Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 242-246.doi: 10.12307/2023.899
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of fascia gun versus stretching on exercise-induced muscle fatigue
Dai Jiansong1, Xin Dongling1, Chen Gangrui2
- 1Department of Sports and Health, 2Department of Competitive Sports, Nanjing Sport Institute, Nanjing 210004, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-23Accepted:2022-12-24Online:2024-01-18Published:2023-06-30 -
About author:Dai Jiansong, Master, Associate professor, Department of Sports and Health, Nanjing Sport Institute, Nanjing 210004, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Scientific Fitness Guidance Content Project of National Administration of Sports, China, No. 2017B002 (to DJS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Jiansong, Xin Dongling, Chen Gangrui. Effects of fascia gun versus stretching on exercise-induced muscle fatigue[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 242-246.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

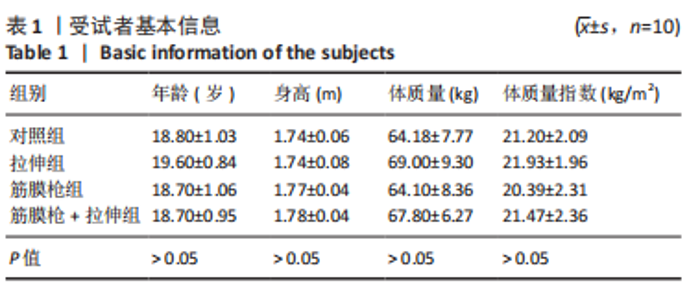
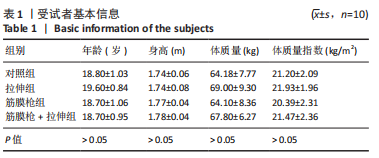
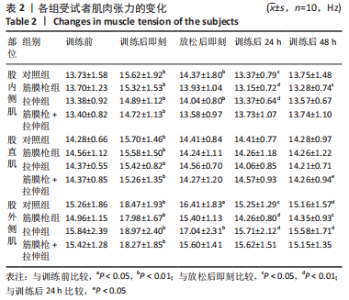
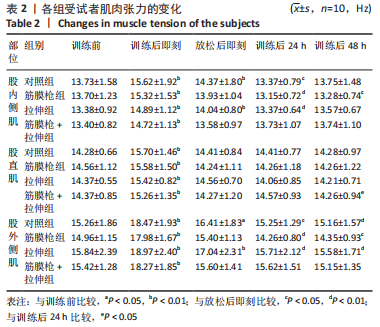
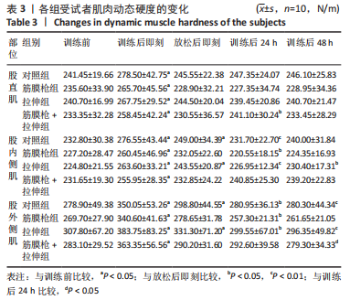
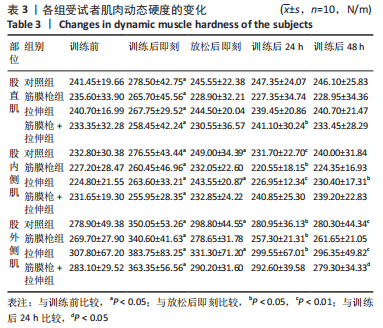
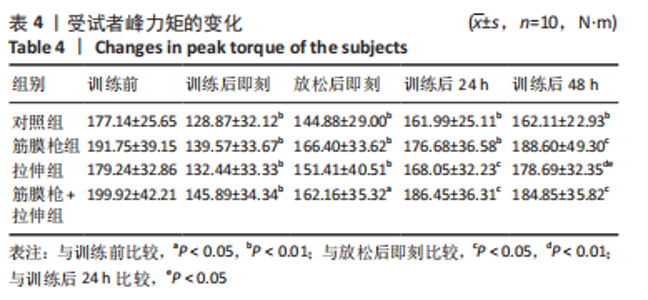
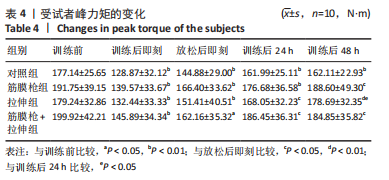
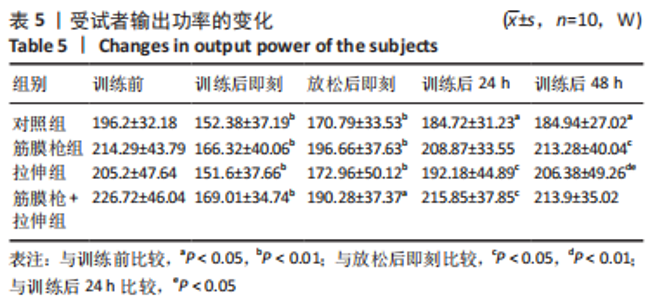
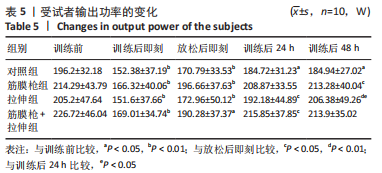
2.4 肌肉张力的变化 经多元方差重复测量分析,股外侧肌、股中间肌、股内侧肌的张力与时间的交互效应具有高度统计学意义(P < 0.01)。放松后即刻,对照组、拉伸组的股外侧肌、股内侧肌张力显著高于训练前(P < 0.01),筋膜枪组、筋膜枪+拉伸组的股外侧肌、股内侧肌张力与训练前相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);训练后24 h,对照组、拉伸组、筋膜枪组的股外侧肌、股内侧肌张力显著低于放松后即刻(P < 0.05);训练后24,48 h,4组与训练前相比均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.5 肌肉动态硬度的变化 经多元方差重复测量分析,股外侧肌、股中间肌、股内侧肌的动态硬度与时间的交互效应具有高度统计学意义(P < 0.01)。放松后即刻,对照组、拉伸组的股外侧肌、股内侧肌动态硬度显著高于训练前(P < 0.01),筋膜枪组、筋膜枪+拉伸组的股外侧肌动态硬度与训练前相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);训练后24 h,对照组、拉伸组、筋膜枪组的股外侧肌、股内侧肌动态硬度显著低于放松后即刻(P < 0.05);训练后24,48 h,4组与训练前相比均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。 2.6 等速肌力指标 经多元方差重复测量分析,各组间的峰力矩、输出功率与时间的交互效应具有高度统计学意义(P < 0.01)。采用单因素方差分析进行组内比较,4组的峰力矩放松后即刻均显著低于训练前(P < 0.01),训练后24 h对照组、筋膜枪组的峰力矩显著低于训练前(P < 0.01),拉伸组、筋膜枪+拉伸组训练后24 h与训练前比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。4组的输出功率,放松后即刻显著低于训练前(P < 0.01),对照组训练后24,48 h与训练前比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),拉伸组、筋膜枪组、筋膜枪+拉伸组训练后24,48 h后与训练前比较均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表4,5。 2.7 不良事件 参与试验的所有受试者在训练和放松过程中,均未发生肌肉损伤,使用筋膜枪后也未发生拉伤等不良事件。"

