Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 3981-3987.doi: 10.12307/2024.171
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of small extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells and tissue on de novo adipose regeneration
Yang Baohua, Zhou Xiaojie, Jing Wei, Tian Weidong, Yu Mei
- National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-13Accepted:2023-06-21Online:2024-09-08Published:2023-11-23 -
Contact:Yu Mei, PhD, Associate professor, National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Yang Baohua, Master candidate, National Engineering Laboratory for Oral Regenerative Medicine, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Key Technology Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province, No. 2019YFS0312 (to YM); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81971319 (to JW); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Innovation and Development Joint Fund), No. U21A20369 (to TWD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Baohua, Zhou Xiaojie, Jing Wei, Tian Weidong, Yu Mei. Comparison of small extracellular vesicles derived from stem cells and tissue on de novo adipose regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3981-3987.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
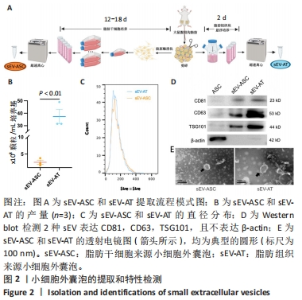
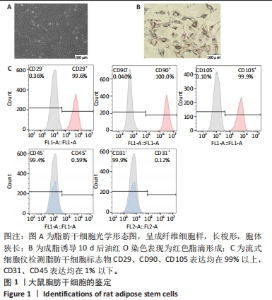
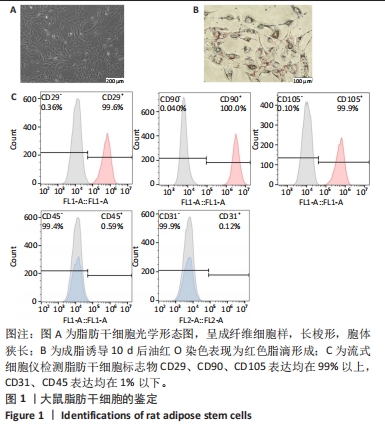
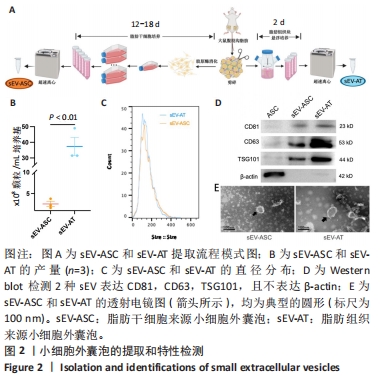
2.2 两种sEV的提取与鉴定结果 sEV-ASC与sEV-AT的提取流程见图2A。根据培养液体积及所获取的sEV颗粒数计算sEV的产率,结果显示sEV-ASC产率为2.45×108颗粒/mL,而sEV-AT产率为3.73×109颗粒/mL,在相同体积的培养液中,sEV-AT颗粒数目是sEV-ASC颗粒数目的15.2倍(P < 0.01),sEV-AT产量远大于sEV-ASC,见图2B。纳米颗粒跟踪分析结果显示,sEV-ASC和sEV-AT的粒径绝大部分在50-200 nm之间,sEV-ASC平均粒径为125 nm,sEV-AT的平均粒径为137 nm,sEV-ASC比sEV-AT的平均直径略小,都符合sEV的直径范围,见图2C;Western blot检测显示sEV-ASC和sEV-AT均表达外泌体标志蛋白CD81、CD63、TSG101,不表达β-actin 蛋白,见图2D。透射电镜结果显示,sEV-ASC和sEV-AT均显示出典型的类圆形囊泡状结构,见图2E。"
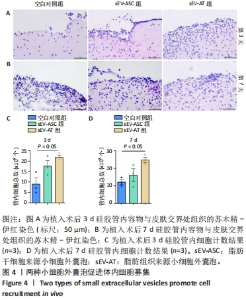
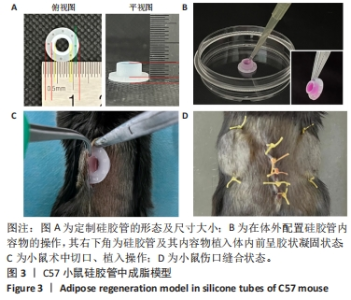
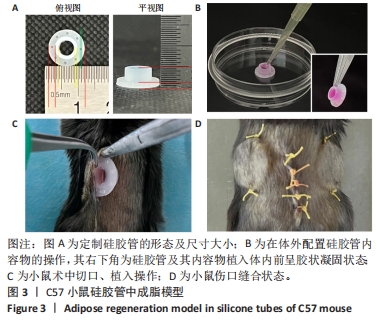
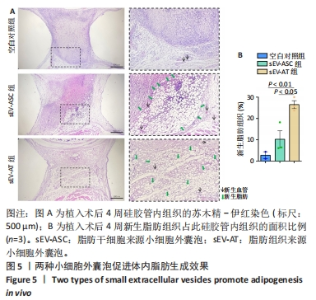
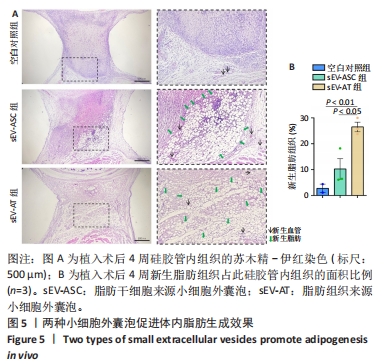
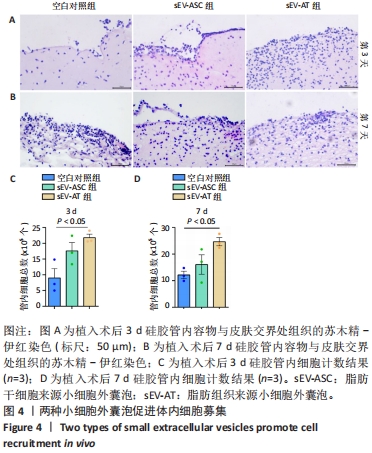
2.4 两种sEV募集宿主细胞效果比较 对小鼠体内植入3 d硅胶管内容物进行苏木精-伊红染色,结果显示,宿主细胞主要集中在植入硅胶管与小鼠皮肤连接处,见图4A,空白对照组的细胞数最少,加入了sEV的2组都比空白对照组募集到更多的细胞。对硅胶管内总细胞数进行计数,结果也显示空白对照组的细胞数最少,平均为8.9×105个,加入了sEV的2组都比空白对照组募集到更多的细胞,且sEV-AT组(平均为2.1×106个)比sEV-ASC组(平均为1.7×106个)募集到的细胞更多,见图4C。 对小鼠体内植入7 d硅胶管内容物进行苏木精-伊红染色,结果显示各组植入硅胶管与小鼠皮肤连接处的浸润细胞比植入3 d时均有增加,见图4B;对硅胶管内总细胞数进行计数,结果显示空白对照组中的细胞数为1.2×106个,sEV-ASC组为1.7×106个,sEV-AT组浸润细胞数最多,平均为2.4×106个,见图4D。"
| [1] PAREKKADAN B, MILWID JM. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:87-117. [2] XIA H, LI X, GAO W, et al. Tissue repair and regeneration with endogenous stem cells. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3(7):174-193. [3] DANESHMANDI L, SHAH S, JAFARI T, et al. Emergence of the Stem Cell Secretome in Regenerative Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020; 38(12):1373-1384. [4] BARRECA MM, CANCEMI P, GERACI F. Mesenchymal and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: The New Frontier for Regenerative Medicine? Cells. 2020;9(5):1163. [5] KOU M, HUANG L, YANG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):580. [6] GUILLAMAT-PRATS R. The Role of MSC in Wound Healing, Scarring and Regeneration. Cells. 2021;10(7):1729. [7] ALONSO-ALONSO ML, GARCÍA-POSADAS L, DIEBOLD Y. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review of Common Cargos. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):854-901. [8] WITWER KW, THÉRY C. Extracellular vesicles or exosomes? On primacy, precision, and popularity influencing a choice of nomenclature. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1648167. [9] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018; 7(1):1535750. [10] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487-514. [11] SHAO H, IM H, CASTRO CM, et al. New Technologies for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Chem Rev. 2018;118(4):1917-1950. [12] JIA Y, YU L, MA T, et al. Small extracellular vesicles isolation and separation: Current techniques, pending questions and clinical applications. Theranostics. 