Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4776-4782.doi: 10.12307/2023.543
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of hierarchical porous cartilage composite scaffolds loaded with stromal cell-derived factor-1 using low-temperature deposition 3D printing
Wu Jiang1, 2, Yin Han2, Yan Zineng1, 2, Tian Guangzhao2, Ding Zhengang1, 2, Yuan Xun1, 2, Fu Liwei2, Tian Zhuang2, Sui Xiang2, Liu Shuyun2, Guo Quanyi1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopedics, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Regenerative Medicine, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2022-08-08Accepted:2022-09-26Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-01 -
Contact:Guo Quanyi, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Institute of Orthopedics, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Regenerative Medicine, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Wu Jiang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Institute of Orthopedics, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Regenerative Medicine, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Plan Project, No. 2019YFA0110600 (to GQY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Jiang, Yin Han, Yan Zineng, Tian Guangzhao, Ding Zhengang, Yuan Xun, Fu Liwei, Tian Zhuang, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi. Preparation of hierarchical porous cartilage composite scaffolds loaded with stromal cell-derived factor-1 using low-temperature deposition 3D printing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4776-4782.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
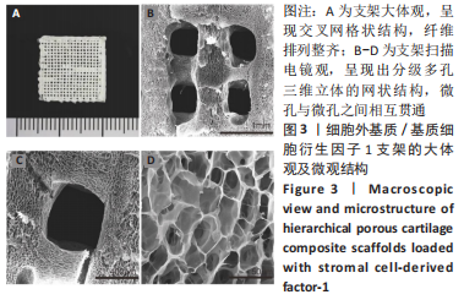
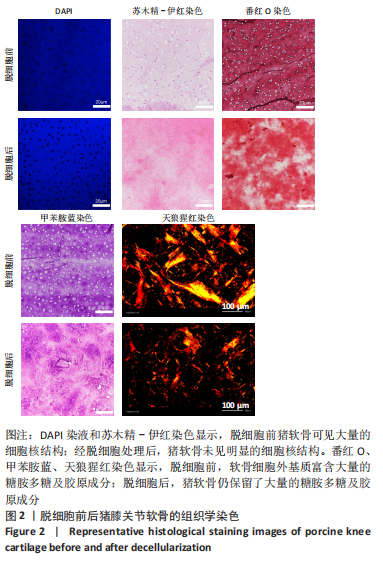
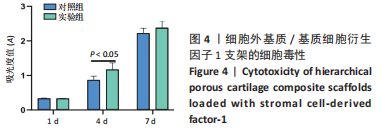
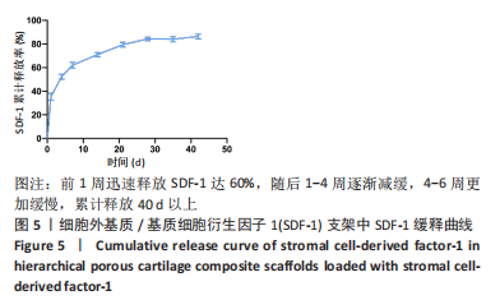
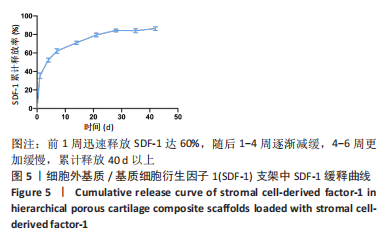
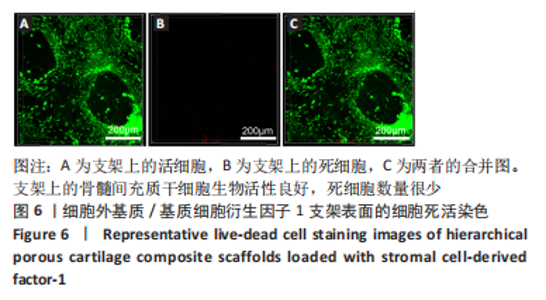
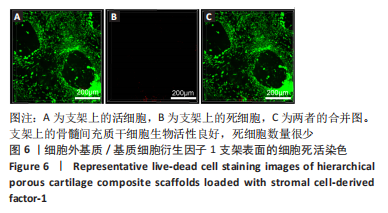
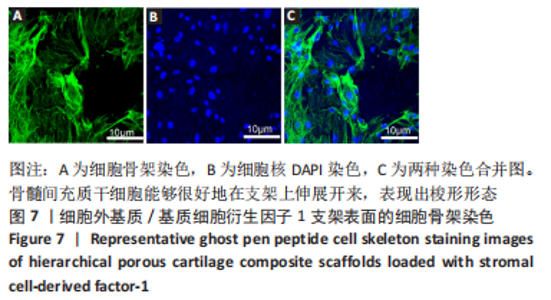
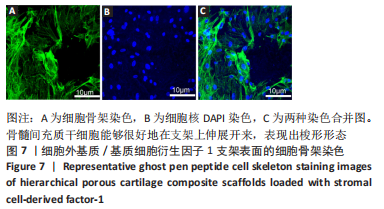
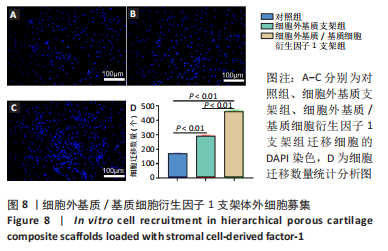
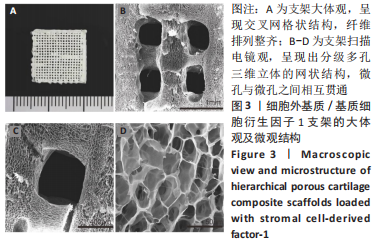
为了评估制备的细胞外基质脱细胞程度,使用DAPI染液和苏木精-伊红对脱细胞前后的软骨进行染色分析。结果显示,脱细胞前猪软骨可见大量的细胞核结构;经脱细胞处理后,猪软骨未见明显的细胞核结构,表明脱细胞成功。 为了评估有效的细胞外基质成分的保留情况,进行了番红O、甲苯胺蓝、天狼猩红染色。结果显示,脱细胞前,软骨细胞外基质富含大量的糖胺多糖及胶原成分;脱细胞后,猪软骨仍保留了大量的糖胺多糖及胶原成分。 2.3 细胞外基质/基质细胞衍生因子1支架的大体观及微观结构 如图3A所示,实验构建的支架打印是成功的,支架大体观呈现交叉网格状结构,纤维排列整齐。不同放大倍率下的扫描电镜,可见支架微观上表现出明显的分级多孔结构,孔径较均匀分布,大孔分布在400-500 μm之间,纤维径上微孔与微孔纵横交错,相互贯通,见图3B-D所示。"
| [1] JOUAN Y, BOUCHEMLA Z, BARDECHE-TRYSTRAM B, et al. Lin28a induces SOX9 and chondrocyte reprogramming via HMGA2 and blunts cartilage loss in mice. Sci Adv. 2022;8(34):eabn3106. [2] LIN X, TSAO CT, KYOMOTO M, et al. Injectable Natural Polymer Hydrogels for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(9):e2101479. [3] JOHNSTONE B, ALINI M, CUCCHIARINI M, et al. Tissue engineering for articular cartilage repair--the state of the art. Eur Cell Mater. 2013;25: 248-267. [4] LI P, FU L, LIAO Z, et al. Chitosan hydrogel/3D-printed poly(epsilon-caprolactone) hybrid scaffold containing synovial mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration based on tetrahedral framework nucleic acid recruitment. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121131. [5] JIANG S, GUO W, TIAN G, et al. Clinical Application Status of Articular Cartilage Regeneration Techniques: Tissue-Engineered Cartilage Brings New Hope. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5690252. [6] LU L, SHANG X, LIU B, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect using adipose-derived stem cell-loaded scaffold derived from native cartilage extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4244-4257. [7] CLAVE A, POTEL JF, SERVIEN E, et al. Third-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation versus mosaicplasty for knee cartilage injury: 2-year randomized trial. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(4):658-665. [8] DORAN PM. Cartilage Tissue Engineering: What Have We Learned in Practice? Methods Mol Biol. 2015;13:403-421. [9] SZYCHLINSKA MA, STODDART MJ, D’AMORA U, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Cartilage Regeneration Approach and Cell Senescence: Can We Manipulate Cell Aging and Function? Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(6):529-539. [10] TAN AR, HUNG CT. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Functional Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Taking Cues from Chondrocyte-Based Constructs. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1295-1303. [11] GRANDE DA, SGAGLIONE NA. Regenerative medicine: self-directed articular resurfacing: a new paradigm? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(12): 677-678. [12] YANG Z, CAO F, LI H, et al. Microenvironmentally optimized 3D-printed TGFbeta-functionalized scaffolds facilitate endogenous cartilage regeneration in sheep. Acta Biomater. 2022;150:181-198. [13] ZHU J, YANG S, QI Y, et al. Stem cell-homing hydrogel-based miR-29b-5p delivery promotes cartilage regeneration by suppressing senescence in an osteoarthritis rat model. Sci Adv. 2022;8(13):eabk0011. [14] HUANG B, LI P, CHEN M, et al. Hydrogel composite scaffolds achieve recruitment and chondrogenesis in cartilage tissue engineering applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):25. [15] ZHANG S, HU B, LIU W, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration: The role of endogenous mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell recruitment and migration. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020;50(2):198-208. [16] YANG Z, LI H, YUAN Z, et al. Endogenous cell recruitment strategy for articular cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;11:431-452. [17] SUN X, YIN H, WANG Y, et al. In Situ Articular Cartilage Regeneration through Endogenous Reparative Cell Homing Using a Functional Bone Marrow-Specific Scaffolding System. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(45):38715-38728. [18] LI J, CHEN H, ZHANG D, et al. The role of stromal cell-derived factor 1 on cartilage development and disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(3):313-322. [19] ZHANG Y, LI X, LI J, et al. Knee Loading Enhances the Migration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells to the Osteoarthritic Sites Through the SDF-1/CXCR4 Regulatory Axis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;111(2):171-184. [20] KANG H, PENG J, LU S, et al. In vivo cartilage repair using adipose-derived stem cell-loaded decellularized cartilage ECM scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(6):442-453. [21] YANG Q, PENG J, GUO Q, et al. A cartilage ECM-derived 3-D porous acellular matrix scaffold for in vivo cartilage tissue engineering with PKH26-labeled chondrogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2008;29(15):2378-2387. [22] CHAWLA S, MIDHA S, SHARMA A, et al. Silk-Based Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(8):e1701204. [23] LIU W, WANG D, HUANG J, et al. Low-temperature deposition manufacturing: A novel and promising rapid prototyping technology for the fabrication of tissue-engineered scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):976-982. [24] WANG C, YUE H, HUANG W, et al. Cryogenic 3D printing of heterogeneous scaffolds with gradient mechanical strengths and spatial delivery of osteogenic peptide/TGF-beta1 for osteochondral tissue regeneration. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025030. [25] LIAN M, SUN B, HAN Y, et al. A low-temperature-printed hierarchical porous sponge-like scaffold that promotes cell-material interaction and modulates paracrine activity of MSCs for vascularized bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120841. [26] CHEN M, LI Y, LIU S, et al. Hierarchical macro-microporous WPU-ECM scaffolds combined with Microfracture Promote in Situ Articular Cartilage Regeneration in Rabbits. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):1932-1944. [27] WANG C, LAI J, LI K, et al. Cryogenic 3D printing of dual-delivery scaffolds for improved bone regeneration with enhanced vascularization. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):137-145. [28] PATI F, JANG J, HA DH, et al. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3935. [29] CHEN P, TAO J, ZHU S, et al. Radially oriented collagen scaffold with SDF-1 promotes osteochondral repair by facilitating cell homing. Biomaterials. 2015;39:114-123. [30] YANG Z, ZHAO T, GAO C, et al. 3D-Bioprinted Difunctional Scaffold for In Situ Cartilage Regeneration Based on Aptamer-Directed Cell Recruitment and Growth Factor-Enhanced Cell Chondrogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(20):23369-23383. [31] 杨振,李浩,付立伟,等.3D生物打印负载转化生长因子β3的软骨复合支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5445-5452. [32] FU L, YANG Z, GAO C, et al. Advances and prospects in biomimetic multilayered scaffolds for articular cartilage regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(6):527-542. [33] MCGONAGLE D, BABOOLAL TG, JONES E. Native joint-resident mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(12):719-730. [34] CHEN SH, WANG XL, XIE XH, et al. Comparative study of osteogenic potential of a composite scaffold incorporating either endogenous bone morphogenetic protein-2 or exogenous phytomolecule icaritin: an in vitro efficacy study. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(8):3128-3137. [35] ALMEIDA HV, ESWARAMOORTHY R, CUNNIFFE GM, et al. Fibrin hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix and incorporating freshly isolated stromal cells as an injectable for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:55-62. [36] BURNSED OA, SCHWARTZ Z, MARCHAND KO, et al. Hydrogels derived from cartilage matrices promote induction of human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2016;43: 139-149. [37] ZHENG X, YANG F, WANG S, et al. Fabrication and cell affinity of biomimetic structured PLGA/articular cartilage ECM composite scaffold. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(3):693-704. [38] MARTIN AR, PATEL JM, LOCKE RC, et al. Nanofibrous hyaluronic acid scaffolds delivering TGF-beta3 and SDF-1alpha for articular cartilage repair in a large animal model. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:170-182. [39] CHEN Y, WU T, HUANG S, et al. Sustained Release SDF-1alpha/TGF-beta1-Loaded Silk Fibroin-Porous Gelatin Scaffold Promotes Cartilage Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(16):14608-14618. [40] TIAN G, JIANG S, LI J, et al. Cell-free decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix scaffolds combined with interleukin 4 promote osteochondral repair through immunomodulatory macrophages: In vitro and in vivo preclinical study. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:131-145. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [3] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [6] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [8] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [9] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [10] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [11] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [12] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [13] | Hu Xiaoshen, Li Huijing, Lyu Junling, Xiao Xianjun, Li Juan, Li Xiang, Liu Ling, Jin Rongjiang. Pathological changes in the total knee joint during spontaneous knee osteoarthritis in guinea pigs at different months of age [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2218-2224. |
| [14] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| [15] | Wang Chenglong , Yang Zhilie , Chang Junli , Zhao Yongjian , Zhao Dongfeng , Dai Weiwei , Wu Hongjin , Zhang Jie , Wang Libo , Xie Ying , Tang Dezhi , Wang Yongjun , Yang Yanping. Restoration of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in mice inhibited by cyclophosphamide with psoralen [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 16-23. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||