| [1] REILLY T, EKBLOM B. The use of recovery methods post ‐ exercise. J Sports Sci. 2005;23(6):619-627. [2] DAVIS HL, ALABED S, CHICO TJA. Effect of sports massage on performance and recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2020;6(1):e000614. [3] 黄浩洁,于成,赵焕彬.泡沫轴滚动对改善成年男性大腿后肌群柔韧性的效用研究[J].体育科学,2016,36(5):46-53. [4] 瞿超艺,徐金成,赵杰修. 超低温冷疗对延迟性肌肉酸痛的作用——系统综述[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(8):754-769. [5] CULLEN ML, CASAZZA GA, DAVIS BA. Passive Recovery Strategies after Exercise: A Narrative Literature Review of the Current Evidence. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2021;20(7):351-358. [6] MACDONALD GZ, BUTTON DC, DRINKWATER EJ, et al. Foam rolling as a recovery tool after an intense bout of physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;1(46):131-142. [7] Pearcey GE, Bradbury-Squires DJ, KAWAMOTO JE, et al. Foam rolling for delayed-onset muscle soreness and recovery of dynamic performance measures. J Athl Train. 2015;1(50):5-13. [8] TAKANOBU O.Acute effects of static VS.ballistic stretching on strength and musclar fatigue between ballet dancers and resistence-trained women.J Strength Cond Res. 2016;30(11):3220-3227. [9] 陈方灿.运动拉伸实用手册[M].北京: 北京体育大学出版社,2008:91-92. [10] 夏雨, 廖远朋.泡沫轴练习与静态拉伸对运动性肌肉疲劳影响的比较研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2019,45(5):122-126. [11] 黄浩洁, 侯莉娟, 刘晓莉,等. 泡沫轴滚动和静态拉伸对成年男性下肢运动能力的急性影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2020,43(2):14. [12] KONRAD A, GLASHÜTTNER C, REINER MM, et al. The Acute Effects of a Percussive Massage Treatment with a Hypervolt Device on Plantar Flexor Muscles’ Range of Motion and Performance. J Sports Sci Med. 2020;19(4):690-694. [13] FENG YN, LI YP, LIU CL, et al. Assessing the elastic properties of skeletal muscle and tendon using shearwave ultrasound elastography and MyotonPRO. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17064. [14] 温红梅, 兰月, 窦祖林, 等. Myoton-3肌肉检测仪在健康成人肌张力测量中的评价者间信度[J].中国康复理论与实践,2013,19(11):1058-1060. [15] YEO SM, KANG H, AN S, et al. Mechanical Properties of Muscles around the Shoulder in Breast Cancer Patients: Intra‐rater and Inter‐rater Reliability of the MyotonPRO. PMcR. 2020;12(4):374-381. [16] WANG JS. Therapeutic effects of massage and electrotherapy on muscle tone, stiffness and muscle contraction following gastrocnemius muscle fatigue. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(1):144-147. [17] BENSAMOUN SF, GLASER KJ, RINGLEB SI, et al. Rapid magnetic resonance elastography of muscle using one‐dimensional projection. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27(5):1083-1088. [18] DE ARAUJO RIBEIRO ALVARES JB, RODRIGUES R, DE AZEVEDO FRANKE R, et al. Inter-machine reliability of the Biodex and Cybex isokinetic dynamometers for knee flexor/extensor isometric, concentric and eccentric tests. Phys Ther Sport. 2015;16(1):59-65. [19] 王剑雄,周谋望,吴同绚,等.膝关节骨性关节炎患者髋外展肌等速肌力的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(12):5. [20] 廖远朋,于万良.泡沫轴练习对运动性肌肉疲劳恢复过程中肌肉功能的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(8):718-721+711. [21] SONG S, LEE K, JUNG S, et al. Effect of Horizontal Whole-Body Vibration Training on Trunk and Lower-Extremity Muscle Tone and Activation, Balance, and Gait in a Child with Cerebral Palsy. Am J Case Rep. 2018;19:1292-1300. [22] WANG JS, LEE SB, MOON SH. The immediate effect of PNF pattern on muscle tone and muscle stiffness in chronic stroke patient. