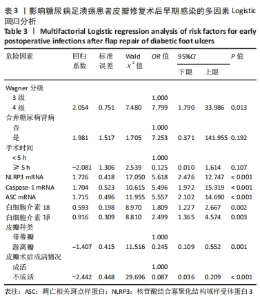
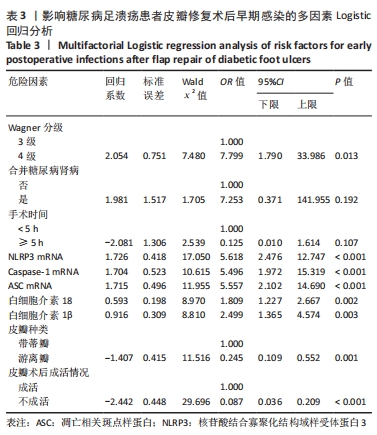
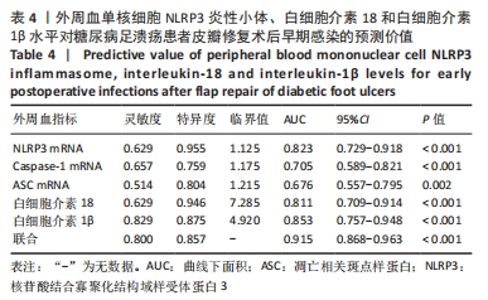
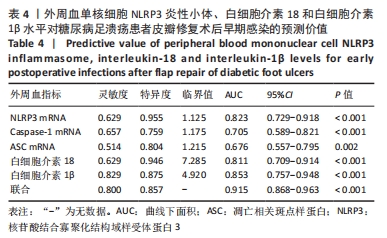
[1] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157(11):107843.
[2] LIN X, XU Y, PAN X, et al. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: an analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14790.
[3] 张悦,周冬梅,李伟,等.影响糖尿病足的危险因素及溃疡严重程度对预后的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(22):4911-4914.
[4] KARTIKA RW, ALWI I, SUYATNA FD, et al. The role of VEGF, PDGF and IL-6 on diabetic foot ulcer after Platelet Rich Fibrin + hyaluronic therapy. Heliyon. 2021;7(9):e07934.
[5] 莫小金,常树森,魏在荣,等.显微削薄胸背动脉穿支皮瓣修复糖
尿病足溃疡的临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(10): 1266-1272.
[6] 苗晋鑫,彭孟凡,任伟宏,等.NLRP3炎症小体在糖尿病及并发症的作用及中药经NLRP3对其影响研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(16):254-260.
[7] 谷涌泉.中国糖尿病足诊治指南[J].中国临床医生杂志,2020,48(1):
19-27.
[8] 中华人民共和国卫生部.医院感染诊断标准(试行)[J].中华医学杂志,2001,81(5):314-320.
[9] BUS SA, VAN NETTEN JJ, HINCHLIFFE RJ, et al. Standards for the development and methodology of the 2019 International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot guidelines. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020; 36 Suppl 1:e3267.
[10] LUO Z, FABRE G, RODWIN VG. Meeting the Challenge of Diabetes in China. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2020;9(2):47-52.
[11] 童利伟,刘素筠,侯雨,等.糖尿病足溃疡合并铜绿假单胞菌感染PI3K-Akt-mTOR 信号通路表达与预后[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2022,32(17):2606-2610.
[12] KERR M, BARRON E, CHADWICK P, et al. The cost of diabetic foot ulcers and amputations to the National Health Service in England. Diabet Med. 2019;36(8):995-1002.
[13] LU J, DEFAZIO MV, LAKHIANI C, et al. Limb Salvage and Functional Outcomes following Free Tissue Transfer for the Treatment of Recalcitrant Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2019;35(2): 117-123.
[14] 孙建新.手部创面皮瓣修复术后感染的相关因素分析[J].中国医刊, 2020,55(9):990-993.
[15] GHOTASLOU R, MEMAR MY, ALIZADEH N. Classification, microbiology and treatment of diabetic foot infections. J Wound Care. 2018;27(7): 434-441.
[16] 童利伟,刘素筠,侯雨,等.糖尿病足溃疡合并铜绿假单胞菌感染PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路表达与预后[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2022,32(17):2606-2610.
[17] 谷宏伟,李希娜,魏华,等.糖尿病足溃疡患者细菌感染特点及耐药影响因素分析[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2022,20(11):76-79.
[18] 中国中西医结合学会周围血管病专业委员会.中西医结合防治糖尿病足中国专家共识(第1版)[J].血管与腔内血管外科杂志,2019, 5(5):379-402.
[19] TAN WS, ARULSELVAN P, NG SF, et al. Improvement of diabetic wound healing by topical application of Vicen‐ in‐2 hydrocolloid film on Sprague Dawley rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):20.
[20] WEIGELT C, ROSE B, POSCHEN U, et al. Immune media tors in patients with acute diabetic foot syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(8): 1491‐1496.
[21] TUTTOLOMONDO A, MAIDA C, PINTO A. Diabetic foot syn‐ drome:Immune‐inflammatory features as possible car‐ diovascular markers in diabetes. World J Orthoped. 2015;6(1):62‐76.
[22] 李小兵,刘洪均,杨超,等.带阔筋膜游离股前外侧皮瓣修复糖尿病足溃疡伴骨外露[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(1):86-91.
[23] 贾慧,鞠上,王刚,等.糖尿病足溃疡Wagner分级与炎性反应指标的关系[J].血管与腔内血管外科杂志,2022,8(7):779-782.
[24] SHARMA BR, KANNEGANTI TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5):550-559.
[25] TARTEY S, KANNEGANTI TD. Differential role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in infection and tumorigenesis. Immunology. 2019; 156(4):329-338.
[26] SHARIF H, WANG L, WANG WL, et al. Structural mechanism for NEK7-licensed activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2019; 570(7761):338-343.
[27] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328.
[28] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(8):477-489.
[29] ZITO G, BUSCETTA M, CIMINO M, et al. Cellular Models and Assays to Study NLRP3 Inflammasome Biology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4294.
[30] 卫会明,郑蕾,魏世杰,等.皮瓣修复术后早期感染血浆NLRP3炎症小体-IL-1β信号通路的表达[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2022, 32(13):1996-2000.
[31] 欧海燕,段娅娟,陈兰.外周血单核细胞NLRP3炎性小体对脓毒症急性肺损伤患者病情严重程度的诊断价值[J].实用医学杂志, 2020,36(3):380-384.
[32] FUSCO R, SIRACUSA R, GENOVESE T, et al. Focus on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4223. |