Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1660-1665.doi: 10.12307/2024.222
Previous Articles Next Articles
The histological and thickness changes of attached gingiva following grafting with different soft tissue substitutes in the labial region of the cuspids in Beagles
Zhang Hongxia, Li Xingchao, Gao Xixin, Zhang Xiao, Mei Shuang, Ma Hanxi, Zhang Tian
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-16Accepted:2023-03-02Online:2024-04-18Published:2023-07-26 -
Contact:Li Xingchao, MD, Chief physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Hongxia, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hebei Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Hebei Provincial Government-funded Clinical Medicine Talent Training and Basic Research Project, No. 361029(MXZB00267) (to LXC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Hongxia, Li Xingchao, Gao Xixin, Zhang Xiao, Mei Shuang, Ma Hanxi, Zhang Tian. The histological and thickness changes of attached gingiva following grafting with different soft tissue substitutes in the labial region of the cuspids in Beagles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1660-1665.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
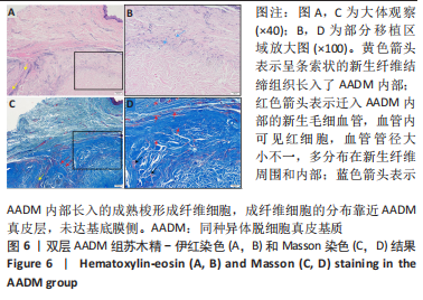
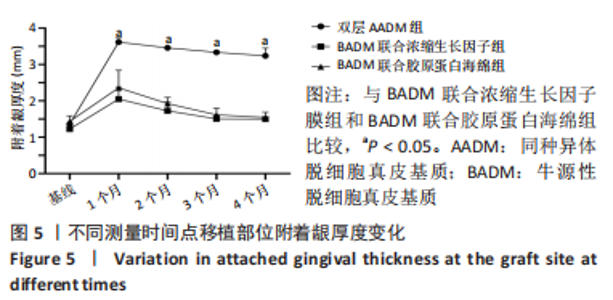
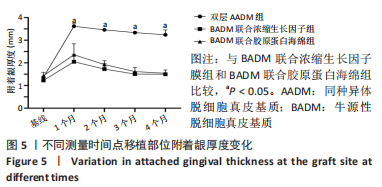
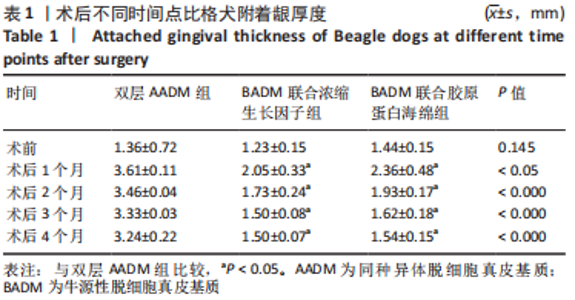
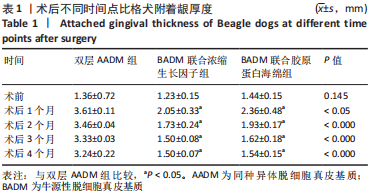
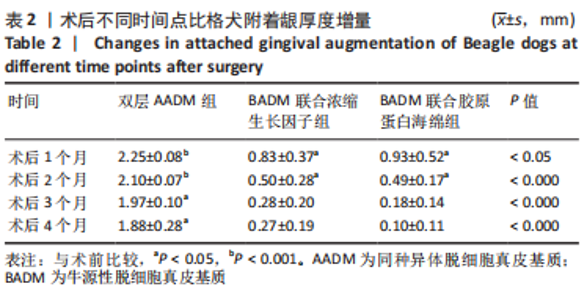
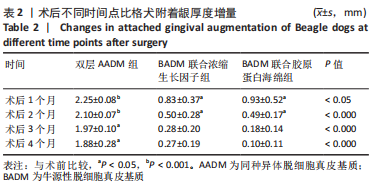
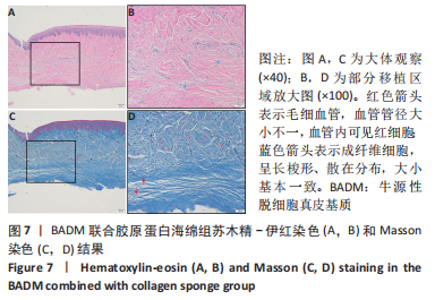
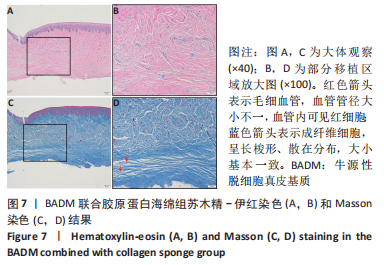
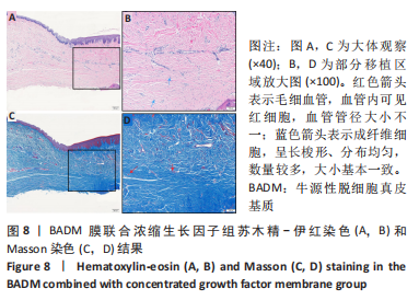
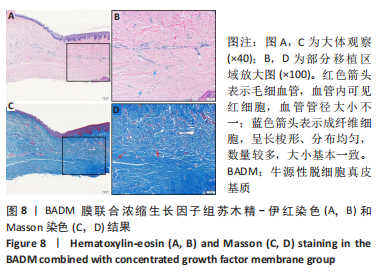
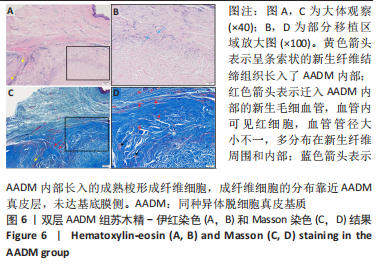
组间比较:术后第1,2,3,4个月,双层AADM组附着龈厚度及附着龈厚度增量均值高于BADM联合浓缩生长因子膜组与BADM联合胶原蛋白海绵组(均P < 0.05),BADM联合胶原蛋白海绵组与BADM联合浓缩生长因子组各个测量时间点比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 组内比较:3组术前附着龈厚度比较差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05),术后1个月附着龈厚度显著增加(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),而后呈下降趋势。术后3个月,BADM联合胶原蛋白海绵组与BADM联合浓缩生长因子组移植区附着龈厚度值逐渐接近,变化趋于平稳,较术前差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);双层AADM组附着龈厚度变化速率也有所下降。术后4个月,双层AADM组附着龈厚度均值较术前仍显著增加(P < 0.05)。第1,2,3,4个月双层AADM组附着龈厚度值最高,其次为BADM联合胶原蛋白海绵组,BADM联合浓缩生长因子组最低。 2.3 描述性组织学结果 组织学分析显示,双层AADM组真皮基质与宿主牙龈组织良好的结合在一起,AADM胶原纤维结构完整,纤维排列致密整齐,新生纤维组织和成纤维细胞长入AADM内,真皮基质内可见新生血管和红细胞,见图6。BADM联合胶原蛋白海绵组和BADM联合浓缩生长因子组移植处被覆复层鳞状上皮,固有层有大量纤维结缔组织,显示出典型的解剖学特征,增量区域成熟的结缔组织富含血管和细胞,主要是胶原结构中散布的成纤维细胞,几乎没有炎症迹象,移植物完全降解,未见植入材料残留物,移植区域改建成与周围宿主组织一致的结构,见图7,8。"
| [1] BASSETTI RG, STÄHLI A, BASSETTI MA, et al. Soft tissue augmentation procedures at second-stage surgery: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(7):1369-1387. [2] ADZHIEVA АB, VORONOV IА, IVANOV SS, et al. Optiminization of regeneration at the stages of soft tissue augmentation using a collagen matrix. Эндодонтия Today. 2021;19(4):317-319. [3] GIANNOBILE WV, JUNG RE, SCHWARZ F, et al. Evidence‐based knowledge on the aesthetics and maintenance of peri‐implant soft tissues: Osteology Foundation Consensus Report Part 1-Effects of soft tissue augmentation procedures on the maintenance of peri‐implant soft tissue health. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 15:7-10. [4] LISSEK M, BOEKER M, HAPPE A. How thick is the oral mucosa around implants after augmentation with different materials: A systematic review of the effectiveness of substitute matrices in comparison to connective tissue grafts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):5043. [5] DADLANI S. Porcine Acellular Dermal Matrix: An Alternative to Connective Tissue Graft-A Narrative Review. Int J Dent. 2021;2021:1652032. [6] TAVELLI L, MCGUIRE MK, ZUCCHELLI G, et al. Extracellular matrix‐based scaffolding technologies for periodontal and peri‐implant soft tissue regeneration. J Periodontol. 2020;91(1):17-25. [7] Cevallos CAR, de Resende DRB, Damante CA, et al. Free gingival graft and acellular dermal matrix for gingival augmentation: A 15-year clinical study. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(3):1197-1203. [8] SHIRAKATA Y, SCULEAN A, SHINOHARA Y, et al. Healing of localized gingival recessions treated with a coronally advanced flap alone or combined with an enamel matrix derivative and a porcine acellular dermal matrix: A preclinical study. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(7):1791-1800. [9] SCHMITT CM, BRÜCKBAUER P, SCHLEGEL KA, et al. Volumetric soft tissue alterations in the early healing phase after peri‐implant soft tissue contour augmentation with a porcine collagen matrix versus the autologous connective tissue graft: A controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(1):145-162. [10] LIU C, SU Y, TAN B, et al. Reconstruction of attached soft tissue around dental implants by acelluar dermal matrix grafts and resin splint. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):4666-4676. [11] 黄江波. 不同修复材料在即刻种植牙膜引导骨再生治疗中的效果比较[J]. 中国民康医学,2022,34(23):148-150. [12] 田媛,马秀岚. 异种脱细胞真皮基质修复耳廓前面皮肤缺损[J]. 中国医科大学学报. 2020,49(12):1136-1139. [13] 胡琼方,胡永琼,梅时友. 异种脱细胞真皮基质,异体脱细胞真皮基质与自体皮瓣修复颌面部软组织缺损疗效对比[J]. 中国美容医学,2020,29(7):61-64. [14] 陈先锋,陈竹林,刘晶. 异种脱细胞真皮基质在口腔颌面部软组织缺损修复的应用[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2021,25(1):66-68. [15] HAN C, CAI Q, LI B, et al. Keratinized mucosa augmentation guided by double xenogeneic collagen matrix membranes around implants in the posterior mandible: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(3):e23609. [16] 周炜丹. 探究CGF与PRF在牙周炎患牙位点保存治疗中的效果[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志,2020,34(2):82-85. [17] LEE H, SHEN E, SHEN J T, et al. Tensile strength, growth factor content and proliferation activities for two platelet concentrates of platelet-rich fibrin and concentrated growth factor. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(2):141-146. [18] 王亚楠,王佐林. 浓缩生长因子促进牙龈软组织缺损修复的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2018,28(3):121-126. [19] FANG D, LONG Z, HOU J. Clinical application of concentrated growth factor fibrin combined with bone repair materials in jaw defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;78(6):882-892. [20] QI L, GE W, CAO N, et al. Effects of autologous concentrated growth factor on gingival thickness in periodontal accelerated osteogenic orthodontics: a 6-month randomized controlled trial. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):1-11. [21] 岑雯,王轶,黄江琴,等. 胶原蛋白海绵在磨牙区即刻种植创口关闭中的应用[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志,2018,23(4):176-179. [22] 李丽曼,赵丽萍,徐涛,等. 罹患重度牙周病变磨牙采取微创拔牙和微翻瓣位点保存术后种植修复效果观察(附1例3年随访报告)[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2020;13(3):139-145. [23] 彭锦辉,钱齐荣,刘宁,等. 