Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1653-1659.doi: 10.12307/2024.229
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of C2 ceramide on dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease
Li Jiahui1, Qi Xue1, Zhu Yuanfeng1, Yu Lu1, Liu Lifeng1, Wang Peng1, 2
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, 2Laboratory of Neurodegenerative Diseases, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-10Accepted:2023-03-24Online:2024-04-18Published:2023-07-26 -
Contact:Wang Peng, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China; Laboratory of Neurodegenerative Diseases, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Li Jiahui, Master candidate, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beihua University, Jilin 132013, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, No. YDZJ202201ZYTS575 (to WP); Jilin Province Health and Health Technology Innovation Project, No. 2018J083 (to WP); Postgraduate Innovative Project of Beihua University, No. [2021]054 (to LJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jiahui, Qi Xue, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Liu Lifeng, Wang Peng. Protective effect of C2 ceramide on dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1653-1659.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
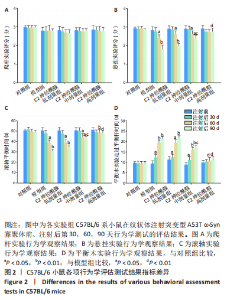
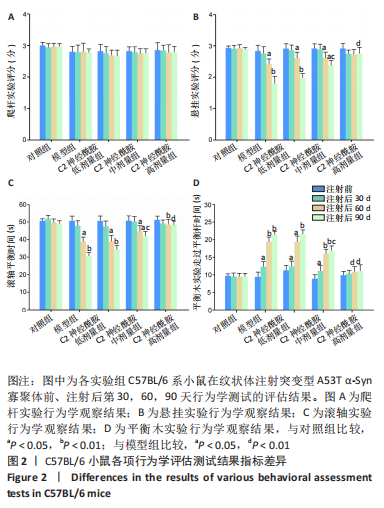
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验中的25只C57BL/6 系小鼠在实验过程中无脱失,最终25只小鼠全部纳入结果分析。 2.2 小鼠一般情况 左侧纹状体注射造模后第30天,模型组小鼠开始出现肢体轻微震颤、行动迟缓,个别小鼠表现为竖毛、后肢张开、背部上弓以及步态不稳等帕金森病样行为学改变。而在造模后第90天,C2神经酰胺高剂量组小鼠较模型组相比,震颤明显减轻,且未见竖毛及后肢张开等异常表现。 2.3 行为学评估 在纹状体注射后的第30,60,90天,各实验组小鼠的爬杆实验结果均与对照组无显著性差异(P > 0.05),见图2A。 悬挂实验和滚轴实验结果显示,注射后的第60天,模型组小鼠较对照组相比,出现运动能力的下降(P < 0.05),随着造模时间的增加,第90天时,模型组小鼠运动能力较对照组相比明显降低(P < 0.01)。悬挂实验以检测小鼠上、下肢肌力为主要评分标准,滚轴实验则主要考察小鼠的反应能力及综合运动能力。结果表明,C2神经酰胺低剂量组(1 μg/g) 小鼠的运动能力与模型组相比无显著性差异,而中剂量组 (5 μg/g)小鼠在第90天时表现为较模型组运动能力的提升 (P < 0.05)。高剂量组小鼠(10 μg/g)则在第90 天时表现出较模型组相比更为明显的运动能力的恢复(P < 0.01),其运动能力与对照组相比无显著性差异(P > 0.05),见图2B,C。 平衡木实验的结果表明:注射后30 d,模型组小鼠较对照组相比出现平衡能力的下降(P < 0.05),且在第60,90天,模型组小鼠平衡能力降低更为明显(P < 0.01)。而在C2神经酰胺各剂量组中,中剂量组小鼠在第90天时出现了较模型组小鼠能力提升(P < 0.05),但仍表现为较对照组小鼠平衡能力的下降(P < 0.01);高剂量组小鼠在造模第30天时,并未表现出与对照组小鼠相比运动能力的显著性差异(P > 0.05),而在第60,90天时,均表现出与模型组小鼠相比更为明显的运动能力的恢复(P < 0.01),见图2D。"

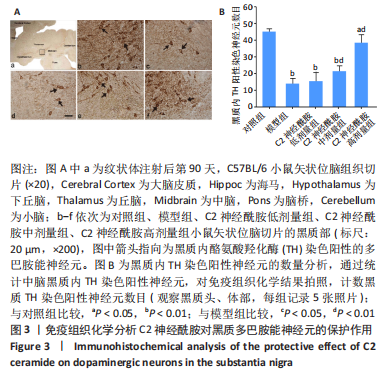
2.4 小鼠黑质多巴胺能神经元数量变化 免疫组织化学染色结果显示,模型组小鼠黑质内酪氨酸羟化酶染色阳性神经元数目较对照组相比显著下降 (P < 0.01)。在给予C2神经酰胺治疗后,低剂量组小鼠黑质内酪氨酸羟化酶染色阳性神经元数目与模型组比较无显著性差异(P > 0.05),依旧与对照组酪氨酸羟化酶染色阳性神经元数目相差显著(P < 0.01)。但随着C2神经酰胺的剂量增加,给予每天一次性灌胃10 μg/g剂量的C2神经酰胺高剂量组小鼠黑质内酪氨酸羟化酶染色阳性神经元数目与对照组相比差异减小(P < 0.05),且出现较模型组相比明显增多的酪氨酸羟化酶染色阳性神经元(P < 0.01),见图3。"
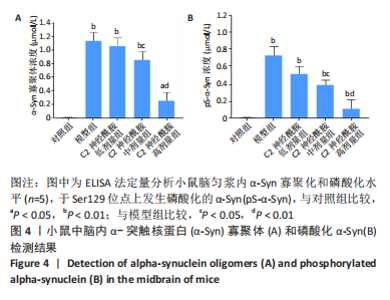
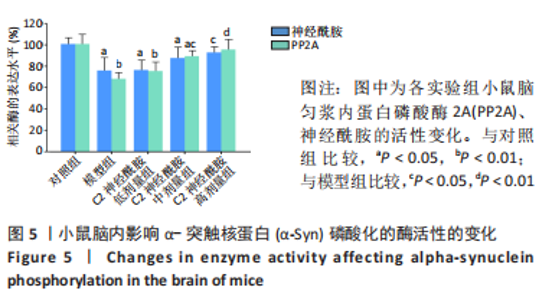
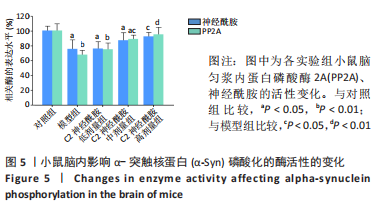
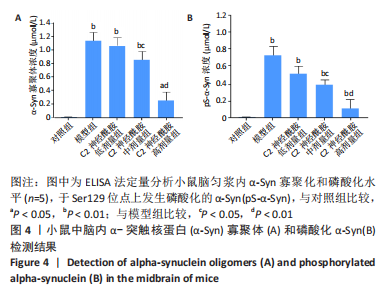
2.5 小鼠脑匀浆内α-Syn寡聚化和磷酸化水平 以双抗体夹心ELISA法定量检测各实验组小鼠在第90天后,中脑内α-Syn的寡聚化和磷酸化水平。结果表明,模型组、C2神经酰胺低、中剂量组均检测到较对照组相比明显增高的α-Syn寡聚体含量(P < 0.01),其中,C2神经酰胺中剂量组小鼠中脑内含有的α-Syn寡聚体水平较模型组有所降低(P < 0.05),而随着剂量的增加,C2神经酰胺高剂量组小鼠中脑表现出较模型组明显减弱的寡聚化水平(P < 0.01),与对照组寡聚化水平差异也有所缩小(P < 0.05),见图4A。另外,并未在对照组中检测出发生Ser129磷酸化的α-Syn(pS-α-Syn),而其他4组在小鼠中脑内均检测到较对照组相比明显增高的pS-α-Syn含量 (P < 0.01),这当中,C2神经酰胺中剂量组pS-α-Syn浓度较模型组相比有所下降(P < 0.05),而高剂量组中α-Syn发生磷酸化异常修饰的水平较模型组差异最大(P < 0.01),见图4B。"
