Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (15): 3820-3831.doi: 10.12307/2026.191
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of effect of passive support of deep intrinsic lumbar muscle groups on the lumbar spine
Li Chunchao1, Julaiti·Maitirouzi1, Xie Xuechen1, Zhang Le1, Wang Yixi2, Paerhati·Rexiti2
- 1School of Intelligent Manufacturing and Modern Industry, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Minimally Invasive Spine and Precision Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Accepted:2025-07-19Online:2026-05-28Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Associate professor, School of Intelligent Manufacturing and Modern Industry, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Chunchao, Master candidate, School of Intelligent Manufacturing and Modern Industry, College of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:"Tianshan Talents" Medical and Health High-level Talent Training Program Fund, No. TSYC202301B026 (to PR); Third China Health and Longevity Innovation Competition Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2022-JKCS-19 (to PR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Chunchao, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xie Xuechen, Zhang Le, Wang Yixi, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of effect of passive support of deep intrinsic lumbar muscle groups on the lumbar spine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3820-3831.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
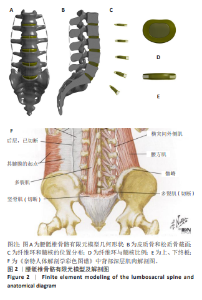
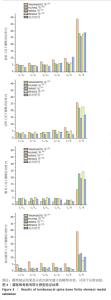
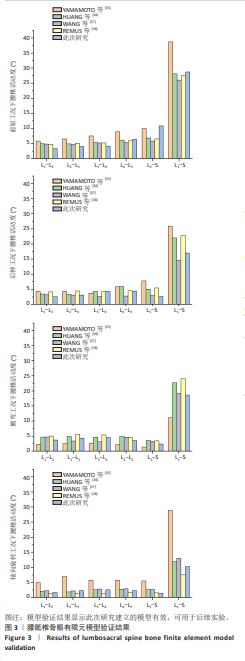
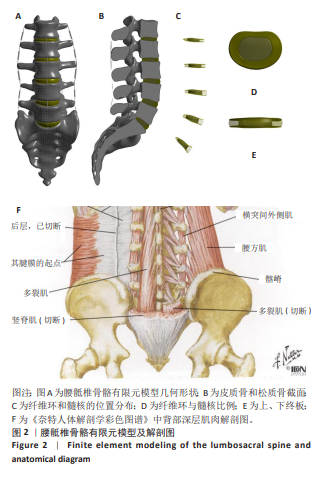
2.1 模型验证 将腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型的几何形状与真实解剖椎体对比,形态无明显差异,见图2A。根据以往研究,将此模型中椎骨皮质骨设置为群体中平均厚度0.73 mm[32],见图2B。椎间盘由髓核、纤维环和终板组成,髓核占椎间盘表面积约44%,纤维环占约56%,且髓核位于椎间盘整体比例中心向后3.5 mm处[33],见图2C,D。椎间盘通过上、下终板与椎体相连接,终板厚度设置为0.5 mm[34],见图2E。此次研究中腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型使用ANSYS Workbench中静力结构模块创建有限元网格,采用二阶四面体单元类型,共生成2 522 937个网格和4 197 465个节点。将此模型的腰椎活动度与文献[35-38]对比,其中左、右侧弯和左、右轴向旋转工况取平均值去对比,腰椎活动度数据差异不大,在合理范围内,见图3。将建立的简化肌肉模型与解剖图作对比,见图2F,相差不大,并根据肌肉的属性预测活动度有减小趋势,与后续结果一致。因此,认为此次研究建立的模型有效,可用于后续实验。"
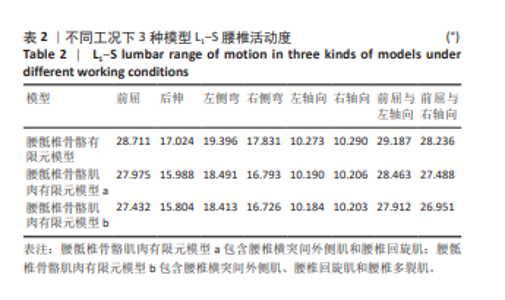
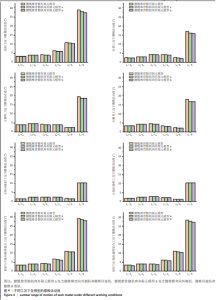
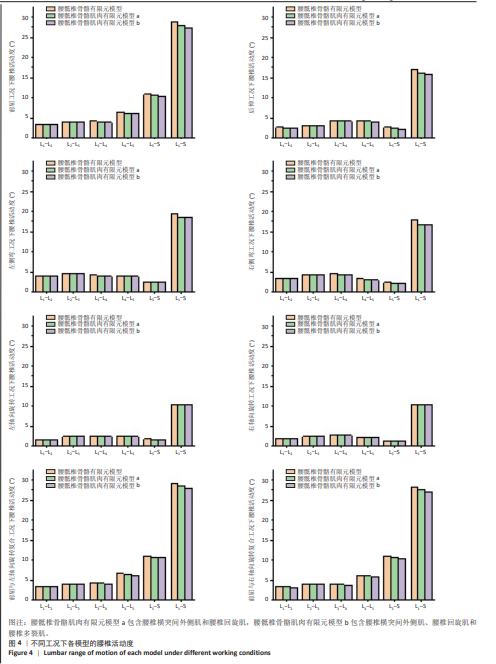
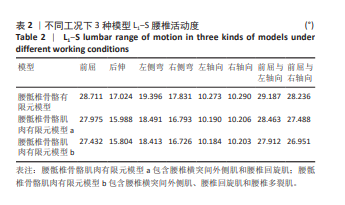
2.2 腰椎活动度 2.2.1 整体腰椎活动度 整体腰椎活动度是指腰椎作为一个功能性整体单元,在三维空间内所能达到的最大活动范围,是评估人们能否完成日常生活、工作和娱乐活动的重要指标。相同的载荷条件,前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左轴向旋转、右轴向旋转、前屈与左轴向旋转复合、前屈与右轴向旋转复合工况中,腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在 L1-S 整体腰椎活动度分别降低了2.56%,6.09%,4.67%,5.82%,0.81%,0.82%,2.48%及2.65%;腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在 L1-S 整体腰椎活动度分别降低了4.45%,7.17%,5.07%,6.20%,0.87%,0.85%,4.37%及4.55%;腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a在 L1-S 整体腰椎活动度分别降低了1.94%,1.15%,0.42%,0.40%,0.06%,0.03%,1.94%及1.95%,见表2。"
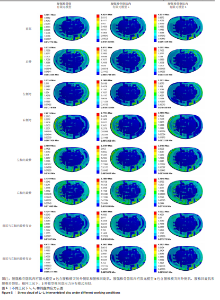
