Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2145-2152.doi: 10.12307/2025.873
Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis
Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming
- Department of Spine Orthopedics, Zengcheng District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-30Accepted:2025-01-17Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-08-20 -
Contact:Deng Weiming, Attending physician, Department of Spine Orthopedics, Zengcheng District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital,Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Huiting, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Orthopedics, Zengcheng District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou 510000,Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
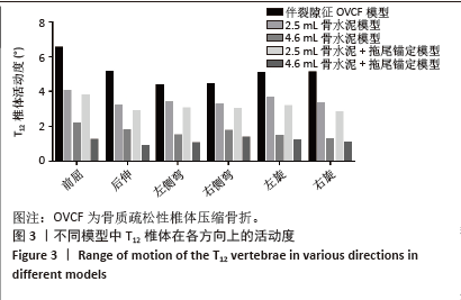
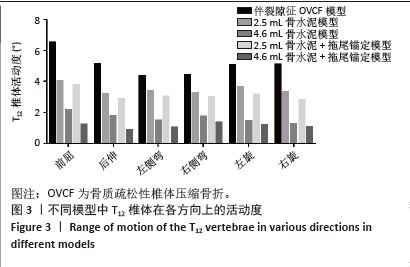
2.1 骨折椎(T12)活动度 在伤椎活动度上,当存在椎体内裂隙征时,T12椎体存在明显的异常活动,在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋时,其活动度分别为6.52°,5.12°,4.39°,4.44°,5.03°和5.11°。在2.5 mL骨水泥模型组和2.5 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定模型组,前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋时,椎体的活动度有部分减少,但异常活动仍可达3°-4°,提示骨折椎的稳定性仍然较差,骨水泥移位的风险较高。在4.6 mL骨水泥模型组,T12椎体活动度下降至1.28°-2.17°,具体的,在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋时,分别为2.17°,1.80°,1.49°,1.74°,1.45°和1.28°。而在4.6 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定模型组,骨折椎的活动度下降更为明显(图3),其活动度较伴裂隙征OVCF模型分别减少81%,83%,77%,69%,76%和79%,说明骨水泥拖尾锚定能有效增加骨折椎的稳定性,降低骨水泥移位的风险。"
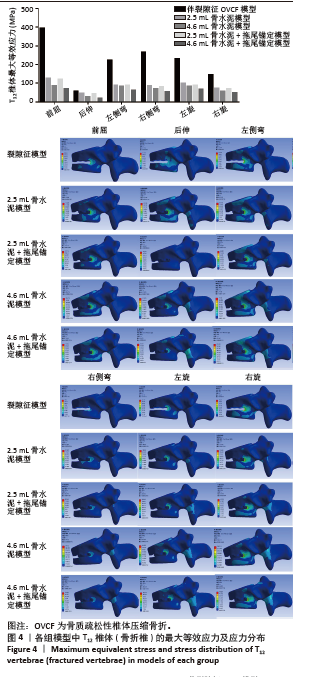
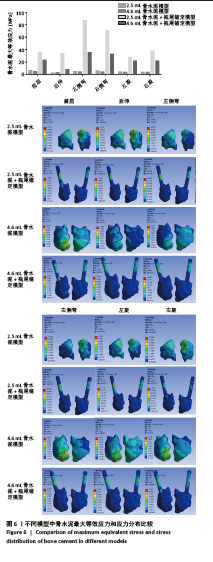
2.2 骨折椎(T12)最大等效应力 在伤椎最大等效应力上,以伴裂隙征OVCF模型的等效应力最大,尤其是在前屈和右侧弯时,其最大等效应力达到了395.82和265.2 MPa,在后伸、左侧弯、左旋和右旋时,T12的最大等效应力分别为57.17,223.68,231.73和146.27 MPa。注入骨水泥后,骨折椎的最大等效应力明显减小,尤其以4.6 mL+拖尾锚定模型应力减少最多,其最大等效应力较伴裂隙征OVCF模型分别减少82%,67%,73%,79%,71%和66%,说明其能较好地稳定骨折椎,减少骨折椎的应力集中。但是在2.5 mL骨水泥组和2.5 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定组,椎体的应力仍然较高,前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋分别为126.09,45.14,89.55,87.66,100.82,73.65和121.76,44.64,88.00,80.55,88.96,69.62 MPa,提示伤椎的应力仍然较为集中,可能存在再骨折的风险(图4)。"
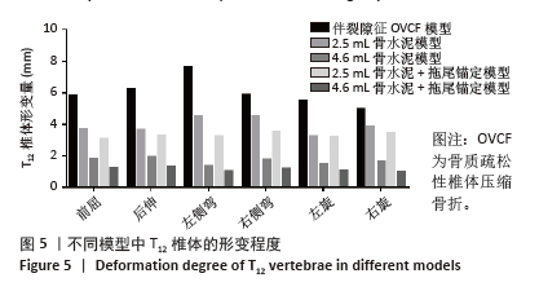
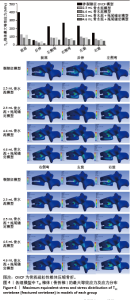
2.3 骨折椎(T12)形变程度 在骨折椎形变程度上,由于伴裂隙征椎体存在明显的异常活动,在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋时,其形变程度较大,达到了5.79,6.23,7.63,5.87,5.5和4.94 mm。 形变程度居中的是2.5 mL骨水泥模型和2.5 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定模型。形变程度最轻的是4.6 mL骨水泥模型和4.6 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定模型,在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋分别为1.81,1.91,1.35,1.75,1.48,1.67 mm和1.22,1.31,1.04,1.19,1.06,0.94 mm(图5)。说明在骨水泥量达到一定程度后,骨折椎体的生物力学稳定性能够得到维持,而拖尾锚定技术能进一步增加骨折椎的稳定性,尤其是能明显减小椎体旋转时的形变量。"
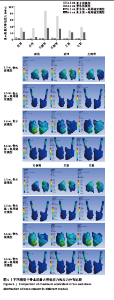
2.4 骨水泥最大等效应力 在骨水泥最大等效应力上,与上述骨折椎活动度和最大等效规律相反的是,在非拖尾征模型中,其骨水泥最大等效应力反而更小。在4.6 mL骨水泥模型组,其前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋和右旋时,骨水泥最大等效应力分别为4.67,3.06,4.47,4.10,3.50和3.44 MPa。而在4.6 mL骨水泥+拖尾锚定模型组中,其屈伸、侧弯、旋转时的应力增大至22.99,7.80,35.09,32.84,21.61,21.87 MPa,分别增大了392%,155%,685%,701%,517%和536% (图6)。 进一步观察显示,在拖尾锚定模型组,其增大的应力主要集中在拖尾部分的骨水泥,尤其是拖尾骨水泥的中后部,这可能与拖尾部分尾端活动度较大、骨水泥周围为较硬的椎弓根皮质骨有关。 "
| [1] 冯骁骁, 吕南宁, 张浩, 等. 低温与常温灌注椎体成形术治疗Kümmell病[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(11):980-985. [2] ROUSING R, KIRKEGAARD AO, NIELSEN M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as treatment of malignant vertebral lesions: a systematic review and GRADE evaluation resulting in a Danish national clinical guideline. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7):1573-1579. [3] ANDREÃO FF, BORGES P, PALAVANI LB, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty versus Nonoperative Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. World Neurosurg. 2024;190:408-421.e5. [4] 邝冠明, 高庆鹏, 杨震宇, 等. 经皮椎体成形术/经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗超高龄患者椎体压缩骨折的疗效和安全性初步研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(12):982-986. [5] 王勤业, 方芳, 常小波. 