Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (26): 4145-4150.doi: 10.12307/2024.430
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visual analysis of the effect of apoptosis on ischemic stroke
Duan Yanzhe1, Hua Jianlin1, 2, Ding Zhibin1, 3, Jiang Nan4, Song Lijuan1, 4, Yan Yuqing1, 5, Ma Cungen1, 5
- 1Key Laboratory of Invigorating Qi and Activating Blood Circulation of Multiple Sclerosis/Neurobiology Research Center, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Neurosurgery, Sinopharm Coal Group General Hospital, Datong 037003, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences), The Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China; 4Key Laboratory of Cell Physiology, Ministry of Education, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 5Department of Neurology, Institute of Brain Science, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-06-05Accepted:2023-07-22Online:2024-09-18Published:2023-09-28 -
Contact:Yan Yuqing, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory of Invigorating Qi and Activating Blood Circulation of Multiple Sclerosis/Neurobiology Research Center, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Neurology, Institute of Brain Science, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China Song Lijuan, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory of Invigorating Qi and Activating Blood Circulation of Multiple Sclerosis/Neurobiology Research Center, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Key Laboratory of Cell Physiology, Ministry of Education, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Ma Cungen, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Key Laboratory of Invigorating Qi and Activating Blood Circulation of Multiple Sclerosis/Neurobiology Research Center, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Neurology, Institute of Brain Science, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Duan Yanzhe, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Invigorating Qi and Activating Blood Circulation of Multiple Sclerosis/Neurobiology Research Center, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82004028 (to SLJ) and 81473577 (to MCG); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2020M680912 (to SLJ); “Zhang Zhongjing Inheritance and Innovation Special Project” of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. GZY-KJS-2022-048-1 (to SLJ); Shanxi Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Talent Young Team Project, No. 202204051001028 (to SLJ); 2022 Annual Science and Technology Innovation Team Project of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022TD2010 (to SLJ and MCG); Medical Science and Technology Leadership Team Project of Shanxi Provincial Healthcare Commission, No. 2020TD05 (to MCG); Cardiovascular Special Fund Project of National