2.3 L4-L5节段椎间盘应力 相同的载荷条件,前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左轴向旋转、右轴向旋转、前屈与左轴向旋转复合、前屈与右轴向旋转复合工况中,腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在椎间盘应力最大值分别减少了1.42%,0.08%,3.16%,4.03%,3.61%,3.03%,1.17%及1.63%;腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在椎间盘应力最大值分别减少了2.52%,0.60%,3.55%,4.36%,3.74%,3.22%,2.10%及2.78%;腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a在椎间盘应力最大值分别减少了1.12%,0.52%,0.40%,0.34%,0.13%,0.19%,0.93%及1.17%。见图5。"
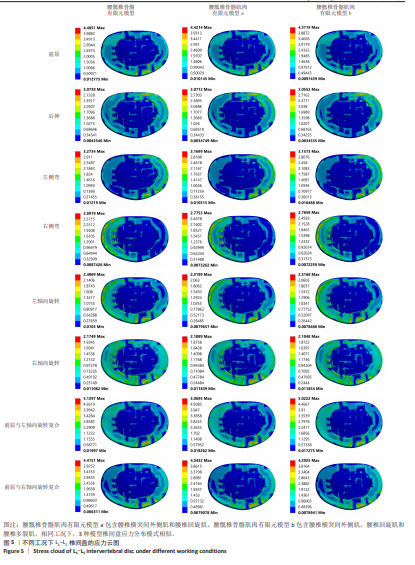
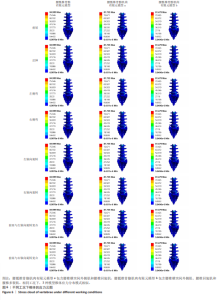
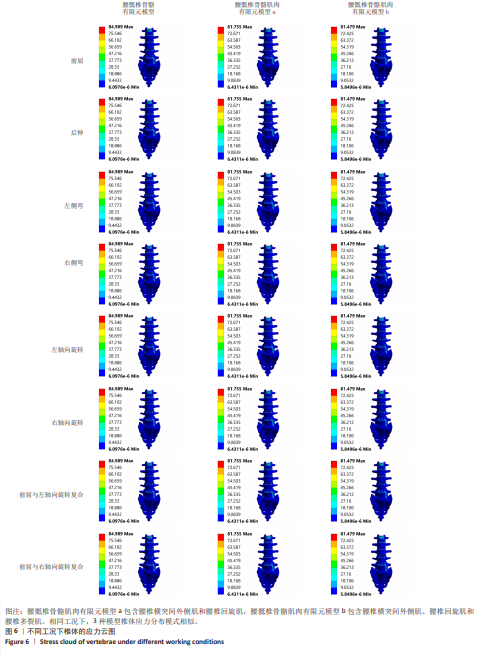
2.4 椎体皮质骨应力 相同的载荷条件,前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左轴向旋转、右轴向旋转、前屈与左轴向旋转复合、前屈与右轴向旋转复合工况中,腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在椎体皮质骨应力最大值分别减小了3.81%,1.81%,4.66%,1.07%,0.06%,0.04%,3.32%及4.17%,腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼有限元模型在椎体皮质骨应力最大值分别减小了4.13%,2.12%,4.97%,1.21%,0.29%,1.20%,3.64%及4.49%,腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型b相对腰骶椎骨骼肌肉有限元模型a在椎体皮质骨应力最大值分别减小了0.34%,0.32%,0.33%,0.14%,0.24%,1.16%,0.33%及0.33%。见图6。 "
| [1] YANG Y, LAI X, LI C, et al. Focus on the impact of social factors and lifestyle on the disease burden of low back pain: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):679. [2] FERREIRA ML, DE LUCA K, HAILE LM, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(6):e316-e329. [3] SHOKRI P, ZAHMATYAR M, FALAH TAFTI M, et al. Non-spinal low back pain: Global epidemiology, trends, and risk factors. Health Sci Rep. 2023; 6(9):e1533. [4] GULAMOVNA DB, GUZAL AN, GULRUH A. Skeletal anatomy. Eur J Med Natural Sci. 2024;4(1-1):48-52. [5] SIVASANKARI S, BALASUBRAMANIAN V. Influence of occupant collision state parameters on the lumbar spinal injury during frontal crash. J Adv Res. 2020;28:17-26. [6] 曹修祥,任闻闻,巩庆雷,等.磁共振成像在胸椎和腰椎骨折中的诊断价值分析[J].影像研究与医学应用,2024,8(2):172-174. [7] 冯良恩.经皮椎间孔镜行腰椎管减压的技术演进[J].中外医学研究, 2023,21(6):163-166. [8] FENG N, TAN S, CHEN S, et al. A cross-sectional association study of paravertebral muscle quality and modic changes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s00586-025-09027-0. [9] SCHÖNNAGEL L, ZHU J, CAMINO-WILLHUBER G, et al. Relationship between lumbar spinal stenosis and axial muscle wasting. Spine J. 2024;24(2): 231-238. [10] XU S, WANG R, MA S, et al. Interventional effect of core stability training on pain and muscle function of youth with chronic non-specific lower back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32818. [11] CHEN M, YANG C, CAI Z, et al. Lumbar posterior group muscle degeneration: influencing factors of adjacent vertebral body re-fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Front Med. 2023;9:1078403. [12] 冯思仪,李艳娇,钟锐,等.四维牵引治疗老年退行性腰椎管狭窄症的疗效、腰肌形态学及力学性能评估[J].实用医学杂志,2025,41(10): 1525-1532. [13] SATO K, KIKUCHI S, YONEZAWA T. In vivo intradiscal pressure measurement in healthy individuals and in patients with ongoing back problems. Spine. 1999; 24(23): 2468. [14] POLGA DJ, BEAUBIEN BP, KALLEMEIER PM, et al. Measurement of in vivo intradiscal pressure in healthy thoracic intervertebral discs. Spine. 2004; 29(12):1320-1324. [15] 邵翌鑫,关天民,朱晔,等.不同模量植入假体与周围骨间的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29):4612-4619. [16] WANG X, LIU W, ZHAO Y, et al. The impact of disc degeneration on the dynamic characteristics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1384187. [17] LI S, DU J, ZHU L, et al. Case series study and finite element analysis of a new cervicothoracic fixation device. