Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5270-5276.doi: 10.12307/2023.707
Previous Articles Next Articles
Schnurri3 regulates osteogenic differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells induced by bone morphogenetic protein 2
Xie Yingchun1, Xu Wenjuan2, Li Yuwan3
- 1Department of Blood Transfusion, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences·Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chongqing Emergency Medical Center, Chongqing 400014, China; 3Department of Sports Medicine, Third Hospital of Peking University, Institute of Sports Medicine of Peking University, Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2022-08-26Accepted:2022-11-08Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-03-29 -
Contact:Li Yuwan, MD, Attending physician, Department of Sports Medicine, Third Hospital of Peking University, Institute of Sports Medicine of Peking University, Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Xie Yingchun, Master, Junior technician, Department of Blood Transfusion, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences·Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China

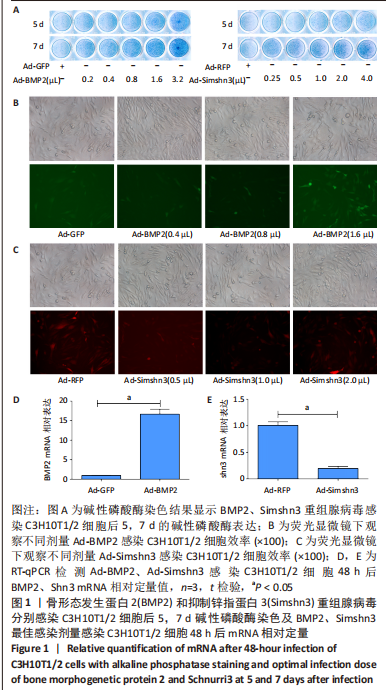
2.1 Ad-BMP2及Ad-Simshn3转染C3H10T1/2细胞 取对数期生长的C3H10T1/2细胞以约1×105/孔的密度铺板至24孔板,细胞贴壁后分别加入不同剂量的重组腺病毒感染,碱性磷酸酶染色观察两组腺病毒处理后5,7 d碱性磷酸酶的表达情况,并参考光学显微镜及荧光显微镜下细胞状态及荧光转染情况选择最佳感染剂量;分别提取最佳感染剂量感染48 h后细胞总mRNA分析BMP2及Shn3的mRNA相对定量值。结果显示:两种重组腺病毒均能成功感染C3H10T1/2细胞;BMP2最佳感染剂量为1.6 μL,Simshn3最佳感染剂量为2.0 μL;1.6 μL Ad-BMP2组较Ad-GFP对照组BMP2 mRNA表达水平显著增高,2.0 μL Ad-Simshn3组较Ad-RFP对照组Shn3 mRNA表达水平显著降低,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见图1。因此,后续实验中Ad-BMP2的使用量为1.6 μL/105个细胞,Ad-Simshn3的使用量为2.0 μL/105个细胞。"

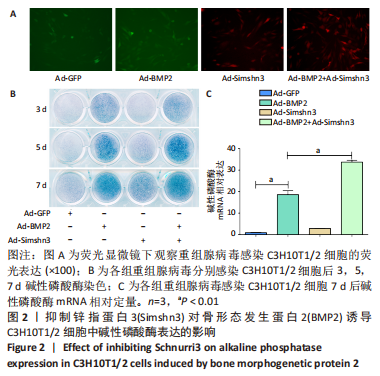
2.2 抑制Shn3后促进了BMP2诱导C3H10T1/2细胞碱性磷酸酶表达 C3H10T1/2 细胞在各组腺病毒(Ad-GFP、Ad-BMP2、Ad-Simshn3及Ad-BMP2+Ad-Simshn3)感染24 h后观察荧光表达,检测各组重组腺病毒作用3,5,7 d后碱性磷酸酶染色及碱性磷酸酶mRNA转录水平,结果显示,Ad-BMP2能诱导碱性磷酸酶的表达,抑制Shn3能增强BMP2诱导细胞碱性磷酸酶的表达;Ad-BMP2组碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达量显著高于Ad-GFP组,Ad-BMP2联合Ad-Simshn3组碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达量显著高于Ad-BMP2组,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见图2。以上结果提示抑制Shn3能显著增强BMP2诱导C3H10T1/2 细胞中碱性磷酸酶的表达。"

2.3 抑制Shn3促进BMP2诱导的C3H10T1/2细胞早、晚期成骨分化 成骨标志物的表达是检测间充质干细胞成骨分化的标准之一,随着细胞分化骨基质矿化不断增多,成骨分化的晚期标志钙盐结节也会增加。RT-qPCR检测各组重组腺病毒作用7 d后骨钙素、成骨细胞特异性转录因子、Runt相关转录因子2、Ⅰ型胶原mRNA转录水平。结果显示,Ad-BMP2组成骨细胞特异性转录因子、骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原、Runt相关转录因子2 mRNA转录水平较Ad-GFP对照组显著增高,抑制Shn3后BMP2诱导的成骨细胞特异性转录因子、骨钙素、Runt相关转录因子2、Ⅰ型胶原mRNA转录水平较Ad-BMP2组显著增高。茜素红染色及半定量分析结果显示,成骨培养基诱导21 d后Ad-GFP组无明显钙盐结节形成,Ad-BMP2组有显著钙盐结节形成,Ad-BMP2联合Ad-Simshn3组相较Ad-BMP2组表现出更显著的钙盐沉积作用,见图3。"