Regional TCM Medical Center, Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. XGZX202115 (to SLJ); Young Scientist Training Program of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021PY-QN-09 (to SLJ); Discipline Construction Fund of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2023XKJS-02 (to MCG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Duan Yanzhe, Hua Jianlin, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Song Lijuan, Yan Yuqing, Ma Cungen. Visual analysis of the effect of apoptosis on ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4145-4150.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

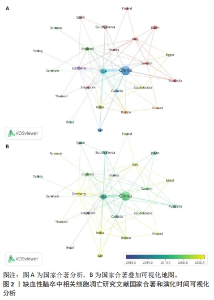
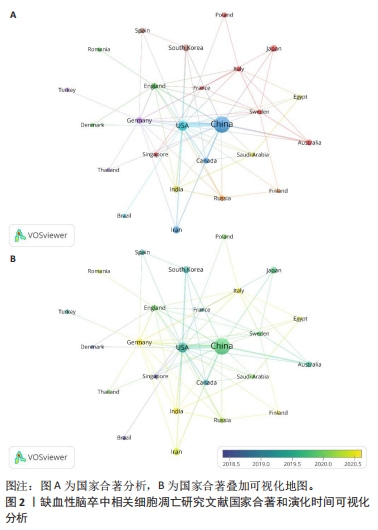
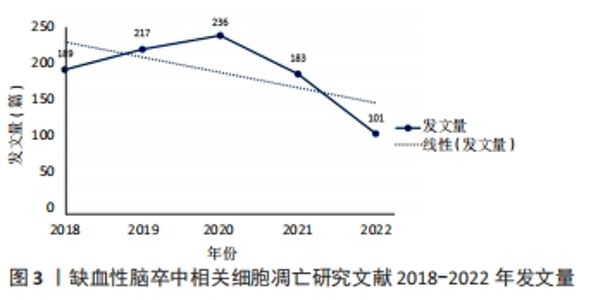
2.1 国家/地区文章产出的分析和相互合作的分析 通过数据的可视化分析,可以看出中国的发文量居于第一(703),是IS和细胞凋亡研究领域最大的贡献者,美国和伊朗分别以105、31篇的发文量位居第二和第三(图1)。从大的区域而言,亚洲以中国为代表,欧洲以德国为代表,北美洲以美国为主,还有大洋洲的澳大利亚都是此领域的重要贡献者。国家共同作者地图可以帮助研究人员了解现有的合作伙伴关系并确定潜在的合作者。作者使用VOSviewer分析了不同国家之间的合作关系,并绘制了合作网络(图2A),最大的一组连接国家是由17个国家组成,集群按代表每个国家的共现术语的频率进行分组,紧密相关的术语被分组到具有相同颜色的同一簇中。一个国家生产的出版物越多,其节点的大小就越大;合作越紧密,连接线就越粗。可以看出中国和美国的合作最紧密,美国的合作国家为最多。同时从协作世界地图中,根据国家和国家间的连线和线的粗细可以看出两者之间的合作程度,也表现出了中美之间的合作最深。从国家合作演化图(图2B)可以看出,一个国家的颜色是基于文章出版的年份。例如,中国的703篇文章主要在2020年出版,以绿色显示。从图中可以看出,美国是青色的(出版年份2019年5月),表明美国研究人员在此期间研究更加活跃;德国、伊朗和印度是黄色的,表明它们在该领域是新活跃的。"


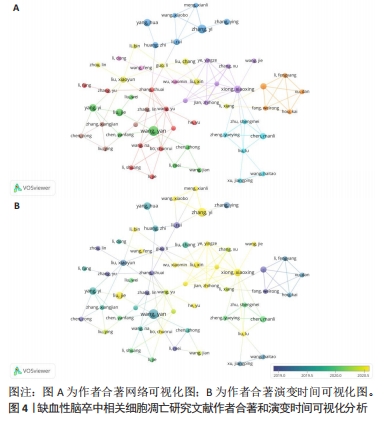
2.3 作者与共同作者的分析 共有5 182名作者在研究IS细胞凋亡的作用方面做出了贡献。共引作者分析是指2个作者的文献同时被第3个作者引用。共引次数越多,学术兴趣越接近,研究密度越接近[27]。对于共同作者分析,群集中研究方向相似的作者成为一组,并以相同的颜色标记。节点的大小代表作者的出版数量,线条的粗细代表作者之间的协作规模。在作者共同引用分析中(图4A),作者的相关性取决于同一篇文章引用他们的文章的次数。每个节点代表至少有25次引用的作者,121个人发表了不少于25次的文章,具有最高总链接强度的最大作者组由120个人组成。在这种情况下,相同的颜色代表在同一感兴趣主题内的作者,而同一集群中的作者则表示基于共同引用关系的紧密联系的群体。此外,每个圆圈的大小代表作者的引用次数,更多的引用产生更大的圆圈。并且,处于小圈子的科学家未来会成为在这一领域的领军者。作者的颜色是基于他们的平均出版年份(图4B)。Zhang Shuai和Guo Li在地图上显示为海蓝宝石,表明自该领域开始以来,他们一直在从事此项研究工作。在许多国家,随着经济的发展,他们也开始投入更多的注意力和资金用于科学研究以保持竞争力,甚至引领当今的前沿领域。同样也吸引了一些科学家的投入,图中的黄色圆圈标点就是较新的研究人员。"
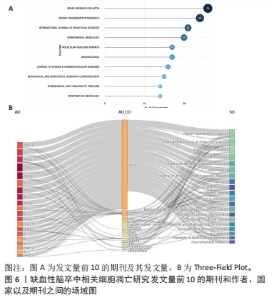
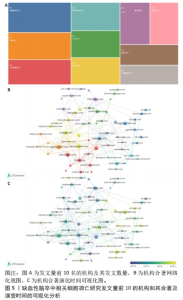
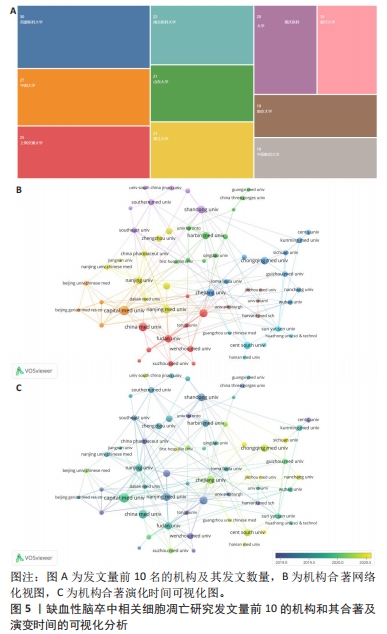
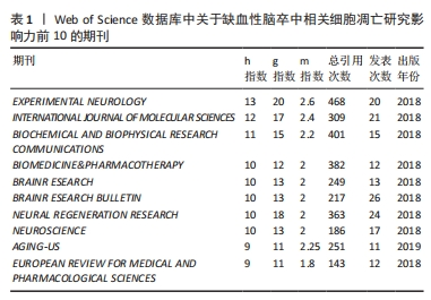
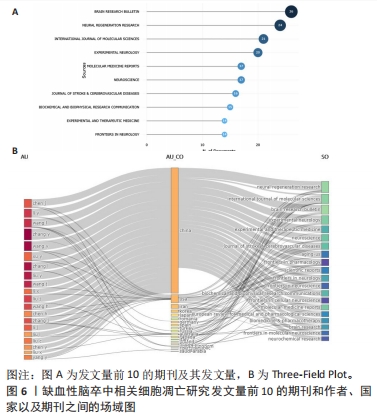
《BRAIN RESEARCH BULLETIN》期刊发表的文章最多,共包括了26篇文章。《NEURAL REGENERATION RESEARCH》发表了24篇文章,《INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES》发表21篇文章,其中排名前2名的期刊均为医学专业期刊,第3名的期刊为化学类期刊但其影响因子高达6.208,分区为Q1(图6A)。为了更好地了解作者、国家和期刊的关系,从Three-Field Plot中可以看到,矩形节点的高度与合作网络中某个国家、机构或期刊的出现频率成正比(图6B)。节点之间的线条宽度与连接数成比例。该图显示,中间表示的是国家,左边表示的是作者,右边表示的是期刊。中国是连接最多的国家,其次是美国和伊朗。作者中大部分都与中国的联系最大,可以明显地看出中国作者的生产力,同时基于规模(指数)影响力的评价指标,以H-index为主来客观评价期刊的影响力(表1),可以更直观地了解到期刊的生产力和影响力。"
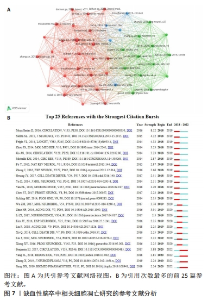
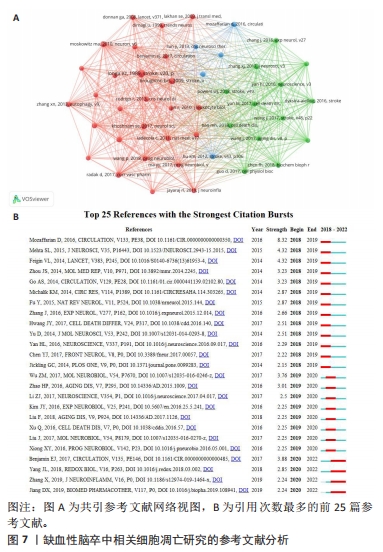