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1): 889. [18] WAN S, XUE B, XIONG Y. Three‐Dimensional Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Middle Aged and Elderly. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:7107702. [19] VERMA S, CHANDA A. State-of-the-art of finite element modelling of the human spine to study the impact of vibrations: a review. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech. 2024;25(4):225-247. [20] LONG Z, ZHOU J, XIONG L, et al. Finite element study on three osteotomy methods for treating thoracolumbar osteoporotic fracture vertebral collapse complicated with neurological dysfunction. Medicine. 2024;103(7):e36987. [21] 张治豪,居来提·买提肉孜,张连鹏,等.新型变径全皮质骨螺纹螺钉设计以及在腰椎改良皮质骨轨迹的应用[J].医用生物力学,2024, 39(1):91-97. [22] LI J, DU Z, CAO S, et al. Quantitative relationships between elastic modulus of rod and biomechanical properties of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025;12: 1510597. [23] 李健,关天民,朱晔.有限元法分析骶椎腰化的力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33):5249-5253. [24] 任东,朱晔,雷蕾,等.矫形力加载肋骨施力区对胸椎段位移及旋转角度影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2812-2816. [25] JU C, YANG K, YANG Q, et al. Multiscale dynamics analysis of lumbar vertebral cortical bone based on the Abaqus submodel finite element method. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):6861. [26] LI R, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The effect of suboccipital muscle dysfunction on the biomechanics of the upper cervical spine: a study based on finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1) 400. [27] ÇELIK M, KARAOĞLU A, ÇEKINMEZ M, et al. Investigation Of The Role Of Multifidus Muscles In The Development Of Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation. Eur Health Sci J. 2025;3(1):8-16. [28] 张连鹏,居来提·买提肉孜,张治豪,等.有限元分析改良皮质骨轨迹置钉在腰椎翻修术中的力学性能[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(3):413-420. [29] KHUYAGBAATAR B, KIM K, KIM YH. Recent developments in finite element analysis of the lumbar spine. Int J Prec Eng Manufact. 2024;25(2):487-496. [30] KANG I, CHOI M, LEE D, et al. Effect of passive support of the spinal muscles on the biomechanics of a lumbar finite element model. Appl Sci. 2020;10(18):6278. [31] ZHANG XY, HAN Y. Comparison of the biomechanical effects of lumbar disc degeneration on normal patients and osteoporotic patients: A finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2023;112:103952. [32] PASOTO SG, AUGUSTO KL, ALVARENGA JC, et al. Cortical bone density and thickness alterations by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography: association with vertebral fractures in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology. 