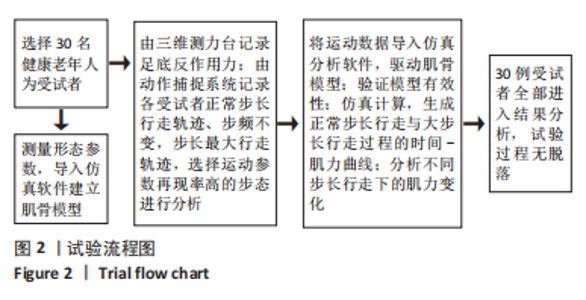
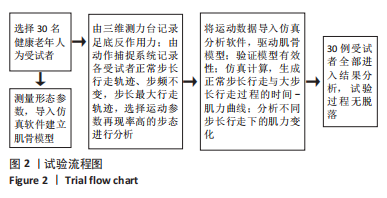
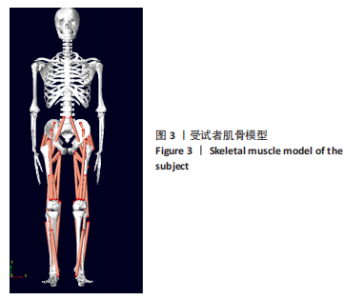
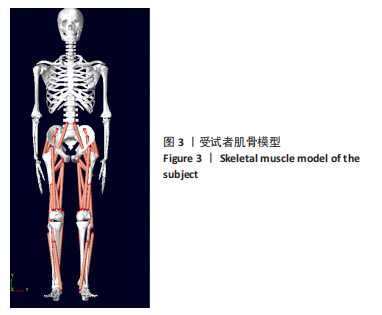
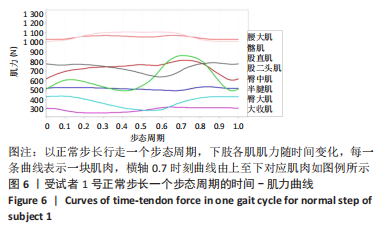
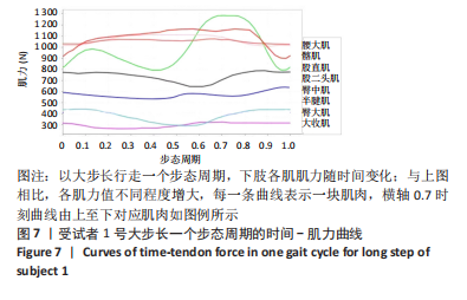
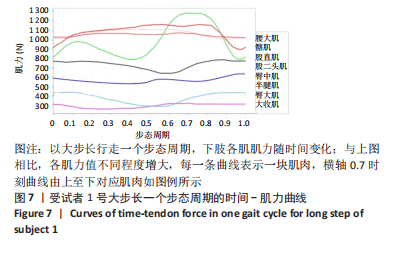
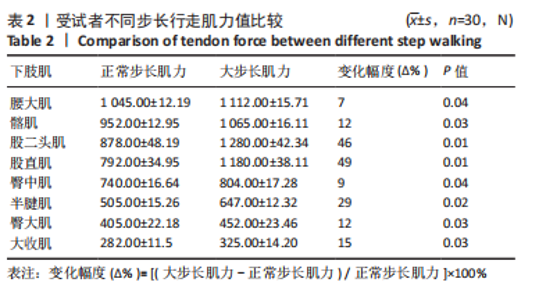
[1] 许锦兰,李密,吴淑华.老年股骨骨折患者流行病学特点[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(5):995-997.
[2] 张翔,尤炯鸣,王勇.老年骨质疏松性股骨远端骨折治疗方法的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2021,37(2):182-186.
[3] 王永胜,侯俊,王楠,等.虚拟现实技术联合常规肌力训练对老年人身体稳定性的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(1): 40-42.
[4] 柏文喜,曹红十,王冰,等.老年人下肢肌力测量方法及其研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(20):4474-4477.
[5] 王浩伦,朱业安,徐唯祎,等.步态识别特征的提取和重要性排序[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2019,36(7):811-817.
[6] FRANCIS P, WHATMAN C, SHEERIN K, et al. The proportion of lower limb running injuries by gender,anatomical location and specific pathology: a systematic review. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(1):21-31.
[7] 王俊清,张希妮,罗震,等.步频和步长的改变对下肢生物力学的影响研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(2):138-144.
[8] 熊然.全膝关节置换术后三维步态分析与个性化多体动力学建模初步探索[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2017.
[9] 刘志宏,张炅,何川,等.活动平台全膝关节假体和单髁膝关节假体置换术后的步态对比分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017, 11(1):17-23.
[10] 束一铭,钱竞光,戎科,等.偏瘫患者步态特征的动力学仿真分析[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(6):535-540.
[11] 尹梦虹,李庆,王文君,等.不同时期膝骨关节炎的膝关节6自由度步态变化[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(11):1341-1343.
