Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2173-2179.doi: 10.12307/2024.303
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model induced by 32P-beta ray radiation and the mechanism of injury
Wu Xiaodan1, 2, 3, 4, Wang Zhiguo1, 2, 3, 4, Zhan Ying1, 2, 3, 4, Zhang Guoxu1, 2, 3, 4
- 1General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 2Nuclear Background Compound War Trauma Treatment Laboratory, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 3Liaoning Key Laboratory of Nuclear Medicine Molecular Imaging, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 4High Quality Disciplines of Department of General Logistics Medicine, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-16Accepted:2023-04-12Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Zhang Guoxu, Master, Chief physician, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wu Xiaodan, Master, Pharmacist in charge, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xiaodan, Wang Zhiguo, Zhan Ying, Zhang Guoxu. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model induced by 32P-beta ray radiation and the mechanism of injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2173-2179.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
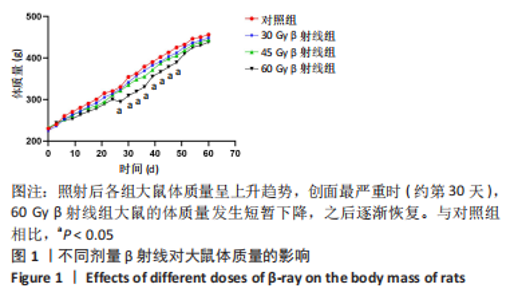
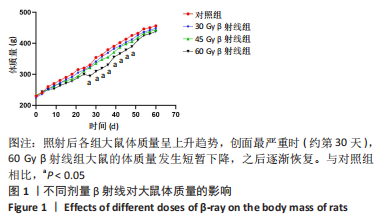
2.1 实验动物数量分析 选取69只SD大鼠,随机分为30 Gy、45 Gy、60 Gy β射线组(n=21)及对照组(n=6),造模后,30,45和60 Gy β射线组分别于照射后第7,15,30,45,60天各取3只大鼠切取皮肤组织观察损伤情况,每组中6只大鼠继续留观直到实验结束,实验过程中无意外死亡,所有大鼠均进入结果分析。 2.2 不同剂量β射线对SD大鼠体质量的影响 30 Gy、45 Gy以及60 Gy β射线单次局部照射后,各组大鼠饮食饮水正常,体质量呈逐渐增加趋势,各剂量组无统计学差异。与对照组相比,60 Gy剂量组在照射后第30天体质量有所下降(P < 0.05),之后逐渐恢复,见图 1。"
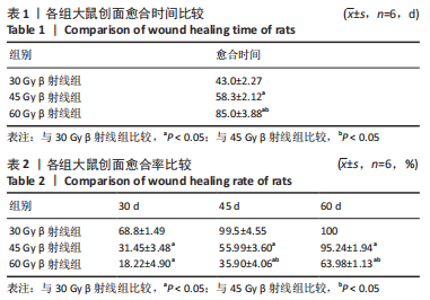
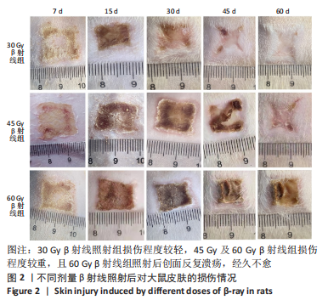
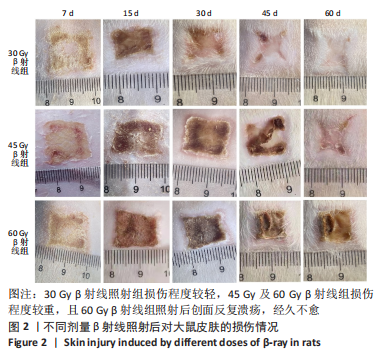
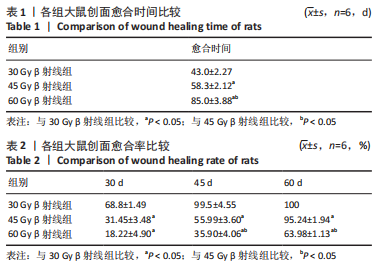
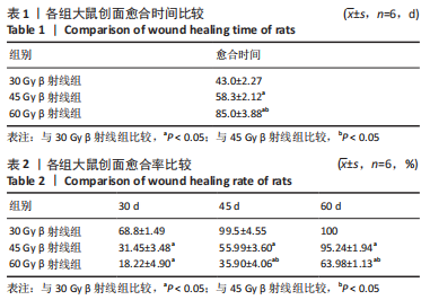
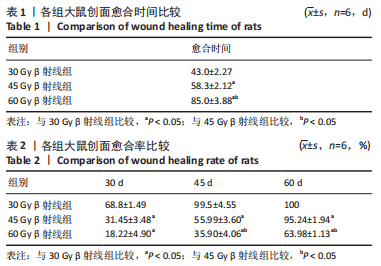
照射后第7天,各组大鼠照射部位均出现干性脱皮,45,60 Gy β射线组开始出现少量充血性红斑。照射后第15天,30 Gy β射线组出现少量片状红斑,45,60 Gy β射线照射部位皮肤红肿,出现显著性片状红斑,结痂,创面扩大。照射后第30天,30 Gy β射线组出现显著性片状红斑,创面结痂;45 Gy β射线组照射野皮肤结痂融合,创面扩大不明显;60 Gy β射线组照射野皮肤结痂加深、融合,有稀薄渗出液。照射后第45天,45 Gy β射线组出现痂皮脱落,60 Gy β射线组出现少量痂皮脱落,创面有收缩趋势,同时可观察到30 Gy β射线组痂皮脱落创面基本恢复。照射后第50天,45 Gy β射线组可见大量新生上皮部分覆盖创面,60 Gy β射线组可见少量痂皮脱落。照射后第60天,45 Gy β射线组大鼠创面基本恢复,未见毛发生长;60 Gy β射线组大鼠创面仍有大部分结痂未脱落,且创面溃疡反复迁延不愈。各组大鼠创面愈合时间及愈合率见表1,2。"
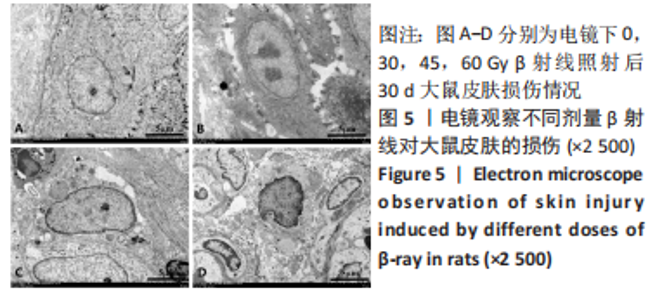
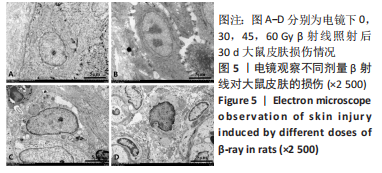
2.4 苏木精-伊红染色和Masson染色观察β射线对大鼠皮肤组织病理学损伤 苏木精-伊红染色和Masson染色结果显示:对照组大鼠皮肤表皮层细胞排列清晰,皮肤附属器结构完整。照射后15 d,30 Gy β射线组表皮细胞、毛囊上皮细胞肿胀,可见到坏死细胞,附属器减少,周围少量炎症细胞浸润;45 Gy以及60 Gy β射线组表皮可见小灶状缺失灶,浅表糜烂加深,真皮内胶原纤维出现水肿、融解、断裂、排列紊乱,其内有散在炎症细胞浸润。照射后30 d,30 Gy β射线组真皮内胶原纤维肿胀,胶原纤维断裂,溶解,排列紊乱;45 Gy β射线组可见上皮细胞变性坏死,真皮层胶原纤维断裂,炎性细胞浸润;60 Gy β射线组真皮层大量断裂,成纤维细胞很少,大量炎性细胞浸润。照射后45 d,30 Gy β射线组有新生上皮覆盖创面,新生肉芽组织明显,胶原纤维增生明显,排列较为整齐;45 Gy β射线组可见大量胶原纤维增生及上皮组织向创面中心爬行,胶原纤维丰富、真皮深层及皮下组织水肿较轻;60 Gy β射线组可见少量胶原纤维增生,真皮层可见大量炎性细胞浸润。照射后60 d,45 Gy β射线组有大量新生上皮覆盖创面,胶原纤维增生明显,排列整齐;60 Gy β射线组真皮层结缔组织有少量增生,皮肤表层结构有明显缺损。见图3,4。"
