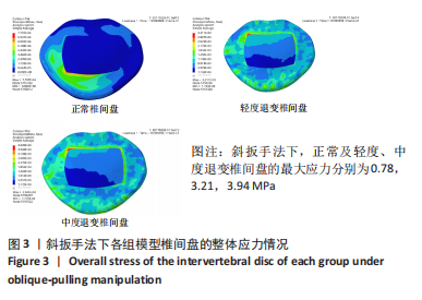
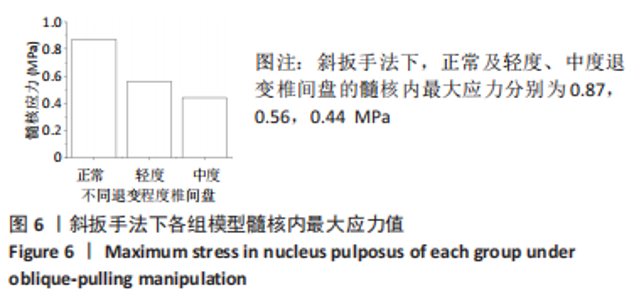
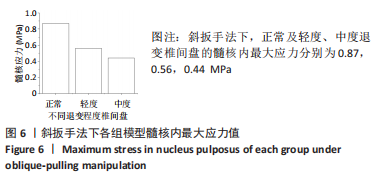
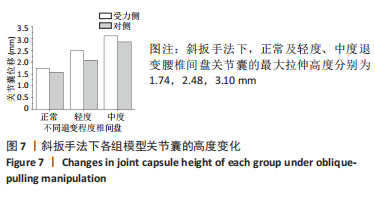
[1] KAISER J, ALLAIRE B, FEIN PM, et al. Correspondence between bone mineral density and intervertebral disc degeneration across age and sex. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13(1):123.
[2] LI W, GONG Y, LIU J, et al. Peripheral and central pathological mechanisms of chronic low back pain: a narrative review. J Pain Res. 2021;14:1483.
[3] KAPETANAKIS S, GKANTSINIKOUDIS N. Anatomy of lumbar facet joint: a comprehensive review. Folia MorphoL. 2021;80(4):799-805.
[4] INOUE N, ORíAS AAE, SEGAMI K. Biomechanics of the Lumbar Facet Joint. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2020;4(1):1-7.
[5] TAKIGAWA T, ESPINOZA ORíAS AA, AN HS, et al. Spinal kinematics and facet load transmission after total disc replacement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(22):E1160-1166.
[6] YIN J, LIU Z, LI C, et al. Effect of facet-joint degeneration on the in vivo motion of the lower lumbar spine. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):340.
[7] MA Y, HUANG P, TU Z, et al. Associations between facet tropism and vertebral rotation in patients with degenerative lumbar disease. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):149.
[8] CRAMER GD, GREGERSON DM, KNUDSEN JT, et al. The effects of side-posture positioning and spinal adjusting on the lumbar Z joints: a randomized controlled trial with sixty-four subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2459-2466.
[9] 毛强,何帮剑,张圣扬,等.异常力学负荷导致椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(12):1-6.
[10] DESMOULIN GT, PRADHAN V, MILNER TE. Mechanical Aspects of Intervertebral Disc Injury and Implications on Biomechanics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(8):E457-e464.
[11] 邱晨生,邓念,相宏飞,等.椎间盘退变相关危险因素的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(10):654-659.
[12] VARLOTTA GP, LEFKOWITZ TR, SCHWEITZER M, et al. The lumbar facet joint: a review of current knowledge: part 1: anatomy, biomechanics, and grading. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(1):13-23.
[13] LI J, MUEHLEMAN C, ABE Y, et al. Prevalence of facet joint degeneration in association with intervertebral joint degeneration in a sample of organ donors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;29(8):1267-1274.
[14] 邓德万,王彬,周震,等.针灸治疗腰椎间盘突出症机制研究概况[J].针灸临床杂志,2020,36(1):91-94.
[15] 张晨晨,李冬,唐树杰.斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的基础研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(10):85-88.
[16] 黄帆,赵思怡,邸安琪,等.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的推拿干预腰椎间盘退变作用机制探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(5): 2991-2994.