经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2024,39(3):288-291. [6] YU W, XIAO X, ZHANG J, et al. Cement Distribution Patterns in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures with Intravertebral Cleft: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e408-e415. [7] 许勇, 官众, 李永霞, 等. 骨填充网袋治疗老年骨质疏松性压缩骨折合并椎体内裂隙征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(10): 1477-1482. [8] 路文超, 王宇鹏, 湛川. 椎体后凸成形治疗Kummell病过程中发生的骨水泥渗漏[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):172-177. [9] 庞巨涛, 张新虎, 孙建华, 等. 经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后椎体再骨折的危险:回顾性多因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(8):1182-1187. [10] LV NN, HOU MZ, ZHOU ZZ, et al. Does the Relationship Between Bone Cement and the Intravertebral Cleft of Kummell Disease Affect the Efficacy of PKP. World Neurosurg. 2022;160:e430-e435. [11] 李永军, 梁永辉, 韦兴, 等. “拖尾征”锚定骨水泥椎体后凸成形术对Kummell’s病的治疗效果[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2020, 19(7):494-498. [12] 陈乃旺, 任国帅, 庄青山, 等. 提高骨水泥注入安全性的改良椎体成形术[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(8):738-741. [13] YONEZAWA N, YONEZAWA Y, NISHIMURA T, et al. Vertebra-Pediculoplasty: A New Approach to Treatment of Split-Type and Delayed-Union Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture with a Risk of Cement Dislodgement. World Neurosurg. 2021;155:e55-e63. [14] GUO HZ, ZHANG SC, GUO DQ, et al. Influence of cement-augmented pedicle screws with different volumes of polymethylmethacrylate in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae over the adjacent segments: a 3D finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):460. [15] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of four different posterior instrumentation techniques for single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6160-6169. [16] 李光晟, 吴如陈, 刘成招, 等. 椎弓根骨水泥锚定对椎体成形术治疗Kümmell’s病骨水泥团块稳定作用的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):823-830. [17] 曾锦源, 谢昀, 陈春永, 等. 骨折复位程度和骨水泥注入量对PKP术后邻近椎体应力影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2023,38(7):698-702. [18] LUO C, JIANG T, TIAN S, et al. Finite element analysis of lumbar spine with different backpack positions in parachuting landing. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(15):1679-1686. [19] 魏源标, 郭惠智, 张顺聪. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定对相邻节段影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2799-2804. [20] 费琦, 赵凡, 杨雍, 等. 腰椎后路融合手术对失稳模型节段稳定性及相邻节段力学的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2015,95(45):3681-3686. [21] FAN R, LIU J, LIU J. Prediction of the natural frequencies of different degrees of degenerated human lumbar segments L2-L3 using dynamic finite element analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;209:106352. [22] ZHANG X, CHEN T, MENG F, et al. A finite element analysis on different bone cement forms and injection volumes injected into lumbar vertebral body in percutaneous kyphoplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):621. [23] MONDAL S, MACMANUS DB, BANCHE-NICLOT F, et al. Finite element analysis of vertebroplasty in the osteoporotic T11-L1 vertebral body: Effects of bone cement formulation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024;112(1):e35359. [24] 史晓林, 刘康. 老年性骨质疏松症中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(7):937-946. [25] 林杰, 金甬, 庞清江. 胃肠道菌群与骨质疏松症关系的研究进展[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2024,42(1):109-111. [26] 马一鸣, 王子豪, 蔡大钊, 等. 椎体后凸成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折后新发骨折危险因素预测模型的建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(23):3700-3706. [27] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会, 章振林. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. [28] BROWN JP, ENGELKE K, KEAVENY TM, et al. Romosozumab improves lumbar spine bone mass and bone strength parameters relative to alendronate in postmenopausal women: results from the Active-Controlled Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis at High Risk (ARCH) trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(11): 2139-2152. [29] 孙亦强, 王秀双, 李建军, 等. 