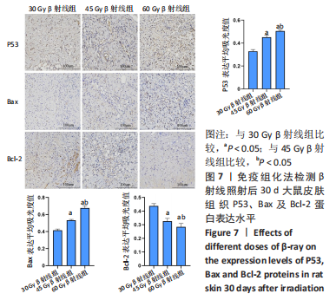
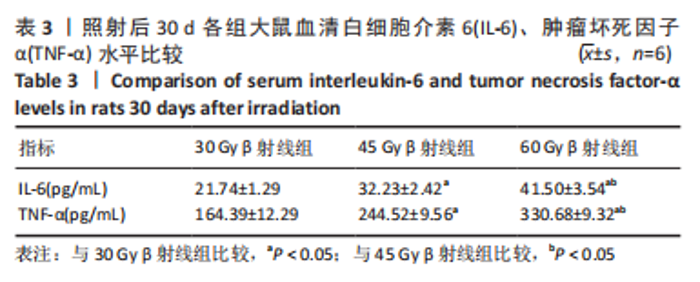
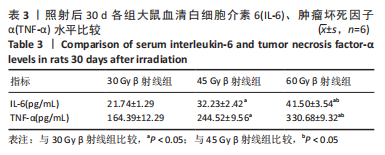
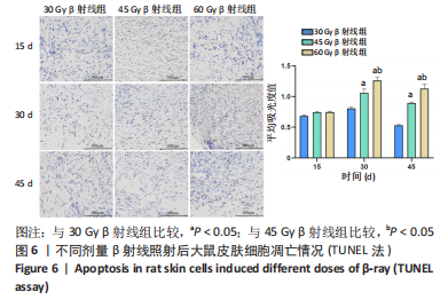
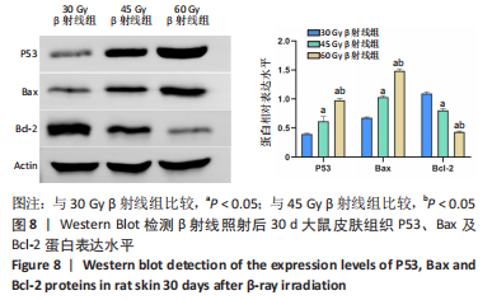
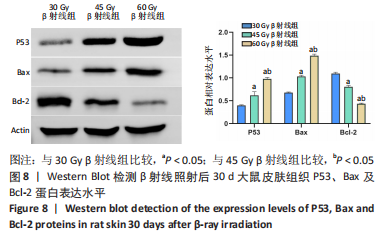
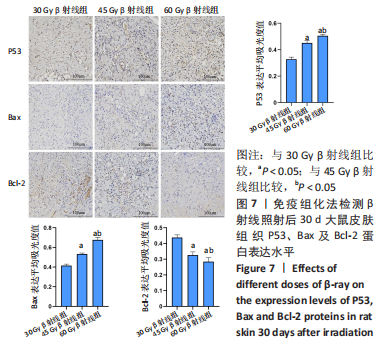
2.8 免疫组化学检测P53、Bax及Bcl-2蛋白表达水平 照射后第15天,3 组大鼠皮肤组织中P53及Bax蛋白的表达均呈阳性,60 Gy及45 Gy β射线组P53、Bax 蛋白的表达水平高于30 Gy β射线组;照射后第30 天,各组表达均呈增长趋势,60 Gy及45 Gy β射线组大鼠皮肤组织 P53、Bax 蛋白的表达水平达峰值,且60 Gy β射线组高于45 Gy β射线组(P < 0.05),45 Gy β射线组高于30 Gy β射线组(P < 0.05);照射后第45 天,60 Gy β射线组P53、Bax 蛋白的表达仍呈较高水平,30 Gy及45 Gy β射线组P53、Bax 蛋白表达明显减弱(P < 0.05)。照射后第15 天,3 组大鼠皮肤组织中Bcl-2 蛋白的表达均呈阳性;照射第30 天,各组Bcl-2表达均呈下降趋势,60 Gy及45 Gy β射线组大鼠皮肤组织Bcl-2蛋白的表达水平达低峰值,且60 Gy β射线组显著低于30 Gy及45 Gy β射线组(P < 0.05),见图7;照射后第45 天,60 Gy β射线组Bcl-2蛋白的表达仍呈较低水平,30 Gy及45 Gy β射线组P53、Bax 蛋白表达显著增加(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] DOCTROW SR, LOPEZ A, SCHOCK AM, et al. A synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic EUK-207 mitigates radiation dermatitis and promotes wound healing in irradiated rat skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(4):1088-1096. [2] 刘玉龙,王优优,郭凯琳,等.南京“5.7”192Ir源放射事故患者的临床救治[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2016,36(5):324-330. [3] TUIENG RJ, CARTMELL SH, KIRWAN CC, et al. The Effects of Ionising and Non-Ionising Electromagnetic Radiation on Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3041. [4] KUMAR A, KUMARCHANDRA R, RAI R, et al. Radiation mitigating activities of Psidium guajava L. against whole-body X-ray-induced damages in albino Wistar rat model.3 Biotech. 2020;10(12):507. [5] DA SILVA SANTIN M, KOEHLER J, ROCHA DM, et al. Initial damage produced by a single 15-Gy x-ray irradiation to the rat calvaria skin. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):32. [6] BORRELLI MR, PATEL RA, SOKOL J, et al. Fat Chance: The Rejuvenation of Irradiated Skin. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7(2):e2092. [7] WAN Y, TU W, Tang Y, et al. Prevention and treatment for radiation-induced skin injury during radiotherapy. Radiat Med Prot. 2020;1(2):60-68. [8] TENORIO C, DE LA MATA D, LEYVA JAF, et al. Mexican radiationdermatitis management consensus. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022;27(5):914-926. [9] CHU CN, HU KC, WU RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):330. [10] 蔡卫超,曹卫红.活性氧与放射性皮肤损伤的研究进展[J].