Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3845-3851.doi: 10.12307/2023.672
Previous Articles Next Articles
Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote the differentiation of rat neural stem cells into neurons
Cai Chuang, Huang Yonghui, Cao Xingbing, Sun Haitao, Guan Shihao, Huang Wenkang, Han Bo
- Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-20Accepted:2022-10-11Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-18 -
Contact:Huang Yonghui, Master, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Cai Chuang, Master candidate, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Zhenjiang Science and Technology Project, No. SH2020053 (to HYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cai Chuang, Huang Yonghui, Cao Xingbing, Sun Haitao, Guan Shihao, Huang Wenkang, Han Bo. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote the differentiation of rat neural stem cells into neurons[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3845-3851.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
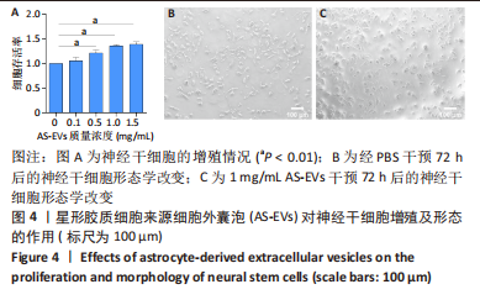
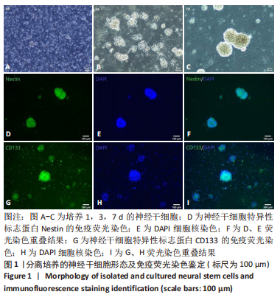
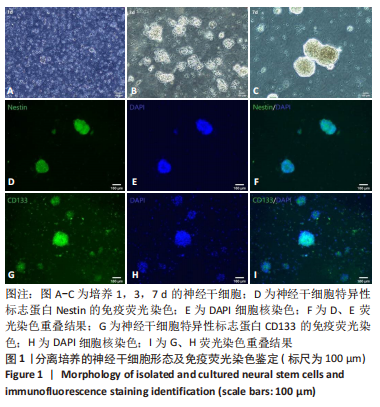
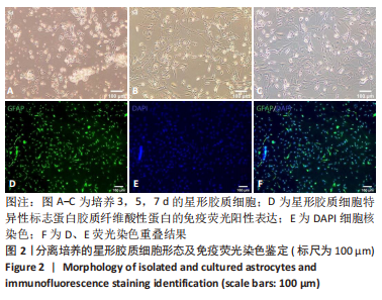
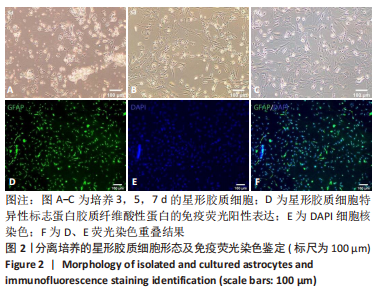
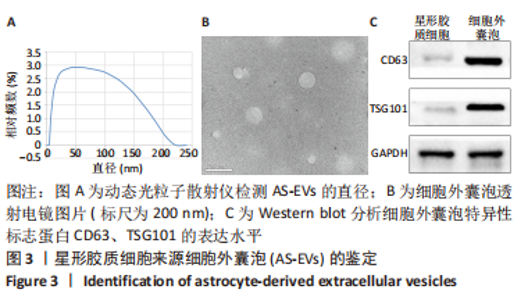
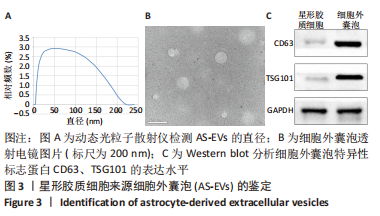
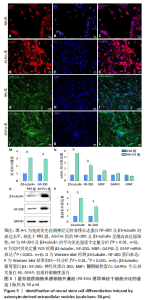
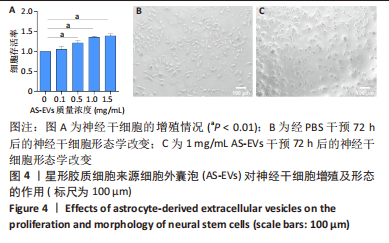
2.4 AS-EVs对神经干细胞存活率的影响 CCK-8结果显示随着AS-EVs质量浓度增加,神经干细胞增殖活性逐渐增强,根据统计学分析1.0 mg/mL与1.5 mg/mL组之间差异无显著性意义,故选用1.0 mg/mL AS-EVs进行后续实验,见图4A。 2.5 神经干细胞经等体积PBS及AS-EVs干预后的形态变化及免疫荧光检测 PBS组神经干细胞少量贴壁分化,贴壁细胞具有细长突起,呈神经元样,见图4B;而AS-EVs组神经干细胞大量贴壁分化,分化细胞胞体饱满,可见明显细长突起,呈神经元样,见图4C。免疫荧光检测结果显示AS-EVs 组较PBS组中神经元特异性标志物神经丝蛋白200、微管蛋白β3呈显著高表达(P < 0.01,n=3),见图5A-M。 2.6 qRT-PCR及Western blot检测经 AS-EVs 干预后神经元细胞特异性指标的表达水平 AS-EVs 组较 PBS 组显著高表达神经元特异性标志物微管蛋白β3及神经丝蛋白200(P均 < 0.001,n=3),见图5N-P,经多种方式验证得AS-EVs可以促进大鼠神经干细胞向神经元分化。"
| [1] HOU B, ZHANG Y, LIANG P, et al. Inhibition of the NLRP3-inflammasome prevents cognitive deficits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice via the alteration of astrocyte phenotype. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(5): 377. [2] LEE JS, HSU YH, CHIU YS, et al. Anti-IL-20 antibody improved motor function and reduced glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):156. [3] LI P, GAO Y, LI X, et al. mRNA and miRNA expression profile reveals the role of miR-31 overexpression in neural stem cell. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):17537. [4] PANG AL, XIONG LL, XIA QJ, et al. Neural Stem Cell Transplantation Is Associated with Inhibition of Apoptosis, Bcl-xL Upregulation, and Recovery of Neurological Function in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(7):1262-1275. [5] ZHAO Z, MA Y, CHEN Z, et al. Effects of Feeder Cells on Dopaminergic Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016; 10:291. [6] LI W, WANG SS, SHAN BQ, et al. miR-103-3p targets Ndel1 to regulate neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(2):401-408. [7] YU X, NAGAI J, KHAKH BS. Improved tools to study astrocytes. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020;21(3):121-138. [8] KIM SK, NABEKURA J, KOIZUMI S. Astrocyte-mediated synapse remodeling in the pathological brain. Glia. 2017;65(11):1719-1727. [9] BALDWIN KT, EROGLU C. Molecular mechanisms of astrocyte-induced synaptogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017;45:113-120. [10] YANG H, YAN H, LI X, et al. Inhibition of Connexin 43 and Phosphorylated NR2B in Spinal Astrocytes Attenuates Bone Cancer Pain in Mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:129. [11] YANG T, DAI Y, CHEN G, et al. Corrigendum: Dissecting the Dual Role of the Glial Scar and