2022;12(15):6548-6575. [13] HAN YD, BAI Y, YAN XL, et al. Co-transplantation of exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned adipose mesenchymal stem cells promotes neovascularization and graft survival in fat grafting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):305-312. [14] BORIANI F, PERUT F. Exosomes Are Comparable to Source Adipose Stem Cells in Fat Graft Retention with Up-Regulating Early Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;146(2):232e. [15] ZHU YZ, ZHANG J, HU X, et al. Supplementation with Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Increases Fat Graft Survival and Browning in Mice: A Cell-Free Approach to Construct Beige Fat from White Fat Grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(5):1183-1195. [16] DONG J, WU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Allogeneic and Xenogeneic Small Extracellular Vesicles in Soft Tissue Repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6975-6991. [17] NIE J, YI Y, ZHU Y. Construction of tissue engineered adipose by human adipose tissue derived extracellular vesicle combined with decellularized adipose tissues scaffold. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(2):226-233. [18] DAI M, YU M, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosome-Like Vesicles Derived from Adipose Tissue Provide Biochemical Cues for Adipose Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(21-22):1221-1230. [19] NIE F, DING P, ZHANG C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from lipoaspirate fluid promote fat graft survival. Adipocyte. 2021;10(1): 293-309. [20] NIE JY, ZHU YZ, WANG JW, et al. Preparing Adipogenic Hydrogel with Neo-Mechanical Isolated Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Adipose Tissue Engineering. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(2): 212e-222e. [21] HONG P, XU X, HU X, et al. Therapeutic potential of small extracellular vesicles derived from lipoma tissue in adipose tissue regeneration-an in vitro and in vivo study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):222. [22] HUANG H, FENG S, ZHANG W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell‑derived extracellular vesicles improve the survival of transplanted fat grafts. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3069-3078. [23] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):555-568. [24] CHEN L, QU J, MEI Q, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MenSCs) as a novel therapeutic impetus in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):433. [25] SUN D, MOU S, CHEN L, et al. High yield engineered nanovesicles from ADSC with enriched miR-21-5p promote angiogenesis in adipose tissue regeneration. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):83. [26] ZHAO R, ZHAO T, HE Z, et al. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 2021; 10(1):587-604. [27] 四川大学.一种用于小动物软组织再生的皮下硅胶管装置及应用: CN201810705889.1[P]. 2018-11-02. [28] 张雪亭.细胞治疗产品发展现状与展望[J].科学与财富,2022, 14(11):25-27. [29] DING Y, LI Y, SUN Z, et al. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles and membranes for tissue repair. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):368. [30] MA ZJ, YANG JJ, LU YB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(8):814-840. [31] LI SR, MAN QW, GAO X, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: Present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175. [32] KELLER S, RIDINGER J, RUPP AK, et al. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med. 2011;9:86. [33] LÄSSER C, ALIKHANI VS, EKSTRÖM K, et al. Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages. J Transl Med. 2011;9:9. [34] LIU H, YUAN W, PANG Q, et al. Single-particle analysis of tear fluid reveals abundant presence of tissue factor-exposing extracellular vesicles with strong coagulation activity. Talanta. 