Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2527-2533.doi: 10.12307/2024.305
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Lipopharyngeal Qibi Formula on swallowing function and apoptosis in central cortical swallowing neurons in rats after stroke
Li Yanjie1, 2, Li Sijin1, Hua Xiaoqiong1, Qin Hewei1, 2, Jin Xiaoqin1, Zhang Zhixin1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-08Accepted:2023-04-20Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-29 -
Contact:Qin Hewei, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Li Yanjie, Master, Chief physician, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Science and Technology Plan Program, No. 222102310569 (to LYJ); Henan Provincial TCM Scientific Research Special Project, No. 2022ZY1083 (to LYJ); Henan Provincial TCM Top Talent Training Project, No. [2018]35 (to LYJ); Central China Young Top Talent Project of Central China Talent Program, No. [2021]1 (to QHW); Henan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. 212300410191 (to JXQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yanjie, Li Sijin, Hua Xiaoqiong, Qin Hewei, Jin Xiaoqin, Zhang Zhixin. Effects of Lipopharyngeal Qibi Formula on swallowing function and apoptosis in central cortical swallowing neurons in rats after stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2527-2533.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
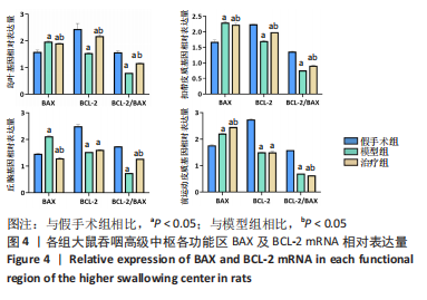
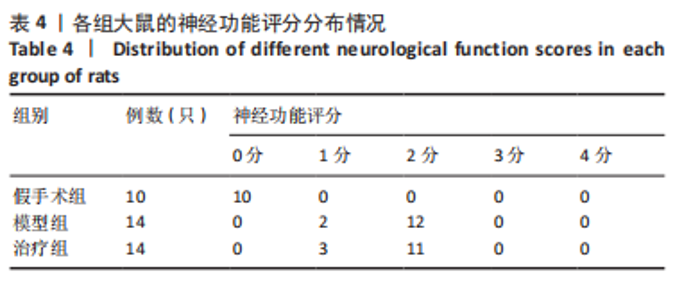
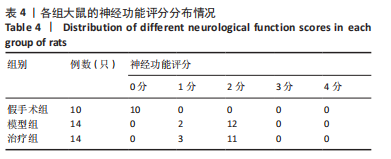
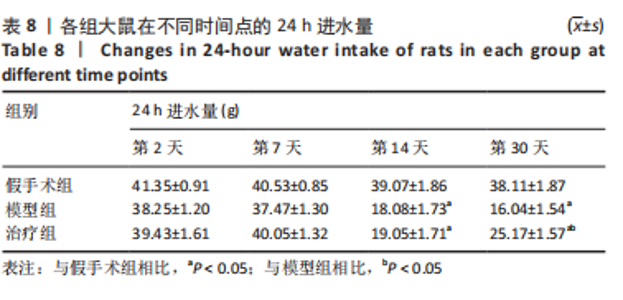
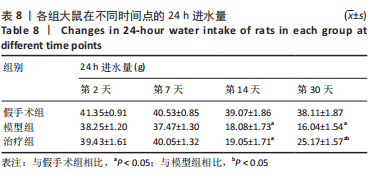
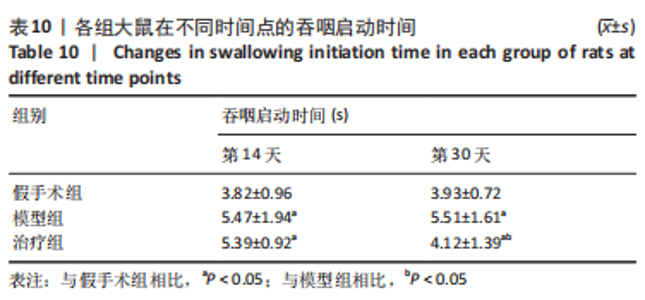
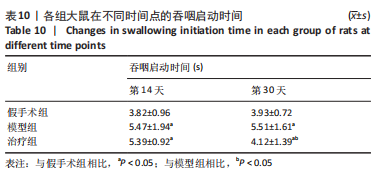
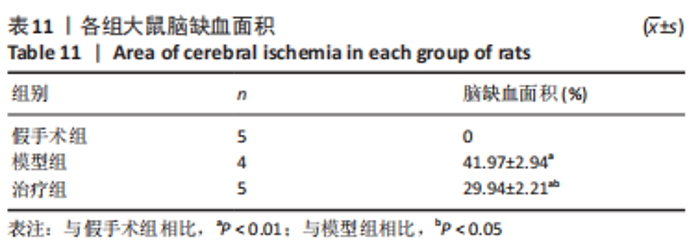
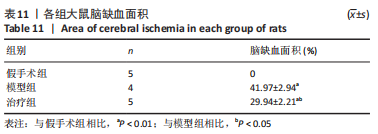
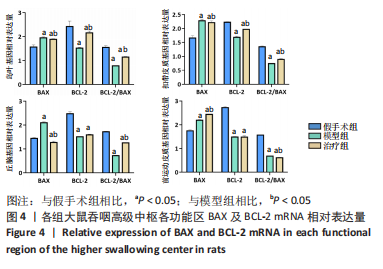
2.8 各组大鼠岛叶、前运动皮质、扣带皮质、丘脑的BAX及BCL-2 mRNA的表达 与假手术组相比,模型组和治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质、丘脑、前运动皮质BCL-2 mRNA表达和BCL-2/BAX比值均下降(P < 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组和治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质、前运动皮质BAX mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.05),模型组丘脑BAX mRNA表达也升高(P < 0.05),而治疗组丘脑BAX mRNA表达下降(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质BCL-2 mRNA表达和BCL-2/BAX比值均升高(P < 0.05),BAX mRNA 表达均下降(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,治疗组前运动皮质BCL-2 mRNA表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),BAX mRNA表达增加(P < 0.05),BCL-2/BAX比值下降(P < 0.05),见图4。"
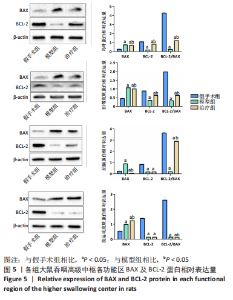