可即邦胶原蛋白海绵在控制膝关节置换术后出血中的价值[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2013,2(3):155-158. [24] DALMIA P, PARTHASARATHY H, TADEPALLI A, et al. Evaluation of Changes in the Palatal Mucosal Thickness Post-augmentation using a Xenogeneic Collagen Matrix-An Interventional Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2022;16(3):1-4. [25] 金鑫,周健. 异种和异体脱细胞真皮基质修复颊部软组织缺损疗效观察[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,6(5):282-284. [26] 曾薇,陈美珍,伍健辉. 脱细胞异体真皮与自体刃厚皮片修复外耳道皮肤缺损的比较[J].中国医药科学,2021,11(14):213-216. [27] NOVAES JR AB, PALIOTO DB. Experimental and clinical studies on plastic periodontal procedures. Periodontol. Periodontol 2000. 2019;79(1):56-80. [28] LU W, QI G, DING Z, et al. Clinical efficacy of acellular dermal matrix for plastic periodontal and implant surgery: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;49(8):1057-1066. [29] PUISYS A, VINDASIUTE E, LINKEVCIENE L, et al. The use of acellular dermal matrix membrane for vertical soft tissue augmentation during submerged implant placement: a case series. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(4):465-470. [30] ZANG J, SU L, LUAN Q, et al. Clinical and histological evaluation of the use of acellular dermal matrix (ADM) membrane in peri‐implant vertical soft tissue augmentation: a controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(6):586-597. [31] AROCA S, MOLNÁR B, WINDISCH P, et al. Treatment of multiple adjacent Miller class I and II gingival recessions with a Modified Coronally Advanced Tunnel (MCAT) technique and a collagen matrix or palatal connective tissue graft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40(7):713-720. [32] 潘腾飞,陶剑,蒋彩云,等. 两种脱细胞支架原位植入转归动物试验研究[J]. 河北工业大学学报,2020,49(3):46-54. [33] LEE J H, KIM H G, LEE W J. Characterization and tissue incorporation of cross-linked human acellular dermal matrix. Biomaterials. 2015;44:195-205. [34] CARLSON TL, LEE KW, PIERCE LM. Effect of cross-linked and non–cross-linked acellular dermal matrices on the expression of mediators involved in wound healing and matrix remodeling. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(4):697-705. [35] SCHMITT CM, SCHLEGEL KA, GAMMEL L, et al. Gingiva thickening with a porcine collagen matrix in a preclinical dog model: Histological outcomes. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46(12):1273-1281. [36] ROTHAMEL D, BENNER M, FIENITZ T, et al. Biodegradation pattern and tissue integration of native and cross-linked porcine collagen soft tissue augmentation matrices–an experimental study in the rat. Head Face Med. 2014;10:10. [37] ABDOLLAHI M, REZAEI M, JAFARPOUR A, et al. Sequential extraction of gel-forming proteins, collagen and collagen hydrolysate from gutted silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix), a biorefinery approach. Food Chem. 2018;242:568-578. [38] LIU X, GOHI BFCA, ZENG H, et al. Effect of collagen peptides-carboxymethyl chitosan microspheres on ultraviolet induced damages. Mater Express. 2015;5(6):497-504. [39] 李菲,乔静,段晋瑜,等. 引导性组织再生术对浓缩生长因子联合植骨术治疗下颌磨牙Ⅱ度根分叉病变临床效果的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2020;52(2):346-352. [40] MA T, SUN W Q, WANG J. Thermophysical stability and biodegradability of regenerative tissue scaffolds. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147(16):8757-8764. [41] AROCA S, KEGLEVICH T, BARBIERI B, et al. Clinical evaluation of a modified coronally advanced flap alone or in combination with a platelet‐rich fibrin membrane for the treatment of adjacent multiple gingival recessions: A 6‐month study. J Periodont. 2009;80(2):244-252. |