椎体内裂隙征引起的椎体动态不稳与神经功能损伤的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18): 2900-2905. [30] QI H, QI J, SUN Y, et al. Bone microarchitecture and metabolism in elderly male patients with signs of intravertebral cleft on MRI. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(6):3931-3943. [31] DONG L, DONG C, ZHU Y, et al. Intravertebral cleft in pathological vertebral fracture resulting from spinal tuberculosis: a case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):619. [32] FAN N, WANG T, WANG A, et al. A predictive nomogram for intradiscal cement leakage in percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures combined with intravertebral cleft. Front Surg. 2022;9:1005220. [33] LV N, FENG X, LIU H, et al. Study on the influence of balloon dilation mode on the intravertebral cleft of osteoporotic fracture. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):351. [34] ZHANG T, KANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Does segmental artery occlusion cause intravertebral cleft following osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a prospective magnetic resonance angiography study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):103. [35] TANG S, FU W, ZHANG H, et al. Efficacy and Safety of High-Viscosity Bone Cement Vertebroplasty in Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures with Intravertebral Cleft. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:e739-e745. [36] ZHANG S, CHEN H, BAO L, et al. Association Between Spinopelvic Parameters and Intravertebral Cleft in Osteoporosis Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2024;183:e813-e817. [37] YONEZAWA Y, YONEZAWA N, KANAZAWA Y, et al. Revision balloon kyphoplasty and vertebra-pediculoplasty using cannulated screws for osteoporotic vertebral fractures with cement dislodgement following conventional balloon kyphoplasty. J Neurointerv Surg.2022;14(8): 844-846. [38] WANG B, ZHAN Y, BAI Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of a novel bone cement bridging screw system for the treatment of Kummell disease: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(10): 7052-7062. [39] WANG B, WANG Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Pediculoplasty combined with vertebroplasty for the treatment of Kummell’s disease without neurological impairment: robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12):8019-8029. [40] LI C, SONG L, XIAO J, et al. Second-generation bone cement-injectable cannulated pedicle screws for osteoporosis: biomechanical and finite element analyses. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):343. [41] ZHANG G, LI J, ZHANG L, et al. Biomechanical Effect of Different Posterior Fixation Techniques on Stability and Adjacent Segment Degeneration in Treating Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture With Osteoporosis: A Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2024; 49(15):E229-E238. |
| [1] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [2] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [3] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [4] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [5] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [6] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [7] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [8] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [9] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [10] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [11] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [12] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Mechanical effect of mechanical wear of abutment screws on the Morse taper connection implant system: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1375-1383. |
| [13] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [14] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [15] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||