辐射防护,2022, 42(3):111-118. [11] JAKUBCZYK K, DEC K, KALDUNSKA J, et al. Reactivr oxygen species-sources,functions,oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020;48(284):124-127. [12] SHI M, HUANG J, SUN X et al. Effect of rivaroxaban on the injury during endotoxin-induced damage to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019;31(4):468-473. [13] WANG C, LI TK, ZENG CH, et al.Iodine-125 seed radiation induces ROS-mediated apoptosis, autophagy and paraptosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(6):2028-2044. [14] HAO Q, CHEN J, LIAO J, et al.p53 induces ARTS to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(2):204-209. [15] OKAZAKI R. Role of p53 in Regulating Radiation Responses. Life (Basel). 2022; 12(7):1099. [16] KIANG JG, CANNON G, OLSON MG, et al.Female Mice are More Resistant to the Mixed-Field (67% Neutron+33% Gamma) Radiation-Induced Injury in Bone Marrow and Small Intestine than Male Mice due to Sustained Increases in G-CSF and the Bcl-2/Bax Ratio and Lower miR-34a and MAPK Activation. Radiat Res. 2022;198(2):120-133. [17] GANS I, ABIAD JE, JAMES AW, et al.Administration of TGF-ß Inhibitor Mitigates Radiation-induced Fibrosis in a Mouse Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(3): 468-474. [18] CHANG HP, CHO JH, LEE WJ, et al. Development of an easy-to-handle murine model for the characterization of radiation-induced gross and molecular changes in skin. Arch Plast Surg. 2018;45(5):403-410. [19] 陈宇彤,李晨晨,刘阳,等.急性放射性皮肤损伤 Wistar大鼠模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):237-241. [20] 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤动物模型的建立与应用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2006,26(6):577-579. [21] YANG X, REN H, GUO X, et al. Radiation-induced skin injury: pathogenesis, treatment, and management. Aging(AlbanyNY). 2020;12(22):23379-23393. [22] HYMES SR, STROM EA, FIFE C, et al. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(1):28-46. [23] MARTIN MT, VULIN A, Hendry JH, et al. Human epidermal stem cells: role in adverse skin reactions and carcinogenesis from radiation. Mutat Res. 2016;770(Pt B):349-368. [24] XIAO Y, MO W, JIA H, et al.Ionizing radiation induces cutaneous lipid remolding and skin adipocytes confer protection against radiation-induced skin injury. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;97(2):152-160. [25] SHERMAN DW, WALSH SM. Promoting Comfort: A Clinician Guide and Evidence-Based Skin Care Plan in the Prevention and Management of Radiation Dermatitis for Patients with Breast Cancer. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10(8):1496. [26] YEE C, LAM E, GALLANT F, et al. A Feasibility Study of Mepitel Film for the Prevention of Breast Radiation Dermatitis in a Canadian Center. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2021;11(1):e36-e45. [27] KIM JW, LEE DW, CHOI WH, et al. Development of a porcine skin injury model and characterization of the dose-dependent response to high-dose radiation. J Radiat Res. 2013;54(5):823-831. [28] FALLAH M, SHEN Y, BRODEN J, et al. Plasminogen activation is required for the development of radiation-induced dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(11):1051. [29] HOLLER V, BUARDV, GAUGLER MH, et al. Pravastatin limits radiationinduced vascular dysfunction in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(5):1280-1291. [30] MEI K, ZHAO S, QIAN L, et al. Hydrogen protects rats from dermatitis caused by local radiation. J Dermatolog Treat. 2014;25(2):182-188. [31] BERNHARDT T, KRIESENS, MANDA K, et al. Induction of Radiodermatitis in Nude Mouse Model Using Gamma Irradiator IBL 637. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):224-234. [32] NIELSEN S, BASSLER N, GRZANKA L, et al. Proton scanning and X-ray beam irradiation induce distinct regulation of inflammatory cytokines in a preclinical mouse model. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020;96(10):1238-1244. [33] CHEN Y, ZHANG Q, WU Y, et al. Short-term influences of radiation on musculofascial healing in a laparotomy rat model. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11896. [34] KESANIEMI J, JERNFORS T, LAVRINIENKO A, et al. Exposure to environmental radionuclides is associated with altered metabolic and immunity pathways in a wild rodent. Mol Ecol. 2019;28(20):4620-4635. [35] KOIKE M, SUGASAWA J, KOIKE A, et al. p53 phosphorylation in mouse skin and in vitro human skin model by high-dose-radiation exposure.J Radiat Res. 2005;46(4):461-468. [36] BERNHARDT T, KRIESEN S, MANDA K, et al. Induction of Radiodermatitis in Nude Mouse Model Using Gamma Irradiator IBL 637. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):224-234. [37] YAO C, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate radiation-induced dermatitis by suppressing apoptosis and downregulating cathepsin F expression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):447. [38] CUI YF, XIA GW, FU XB, et al.Relationship between expression of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis in radiation compound wound healing of rats.Chin J Traumatol. 2003;6(3):135-138. [39] 赵小瑜,何罕亮,祁强,等.急性β射线皮肤损伤创面愈合过程中相关凋亡基因的表达[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2012,32(6):853-857+878. |
| [1] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [2] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [3] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [4] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [5] | Hu Zhixing, Li Qun, Yang Chao, Wang Xiaoxiao, Fang Luochangting, Hou Wuqiong, Lin Na, Chen Weiheng, Liu Chunfang, Lin Ya. Network meta-analysis of the modeling effects of different factors on rabbit models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [6] | Zhou Shibo, Guan Jianbin, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Liu Tao. Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 633-638. |
