Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (27): 4271-4276.doi: 10.12307/2023.619
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of oblique-pulling manipulation in the treatment of lumbar synovial incarceration
Lu Yu1, 2, Xiang Junyi1, 2, Yin Benjing1, 2, Bao Chaoyu1, 2, Bi Heng1, 2, Li Jizheng1, 2, Chen Shuai1, 2, He Guangxiong1, 2, Li Jubao1, 2
- 1Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-28Accepted:2022-08-08Online:2023-09-28Published:2022-11-07 -
Contact:Li Jubao, MD, Associate chief physician, Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Lu Yu, Master, Attending physician, Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860862, 81460736 (to LJB); Yunnan Province Applied Basic Research Program (General Project), No. 2011FB146 (to LJB); Young and Middle-Aged Academic and Technical Leaders in Yunnan Province Person Reserve Talent, No. [2019]7 (to LJB); Yunnan Provincial High-level Chinese Medicine Talent Discipline Leader and Yunnan Provincial Health Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 2017NS161 (to LJB); Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology-Yunnan College of Traditional Chinese Medicine Applied Basic Research Joint Special Youth Project, No. 11372110236 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Yu, Xiang Junyi, Yin Benjing, Bao Chaoyu, Bi Heng, Li Jizheng, Chen Shuai, He Guangxiong, Li Jubao. Finite element analysis of oblique-pulling manipulation in the treatment of lumbar synovial incarceration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4271-4276.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
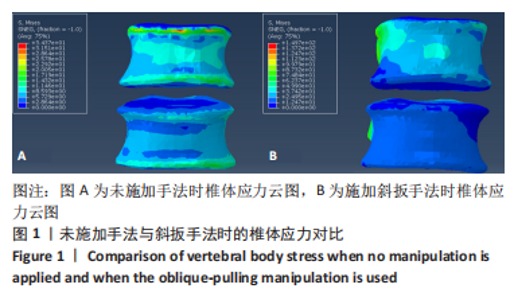
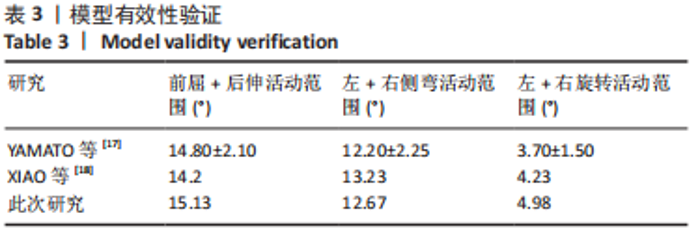
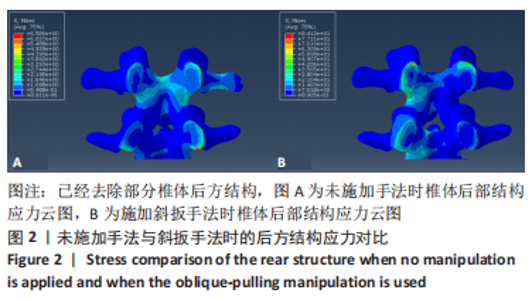
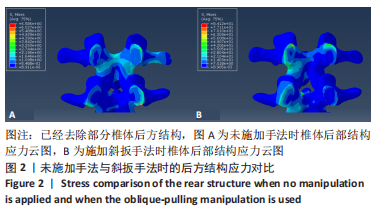
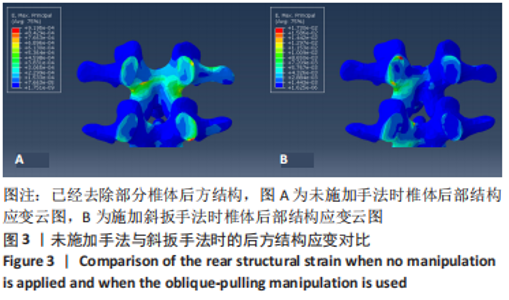
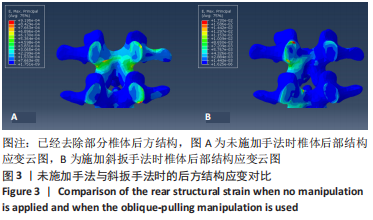
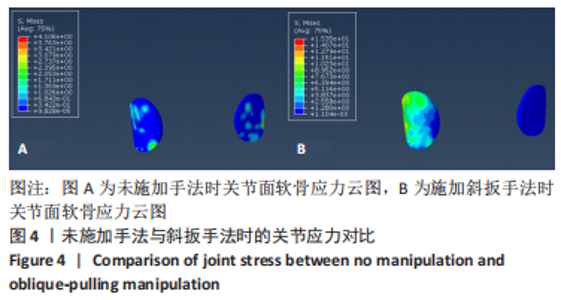
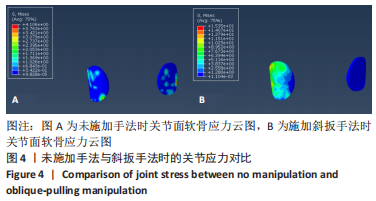
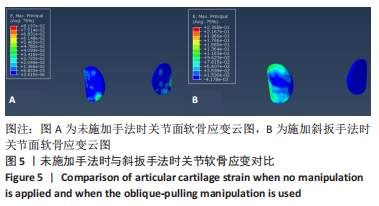
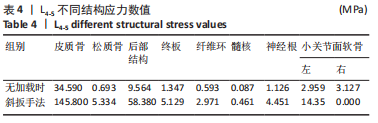
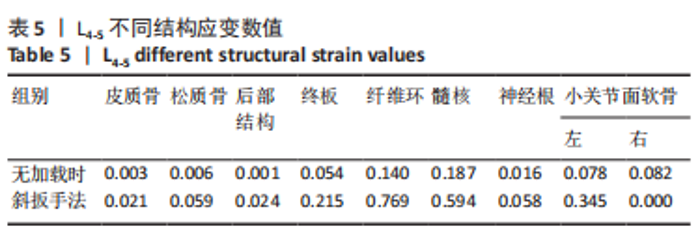
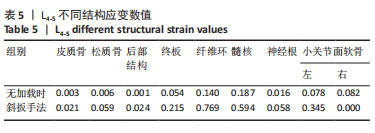
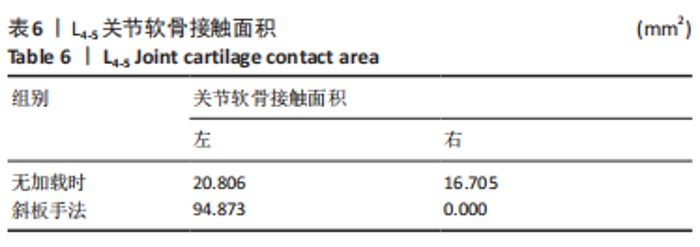
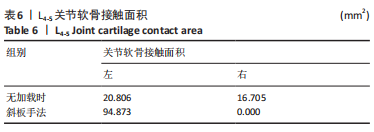
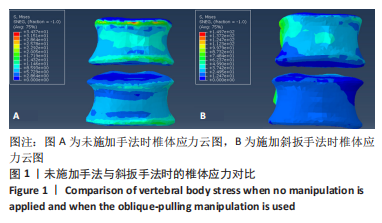
2.3 斜扳手法对腰椎L4-5节段各组织结构的生物力学影响 从应力云图可见,在模拟重力进行加载、未施加斜扳手法时,L4椎体的上终板受到的应力最大,其次为L5的下终板;而在施加斜扳手法时,椎体应力的分布会在左侧明显增加(图1)。从脊柱后部结构(去除了部分后方附件)的应力情况来看,未施加手法时,应力主要集中在峡部及关节突位置,双侧应力大小基本一致;而在施加斜扳手法时,后方结构的应力明显集中于左侧,右侧的应力会明显减小,后方结构的应变情况与应力结果相似(图2,3);小关节软骨情况,未施加斜扳手法时,左侧小关节软骨应力值大小为2.959 MPa,右侧为3.127 MPa;而施加斜扳手法后,左侧小关节软骨应力值大小为14.35 MPa,右侧为0 MPa(图4),在观察应变情况时,可以得出与应力类似的结果,在未施加斜扳手法时,左侧小关节软骨应变值大小为0.078 34,右侧为0.081 96,两侧应变基本一致;而在施加斜扳手法时,左侧小关节软骨的应变会明显增大,而右侧减小,其中左侧小关节软骨应变值大小为0.345 1,而右侧为0(图5)。上下关节突的关键软骨接触面积也与其应力和应变趋势一致,在未施加斜扳手法时左侧小关节软骨接触面积为20.806 2 mm2,右侧为16.705 3 mm2;在施加斜扳手法时,左侧小关节软骨接触面积为94.872 7 mm2,右侧0 mm2。见表4-6。"