Scar-Forming Astrocytes in Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:270. [12] SHIGETOMI E, SAITO K, SANO F, et al. Aberrant Calcium Signals in Reactive Astrocytes: A Key Process in Neurological Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(4):996. [13] LI X, LI M, TIAN L, et al. Reactive Astrogliosis: Implications in Spinal Cord Injury Progression and Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9494352. [14] PATEL MR, WEAVER AM. Astrocyte-derived small extracellular vesicles promote synapse formation via fibulin-2-mediated TGF-β signaling. Cell Rep. 2021;34(10):108829. [15] LIU X, LV X, LIU Z, et al. MircoRNA-29a in Astrocyte-derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppresses Brain Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via TP53INP1 and the NF-κB/NLRP3 Axis. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022;42(5):1487-1500. [16] CHUN C, SMITH AST, KIM H, et al. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles enhance the survival and electrophysiological function of human cortical neurons in vitro. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120700. [17] GBD 2016 NEUROLOGY COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5):459-480. [18] KOMATSU F, FARKAS I, AKATSU H, et al. Potential neural progenitor cells in fetal liver and regenerating liver. Cytotechnology. 2008;56(3):209-217. [19] 何欣然,孙浩,秦晓颖,等.星形胶质细胞在突触可塑性中的研究进展[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2022,17(4):215-217,233. [20] D’ARRIGO G, GABRIELLI M, SCARONI F, et al. Astrocytes-derived extracellular vesicles in motion at the neuron surface: Involvement of the prion protein. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(9):e12114. [21] PEI X, LI Y, ZHU L, et al. Astrocyte-derived exosomes suppress autophagy and ameliorate neuronal damage in experimental ischemic stroke. Exp Cell Res. 2019;382(2):111474. [22] PEI X, LI Y, ZHU L, et al. Astrocyte-derived exosomes transfer miR-190b to inhibit oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced autophagy and neuronal apoptosis. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(8):906-917. [23] 裴美娟,李娅丽,涂悦,等.星形胶质细胞分泌的外泌体在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用机制研究进展[J].武警医学,2021,32(9):817-820. [24] NOGUERAS-ORTIZ CJ, MAHAIRAKI V, DELGADO-PERAZA F, et al. Astrocyte- and Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Effect Complement-Mediated Neurotoxicity. Cells. 2020;9(7):1618. [25] ROSAS-HERNANDEZ H, CUEVAS E, RAYMICK JB, et al. Characterization of Serum Exosomes from a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019;16(5):388-395. [26] SILVERMAN JM, CHRISTY D, SHYU CC, et al. CNS-derived extracellular vesicles from superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1)G93A ALS mice originate from astrocytes and neurons and carry misfolded SOD1. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(10):3744-3759. [27] CHEN Y, XIA K, CHEN L, et al. Increased Interleukin-6 Levels in the Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:574. [28] BASSO M, POZZI S, TORTAROLO M, et al. Mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD1) induces protein secretion pathway alterations and exosome release in astrocytes: implications for disease spreading and motor neuron pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288(22):15699-15711. [29] ISHII T, WARABI E, MANN GE. Circadian control of BDNF-mediated Nrf2 activation in astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:169-178. [30] WANG J, RONG Y, JI C, et al. MicroRNA-421-3p-abundant small extracellular vesicles derived from M2 bone marrow-derived macrophages attenuate apoptosis and promote motor function recovery via inhibition of mTOR in spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):72. [31] HE B, CHEN W, ZENG J, et al. Long noncoding RNA NKILA transferred by astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles protects against neuronal injury by upregulating NLRX1 through binding to mir-195 in traumatic brain injury. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(6):8127-8145. [32] 刘宗秀,张紫微,成媛,等.Notch信号通路对脑缺血大鼠神经干细胞移植后神经再生的影响[J].解剖学报,2020,51(1):15-20. [33] LI J, HAN Y, LI M, et al. Curcumin Promotes Proliferation of Adult Neural Stem Cells and the Birth of Neurons in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice via Notch Signaling Pathway. Cell Reprogram. 2019;21(3):152-161. [34] WU Y, GAO Q, ZHU S, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells through notch signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(3):793-798. [35] HU N, ZOU L. Multiple functions of Hes genes in the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Ann Anat. 2022;239:151848. [36] WANG C, CHEN JC, XIAO HH, et al. Jujuboside a promotes proliferation and neuronal differentiation of APPswe-overexpressing neural stem cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2022; 772:136473. [37] QIAO J, ZHAO J, CHANG S, et al. MicroRNA-153 improves the neurogenesis of neural stem cells and enhances the cognitive ability of aged mice through the notch signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(2):808-825. [38] BAI W, ZHANG X, SU X, et al. Activation of miR-124-3p/Notch pathway promotes proliferation and differentiation of rat neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;36(1):49-55. [39] PAN WL, CHOPP M, FAN B, et al. Ablation of the microRNA-17-92 cluster in neural stem cells diminishes adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive function. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):5257-5267. [40] WU H, DING L, WANG Y, et al. MiR-615 Regulates NSC Differentiation In Vitro and Contributes to Spinal Cord Injury Repair by Targeting LINGO-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(7):3057-3074. [41] SUZUKI F, OKUNO M, TANAKA T, et al. Overexpression of neural miRNAs miR-9/9* and miR-124 suppresses differentiation to Müller glia and promotes differentiation to neurons in mouse retina in vivo. Genes Cells. 2020;25(11):741-752. [42] MA R, WANG M, GAO S, et al. miR-29a Promotes the Neurite Outgrowth of Rat Neural Stem Cells by Targeting Extracellular Matrix to Repair Brain Injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(9):599-614. |
| [1] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [3] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [4] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [5] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [6] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [7] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [8] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [9] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [10] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [11] | Liao Yidong, Ming Jiang, Song Wenxue, Wang Zili, Zhang Yu, Liao Yifei, Xu Kaya, Yang Hua. An experimental method for simultaneously culturing primary cortical and hippocampal neurons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 897-902. |
| [12] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [13] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [14] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [15] | Zhao Siqi, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effects of enriched environment combined with melatonin on learning and memory function and brain neuron apoptosis in SAMP8 mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 701-706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||