Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4783-4789.doi: 10.12307/2023.555
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of silane coupling agent composite graphene oxide coating on biological behavior of Schwann cells on pure titanium
Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang
- School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-11Accepted:2022-10-14Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-01 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xu Xingxing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860192 (to DQ); the Scientific Research Fund of Stomatological College of Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. GYKQKY-2020-05 (to WCJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Effect of silane coupling agent composite graphene oxide coating on biological behavior of Schwann cells on pure titanium[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4783-4789.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
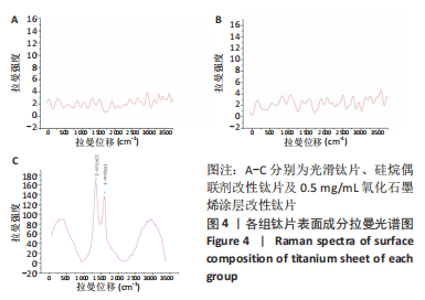
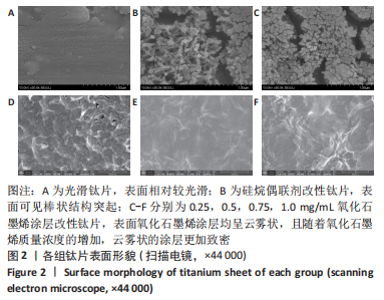
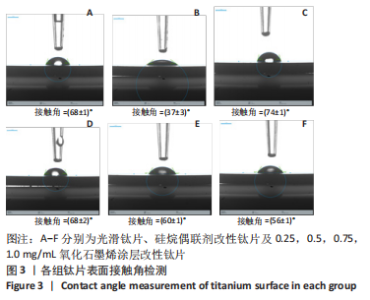
检测结果显示,与SS组比较,Ti-APTES组接触角明显减少(P < 0.05),0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组接触角增大(P < 0.05);随着氧化石墨烯质量浓度的增加,钛片表面接触角逐渐减少,其中0.75-Ti-APTES-GO、1.0-Ti-APTES-GO组接触角小于SS组(P < 0.05)。 2.3 各组钛片表面成分检测 拉曼光谱是对高拉曼强度的碳基材料有效的表征手段,一般来说,碳基材料的拉曼光谱在 1 350 cm-1及 1 580 cm-1附近处会有明显的 D峰和 G 峰。G 峰是石墨烯材料的主要特征峰,是由碳原子sp2轨道面内震动引起用于表征石墨烯样品中碳原子的层间堆垛方式。而D峰通常被认为是石墨烯的无序振动峰,用于表征石墨烯样品中的结构缺陷或边缘[15]。实验组中仅以0.5-Ti-APTES-GO为例,在1 592 cm-1和1 347 cm-1附近处可清楚地观察到2个特征峰的存在,分别属于氧化石墨烯的G峰和D峰[15],表明氧化石墨烯涂层成功地制备在钛片表面;Ti-APTES、光滑钛片组无石墨烯类特征峰的存在,几乎呈一条直线,见图4。"

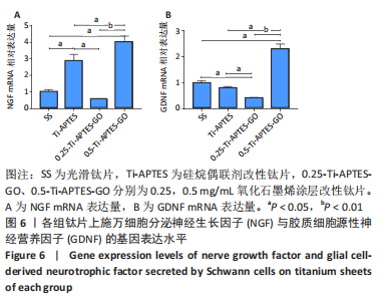
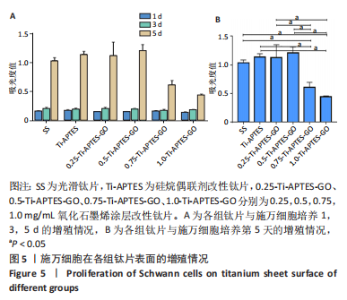
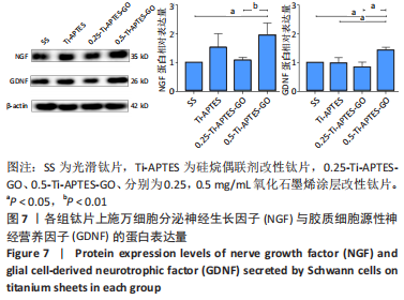
综合考虑高质量浓度氧化石墨烯涂层(即0.75-Ti-APTES-GO和1.0-Ti-APTES-GO两组)对施万细胞增殖及细胞活力存在一定的细胞毒性,该作用原则上不符合临床医疗的要求。故后续实验探讨光滑钛片组、Ti-APTES、0.25-Ti-APTES-GO、0.5-Ti-APTES-GO组钛片表面对施万细胞分泌神经生长因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子的影响。 2.5 各组钛片表面施万细胞分泌神经生长因子与胶质细胞源性神经营养因子情况 2.5.1 RT-qPCR检测结果 结果显示,Ti-APTES组神经生长因子mRNA表达量高于SS组、0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组(P < 0.05),0.5-Ti-APTES-GO组神经生长因子mRNA表达量高于SS组、Ti-APTES组、0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组(P<0.05),SS组与0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组神经生长因子mRNA表达量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6A。 0.5-Ti-APTES-GO组胶质细胞源性神经营养因子mRNA表达量高于SS组、Ti-APTES、0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组(P < 0.05),SS组、Ti-APTES组胶质细胞源性神经营养因子mRNA表达量高于0.25-Ti-APTES-GO组(P < 0.05),SS组、Ti-APTES组胶质细胞源性神经营养因子mRNA表达量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6B。"

| [1] 杨帮成,周学东,于海洋,等.钛种植体表面改性方法[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2019,37(2):124-129. [2] KLINEBERG I, MURRAY G. Osseoperception: sensory function and proprioception. Adv Dent Res. 1999;13:120-9.11276734. [3] KARAPOLAT I, KARAPOLAT HU, KIRAZLI Y, et al. Longitudinal study of bone loss in chronic spinal cord injury patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27:1429-1433. [4] 赵文迪,刘晓秋.氧化石墨烯在钛植入物表面改性应用中的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(11):1000-1003. [5] SENNA PM, DE ALMEIDA BARROS MOURÃO CF, MELLO-MACHADO RC, et al. Silane-Coating Strategy for Titanium Functionalization Does Not Impair Osteogenesis In Vivo. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(7):1814. [6] SHARAN J, KOUL V, DINDA AK, et al. Bio-functionalization of grade V titanium alloy with type I human collagen for enhancing and promoting human periodontal fibroblast cell adhesion - an in-vitro study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018; 161:1-9. [7] QIAN WH, QIU JJ, LIU XY. Minocycline hydrochloride-loaded graphene oxide films on implant abutments for peri-implantitis treatment in beagle dogs. J Periodontol. 2020;91:792-799. [8] LI QF, WANG ZL. Involvement of FAK/P38 Signaling Pathways in Mediating the Enhanced Osteogenesis Induced by Nano-Graphene Oxide Modification on Titanium Implant Surface. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:4659-4676. [9] KANG MS, JEONG SJ, LEE SH, et al. Reduced graphene oxide coating enhances osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on Ti surfaces. Biomater Res. 2021;25(1):1-9. [10] JANG W, KIM HS, ALAM K, et al. Direct-Deposited Graphene Oxide on Dental Implants for Antimicrobial Activities and Osteogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021; 16:5745-5754. [11] ŁAWKOWSKA K, POKRYWCZYŃSKA M, KOPER K, et al. Application of Graphene in Tissue Engineering of the Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):33. [12] ZHAO Y, WANG Y, NIU C, et al. Construction of polyacrylamide/graphene oxide/gelatin/sodium alginate composite hydrogel with bioactivity for promoting Schwann cells growth. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106:1951-1964. [13] CHEN S, ZHAO Y, YAN X, et al. PAM/GO/gel/SA composite hydrogel conduit with bioactivity for repairing peripheral nerve injury. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(6):1273-1283. [14] TAN G, ZHANG L, NING C, et al. Preparation and characterization of APTES films on modification titanium by SAMs. Thin solid films. 2011;519(15):4997-5001. [15] 王楠.不同还原程度的还原型氧化石墨烯体外促成骨研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2020. [16] BORAH R, INGAVLE GC, KUMAR A, et al. Surface-Functionalized Conducting Nanofibers for Electrically Stimulated Neural Cell Function. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22:594-611. [17] 王艳颖,宫苹,张健.不同种植体表面性质对雪旺细胞生物学行为影响的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2021,39(3):279-285. [18] LLEWELLYN SH, FARONI A, ILIUT M, et al. Graphene Oxide Substrate Promotes Neurotrophic Factor Secretion and Survival of Human Schwann-Like Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021;5(4):e2000271. [19] ZHANG K, ZHENG H, LIANG S, et al. Aligned PLLA nanofibrous scaffolds coated with graphene oxide for promoting neural cell growth. Acta Biomater. 2016;37: 131-142. [20] 冯曦,王佐林.钛表面氧化石墨烯涂层对施旺氏细胞黏附与增殖的影响[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2019,29(2):61-68. [21] 孟帅岑,赵静辉,张天首,等.牙种植体周围神经再生的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2017,43(2):459-462. [22] YUAN Q, LIAO DP, YANG XM, et al. Effect of implant surface microtopography on proliferation, neurotrophin secretion, and gene expression of Schwann cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93:381-288. [23] ZHAO JH, GUO Y, LAN A, et al. The effect of amino plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition-treated titanium surface on Schwann cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106:265-271. [24] LAN A, XU W, ZHAO J, et al. Surface functionalization of TiO nanotubes with minocycline and its in vitro biological effects on Schwann cells. Biomed Eng Online. 2018;17:88. [25] 程景阳.载锂二氧化钛纳米复合涂层对大鼠施万细胞生物学性能的影响[D].兰州:兰州大学,2021. [26] ZHENG D, NEOH KG, SHI Z, et al. Assessment of stability of surface anchors for antibacterial coatings and immobilized growth factors on titanium. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;406:238-246. [27] OU JF, WANG JQ, LIU S, et al. Tribology study of reduced graphene oxide sheets on silicon substrate synthesized via covalent assembly. Langmuir. 2010;26:15830-15836. [28] FELGUEIRAS HP, EVANS MDM, MIGONNEY V. Contribution of fibronectin and vitronectin to the adhesion and morphology of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells to poly(NaSS) grafted Ti6Al4V. Acta Biomater. 2015;28:225-233. [29] GRIJALVO S, DÍAZ DD. Graphene-based hybrid materials as promising scaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurochem Int. 2021;147:105005. [30] SHAH S, YIN PT, UEHARA TM, et al. Guiding stem cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes using graphene-nanofiber hybrid scaffolds. Adv Mater. 2014;26: 3673-3680. [31] QIAN Y ,SONG J, ZHAO X, et al. 3D Fabrication with Integration Molding of a Graphene Oxide/Polycaprolactone Nanoscaffold for Neurite Regeneration and Angiogenesis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5:1700499. [32] RICCI A, CATALDI A, ZARA S, et al. Graphene-Oxide-Enriched Biomaterials: A Focus on Osteo and Chondroinductive Properties and Immunomodulation. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(6):2229. [33] 姚汝瞻,王炳武,王光林.石墨烯及其衍生物修复周围神经缺损的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(11):1483-1487. [34] GARDIN C, PIATTELLI A, ZAVAN B. Graphene in Regenerative Medicine: Focus on Stem Cells and Neuronal Differentiation. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34:435-437. [35] BARANOWSKI A, KLEIN A, RITZ U, et al. Surface functionalization of orthopedic titanium implants with bone sialoprotein. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153978. [36] MISHRA SK, TEOTIA AK, KUMAR A, et al. Mechanically tuned nanocomposite coating on titanium metal with integrated properties of biofilm inhibition, cell proliferation, and sustained drug delivery. Nanomedicine. 2017;13:23-35. [37] 古丽巴努·依马木,徐国强,迪丽努尔·阿吉,等.硅烷偶联剂对纯钛表面改性及细胞相容性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1864-1869. [38] PAWLIK A, SOCHA RP, HUBALEK KALBACOVA M, et al. Surface modification of nanoporous anodic titanium dioxide layers for drug delivery systems and enhanced SAOS-2 cell response. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;171:58-66. [39] TAYLOR CS, CHEN R, D’ SA R, et al. Cost effective optimised synthetic surface modification strategies for enhanced control of neuronal cell differentiation and supporting neuronal and Schwann cell viability. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109:1713-1723. [40] YUAN Q, GONG P, TAN Z. Schwann cell graft: a method to promote sensory responses of osseointegrated implants. Med Hypotheses. 2007;69:800-803. [41] YE J, HUANG B, GONG P. Nerve growth factor-chondroitin sulfate/hydroxyapatite-coating composite implant induces early osseointegration and nerve regeneration of peri-implant tissues in Beagle dogs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16:51. [42] 黄峰,项立新,徐国超.神经生长因子-明胶海绵复合体修复种植体周围骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2013,48(1):23-26. |
| [1] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [2] | Liu Zan, An Ran, Li Baocheng. Effect of pravastatin on functional recovery from sciatic nerve crush injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 942-950. |
| [3] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [4] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [5] | Duan Kunling, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Autophagy protects neurons against facial nerve injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4378-4382. |
| [6] | Liu Xinxin, Geng Zhizhong, Chen Jian. Effects of high-intensity interval training with different intervention durations on cognitive function in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2282-2289. |
| [7] | Lyu Shangyi, He Huiyu, Wufanbieke · Baheti, Yang Quan, Ma Lisha, Han Xiangzhen. Physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite composite coating materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1477-1483. |
| [8] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [9] | Li Jingxuan, Shi Dai, Wu Guofeng. Regulatory effects of cAMP response element-binding protein on hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor level in a rat model of drug-resistant epilepsy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5659-5664. |
| [10] | Huang Qian, Hao Liying, He Longlong, Du Liangzhi. Graphene oxide-chitosan composite coating affects the biological behavior of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5430-5435. |
| [11] | Huang Jinsheng, Zhang Geyi, Li Senrui, Li Jiangnan, Lu Laijin, Zhou Nan. Lymphatic endothelial cells-derived exosomes promote axonal regeneration following peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5314-5319. |
| [12] | Ma Ruixin, Liu Pan, Zhang Qiong, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Molecular mechanism of total flavonoids of hawthorn leaves regulating astrocytes to repair spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5327-5333. |
| [13] | Yang Yazhu, Du Juan, Qu Haifeng, Li Jianmin, Zhang Yuxin, Liu Junjie. Effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on learning and memory ability of brain aging mice induced by D-galactose [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4487-4493. |
| [14] | An Hepeng, Liu Zhenteng, Li Lixin, Xu Yafang, Fan Guofeng. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neuronal activity, pain, and related cytokines in rats with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4120-4125. |
| [15] | Zhang Boya, Duan Hongmei, Bai Tianyu, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Li Xiaoguang, Yang Zhaoyang. Neurotrophic factor 3-chitosan carrier induces neural stem cells to differentiate into neuronal subtypes and their electrophysiological properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4020-4027. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||