| [1] FABER F. Lumbar facet joint disease: Classification, clinical diagnostics, and minimally invasive treatment. Orthopade. 2019;48(1):77-83. [2] YU X, ZHANG J, WANG MY, et al. Clinical Effects and Safety of the Use of Methylene Blue for the Treatment of Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome. Pain Physician. 2022;25(1):E15-E26. [3] JACOBSON RE, PALEA O, GRANVILLE M. Bipolar Radiofrequency Facet Ablation of the Lumbar Facet Capsule: An Adjunct to Conventional Radiofrequency Ablation for Pain Management. Cureus. 2017;9(9):e1635. [4] 谢幸财.腰椎小关节紊乱症的发病机理及手法治疗探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2006,14(S2):17-20. [5] SAE-JUNG S, JIRARATTANAPHOCHAI K. Outcomes of lumbar facet syndrome treated with oral diclofenac or methylprednisolone facet injection: a randomized trial. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1091-1098. [6] WU T, ZHAO WH, DONG Y, et al. Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Fluoroscopy or Computed Tomography Scanning Guidance in Lumbar Facet Joint Injections in Adults With Facet Joint Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(9):1558-1563. [7] 王志恒. 旋转复位法治疗急性腰椎后关节滑膜嵌顿症186例[J]. 中国临床康复,2002,6(8):1186. [8] 王亚楠,赵锦秀,侯海涛,等.消肿止痛胶囊联合腰椎斜扳法治疗急性腰扭伤的临床观察[J].中国中医急症,2022,31(3):456-458. [9] 祝波,张卓,蒋灼,等.体外冲击波联合手法复位治疗腰椎小关节紊乱疗效观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(4):496-497. [10] 卢钰,郑太才,王琪,等.不同体位下斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36):5872-5877. [11] 王辉昊,王宽,邓真,等.定位与非定位颈椎旋转手法应力作用比较:三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(S1):55. [12] ZHONG ZC, WEI SH, WANG JP, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys. 2006; 28(1):90-98. [13] DU HG, LIAO SH, JIANG Z, et al. Biomechanical analysis of press-extension technique on degenerative lumbar with disc herniation and staggered facet joint. Saudi Pharm J. 2016;24(3):305-311. [14] 黄学成,叶林强,梁德, 等.三维有限元模型分析旋转手法中旋转方向对颈椎间盘位移和椎间孔容积的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(3):404-408. [15] LEE SH, IM YJ, KIM KT, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed- and mobile-core artificial disc replacement: a finite element analysis. Spine. 2011;36(9):700-708. [16] MO Z, ZHAO Y, DU C, et al. Does location of rotation center in artificial disc affect cervical biomechanics? Spine. 2015;40(8):E469-E475. [17] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260. [18] XIAO Z, WANG L, GONG H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three surgical scenarios of posterior lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2012;11:31. [19] 徐海涛, 李松, 刘澜, 等. 腰椎斜扳手法时椎间盘的有限元分析 [J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2335-2338. [20] PEROLAT R, KASTLER A, NICOT B, et al. Facet joint syndrome: from diagnosis to interventional management. Insights Imaging. 2018;9(5):773-789. [21] DE ANDRÉS ARES J, GILSANZ F. Diagnostic nerve blocks in the management of low back pain secondary to facet joint syndrome. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim (Engl Ed). 2019;66(4):213-221. [22] KARKUCAK M, BATMAZ I, KERIMOGLU S, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes of ultrasonography-guided and blind local injections in facet syndrome: A 6-week randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020;33(3):431-436. [23] WON HS, YANG M, KIM YD. Facet joint injections for management of low back pain: a clinically focused review. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2020;15(1):8-18. [24] MOUSSA WM, KHEDR W. Percutaneous radiofrequency facet capsule denervation as an alternative target in lumbar facet syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 150:96-104. [25] Walter SG, Struwe C, Scheidt S, et al. Endoscopic facet joint denervation for treatment of chronic lower back pain. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;195:105904. [26] YUAN HJ, WANG CY, WANG YF. Endoscopic joint capsule and articular process excision to treat lumbar facet joint syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(28):8545-8551. [27] GÜNDOğDU Z, ÖTERKUş M, KARATEPE Ü. Evaluation of the Effect of Radiofrequency Denervation on Quality of Life of Patients with Facet Joint Syndrome by Oswestry Disability Index Score and Visual Analogue Scale Score. Prague Med Rep. 2021;122(4):278-284. [28] 刘德华. 腕踝针、芒针透刺结合腰部斜扳法治疗腰椎后关节滑膜嵌顿40例[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(6):1317-1318. [29] XIE Y, WANG X, JIAN Q, et al. Three dimensional finite element analysis used to study the influence of the stress and strain of the operative and adjacent segments through different foraminnoplasty technique in the PELD: Study protocol clinical trial (SPIRIT Compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(15):e19670. [30] CAO S, CHEN Y, ZHANG F, et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of “Three-Dimensional Balanced Manipulation” in the Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy by Finite Element Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5563296. [31] DEHGHAN-HAMANI I, ARJMAND N, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Subject-specific loads on the lumbar spine in detailed finite element models scaled geometrically and kinematic-driven by radiography images. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2019; 35(4):e3182. [32] FAN W, GUO LX. Biomechanical comparison of the effects of anterior, posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion on vibration characteristics of the human lumbar spine. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(5): 490-498. [33] 李民,周灵,汪桂珍,等.不同腰椎生理曲度下牵引的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3162-3167. [34] YIN J, LIU Z, LI C, et al. Effect of facet-joint degeneration on the in vivo motion of the lower lumbar spine. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):340. [35] URITS I, BURSHTEIN A, SHARMA M, et al. Low Back Pain, a Comprehensive Review: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2019;23(3):23. [36] 贺志亮,王德成,张慧. 脊柱定点旋转复位法结合小针刀松解治疗腰椎小关节紊乱症的临床疗效分析[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2019,25(6):991-997. [37] 刘慧,沈国权,张喜林,等.肌肉加载下腰椎间盘突出的有限元研究[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):493-499. [38] GALBUSERA F, CINA A, PANICO M, et al. Image-based biomechanical models of the musculoskeletal system. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):49. [39] GRAY RJ, THOM M, RIDDLE M, et al. Image-Based Comparison Between the Bilateral Symmetry of the Distal Radii Through Established Measures. J Hand Surg Am. 2019;44(11):966-972. [40] MONTEFIORI E, MODENESE L, DI MARCO R, et al. An image-based kinematic model of the tibiotalar and subtalar joints and its application to gait analysis in children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. J Biomech. 