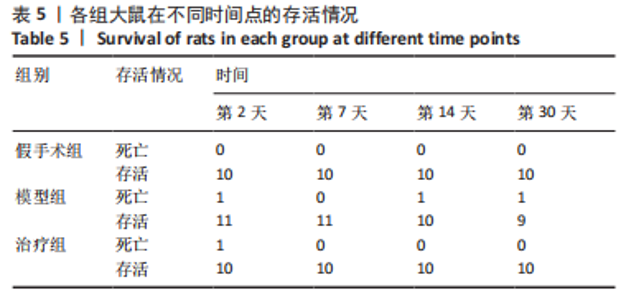
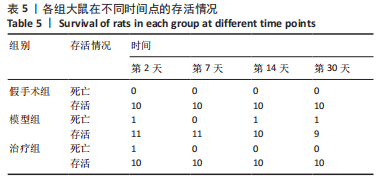
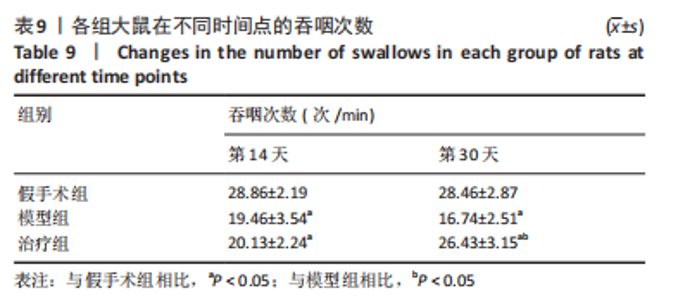
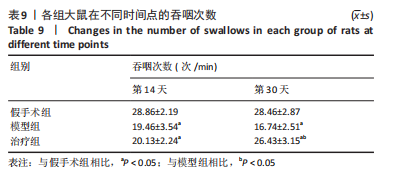
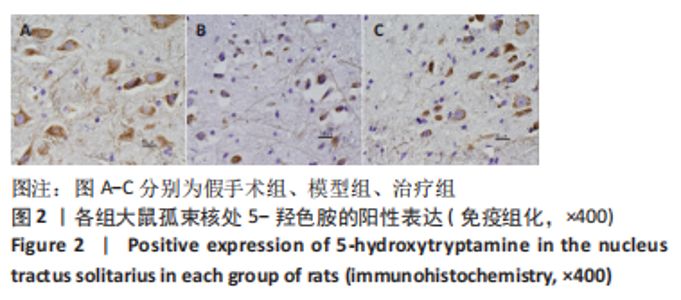
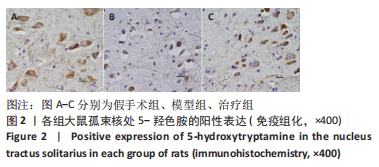
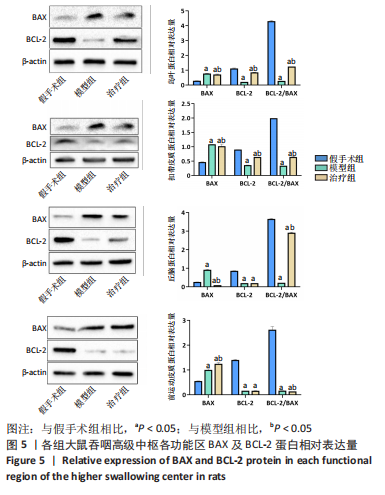
2.9 各组大鼠岛叶、前运动皮质、扣带皮质、丘脑的BAX及BCL-2蛋白表达 与假手术组相比,模型组和治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质、丘脑、前运动皮质BCL-2蛋白表达和BCL-2/BAX比值均下降(P < 0.05);与假手术组相比,模型组和治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质、前运动皮质BAX蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05),模型组丘脑BAX蛋白表达也升高(P < 0.05),而治疗组丘脑BAX蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,治疗组岛叶、扣带皮质BCL-2蛋白表达和BCL-2/BAX比值均升高(P < 0.05),BAX 蛋白表达均下降(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,治疗组前运动皮质BCL-2蛋白表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),BAX蛋白表达增加(P < 0.05),BCL-2/BAX比值下降(P < 0.05),见图5。"
| [1] BATH PM, LEE HS, EVERTON LF. Swallowing therapy for dysphagia in acute and subacute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;10(10): CD000323. [2] ROFES L, MURIANA D, PALOMERAS E, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and complications of oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients: A cohort study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018:e13338. [3] LOPES M, FREITAS E, OLIVEIRA M, et al. Impact of the systematic use of the Gugging Swallowing Screen in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2019;26(5):722-726. [4] ARNOLD M, LIESIROVA K, BROEG-MORVAY A, et al. Dysphagia in Acute Stroke: Incidence, Burden and Impact on Clinical Outcome. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148424. [5] YANG X, XIANG X, LIU S. A Rare Cause of Dysphagia: Diagnosis and Treatment. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(6):e28-e30. [6] 河南中医药大学. 一种治疗脑卒中后吞咽障碍的中药: CN201710010969.0[P]. 2017-03-15. [7] SUGIYAMA N, NISHIYAMA E, NISHIKAWA Y, et al. A novel animal model of dysphagia following stroke. Dysphagia. 2014;29(1):61-67. [8] 李彩彩.通咽喷雾剂对脑卒中后吞咽困难大鼠的治疗作用及机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2018. [9] 袁清洁,冯学功,刘建勋,等.通咽喷雾剂对短暂性大脑中动脉栓塞模型大鼠吞咽功能的干预效应[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2019,17(13):1965-1969. [10] CULLINS MJ, CONNOR NP. Reduced tongue force and functional swallowing changes in a rat model of post stroke dysphagia. Brain Res. 2019;1717:160-166. [11] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91. [12] PAXINOS G, WATSON C.大鼠脑立体定位图谱[M].诸葛启钏主译.