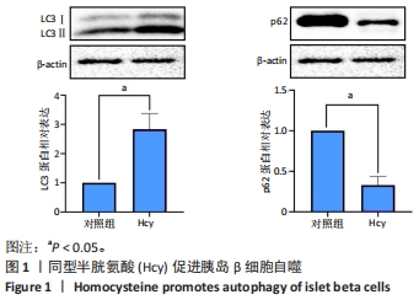
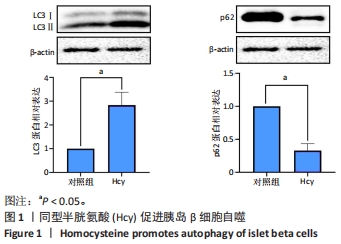
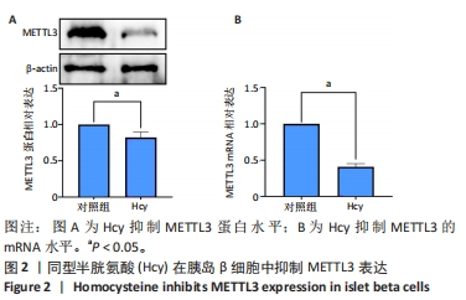
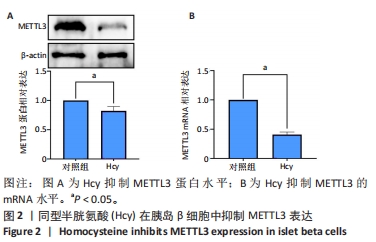
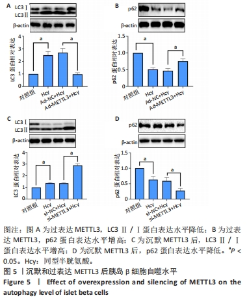
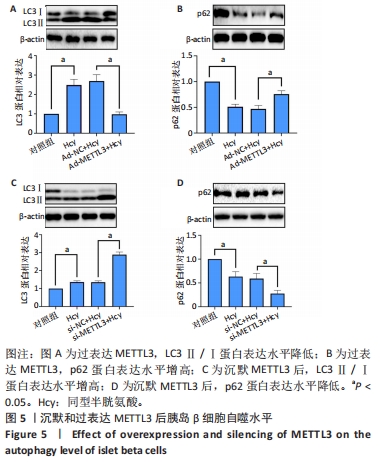
[1] GUIEU R, RUF J, MOTTOLA G. Hyperhomocysteinemia and cardiovascular diseases. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2022;80(1):7-14.
[2] CHENG Y, WANG C, ZHANG X, et al. Circulating homocysteine and folate concentrations and risk of type 2 diabetes: A retrospective observational study in Chinese adults and a Mendelian randomization analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:978-998.
[3] 陈辛玲,王生兰.细胞自噬过程、通路、调控及其与肺动脉高压的多重相关性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):311-316.
[4] 丁宇,王彦丰,李小溪,等.细胞自噬与常见老年病的关联性研究进展[J].国际老年医学杂志,2022,43(4):468-471.
[5] 高源,揭育祯,马天龙,等.miR-488-3p靶向调控RAP1A在同型半胱氨酸介导肝细胞自噬的作用研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2022,32(9):1-9.
[6] 赵钎汐,杨淑德,郭澍.METTL3对细胞分化调控的研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2022,33(8):508-509,514-515.
[7] LI X, JIANG Y, SUN X, et al. METTL3 is required for maintaining β-cell function. Metabolism. 2021;116:154702.
[8] 张晴,高春兰,于飞飞,等.同型半胱氨酸致胰岛β细胞凋亡中肝配蛋白A型受体2 DNA甲基化升高[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(5):714-719.
[9] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119.
[10] KOTWAS A, KARAKIEWICZ B, ZABIELSKA P, et al. Epidemiological factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus: evidence from the Global Burden of Disease. Arch Public Health. 2021;79(1):110.