2016;55(12):2200-2211. [33] LIU X, MA J, PARK P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of multilevel lateral interbody fusion with and without supplementary instrumentation: a three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):63. [34] ZHAO X, DU L, XIE Y, et al. Effect of lumbar lordosis on the adjacent segment in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e114-e120. [35] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11): 1256-1260. [36] HUANG YP, DU CF, CHENG CK, et al. Preserving posterior complex can prevent adjacent segment disease following posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgeries: a finite element analysis. PloS One. 2016;11(11): e0166452. [37] WANG Y, MAIMAITI A, XIAO Y, et al. Hybrid cortical bone trajectory and modified cortical bone trajectory techniques in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion at L4-L5 segment: A finite element analysis. Heliyon. 2024;10(5):e26294. [38] REMUS R, LIPPHAUS A, NEUMANN M, et al. Calibration and validation of a novel hybrid model of the lumbosacral spine in ArtiSynth–The passive structures. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0250456. [39] LI Z, ZHANG Y, LIN Y, et al. The role of paraspinal muscle degeneration in cervical spondylosis. Eur Spine J. 2025;34(3):1187-1197. [40] DING J, KONG C, LI X, et al. Different degeneration patterns of paraspinal muscles in degenerative lumbar diseases: a MRI analysis of 154 patients. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(3):764-773. [41] CHOU SH, LIN SY, SHEN PC, et al. Pain control affects the radiographic diagnosis of segmental instability in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Clin Med. 2021;10(17):3984. [42] 邹峰.慢性非特异性腰痛柔道运动员核心部位特征研究[D].南京:南京体育学院,2021. [43] JIANG J, HUANG Y, HE B. Advances in the interaction between lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration and fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles: critical summarization, classification, and perspectives. Front Endocrinol. 2024;15:1353087. [44] DANNEELS LA, VANDERSTRAETEN GG, CAMBIER DC, et al. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(4):266-272. [45] KALICHMAN L, CARMELI E, BEEN E. The association between imaging parameters of the paraspinal muscles, spinal degeneration, and low back pain. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017(1):2562957. [46] BARKER KL, SHAMLEY DR, JACKSON D. Changes in the cross-sectional area of multifidus and psoas in patients with unilateral back pain: the relationship to pain and disability. Spine. 2004;29(22):E515-E519. [47] KIM S, KIM H, CHUNG J. Effects of spinal stabilization exercise on the cross-sectional areas of the lumbar multifidus and psoas major muscles, pain intensity, and lumbar muscle strength of patients with degenerative disc disease. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014;26(4):579-582. [48] KANG S, PARK CH, JUNG H, et al. Analysis of the physiological load on lumbar vertebrae in patients with osteoporosis: a finite-element study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11001. [49] PRADEEP K, PAL B. Finite element analysis of an intact lumbar spine model: Effects of loading under different coordinate systems. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2023;237(7):815-828. [50] WARREN JM, HEY LA, MAZZOLENI AP. A finite element study of the relationship between upper body weight and the loads experienced by the human lumbosacral spine, and fusion instrumentation, in a standing upright posture. Biomed Eng Adv. 2021;2:100023. [51] GUVEN AE, SCHÖNNAGEL L, CHIAPPARELLI E, et al. Relationship Between Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis and Multifidus Muscle Atrophy: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Spine. 