2.5 共同引用文献参考分析 文献共引分析通过分析文献被引用的频率来表达文献之间的关系[28]。知识库由共同引用的文章集合组成,而研究前沿由引用文章集合组成[29],同时共同引文网络强调与特定领域密切相关的研究主题[30]。考虑到引用的参考文献数量,参考文献的最小引用次数设置为20,共计分析所检索出的45篇文献。从可视化的图中可以看出,2个节点之间的线表示两者都在一篇出版物中被引用,较短的线表示2篇论文之间更密切的关系(图7A)。节点的大小表示总链接强度,表示文献的共同引用总数。此外,使用不同颜色的节点将论文划分为不同的簇:第1类(红色)包括27篇参考文献,主要关注神经元死亡和IS;第2簇(绿色)主要关注非编码RNA和IS的关系;第3类(蓝色)以基因方面为入手点。同时共同引用的参考文献爆发为研究重点的研究足迹提供了有用的见解,在CiteSpace中,状态数设置为2,g[0,1]=1.0,最小持续时间=1。图7B记录了具有强爆发的前25个共同引用的参考文献。其中爆发力最强(强度=8.32)的文章为“Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update A Report From the American Heart Association”在2018,2019两年间爆发[31]。值得注意的是,直到2022年,有4篇参考文献处于爆发状态,这表明接下来会继续进行此方向的深入研究[32-35]。"

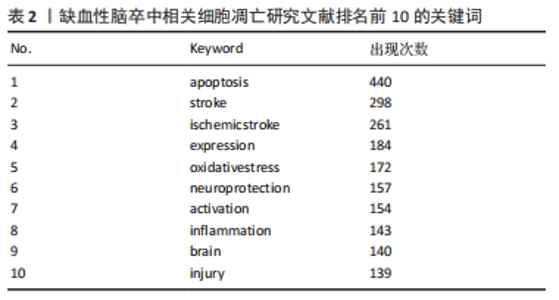
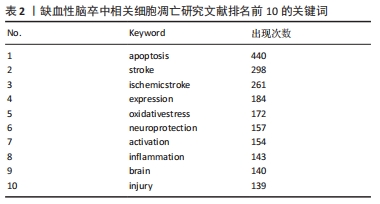
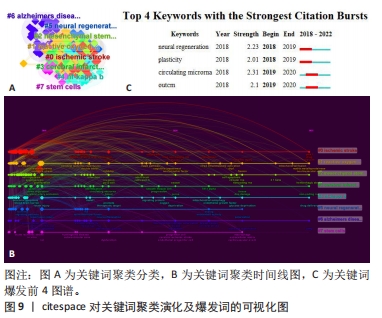
2.6 关键词共现聚类分析 关键词是对科学研究相关特征经高度凝练后的内容,可反映领域内热点及热点间联系。数据分析所分析的关键词共3 481个,将关键词阈值均设定为10,利用VOSviewer构建关键词共现网络,其中有181个关键词出现了10次以上。对其进行了可视化和聚类分析,其中圆圈越大说明其在文章中出现的次数越多,“apoptosis”出现的频率最多,通过在其出现时间可视化图中(图8A),颜色为青绿色,说明它出现的文章大概是在2019年发文量较多,其中黄色标点代表其近期出现的频率比较多,是新的热点。紧接着对关键词进行了图谱共现分析(图8B),靠近中心的颜色高亮区是出现频率最高的关键词,同时依据关键词出现的频率进行统计,排名前10的关键词见表2。结果显示,细胞凋亡、氧化应激、炎症是研究IS的主要病理因素。神经保护也成了一种主要的预防后遗症和康复治疗的手段。在关键词共现网络的基础上,利用局部线性回归算法对关键词进行聚类分析。通过citespace对关键词进行了编号聚类(图9A),共分为了7大类,数字越小说明聚类中包含的关键词越多,每个聚类是有多个紧密相关的词组成的。对于聚类分析,一般Q > 0.3意味着聚类结构显著,S > 0.5意味着聚类是合理的[36-38]。而此张图的Q=0.340 9,S=0.665 3这2个数值均达到了标准,说明此次数据分析合理。结果显示,聚类图谱中大多数聚类较集中,提示各聚类间联系紧密,研究主题接近。由于搜索主题为IS,故聚类#0为IS。聚类#1涉及活性氧的研究,聚类#2和聚类#7涉及干细胞的研究,聚类#4涉及核因子κB的研究,聚类#3和聚类#6分别涉及脑梗死和阿尔茨海默症的研究,聚类#5涉及神经再生的研究。同时对聚类的关键词从时间线上进行分析(图9B),可以看出每个关键词的出现在其年份的研究情况,前5个聚类时间跨度持续至整个X轴,说明是近些年来研究的主要方面的热点。同时还做了关键词的突现(图9C),关键词突现主要分析的是通过算法推导出能够反映时间段内兴起的或者持续受到关注的研究热点,反应研究领域内的热点变化及趋势。数据分析出4个爆发词,一般认为strength值大于2,这个词可以作为爆发词来进行参考。从4个词中可以看出神经再生、环状RNA等是近期和未来一段时间的研究热点。对于IS和细胞凋亡,虽然近期不是热点,但前几年的文章和研究提供了宝贵的研究数据。"

| [1] FESKE SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021;134(12):1457-1464. [2] SAINI V, GUADA L, YAVAGAL DR. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology. 2021;97(20 Suppl 2):S6-S16. [3] GUZIK A, BUSHNELL C. Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2017;23(1):15-39. [4] BELAGAJE SR. Stroke Rehabilitation. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2017;23(1):238-253. [5] LI J,WANG L,CHAO BH, et al. Prevalence of stroke in China:an epidemiological study based on the National Stroke Screening Survey. Lancet. 2015;386(S381):S349. [6] 吴亚哲,陈伟伟. 中国脑卒中流行概况[J]. 心脑血管病防治,2016,16(6):410-414. [7] COLEMAN ER, MOUDGAL R, LANG K, et al. Early Rehabilitation After Stroke: a Narrative Review. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017;19(12):59. [8] DURUKAN A, TATLISUMAK T. Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2007; 87(1):179-197. [9] DIRNAGL U, IADECOLA C, MOSKOWITZ MA. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22(9):391-397. [10] TANG H, GAMDZYK M, HUANG L, et al. Delayed recanalization after MCAO ameliorates ischemic stroke by inhibiting apoptosis via HGF/c-Met/STAT3/Bcl-2 pathway in rats. Exp Neurol. 