2.6 抑制Shn3增强小鼠脑微血管内皮细胞小管形成 小管形成实验是对血管内皮细胞血管生成的功能性评价,因此进一步检测抑制Shn3对BMP2诱导成骨过程中血管生成的影响。bEnd.3细胞铺板4 h后于光学显微镜下观察到Ad-GFP组、Ad-BMP2组、Ad-Simshn3组均未形成明显小管,Ad-BMP2联合Ad-Simshn3组开始出现小管雏形;Ad-Simshn3组培养8 h后开始出现小管,至12 h时出现多个显著小管;Ad-BMP2联合Ad-Simshn3组12 h后小管密度逐渐增高且部分区域出现管腔减小的现象;持续8 h及12 h后观察Ad-Simshn3组亦出现小管,并随培养时间延长而增多,见图6。血管生成实验是对血管内皮细胞的功能性评价,可以反映小鼠脑微血管内皮细胞在体外形成血管环的能力。"


2.7 抑制Shn3增强BMP2诱导C3H10T1/2细胞裸鼠皮下异位成骨 上述实验证实抑制Shn3显著增强BMP2诱导C3H10T1/2细胞成骨分化及血管形成,因此进一步在裸鼠皮下植入各组腺病毒处理后的C3H10T1/2细胞以观察皮下异位骨块形成情况。结果显示:小动物X射线片检测显示 Ad-GFP组不形成异位骨块,Ad-BMP2组在裸鼠皮下形成的异位骨块显著大于Ad-Simshn3组,但Ad-BMP2+Ad-Simshn3组骨块显著大于Ad-BMP2组,见图7A,B;苏木精-伊红染色及Masson染色结果显示Ad-BMP2+Ad-Simhn3组成熟骨组织相较Ad-BMP2及Ad-Simshn3单独作用组显著增高,见图7C。"