2025;50(10):702-706. [52] DE SIMONE M, CHOUCHA A, CIAGLIA E, et al. Discogenic low back pain: Anatomic and pathophysiologic characterization, clinical evaluation, biomarkers, AI, and treatment options. J Clin Med. 2024;13(19):5915. [53] 罗金伟,徐国康,屠玉兰,等.TLIF与OLIF联合后路内固定治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效比较[J].浙江临床医学,2024,26(1):93-95. [54] FENG C, HU Z, ZHAO M, et al. Region-specific mitophagy in nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus, and cartilage endplate of intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol. 2025;16:1579507. [55] SCARCIA L, PILEGGI M, CAMILLI A, et al. Degenerative disc disease of the spine: from anatomy to pathophysiology and radiological appearance, with morphological and functional considerations. J Personalized Med. 2022;12(11):1810. [56] DIWAN AD, MELROSE J. Intervertebral disc degeneration and how it leads to low back pain. JOR Spine. 2023;6(1):e1231. [57] CHENG Z, LI Y, LI M, et al. Correlation between posterior paraspinal muscle atrophy and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in patients with chronic low back pain. Int Orthop. 2023;47(3):793-801. [58] OEFNER C, RIEMER E, FUNKE K, et al. Determination of anisotropic elastic parameters from morphological parameters of cancellous bone for osteoporotic lumbar spine. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022;60(1):263-278. [59] LI J, GONG H. Fatigue behavior of cortical bone: a review. Acta Mechanica Sinica. 2021;37(3):516-526. [60] KARACAN I, TÜRKER KS. Exploring neuronal mechanisms of osteosarcopenia in older adults. J Physiol. 2024. doi: 10.1113/JP285666. |
| [1] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [2] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [3] | Wu Hongxu, Liu Xuanyu, Wang Taoyu, Wang Shiyao, Cheng Jingyi, Zhang Mingwen, Zhang Yinxia, Liu Zhihua, Wang Xiaojie. Finite element simulation of scoliosis with muscle unit introduction: verification of correction effect under bidirectional load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2172-2181. |
| [4] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [5] | Shi Yaozhou, Jia Fanglin, Zhang Heling, Song Hanlin, Gao Haoran, Gao Xiao, Sun Wei, Feng Hu. Establishment and validation of a prediction model for axial symptoms after laminectomy with lateral mass screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2269-2277. |
| [6] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [7] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [8] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [9] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [10] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [11] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [12] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [13] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [14] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [15] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||