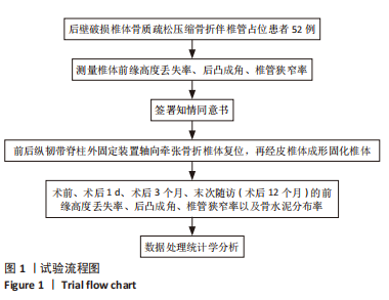
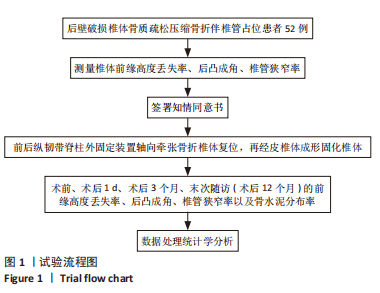
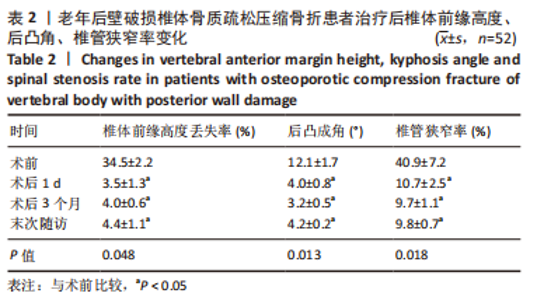
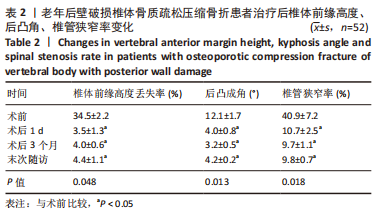
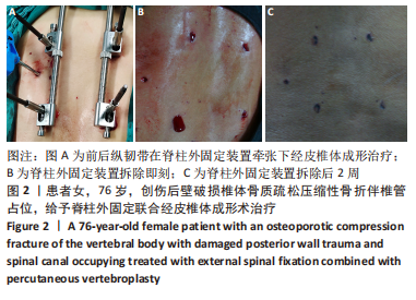
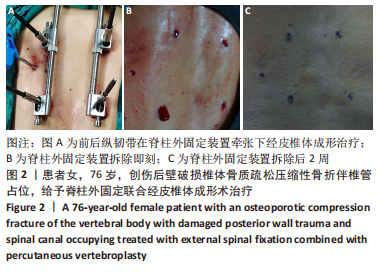
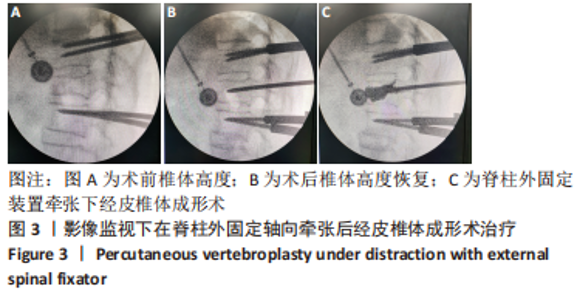
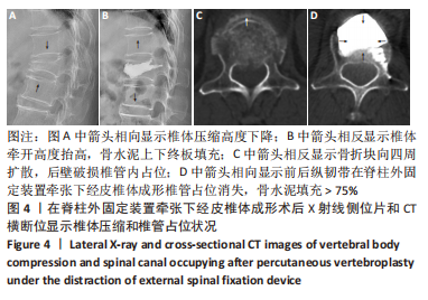
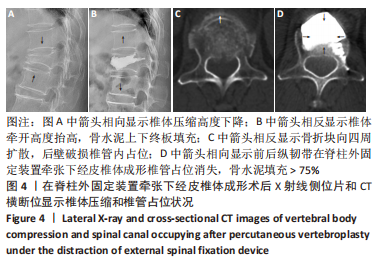
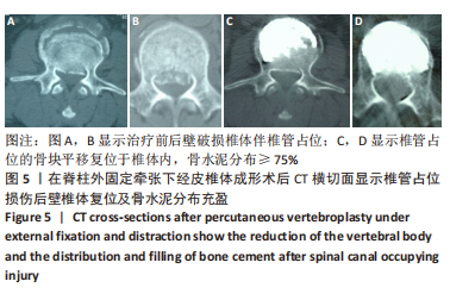
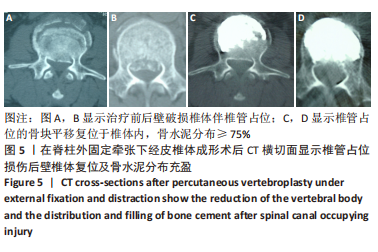
[1] ZHANG GA, ZHANG WP, CHEN YC, et al. Efficacy of Vertebroplasty in Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation of Thoracolumbar Fractures: A Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9483-9489.
[2] HOYT D, URITS I, ORHURHU V, et al. Current Concepts in the Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2020;24(5):16.