[12] 张子华,纪仲秋,庞博,等.老年人步态稳定性、步态评价与跌倒风险的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(7):793-796.
[13] VARADY NH, GRODZINSKY AJ. Osteoarthritis Yearin Review 2015: Mechanics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(1):27-35.
[14] 黄萍,钟慧敏,陈博,等.正常青年人三维步态:时空及运动学和运动力学参数分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(24):3882-3888.
[15] 张书涛.用于功能评估的步态运动测量与特征提取研究[D].上海:上海大学,2016.
[16] 刘锦仪. 低负荷核心肌群训练对帕金森病患者步态及平衡功能的影响[D]. 广州:广州医科大学,2016.
[17] 胡少康. 基于表面肌电的手部运动康复与量化评估技术研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学,2021.
[18] 刘培培,于宁波,于洋,等.帕金森病患者上肢运动迟缓数字化测评[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2020,20(8):721-726.
[19] 唐晓. 基于表面肌电的运动单位活动特性分析及应用[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学,2021.
[20] MATEUS RB, FERRER-ROCA V, JOÃO F, et al. Muscle contributions to maximal single-leg forward braking and backward acceleration in elite athletes. J Biomech. 2020;112:110047.
[21] 崔伟玲,陈维毅,王长江,等.基于nmsBuilder和OpenSim建立个性化骨肌模型及其验证[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(6):608-614.
[22] WEINHANDL JT, BENNETT HJ. Musculoskeletal model choice influences hip joint load estimations during gait. J Biomech. 2019;91:124-132.
[23] 张希安,叶铭,王成焘. 基于骨肌模型的肌肉力计算方法及其面临的若干问题[J]. 医用生物力学,2008,23(6):475-479.
[24] 杨洋,张希妮,罗震,等.跑姿再训练对冲击力、下肢生物力学及刚度的影响[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(6):665-671.
[25] 冯晓东,王慧灵,刘承梅,等.运用步态分析系统评价益阳灸对中风后痉挛性偏瘫步态的疗效[J].时珍国医国药,2017,28(10):2461-2463.
[26] 李亚楠,钱秀清,孙翠莲,等.大腿假肢支撑期有限元分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2018,37(2):116-121.
[27] 王航辉,宋依芯,韩为华,等.老年与青年下肢关节生物力学特征研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(12):1089-1092.
[28] 中山大学附属第一医院,广东邦邦健康管理有限公司.肌力评定方法、系统和计算机可读存储介质:CN202210017860.0[P].2022-04-15.
[29] 柏豪豪,张叙,马剑雄,等. 自然行走对人体足底压力与下肢表面肌电信号影响的研究[J]. 国际生物医学工程杂志,2017,40(2):103-107,后插6.
[30] 杨红春,杨静,林辉杰,等.肌电图驱动估算方法在腰背肌力量研究中的应用进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(12):1052-1058.
[31] 刘军.运动强度对不同性别代谢综合征患者骨骼肌mRNA表达谱的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2019,48(12):1106-1111.
[32] 赵永才,高炳宏.运动诱导骨骼肌线粒体生物合成调控机制研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(1):79-84.
[33] 徐京朝,李晓智.中国老年人体育锻炼行为特征[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(3):649-654.
[34] ALJEHANI AM, BANJAR SA, ALSHEHRI GA, et al. Primary Uterine Rhabdomyosarcoma in a 54-Year-Old Postmenopausal Woman. Cureus. 2020;12(8):e9841.
[35] 单莎瑞,黄旭明,张明兴,等.基于三维步态分析仪对社区老人平衡能力与步态时空参数的相关性分析[J].广东医学,2021,42(3): 365-369.
[36] KO SU, JEROME GJ, SIMONSIEK EM, et al. Differential associations between dual-task Walking abilities and usual gait patterns in healthy older adults-results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Gait Posture. 2018;63(6):63-67.
[37] 侯慧磊,刘习方,田素斋,等.步态平衡训练对老年人平衡功能、神经功能及抗跌倒风险的影响[J].河北医学,2020,42(8):1227-1230.
[38] 陈良慈.核心稳定训练对骨质疏松症患者平衡功能、下肢肌力及跌倒发生的影响[J].临床研究,2019,27(3):15-17.
[39] 俞兵,周涛,吴健,等.肌电生物反馈联合康复训练对不完全性脊髓损伤下肢肌力及步态的影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(5):618-621.
[40] 刘姁霖,王丹,杨伟伟.步态训练在帕金森病康复治疗中的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(3):354-359.
[41] 刘云清,高瑞芳. 优秀女子手球运动员膝关节和踝关节屈伸旋转等速肌力评估[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2022,43(6):536-540.
[42] 徐小明,钱雨欣.股骨骨折合并脑外伤内固定方法的对比研究[J].浙江临床医学,2021,23(4):531-533.
[43] 文淑梅.脑小血管病患者步态、认知特征与相关性研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2020.
|