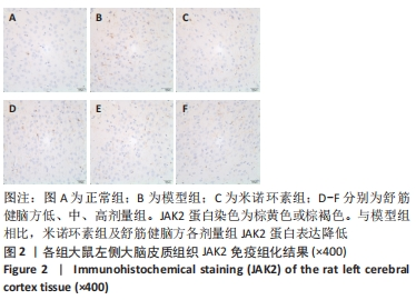
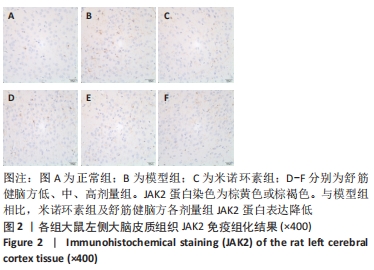
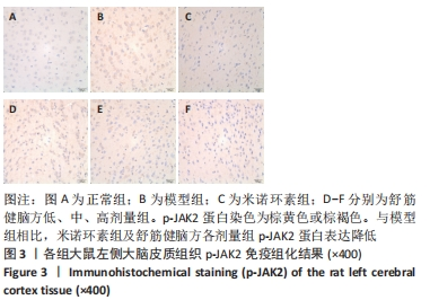
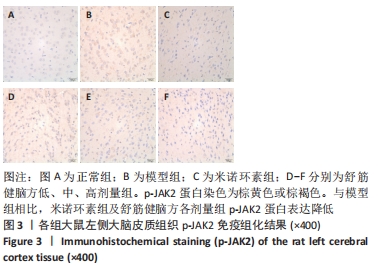
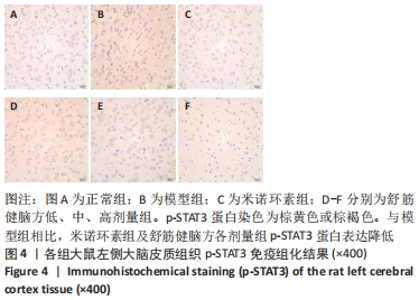
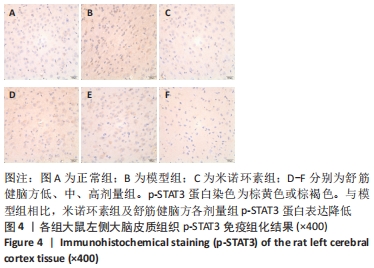
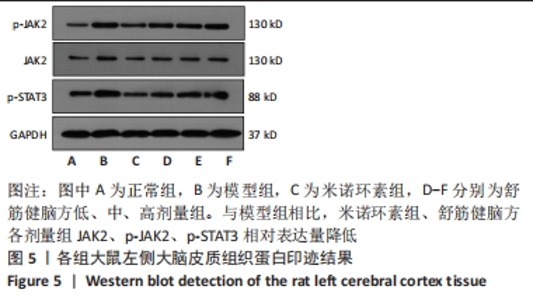
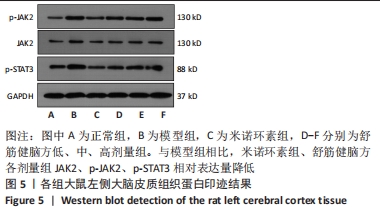
[1] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会,中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑性瘫痪康复专业委员会,中国医师协会康复医师分会儿童康复专业委员会等.中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2022)第三章:ICF-CY框架下的儿童脑瘫评定[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2022,37(15): 1121-1141.
[2] 封玉霞,庞伟,李鑫,等.中国0~6岁儿童脑瘫患病率的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2021,24(5):603-607.
[3] 中国康复医学会儿童康复专业委员会,中国残疾人康复协会小儿脑性瘫痪康复专业委员会,中国医师协会康复医师分会儿童康复专业委员会等.中国脑性瘫痪康复指南(2022)第四章:康复治疗(下)[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2022,37(17):1281-1309.
[4] LI B, CONCEPCION K, MENG X, et al. Brain-immune interactions in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;159:50-68.
[5] WU G, CHEN Z, WANG P, et al. Hydrogen inhalation protects hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by attenuating inflammation and apoptosis in neonatal rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019;244(12):1017-1027.
[6] PEEPLES ES, GENARO-MATTOS TC. Ferroptosis: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(13):7420.
[7] 袁巧,谢丽英,陈朝俊.黄芪多糖减轻大脑中动脉闭塞模型大鼠的血脑屏障损伤:基于抑制P2X7R通道[J].南方医科大学学报,2022, 42(11):1705-1711.
[8] LI J, DU Q, LI N, et al. Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus and Alzheimer’s disease: An update and current perspective on this traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;135:111167.
[9] RICE JE 3RD, VANNUCCI RC, BRIERLEY JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981;9(2): 131-141.
[10] TAI WC, BURKE KA, DOMINGUEZ JF, et al. Growth deficits in a postnatal day 3 rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Behav Brain Res. 2009;202(1):40-49.