2020;330:113359. [11] MAO R, ZONG N, HU Y, et al. Neuronal Death Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategy in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2022;38(10):1229-1247. [12] CANCINO CA, MERIGO JM, CORONADO F, et al. Forty Years ofComputers&Industrial Engineering:A Bibliometric Analysis. Comput Ind Eng. 2017;113:614-629. [13] DING Y, CHOWDHURY GG, FOO S. Bibliometric Cartography of Information Retrieval Research by Using Co-Word Analysis. Inform Process Manag. 2001;37(6):817-842. [14] QIU Y, YANG W, WANG Q, et al. Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women in this decade: a bibliometric assessment of current research and future hotspots. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13(1):121. [15] HE J, HE L, GENG B, et al. Bibliometric Analysis of the Top-Cited Articles on Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(5):1810-1818.e3. [16] HUANG X, LIU X, SHANG Y, et al. Current Trends in Research on Bone Regeneration: A Bibliometric Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8787394. [17] CHEN J, YAO M, ZHAO Y, et al. Use of acupuncture to treat cerebral infarction in the last 10 years: A Scopus-based literature analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(36):2944-2951. [18] 戴敏,王元姣.国内脑卒中患者排尿障碍的文献计量学分析[J]. 护理与康复,2019,18(12):9-12+16. [19] FENG X, LIU C, GUO Q, et al. Research progress in rehabilitation treatment of stroke patients: A bibliometric analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(15):1423-1430. [20] MA C, SU H, LI H. Global Research Trends on Prostate Diseases and Erectile Dysfunction: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study. Front Oncol. 2021;10:627891. [21] MA D, YANG B, GUAN B, et al. A Bibliometric Analysis of Pyroptosis From 2001 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2021;12:731933. [22] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [23] ARIA M, CUCCURULLO C. Bibliometrix: AnR-Toolfor Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J Informetr. 2017;11(4):959-975. [24] ROMERO L, PORTILLO-SALIDO E. Trends in Sigma-1 Receptor Research: A 25-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:564. [25] FERNANDES S, JIT M, BOZZANI F, et al. A bibliometric analysis of systematic reviews on vaccines and immunisation. Vaccine. 2018;36(17):2254-2261. [26] YIN J, WAN J, ZHU J, et al. Global trends and prospects about inflammasomes in stroke: a bibliometric analysis. Chin Med. 2021;16(1):53. [27] CHENG P, TANG H, DONG Y, et al. Knowledge Mapping of Research on Land Use Change and Food Security: A Visual Analysis Using CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(24):13065. [28] YANG X, WANG X, LI X, et al. Exploring emerging IoT technologies in smart health research: a knowledge graph analysis. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020;20(1):260. [29] CHEN S, BIE R, LAI Y, et al. Trends and Development in Enteral Nutrition Application for Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: A Scientometric Research Study (1996-2018). Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:246. [30] SU Y, YU Y, ZHANG N. Carbon emissions and environmental management based on Big Data and Streaming Data: A bibliometric analysis. Sci Total Environ. 2020;733:138984. [31] WRITING GROUP MEMBERS, MOZAFFARIAN D, BENJAMIN EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38-e360. [32] BENJAMIN EJ, BLAHA MJ, CHIUVE SE, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135(10):e146-e603. [33] YANG JL, MUKDA S, CHEN SD. Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2018;16:263-275. [34] ZHANG X, ZHU XL, JI BY, et al. LncRNA-1810034E14Rik reduces microglia activation in experimental ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):75. [35] JIANG D, SUN X, WANG S, et al. Upregulation of miR-874-3p decreases cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by directly targeting BMF and BCL2L13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:108941. [36] LIU X, LIU N, ZHOU M, et al. Bibliometric analysis of global research on the rehabilitation of spinal cord injury in the past two decades. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;15:1-14. [37] LIU ZG, YIN YM, LIU WD, et al.Visualizing the intellectual structure and evolution of innovation systems research:a bibliometric analysis.Scientometrics.2015;103(1):135-158. [38] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310. [39] SONG Y, LI Z, HE T, et al. M2 microglia-derived exosomes protect the mouse brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury via exosomal miR-124. Theranostics. 2019;9(10):2910-2923. [40] WU F, HAN B, WU S, et al. Circular RNA TLK1 Aggravates Neuronal Injury and Neurological Deficits after Ischemic Stroke via miR-335-3p/TIPARP. J Neurosci. 2019;39(37):7369-7393. [41] SCHMITZ SU, GROTE P, HERRMANN BG. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(13):2491-2509. [42] DENG QW, LI S, WANG H, et al. Differential long noncoding RNA expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for detection of acute ischemic stroke. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132(14):1597-1614. [43] WANG Q, LIU X, ZHU R. Long Noncoding RNAs as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Ischemic Stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(10):1115-1121. [44] WANG P, SHAO BZ, DENG Z, et al. Autophagy in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;163-164:98-117. [45] YANG JL, MUKDA S, CHEN SD. Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2018;16:263-275. [46] WU L, XIONG X, WU X, et al. Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Prevent Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;13:28. [47] DATTA A, SARMAH D, MOUNICA L, et al. Cell Death Pathways in Ischemic Stroke and Targeted Pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(6):1185-1202. [48] ANASTASIOU E, LORENTZ KO, STEIN GJ, et al. Prehistoric schistosomiasis parasite found in the Middle East. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(7):553-554. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [2] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [3] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [4] | Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497. |
| [5] | Guan Jinqi, Sun Pingping, Bian Jing, Yan Xue, Zhang Weimin. Gastrodin intervention attenuates inflammatory injury in ischemic stroke rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4535-4540. |
| [6] | Ma Wanli, Yang Hongsheng, Qu Bo, Zhang Zhengdong, Gong Kai, Lin Yanshui. Mechanisms by which baicalein protects against steriod-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3661-3668. |
| [7] | Xia Tianqing, Rong Mengwei, Dan Cunyan, Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Song Lijuan, Ma Cungen. Frontier hot trends in ischemic stroke and vascular regeneration based on bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3692-3698. |
| [8] | Hou Zhaomeng, Su Shaoting, Chen Longhao, Wei Guikang, Zhou Honghai. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and trends in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3424-3430. |
| [9] | Wan Jun, Bai Yanjie, Wang Yan, Chen Shuying, Chen Limin, Xiao Yuqian, Sun Kexin. Mechanism of action and related signaling pathways of long non-coding RNAs in neuroimmuno-inflammatory response after ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3265-3271. |
| [10] | Chen Simin, Hu Yingjun, Yan Wenrui, Ji Le, Shao Mengli, Sun Ze, Zheng Hongxing, Qi Shanshan. Establishment and evaluation of a streptozotocin-induced diabetic encephalopathy rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 237-241. |
| [11] | Xie Enli, Tao Huimin. Application trends of blood flow restriction training in clinical rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 258-262. |
| [12] | Chen Na, Wang Yanlin, Sun Huifang, Fan Feiyan, Li Donghong, Zhang Yunke. Shexiang Huangqi compound dripping pills-containing serum promotes proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2960-2966. |
| [13] | Hong Jing, Lu Congfei, Huang Chenbin, Jiang Qian, Liu Jingxiong. Visualization analysis of hot spots and trends in material biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2358-2363. |
| [14] | Zheng Ying, Huang Kemin. Bibliometrics and visualization-based analysis of research landscape of exosomes and foresight [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2126-2132. |
| [15] | Fan Zhihong, Zhang Xian, Li Chao. Wnt signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1950-1955. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||