[11] 吕承安,王若然,孟卓贤.2型糖尿病进程中胰岛β细胞功能变化的分子机制[J].遗传,2022,44(10):840-852.
[12] CASSIDY FC, SHORTISS C, MURPHY CG, et al. Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on human bone marrow stromal cell number and phenotypic characteristics. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:2476.
[13] 陈艳,王萍.同型半胱氨酸和总胆红素对胰岛β细胞功能的交互作用分析[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2023,31(1):47-52.
[14] 揭育祯,杨慧霞,周瑜瑾,等.TRPC6 DNA甲基化在同型半胱氨酸致胰岛β细胞焦亡中的作用研究[J].广东医学,2022,43(2):162-168.
[15] MIZUSHIMA N, LEVINE B. Autophagy in Human Diseases. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(16): 1564-1576.
[16] GE X, WANG L, FEI A, et al. Research progress on the relationship between autophagy and chronic complications of diabetes. Front Physiol. 2022;13:956344.
[17] KIM J, PARK K, KIM MJ, et al. An autophagy enhancer ameliorates diabetes of human IAPP-transgenic mice through clearance of amyloidogenic oligomer. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):183.
[18] 任海文,王林华,龚权,等.胰岛β细胞自噬及其影响因素[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 2022,30(10):796-800.
[19] ZHANG Y, ZHOU XA, LIU C, et al. Vitamin B6 Inhibits High Glucose-Induced IsletβCell Apoptosis by Upregulating Autophagy. Metabolites. 2022;12(11):1048.
[20] CAI XS, SHE MQ, XU MY, et al. GLP - 1 treatment protects endothelial cells from oxidative stress -induced autophagy and endothelial dysfunction. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14: 1696-1708.
[21] LAMBELET M, TERRA LF, FUKAYA M, et al. Dysfunctional autophagy following exposure to pro - inflammatory cytokines contributes to pancreatic β-cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):96.
[22] MARIÑO G, NISO SM, BAEHRECKE EH, et al. Self-consumption: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(2):81-94.
[23] SU X, QU Y, MU D. The Regulatory Network of METTL3 in the Nervous System: Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules. 2023;13(4):664.
[24] WANG JN, WANG F, KE J, et al. Inhibition of METTL3 attenuates renal injury and inflammation by alleviating TAB3 m6A modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(640):eabk2709.
[25] LI X, YUAN B, LU M, et al. The methyltransferase METTL3 negatively regulates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) progression. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):7213.
[26] CHEN H, PAN Y, ZHOU Q, et al. METTL3 Inhibits Antitumor Immunity by Targeting m 6 A-BHLHE41-CXCL1/CXCR2 Axis to Promote Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(4):891-907.
[27] PENG Z, GONG Y, WANG X, et al. METTL3-m 6 A-Rubicon axis inhibits autophagy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Ther. 2022;30(2):932-946.
[28] 伍义文,曹健斌,黄维佳,等.m6A甲基转移酶METTL3介导miR-127调控非小细胞肺癌细胞系自噬的机制研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2022,37(2):12-16+32.
[29] ZHOU S,SUN Y,XING Y, et al. Exenatide ameliorates hydrogen peroxide-induced pancreaticβ-cell apoptosis through regulation of METTL3-mediated m 6 A methylation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;924:174960.
[30] WANG Y, SUN J, LIN Z, et al. m6A mRNA Methylaon Controls Funconal Maturaon in Neonatal Murine β-Cells. Diabetes. 2020;69(8):1708-1722.
[31] CHENG Y, YAO XM, ZHOU SM, et al. The m 6 A Methyltransferase METTL3 Ameliorates Methylglyoxal-Induced Impairment of Insulin Secretion in PancreaticβCells by Regulating MafA Expression. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:910868.
[32] FANG J, CHEN Z, LAI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived HIF-1α-overexpressed extracellular vesicles ameliorate hypoxia-induced pancreaticβcell apoptosis and senescence through activating YTHDF1-mediated protective autophagy. Bioorg Chem. 2022;129:106194.
|