北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:64-148. [13] WILMSKOETTER J, BONILHA L, MARTIN-HARRIS B, et al. Mapping acute lesion locations to physiological swallow impairments after stroke. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101685. [14] HUANG PL, WANG SJ, SUN RF, et al. Increased activation of the caudate nucleus and parahippocampal gyrus in Parkinson’s disease patients with dysphagia after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: a case-control study. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(5):1051-1058. [15] KIST M, VUCIC D. Cell death pathways: intricate connections and disease implications. EMBO J. 2021;40(5):e106700. [16] 王卫东,陈正堂.Bcl-2/Bax比率与细胞“命运”[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2007,14(4):393-396. [17] 覃小军,冯爱平,黄其军,等.黄连对糖尿病脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠Bax和Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响[J].实用老年医学,2017,31(11):1021-1024. [18] KESSLER JP, JEAN A. Inhibition of the swallowing reflex by local application of serotonergic agents into the nucleus of the solitary tract. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985;118(1-2):77-85. [19] BIEGER D. Role of bulbar serotonergic neurotransmission in the initiation of swallowing in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1981;20(11): 1073-1083. [20] 郭威. GAD67-GFP基因敲入小鼠谷氨酸能、5-HT能和SP能终末与三叉神经中脑核神经元联系的形态学研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008. [21] 王炯妹.任督通调针刺法联合单元综合疗法治疗卒中后吞咽障碍[J].中医学报,2020,35(11):2459-2463. |
| [1] | Zhang Ming, Wang Bin, Jia Fan, Chen Jie, Tang Wei. Application of brain-computer interface technology based on electroencephalogram in upper limb motor function rehabilitation of stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [2] | Chang Wanpeng, Zhang Zhongwen, Yang Yulin, Zi Yang, Yang Mengqi, Du Bingyu, Wang Nan, Yu Shaohong. Efficacy of rehabilitation exoskeleton robots on post-stroke lower limb motor dysfunction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 321-328. |
| [3] | Wu Xiaodan, Wang Zhiguo, Zhan Ying, Zhang Guoxu. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model induced by 32P-beta ray radiation and the mechanism of injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2173-2179. |
| [4] | Xu Kangli, An Lanhua, Zhang Jinsheng, Du Xiaoyan, Yin Lele, Zhang Xixian. Research hotspots and frontiers of functional magnetic resonance imaging in treatment of ischemic stroke by traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1789-1796. |