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(3):967-970. [23] WANG JS. Therapeutic effects of massage and electrotherapy on muscle tone, stiffness and muscle contraction following gastrocnemius muscle fatigue. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(1):144-147. [24] 赵华伟, 戴剑松, 顾忠科, 等. 基于新型无创测量技术研究不同形式力量训练对肌肉疲劳及恢复的影响[J]. 南京体育学院学报(自然科学版),2016,15(5):32-38. [25] SOUZA A, SANCHOTENE CG, LOPES CMDS, et al. Acute Effect of 2 Self-Myofascial Release Protocols on Hip and Ankle Range of Motion. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(2):159-164. [26] NAKAMURA M, KASAHARA K, YOSHIDA R, et al. Comparison of The Effect of High- and Low-Frequency Vibration Foam Rolling on The Quadriceps Muscle. J Sports Sci Med. 2022;21(3):376-382. [27] AFONSO J, CLEMENTE FM, NAKAMURA FY, et al. The Effectiveness of Post-exercise Stretching in Short-Term and Delayed Recovery of Strength, Range of Motion and Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Physiol. 2021;12:677581. [28] GHASEMI M, BAGHERI H, OLYAEI G, et al.Effects of cyclic static stretch on fatigue recovery of triceps surae in female basketball players. Biol Sport. 2013;30(2):97-102. [29] MOORE JC. The Golgi tendon organ: a review and update. Am J Occup Ther. 1984; 38:227-236. [30] 周桂琴. 振动训练对生理机制影响综述[J].黄石理工学院学报,2011,27(5):49-53. [31] 彭春政, 危小焰, 张晓韵. 振动力量训练的机制和作用效果的研究进展[J].西安体育学院学报,2002,19(3):45-48. [32] 陈谦. 振动训练国内外研究近况[C]. 浙江省第十三届运动会体育科学论文报告会论文集.2006. [33] WANG Z, WEI Z, LI X, et al. Effect of whole-body vibration on neuromuscular activation and explosive power of lower limb: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. 2022;17(12):e0278637. [34] WANG F, ZHANG Z, LI C, et al. Acute effects of vibration foam rolling and local vibration during warm-up on athletic performance in tennis players. PloS One. 2022;17(5):e0268515. [35] POJSKIC HPJE. Acute effects of loaded whole body vibration training on performance. Asian J Sports Med. 2015;6(1):e24054. [36] IMTIYAZ S, VEQAR Z, SHAREEF MY. To Compare the Effect of Vibration Therapy and Massage in Prevention of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS). J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(1):133-136. |
| [1] | Lyu Moran, Xu Wenxin, Wang Di, Li Ming. New trends and developments of functional training research in the field of health care [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 302-307. |
| [2] | Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812. |
| [3] | Liang Xiao, Zhao Panchao, Li Jiahui, Ji Zhongqiu, Jiang Guiping. Gait and biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in multi-task walking of 4-6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 505-512. |
| [4] | Chen Peng, Wang Ling, Dong Shiyu, Ding Yue, Jia Shaohui, Kou Xianjuan, Zheng Cheng. Effects of whole-body vibration training on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5875-5883. |
| [5] | Zhang Xuebin, Ao Wenjun, Jiang Xin, Song Chenglin. Improvement of delayed-onset muscle soreness by pre-exercise whole-body vibration at 50 Hz [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5085-5090. |