[11] 宋红花,吴尤佳,李海英.新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤模型的早期鉴定[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2017,37(5):452-455.
[12] 陈刚,王伟哲,陈明钊,等.新生幼鼠缺血缺氧性脑损伤模型的实验研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012,18(7):612-614.
[13] 付许伟. 成年大鼠痉挛型脑瘫模型构建与评估的实验研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2018.
[14] ASGARI TAEI A, DARGAHI L, NASOOHI S, et al. The conditioned medium of human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviates neurological deficits and improves synaptic recovery in experimental stroke. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(3):1967-1979.
[15] 黄继汉,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9):1069-1072.
[16] 曾杰,赵亚林,徐林,等.基于“五迟五硬”探讨益肾健脾调肝法治疗痉挛型脑瘫的思路[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(10):5071-5073.
[17] CELORRIO M, SHUMILOV K, PAYNE C, et al. Acute minocycline administration reduces brain injury and improves long-term functional outcomes after delayed hypoxemia following traumatic brain injury.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022;10(1):10.
[18] BALLABH P, DE VRIES LS. White matter injury in infants with intraventricular haemorrhage: mechanisms and therapies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(4):199-214.
[19] HEMONNOT AL, HUA J, ULMANN L, et al. Microglia in Alzheimer Disease: Well-Known Targets and New Opportunities. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019;11:233.
[20] SILVIN A, UDERHARDT S, PIOT C, et al. Dual ontogeny of disease-associated microglia and disease inflammatory macrophages in aging and neurodegeneration. Immunity. 2022;55(8):1448-1465.
[21] YIN XY, WANG CC, DU P, et al. Muse cells decrease the neuroinflammatory response by modulating the proportion of M1 and M2 microglia in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(1):213-218.
[22] LIDDELOW SA, GUTTENPLAN KA, CLARKE LE, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. 2017;541(7638): 481-487.
[23] LUKENS JR, EYO UB. Microglia and Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2022;45:425-445.
[24] 刘洪俊. IL-6、IL-10和TNF-α参与脑性瘫痪患儿脑损伤的相关性研究[D].新乡:新乡医学院,2017.
[25] HAO N, ZHOU Z, ZHANG F, et al. Interleukin-29 Accelerates Vascular Calcification via JAK2/STAT3/BMP2 Signaling. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023; 12(1):e027222.
[26] DAI XY, LIU L, SONG FH, et al. Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway for chronic pain. Aging Dis. 2023. doi:10.14336/AD.2023.0515.
[27] YU L, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q, et al. Formononetin protects against inflammation associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;149:112836.
[28] ZHONG Y, GU L, YE Y, et al. JAK2/STAT3 Axis Intermediates Microglia/Macrophage Polarization During Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Neuroscience. 2022;496:119-128.
[29] ZHONG Y, YIN B, YE Y, et al. The bidirectional role of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and related mechanisms in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Neurol. 2021;341:113690.
[30] LONG QH, WU YG, HE LL, et al. Suan-Zao-Ren Decoction ameliorates synaptic plasticity through inhibition of the Aβ deposition and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in AD model of APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Chin Med. 2021;16(1):14.
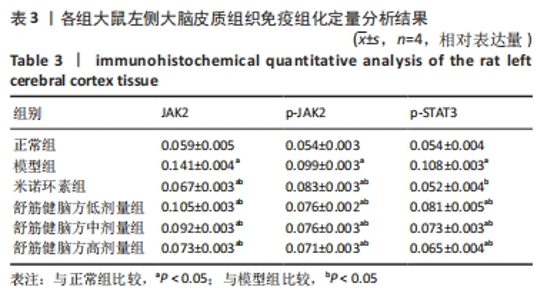
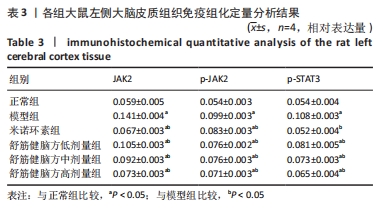
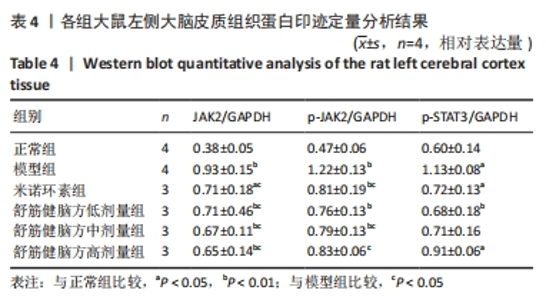
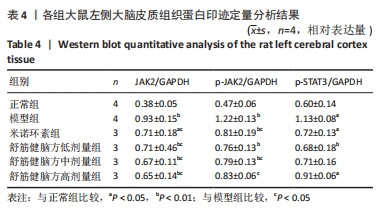
[31] 曾杰,赵亚林,邓博文,等.JAK2/STAT3信号通路在大脑缺血缺氧后小胶质细胞活化中的作用[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(2):190-194.
|