| [5] | Ying Chunmiao, Pan Xiaolong, Liu Feixiang, Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 121-130. |
| [6] | Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Han Hongxia, Hou Miaomiao, Ma Cungen, Song Lijuan, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate glial scar formation in cerebral ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [7] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [8] | Yu Wenqiang, Ren Fuchao, Shi Guohong, Xu Yuanjing, Liu Tongyou, Xie Youzhuan, Wang Jinwu, . Methods and application of gait analysis of lower limbs after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1257-1263. |
| [9] | Liu Shiwen, Liu Quanfeng, Yang Zhibo, Duan Changqiu, Zhang Baoying, Tan Yue, Ai Changshan, Jiang Huiqiang, Feng Xugang, Kong Nianhua. Rhythmic auditory stimulation for non-acute dyskinesia in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5583-5588. |
| [10] | Wang Shaona, Liu Feixiang, Ying Chunmiao, Gao Chen, Zhang Yunke. Action mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in regulating blood-brain barrier after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5377-5384. |
| [11] | Zhu Junjie, Wang Haihuang, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Meta-analysis of the association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms and hemorrhagic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3763-3772. |
| [12] | Yin Yikun, Wang Jialin, Sun Junzhi. Therapeutic effect of different-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations on post-stroke cognitive impairment: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3274-3280. |
| [13] | Wei Zhihui, Liu Feixiang, Pan Xiaolong, Sun Shibiao, Zhang Yunke. Mechanism of Rehmannia glutinosa combined with mesenchymal stem cells in treating ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 3070-3076. |
| [14] | Hu Lingling, Ni Jun, Fu Gang, Zhang Jing. Pathological changes and expression of related adhesion molecules in vascular endothelial cell injury in heatstroke pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2644-2650. |
| [15] | Li Yong, Yuan Jianmei, Lu Danni, Ren Mihong, Deng Bowen, Wang Jiajun, Ma Rong, Xie Qian, Li Jinxiu, Xu Zhuo, Wang Jian. Comparison of cerebral microcirculation perfusion in rat models of middle cerebral artery occlusion prepared through common carotid artery insertion and external carotid artery insertion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1683-1691. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||