2019;85:27-36. [41] LANDGRAEBER S, PAULI J. Kinematic examination of the musculoskeletal system: Use of methods of image and image sequence analyses as well as shape and motion models. Orthopade. 2018;47(10):834-841. [42] ESKANDARI AH, ARJMAND N, SHIRAZI-ADL A, et al. Hypersensitivity of trunk biomechanical model predictions to errors in image-based kinematics when using fully displacement-control techniques. J Biomech. 2019;84:161-171. [43] ESKANDARI AH, ARJMAND N, SHIRAZI-ADL A, et al. Subject-specific 2D/3D image registration and kinematics-driven musculoskeletal model of the spine. J Biomech. 2017;57:18-26. [44] BONARETTI S, SEILER C, BOICHON C, et al. Image-based vs. mesh-based statistical appearance models of the human femur: implications for finite element simulations. Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(12):1626-1635. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Wu Taoguang, Nie Shaobo, Chen Hua, Zhu Zhengguo, Qi Lin, Tang Peifu. Biomechanical characteristics of a new multi-dimensional cross locking plate in the treatment of subtrochanteric nonunion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1330-1334. |
| [3] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [5] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [6] | Liu Jiaxin, Jia Peng, Men Yutao, Liu Lu, Wang Yeming, Ye Jinduo. Design and optimization of bone trabecular structure with triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 992-997. |
| [7] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [8] | Li Huiqin, Wang Chunjuan, Wang Yu, Wang Weifeng, Chen Dinggen, Li Na. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular teeth with different shapes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1050-1054. |
| [9] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [10] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Zhan Yi, Wang Biao, Ma Yuli, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun. Biomechanical comparison between a novel bone cement screw system and common surgical methods for the treatment of Kummell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 385-390. |
| [12] | Lu Hui, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Finite element analysis and application of unilateral and bilateral bone-filling mesh container in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 391-397. |
| [13] | Xu Guangming, Liang Ziyang, Wang Hongbo, Zhang Zhen, Xiao Qinghua, Yang Jiyong, Lin Xiaosheng. Mechanical effect of oblique-pulling manipulation on triarticular complex after human lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4277-4282. |
| [14] | Liu Baijie, Zhou Honghai, He Xinyu, Qin Hongtu, Chen Longhao, Tian Junming, Lu Qingwang. Three-dimensional finite element method to analyze biomechanical characteristics of spinal manipulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4385-4392. |
| [15] | Peng Lu, Duan Zhili, Li Zhenyu, Li Junhui, Li Yunhong, Wang Song, Liu Weiqiang. Research status and progress of establishment and validation of finite element model of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4393-4400. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||