[3] SEZER C, SEZER C. Pedicle Screw Fixation with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Traumatic Thoracolumbar Vertebral Compression Fracture. Niger J Clin Pract. 2021;24(9):1360-1365.
[4] 王蒙,冉伟鹏,李宏健.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定技术的研究进展[J].中国医药科学,2020,12(10):68-71.
[5] 陈建颖.中西医结合疗法治疗疼痛性骨质疏松性脊柱骨折的疗效及对生活质量的影响[J].中国医药指南,2021,11(19):39-41.
[6] WEN Z, MO X, ZHAO S, et al. Comparison of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treatment of Thoracolumbar Severe Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture with Kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2021;152:e589-e596.
[7] CHMIELNICKI M, PROKOP A, KANDZIORA F, et al. Surgical and Non-surgical Treatment of Vertebral Fractures in Elderly. Z Orthop Unfall. 2019;157(6):654-667.
[8] 黄健华,包朝鲁,李业,等. PKP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的预后评价及继发危险因素分析[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(12): 2390-2395.
[9] 郑文鑫.腰椎管狭窄手术前后CT测量椎管容积的价值研究[D].海口:海南医学院,2018.
[10] 姚勇.经伤椎固定在胸腰段脊柱骨折患者中的实施效果及对JOY评分、VAS评分的影响[J].中国医药指南,2020,18(32):70-74.
[11] 王健,姜振先,彭梦瑶,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折患者影像学参数、Oswestry功能障碍指数及并发症的影响[J].解放军医药杂志,2021,33(10):59-62.
[12] MOLLOY S, MATHIS JM, BELKOFF SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1549-1554.
[13] 赵玉波,张庆明.椎体成形术中骨水泥弥散分布等级的量效关系[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):63-65.
[14] HE S, ZHANG Y, LV N, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50): e18217.
[15] XU K, LI YL, SONG F, et al. Influence of the distribution of bone cement along the fracture line on the curative effect of vertebral augmentation. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(9):4505-4513.
[16] ZHANG S, WANG GJ, WANG Q, et al. A mysterious risk factor for bone cement leakage into the spinal canal through the Batson vein during percutaneous kyphoplasty: a case control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):423.
[17] CHEN Z, CHEN Z, WU Y, et al. Risk Factors of Secondary Vertebral Compression Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty: A Retrospective Study of 650 Patients. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9255-9261.
[18] 王楠,许建柱,陈恩良,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉结合椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段骨折[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(4):339-346.
[19] NEZAMI N, JARMAKANI H, LATICH I, et al. Vertebroplasty-associated cement leak leading to iatrogenic venous compression and thrombosis. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2019;5(4):561-565.
[20] 朱立国,李金学.脊柱骨伤科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2015: 57-58.
[21] 蔡福金,沈根标,阮狄克.后纵韧带对椎体爆裂骨折椎管内骨块复位作用的生物力学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2001,11(6):351-354.
[22] 张蒲,顾志华,吕喜增.夹板外固定内在效应的生物力学分析[J].中医正骨,1993(1):17-18.
[23] CHEN F, SHI T, LI Y, et al. Multiple parameters for evaluating posterior longitudinal ligaments in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Orthopade. 2019;48(5):420-425.
[24] BERTON A, SALVATORE G, GIAMBINI H, et al. A 3D finite element model of prophylactic vertebroplasty in the metastatic spine: Vertebral stability and stress distribution on adjacent vertebrae. J Spinal Cord Med. 2020;43(1):39-45.
[25] ŞENTURK S, AKYOLDAS G, ÜNSAL ÜÜ, et al. Minimally Invasive Translaminar Endoscopic Approach to Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Cement Leakage: Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:15-19.
[26] LIU Z, ZHOU Y, LEI F, et al. Effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty with different phases bone cement for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(4):435-441.
[27] YOKOYAMA K, KAWANISHI M, YAMADA M, et al. Validity of intervertebral bone cement infusion for painful vertebral compression fractures based on the presence of vertebral mobility. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(1):228-232.
[28] ZHANG ZF, LIU DH, WU PY, et al. Ultra-early injection of low-viscosity cement in vertebroplasty procedure for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018; 52:35-39.
[29] YU W, XIAO X, ZHANG J, et al. Cement Distribution Patterns in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures with Intravertebral Cleft: Effect on Therapeutic Efficacy. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e408-e415.
[30] HE S,ZHANG Y,LV N,et al.The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50): 182-186.
[31] 应航,赵家璧.夹板固定中固定力的来源及断端生物力学效应[J].中国中医药科技,1996(2):37-38.
[32] HUANG S, ZHU X, XIAO D, et al. Therapeutic effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with anti-osteoporosis drug on postmenopausal women with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and analysis of postoperative bone cement leakage risk factors: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):452.
[33] FILIPPIADIS DK, MARCIA S, MASALA S, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Current Status, New Developments and Old Controversies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(12):1815-1823. |