| [6] | Sun Lingjuan, Song Xizheng, Li Daming, Han Zhenxue, Kang Yu, Xiang Hanrui, Sheng Kai. Percutaneous vertebroplasty under distraction with external spinal fixator for vertebral osteoporotic compression fractures with posterior wall damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4954-4958. |
| [7] | Bai Xing, Wang Guojun, Wang Shaokun. Improvement of cognitive function by blood flow restriction training: mechanisms and applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4577-4585. |
| [8] | Lei Senlin, Zhang Minghui, Ma Chunlian, Gao Weifeng, Xia Xiaoyan, Dong Kunwei. Muscle effect, dose-effect relationship, and physiological mechanism of KAATSU-resistance training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4254-4264. |
| [9] | Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi, Liu Jie, Yang Tieli, Zou Yuqi, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Zhang Qinyang, Chen Song, Che Tongtong, Li Zhiyuan, Guan Rongxin, Wang Chunlu. Maintenance and attenuation trajectory of increased muscle strength after exposure to short-term low-frequency pulsed magnetic field via activation of classical transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3721-3727. |
| [10] | Song Cuirong, Chen Tongzhen, Liu Meixiao, Zhang Haifeng. Simulated analysis of influence of walking step length on lower limb muscle strength in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3486-3491. |
| [11] | Liu Xiuqi, Chen Fang, Zhong Hehe, Xiong Huazhang, Lyu Guoqing, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Partial peroneus longus tendon reconstruction in the treatment of posterolateral complex injury of the knee joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2093-2098. |
| [12] | Li Zhongshan, Wang Chunlu, Liu Jie, Yang Tieli, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Zhang Qinyang, Chen Song, Che Tongtong, Li Zhiyuan, Guan Rongxin, Bai Shi. Effects of short-term low-frequency pulsed electrical magnetic field-induced classical transient receptor potential channel 1 on maximum voluntary contraction and strength endurance of the biceps brachii [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1796-1804. |
| [13] | Zheng Wei, Sun Libing, Xiong Yingzhe, Zhang Yichi, You Jing, Huang Wenqi, Guo Yanhua, Liu Hongjun. Effect of eccentric strengthening on hamstring strength: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4749-4756. |
| [14] | Hao Zhixin, Wu Yixin, Wang Xin, Xia Zhongliang. Effect of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on muscle strength and endurance: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3273-3280. |
| [15] | Chen Keyi, Wang Dingxuan, Zhao Sike, Xia Zhangrong. Research hotspots of pressure training in rehabilitation and visualized analysis of relevant literature data in the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2406-2411. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||