2022;239:123089. [35] MURAOKA S, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, YANAMANDRA K, et al. Proteomic Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Cerebrospinal Fluid of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: A Pilot Study. Cells. 2020;9(9):1959. [36] HA DH, KIM HK, LEE J, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells. 2020;9(5):1157. [37] LO SICCO C, REVERBERI D, BALBI C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Endorsement of Macrophage Polarization. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):1018-1028. [38] CHEN K, XIONG J, XU S, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Exosomes Improve Fat Graft Survival by Promoting Prolipogenetic Abilities through Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:5014895. [39] ZHI Z, SUN Q, TANG W. Research advances and challenges in tissue-derived extracellular vesicles. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:1036746. [40] DONG J, WU B, TIAN W. Adipose tissue-derived small extracellular vesicles modulate macrophages to improve the homing of adipocyte precursors and endothelial cells in adipose tissue regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1075233. [41] THOMOU T, MORI MA, DREYFUSS JM, et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017;542(7642):450-455. [42] ZHANG Y, YU M, DAI M, et al. miR-450a-5p within rat adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles promotes adipogenic differentiation by targeting WISP2. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(6):1158-1168. |
| [1] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [2] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [3] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [4] | Zhuge Xiaoxuan, Li Ce, Bao Guangjie, Kang Hong. Potential value of canonical and non-canonical roles of connexin 43 in disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [6] | Guo Zehua, Li Zhaoyong, Chen Long, Duan Jiahao, Jiang Haobo, Chen Guangxue, Su Youxian, Liu Enxu, Yang Shaofeng. Action mechanism of Bushenhuoxue decoction on promoting nucleus pulposus-like differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3974-3980. |
| [7] | Li Zhen, Sun Xiao, Xie Yongpeng, Rong Wang, Sun Haitao. Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles promote neurogenesis of neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3994-3999. |
| [8] | Wang Yanyang, Liu Chan, Yu Limei, He Zhixu. Current status and future of treatment of pulmonary fibrosis by mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4079-4086. |
| [9] | Long Yi, Yang Jiaming, Ye Hua, Zhong Yanbiao, Wang Maoyuan. Extracellular vesicles in sarcopenic obesity: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| [10] | Zhao Lixin, Tang Qingxi, Zhang Kezhong. Influence of adipose tissue and its derivative on wound repair and vascularization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2120-2125. |
| [11] | Bai Siqi, Xiao Zhen, Liu Jing. Application potential of adipose-derived stem cells in female pelvic floor dysfunction diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 921-927. |
| [12] | Li Yujiao, Su Kunxia. High-intensity endurance exercise influences browning of white adipose tissue in a mouse model of high-fat diet induced obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 707-713. |
| [13] | Chen Hongcai, Wang Shaohong, Wang Yuanyuan, Gu Jiamei, Liu Chunpeng, Zhao Yongqiang, Qiu Xiaoyang, Zhan Xiaofen. Application value of environment-friendly tissue sample preparation solution in the detection of different adipocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5510-5515. |
| [14] | Peng Fengli, Li Chaofu, Shi Bei. Application of the nanovesicle delivery system in cardiovascular diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4862-4868. |
| [15] | Cai Chuang, Huang Yonghui, Cao Xingbing, Sun Haitao, Guan Shihao, Huang Wenkang, Han Bo. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote the differentiation of rat neural stem cells into neurons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3845-3851. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||