| [1] | Wang Zhongqing, Xiong Xianmei, Zhang Yan, Li Shijie, Ma Liqiong, Lu Zesheng, Gao Yijia. Panax notoginseng saponin promotes fracture healing by upregulating concentrated growth factors in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1678-1683. |
| [2] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| [3] | He Ruya, Liu Yunling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Repairing equivalent injury of oral mucosa with concentrated growth factor fibrin membrane combined with recombinant human epidermal growth factor active protein polypeptide complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1848-1855. |
| [4] | Liu Yunling, He Ruya, Nie Minhai, Li Tengyan, Liu Xuqian. Application of concentrated growth factor and epidermal growth factor in the field of oral and maxillofacial soft and hard tissue injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 105-113. |
| [5] | Tang Kai, Zhao Wenhua, Shang Qi, Shen Gengyang, Zhang Zhida, He Jiahui, Zhang Peng, Yu Fuyong, Chen Guifeng, Ren Hui, Jiang Xiaobing, Yu Xiang. Effects of concentrated growth factors on the proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and migration of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4935-4939. |
| [6] | Li Jing, Qiao Wei, Ren Xiaoqi, Shi Hao, Yang Ting, Ma Shaoying, Su Chengzhong, Li Baoxing, Zhao Yaping. Calcined bovine bone combined with acellular dermal matrix for maintaining the alveolar ridge in dog [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3445-3449. |
| [7] | Yan Qifang, Xie Cuiliu, Yan Guowei. Effect of concentrated growth factor and bioceramic material iRoot BP on survival, proliferation and mineralization of human dental pulp cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3363-3368. |
| [8] | Li Tengyan, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Effects of concentrated growth factor combined with epidermal growth factor on the proliferation and aging of oral mucosa equivalents [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3164-3172. |
| [9] | Hu Kai, Chen Weiming, Luo Jingwan, Li Miao, Wang Jingjing, Li Mao, Shen Yajun, Chen Jinfa, Bai Yulong. Effect of peracetic acid/ethanol on the properties of allogeneic skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1537-1543. |
| [10] | Zhou Yi, Liu Xiaoyan, Xiang Bingyan. Application advantages of concentrated growth factors in the field of tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1631-1640. |
| [11] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [12] | Xiao Deli, Sun Yinzhe, Cui Cheng, Liu Bo. Preparation and degradation properties of concentrated growth factor fibrin membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5413-5419. |
| [13] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [14] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [15] | Jin Shaofeng, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Chen Lei, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with acellular dermal matrix repair beagle dog articular cartilage defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 532-537. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||