| [1] KOSTENUIK P, MIRZA FM. Fracture healing physiology and the quest for therapies for delayed healing and nonunion. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(2):213-223. [2] 王钊,闫石.应用Masquelet技术治疗大段骨缺损减少自体骨用量的可能性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3862-3869. [3] 彭鑫,彭中华,谭奇超,等.骨组织工程学中复合支架及其应用研究进展[J].医学综述, 2022,28(13):2548-2554. [4] 程永刚,宋晓阳,刘浩,等.股骨头缺血性坏死髋关节外科脱位入路打压植骨术后截骨端不愈合1例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(12):1340-1341. [5] KATAGIRI T, WATABE T. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016; 8(6):a021899. [6] PARK SH, KWON JS, LEE BS, et al. BMP2-modified injectable hydrogel for osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6603. [7] 从凯,李善龙,王飞,等.骨形态发生蛋白2,7治疗骨不连的效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(26):4243-4250. [8] SHEIKH Z, JAVAID MA, HAMDAN N, et al. Bone Regeneration Using Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Various Biomaterial Carriers. Materials (Basel). 2015;8(4):1778-1816. [9] PENG Y, KANG Q, CHENG H, et al. Transcriptional characterization of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)-mediated osteogenic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90(6):1149-1165. [10] ZHANG L, LUO Q, SHU Y, et al. Transcriptomic landscape regulated by the 14 types of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in lineage commitment and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Genes Dis. 2019;6(3):258-275. [11] RAHMAN MS, AKHTAR N, JAMIL HM, et al. TGF-β/BMP signaling and other molecular events: regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone formation. Bone Res. 2015;3:15005. [12] RAUNER M, BASCHANT U, ROETTO A, et al. Transferrin receptor 2 controls bone mass and pathological bone formation via BMP and Wnt signaling. Nat Metab. 2019;1(1):111-124. [13] CAHILL KS, CHI JH, DAY A, et al. Prevalence, complications, and hospital charges associated with use of bone-morphogenetic proteins in spinal fusion procedures. JAMA. 2009;302(1):58-66. [14] FU M, BLACKSHEAR PJ. RNA-binding proteins in immune regulation: a focus on CCCH zinc finger proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(2):130-143. [15] MACKEH R, MARR AK, FADDA A,et al. C2H2-Type Zinc Finger Proteins: Evolutionarily Old and New Partners of the Nuclear Hormone Receptors. Nucl Recept Signal. 2018;15: 1550762918801071. [16] JIN W, TAKAGI T, KANESASHI SN, et al. Schnurri-2 controls BMP-dependent adipogenesis via interaction with Smad proteins. Dev Cell. 2006;10(4):461-471. [17] CASSANDRI M, SMIRNOV A, NOVELLI F, et al. Zinc-finger proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017;3:17071. [18] WEI S, ZHANG L, ZHOU X, et al. Emerging roles of zinc finger proteins in regulating adipogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(23):4569-4584. [19] UPADHYAY A, MOSS-TAYLOR L, KIM MJ, et al. TGF-β Family Signaling in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9(9):a022152. [20] STROEBELE E, ERIVES A. Integration of Orthogonal Signaling by the Notch and Dpp Pathways in Drosophila. Genetics. 2016;203(1):219-240. [21] AFFOLTER M, BASLER K. The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(9):663-674. [22] VAN BORTLE K, PETERSON AJ, TAKENAKA N, et al. CTCF-dependent co-localization of canonical Smad signaling factors at architectural protein binding sites in D. melanogaster. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(16):2677-2687. [23] 孙鹏宇,张艳玲,荆玉明,等.腺病毒滴度不同测定方法比较[J].南方医科大学学报, 2011,31(2):234-238. [24] CHEN L, JIANG W, HUANG J, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(11):2447-2459. [25] 任明诗,丁羽,李子涵,等.成骨细胞与破骨细胞相互调节作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):822-827. [26] 王布雨,张勇,李飞非,等.骨软骨缺损修复中骨形态发生蛋白2 的作用与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(20):3259-3265. [27] HO SS, VOLLMER NL, REFAAT MI, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Promotes Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival and Resultant Bone Formation When Entrapped in Photocrosslinked Alginate Hydrogels. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(19):2501-2509. [28] JAMES AW, LACHAUD G, SHEN J, et al. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016;22(4):284-297. [29] KRISHNAN L, PRIDDY LB, ESANCY C, et al. Delivery vehicle effects on bone regeneration and heterotopic ossification induced by high dose BMP-2. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:101-112. [30] ZHANG C, MENG C, GUAN D, et al. BMP2 and VEGF165 transfection to bone marrow stromal stem cells regulate osteogenic potential in vitro. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(5):e9787. [31] MCBRIDE-GAGYI SH, MCKENZIE JA, BUETTMANN EG, et al. Bmp2 conditional knockout in osteoblasts and endothelial cells does not impair bone formation after injury or mechanical loading in adult mice. Bone. 2015;81:533-543. [32] MANNION RJ, NOWITZKE AM, WOOD MJ. Promoting fusion in minimally invasive lumbar interbody stabilization with low-dose bone morphogenic protein-2--but what is the cost? Spine J. 2011;11(6):527-533. [33] RAZZOUK S, SARKIS R. BMP-2: biological challenges to its clinical use. N Y State Dent J. 2012; 78(5):37-39. [34] YANG YS, XIE J, WANG D, et al. Bone-targeting AAV-mediated silencing of Schnurri-3 prevents bone loss in osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2958. [35] JONES DC, WEIN MN, OUKKA M, et al. Regulation of adult bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3. Science. 2006;312(5777):1223-1227. [36] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional Relationship between Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis in Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242. [37] SARAN U, GEMINI PIPERNI S, CHATTERJEE S. Role of angiogenesis in bone repair. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561:109-117. [38] SHARMA S, XUE Y, XING Z, et al. Adenoviral mediated mono delivery of BMP2 is superior to the combined delivery of BMP2 and VEGFA in bone regeneration in a critical-sized rat calvarial bone defect. Bone Rep. 2019;10:100205. [39] SHARMA S, SAPKOTA D, XUE Y, et al. Delivery of VEGFA in bone marrow stromal cells seeded in copolymer scaffold enhances angiogenesis, but is inadequate for osteogenesis as compared with the dual delivery of VEGFA and BMP2 in a subcutaneous mouse model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):23. [40] SHARMA S, SAPKOTA D, XUE Y, et al. Adenoviral Mediated Expression of BMP2 by Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Cultured in 3D Copolymer Scaffolds Enhances Bone Formation. PLoS One. 2016; 11(1):e0147507. [41] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328. [42] ZHANG J, PAN J, JING W. Motivating role of type H vessels in bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(9):e12874. [43] XU R, YALLOWITZ A, QIN A, et al. Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):823-833. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [3] | Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| [4] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [5] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [6] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [7] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [8] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [9] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [10] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [11] | Huang Guijiang, Ji Yuwei, Zhao Xin, Yang Yi, Zhao Yulan, Wang Peijin, Tang Wei, Jiao Jianlin. Effect and mechanism of different administration routes of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of tree shrews with osteoporotic fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 909-914. |
| [12] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [13] | Xiong Juan, Guan Yalin, Yang Yutong, Wang Fan, Liu Zhongshan. Application of stem cells to skin anti-aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 948-954. |
| [14] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [15] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 125
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 304
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