| [7] | Liu Penghui, Wu Fan, Wang Zejie, Wu Gaoyi, Zhou Libo. Constructing an animal model of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in Sprague-Dawley rats by digital technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5642-5648. |
| [8] | Niu Xiaolong, Chen Jialiang, Zheng Huaqun, Yang Guimei, Yao Guangtao. Preparation and characteristics comparison of three acute pancreatitis rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5480-5486. |
| [9] | Yin Linwei, Huang Xiarong, Sun Guanghua, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Wang Jinling, Chen Jiaqian, Wen Xing, Gan Shaoting, Hu Wentao, Li Mengmeng, Zhou Jun. Pulsed electromagnetic fields inhibit knee cartilage degeneration in aged rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4522-4527. |
| [10] | Yang Cheng, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Shang Man, Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Fan Fangyang, Zhang Chenglong, Zhang Xiaoyu, Zhang Juntao. Establishment and validation of the Sprague-Dawley rat model of osteoarthritis with kidney deficiency and blood stagnation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4273-4280. |
| [11] | Gao Simiao, Wu Xiaoguang, Han Xue, Xu Shiqi, Li Kuihua, Peng Yong. Establishment of a rat model of traumatic brain injury using the modified Feeney’s free-fall method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4164-4169. |
| [12] | Yang Zongrui, Ge Haiya, Shi Jinyu, Wang Zhengming, Wang Yuanyuan, Li Zhengyan, Du Guoqing, Zhan Hongsheng. Characteristic changes in morphology and function of skeletal muscles in a rat model of “tendon off-position” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4170-4177. |
| [13] | Lyu Lijun, Peng Wei, Li Chuangbing, Ye Shuo, Gao Qiuming. Establishment of a rat femoral nonunion model by intramedullary fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4189-4153. |
| [14] | Huang Jiacheng, Shao Xinxin, Li Haomiao, Du Shaohua, Dai Shuangwu. Construction of an animal model for treating early postoperative infected bacterial biofilms by irrigating after internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3704-3708. |
| [15] | Xiong Bohan, Yu Yang, Zheng Liling, Yang Tengyun, Lu Xiaojun, Wang Xu, Li Kaiwei, Yu Hong, Li Yajuan, Dong Kaiyan, Zhang Yaozhang, Liu Jinrui, Gu Ziming, Hu Bigeng, Li Yanlin. Constructing a model of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autologous Achilles tendon in southern Yunnan small-ear pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3157-3163. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||