| [1] MONTEMURRO N, ALIAGA N, GRAFF P, et al. New targets and new technologies in the treatment of parkinson’s disease: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8799. [2] COSTA HN, ESTEVES AR, EMPADINHAS N, et al. Parkinson’s disease: a multisystem disorder. Neurosci Bull. 2023;39(1):113-124. [3] MYERS PS, O’DONNELL JL, JACKSON JJ, et al. Proteinopathy and longitudinal cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2022;99(1):e66-e76. [4] SIMON C, SOGA T, OKANO HJ, et al. α-Synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies: the pathobiology of a paradox. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):196. [5] BARBA L, PAOLINI PAOLETTI F, BELLOMO G, et al. Alpha and beta synucleins: from pathophysiology to clinical application as biomarkers. Mov Disord. 2022;37(4):669-683. [6] BELL R, THRUSH RJ, CASTELLANA-CRUZ M, et al. N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein slows down its aggregation process and alters the morphology of the resulting aggregates. Biochemistry. 2022;61(17):1743-1756. [7] SALAMON A, ZADORI D, SZPISJAK L, et al. The genetic background of Parkinson’s disease and novel therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022;26(10):827-836. [8] GUHATHAKURTA S, SONG MK, BASU S, et al. Regulation of αlpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) by epigenetic modifier TET1 in Parkinson disease. Int Neurourol J. 2022;26(Suppl 2):S85-S93. [9] 王鹏,历春,王海鹏,等.Alpha-突触核蛋白寡聚体致帕金森病小鼠模型的行为学变化[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(21):5227-5230. [10] GHANEM SS, MAJBOUR NK, VAIKATH NN, et al. α-Synuclein phosphorylation at serine 129 occurs after initial protein deposition and inhibits seeded fibril formation and toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(15):e2109617119. [11] WANG R, WANG Y, QU L, et al. Iron-induced oxidative stress contributes to α-synuclein phosphorylation and up-regulation via polo-like kinase 2 and casein kinase 2. Neurochem Int. 2019;125:127-135. [12] SHIN WH, CHUNG KC. Death-associated protein kinase 1 phosphorylates α-synuclein at Ser129 and exacerbates rotenone-induced toxic aggregation of α-synuclein in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Exp Neurobiol. 2020;29(3): 207-218. [13] LASHUEL HA, MAHUL-MELLIER AL, NOVELLO S, et al. Revisiting the specificity and ability of phospho-S129 antibodies to capture alpha-synuclein biochemical and pathological diversity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022; 8(1):136. [14] DENT SE, KING DP, OSTERBERG VR, et al. Phosphorylation of the aggregate-forming protein alpha-synuclein on serine-129 inhibits its DNA-bending properties. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(2):101552. [15] KAWAHATA I, FINKELSTEIN DI, FUKUNAGA K. Pathogenic impact of α-synuclein phosphorylation and its kinases in α-synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6216. [16] UEDA S, NISHIHARA M, HIOKA Y, et al. Polo-like kinase 2 plays an essential role in cytoprotection against MG132-induced proteasome inhibition via phosphorylation of serine 19 in HSPB5. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11257. [17] ZHANG C, NI C, LU H. Polo-like kinase 2: from principle to practice. Front Oncol. 2022;12(8):956225. [18] TIAN H, LU Y, LIU J, et al. Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase downregulation and protein phosphatase methylesterase upregulation contribute toward the inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A by α-synuclein. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:173. [19] DEHGHAN A, PINTO RC, KARAMAN I, et al. Metabolome-wide association study on ABCA7 indicates a role of ceramide metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(43):e2206083119. [20] ZHUO C, ZHAO F, TIAN H, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in schizophrenia: implications for therapeutic intervention as a potential novel target. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12(1):260. [21] ZHANG Y, JI S, ZHANG X, et al. Human CPTP promotes growth and metastasis via sphingolipid metabolite ceramide and PI4KA/AKT signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(13):4963-4983. [22] PLOTEGHER N, BUBACCO L, GREGGIO E, et al. Ceramides in Parkinson’s disease: from recent evidence to new hypotheses. Front Neurosci. 2019; 13:330. [23] CLARK AR, OHLMEYER M. Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;201(9):181-201. [24] CUSTODIA A, ARAMBURU-NÚÑEZ M, CORREA-PAZ C, et al. Ceramide metabolism and Parkinson’s disease-therapeutic targets. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):945. [25] 韩燕银.C2-神经酰胺抑制α-synuclein聚集的研究[D].桂林:桂林医学院,2019. [26] 张天华,李永春,李宪伟,等.C2-神经酰胺对间皮瘤细胞裸鼠移植瘤生长的抑制作用[J].现代肿瘤医学,2014,22(9):2038-2043. [27] CHOONG CJ, MOCHIZUKI H. Neuropathology of α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology. 2022;42(2):93-103. [28] PAN L, LI C, MENG L, et al. Tau accelerates α-synuclein aggregation and spreading in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2022;145(10):3454-3471. [29] TIJMS BM, GOBOM J, REUS L, et al. Pathophysiological subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on cerebrospinal fluid proteomics. Brain. 2020; 143(12):3776-3792. [30] SEPPI K, RAY CHAUDHURI K, COELHO M, et al. Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease-an evidence-based medicine review. Mov Disord. 2019;34(2):180-198. [31] ELLIS TD, COLÓN-SEMENZA C, DEANGELIS TR, et al. Evidence for early and regular physical therapy and exercise in Parkinson’s disease. Semin Neurol. 2021;41(2):189-205. [32] YOO H, LEE J, KIM B, et al. Role of post-translational modifications on the alpha-synuclein aggregation-related pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep. 2022;55(7):323-335. [33] RAMALINGAM N, JIN SX, MOORS TE, et al. Dynamic physiological α-synuclein S129 phosphorylation is driven by neuronal activity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023;9(1):4. [34] PENG WANG, XIN LI, XURAN LI, et al. Blood plasma of patients with Parkinson’s disease increases alpha-synuclein aggregation and neurotoxicity. Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2016:7596482. [35] LUNGHI G, CASNNA EV, LOBERTO N, et al. β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency activates an aberrant lysosome-plasma membrane axis responsible for the onset of neurodegeneration. Cells. 2022;11(15):2343. [36] SMITH L, SCHAPIRA AHV. GBA variants and Parkinson disease: mechanisms and treatments. Cells. 2022;11(8):1261. [37] SMITH JK, MELLICK GD, SYKES AM. The role of the endolysosomal pathway in α-synuclein pathogenesis in Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;16:1081426. [38] 王鹏,李昕,陈予东,等.α-突触核蛋白寡聚体抑制大鼠原代培养神经元突起早期生长[J].首都医科大学学报,2014,35(5):587-591. [39] TRINGALI C, GIUSSANI P. Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in neurodegenerative disorders and their potential involvement in therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7806. [40] DEN HOEDT S, CRIVELLI SM, LEIJTEN FPJ, et al. Effects of sex, age, and apolipoprotein e genotype on brain ceramides and sphingosine-1-phosphate in alzheimer’s disease and control mice. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:765252. [41] AYUB M, JIN HK, BAE JS. Novelty of sphingolipids in the central nervous system physiology and disease: focusing on the sphingolipid hypothesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7353. [42] MINGIONE A, PIVARI F, PLOTEGHER N, et al. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis reduces α-synuclein proteinopathy in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6469. [43] BHUMKAR A, MAGNAN C, LAU D, et al. Single-molecule counting coupled to rapid amplification enables detection of α-synuclein aggregates in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease patients. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(21):11874-11883. [44] POGGIOLINI I, GUPTA V, LAWTON M, et al. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein seed quantification in synucleinopathies. Brain. 2022; 145(2):584-595. [45] ZHAO X, HE H, XIONG X, et al. Lewy body-associated proteins a-synuclein (a-syn) as a plasma-based biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:869797. |
| [1] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [2] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| [3] | Yang Yulin, Chang Wanpeng, Ding Jiangtao, Xu Hongli, Wu Xiao, Xiao Boheng, Ma Lihong. Transcranial direct current stimulation at different targets for Parkinson’s disease: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1797-1804. |
| [4] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Phosphorylation modification of alpha synuclein in serum of patients with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5577-5582. |
| [5] | Zheng Xiaohan, Feng Xiaoli, Hu Lan, Gao Shijun, Wei Yanzhao, Huang Ting, Sun Shengtong, Wei Xufang, Wang Tan, Zhao Zhenqiang. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into ventral midbrain dopaminergic neural progenitor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5348-5356. |
| [6] | Wang Yiying, Li Ruiqing, Li Jingwen, Mei Jinjin, Zhang Jianyun, Zhang Lihong, Fan Yongfu, Guo Jian. Exosome-mediated cellular communication: a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3883-3891. |
| [7] | Chen Shijian, Li Ge, Zhang Yu, Guan Yalun, Li Xuejiao, Liu Shuhua, Li Yongchao, Li Yunfeng, Gao Jinfeng, Wei Xiaoyue, Zhao Yuhong. Comparison and evaluation of MPTP-induced subacute and chronic models of Parkinson’s disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1247-1252. |
| [8] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [9] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [10] | Zhang Ansheng, Zhang Haiou, Ni Longxing. Regulating the expression of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome-related molecules in dental pulp fibroblasts under inflammation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4107-4112. |
| [11] | Wei Yufan, Fan Feiyan, Li Shuangli, Zhang Yunke. Future of exosomes and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4076-4083. |
| [12] | Liu Qiqi, Liu Min, Yang Jian, Yu Ke. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the expression of interleukin-6 and nuclear factor kappa B receptor activator ligand in mouse MLO-Y4 osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3121-3126. |
| [13] | Huo Hua, Liu Guanjuan, Song Na, Zhou Qian, Cheng Yuting, Luo Shanshan, Liao Jian. Effects of zoledronic acid on alveolar bone metabolism and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome in the alveolar bone of ovariectomized osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2660-2666. |
| [14] | Zhang Shuling, Li Junhan, Wang Jiaqian, Li Yalong, Wang Chun. Effects of aerobic exercises on JAK2/STAT5 signal pathway in the liver of mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2690-2695. |
| [15] | You Kun, Liu Yuanxin. Protective effect of exercise preconditioning on lung injury induced by hypobaric hypoxia in rats based on the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element signal pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2702-2707. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||