[17] 卢钰,郑太才,王琪,等.不同体位下斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36):5872-5877.
[18] 田强,钟侨霖,郭汝松,等.两种腰椎脊柱推拿手法推扳力的研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):324-326.
[19] 李文银,尹红灵,蒋钰钢.PVP术中腰椎不同骨水泥注入量的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(18):1695-1700.
[20] GOEL VK, MONROE BT, GILBERTSON LG, et al. Interlaminar Shear Stresses and Laminae Separation in a Disc: Finite Element Analysis of the L3-L4 Motion Segment Subjected to Axial Compressive Loads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(6):689-698.
[21] CAI XY, SUN MS, HUANG YP, et al. Biomechanical Effect of L(4) -L(5) Intervertebral Disc Degeneration on the Lower Lumbar Spine: A Finite Element Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):917-930.
[22] ZHONG ZC, CHEN SH, HUNG CH. Load- and displacement-controlled finite element analyses on fusion and non-fusion spinal implants. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009;223(2):143-157.
[23] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827.
[24] 徐海涛,李松,刘澜,等.腰椎斜扳手法时椎间盘的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2335-2338.
[25] STEMPER BD, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR FA. Gender- and region-dependent local facet joint kinematics in rear impact: implications in whiplash injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(16):1764-1771.
[26] WAN S, XUE B, XIONG Y. Three-Dimensional Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Middle Aged and Elderly. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:7107702.
[27] SHARMA A, WALK RE, TANG SY, et al. Variability of T2-Relaxation Times of Healthy Lumbar Intervertebral Discs is More Homogeneous within an Individual Than across Healthy Individuals. Am J Neuroradiol. 2020; 41(11):2160-2165.
[28] TAVAKOLI J, TIPPER JL. Detailed mechanical characterization of the transition zone: New insight into the integration between the annulus and nucleus of the intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater. 2022;143:87-99.
[29] ZHANG S, HU B, LIU W, et al. The role of structure and function changes of sensory nervous system in intervertebral disc-related low back pain. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2021;29(1):17-27.
[30] CAI XY, SUN MS, HUANG YP, et al. Biomechanical Effect of L4–L5 Intervertebral Disc Degeneration on the Lower Lumbar Spine: A Finite Element Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):917-930.
[31] OICHI T, TANIGUCHI Y, OSHIMA Y, et al. Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1076.
[32] SONG Q, LIU X, CHEN DJ, et al. Evaluation of MRI and CT parameters to analyze the correlation between disc and facet joint degeneration in the lumbar three-joint complex. Medicine. 2019;98(40):e17336.
[33] 张先予,李正维,吴立军,等.退变性椎间盘应力分布变化的有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(4):359-363.
[34] BASHKUEV M, REITMAIER S, SCHMIDT H. Effect of disc degeneration on the mechanical behavior of the human lumbar spine: a probabilistic finite element study. Spine J. 2018;18(10):1910-1920.
[35] NEWELL N, CARPANEN D, GRIGORIADIS G, et al. Material properties of human lumbar intervertebral discs across strain rates. Spine J. 2019; 19(12):2013-2024.
[36] 麦敏军,黄尚君,古波,等.腰椎定位斜扳法治疗腰椎失稳[J].中医正骨,2018,30(4):19-22+27.
[37] 王国玉,赵道洲,宋敏,等.腰部斜扳手法的生物力学研究进展[J].中医临床研究,2014,6(13):142-144.
[38] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745.
[39] 李棋龙,陈芯仪,吕倩忆,等.基于有限元模型探讨不同角度肘按法对腰椎间盘位移的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2021,41(8): 1223-1229.
[40] 胡迎春,欧亚龙,胡裔志,等.椎间盘退变对L4-L5在垂直载荷下生物力学行为特性的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015,32(1):55-58+66.
[41] 蔡明,马朋朋,张春林,等.L4-5椎间盘退变在不同方向应力下有限元建模与分析[J].中国数字医学,2019,14(12):62-64.
[42] OLDWEILER B, MARTIN JT. In vivo relationships between lumbar facet joint and intervertebral disc composition and diurnal deformation. Clin Biomech. 2021;88:105425. |