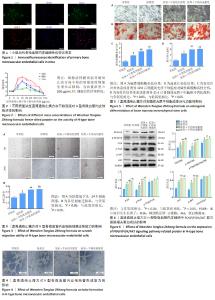
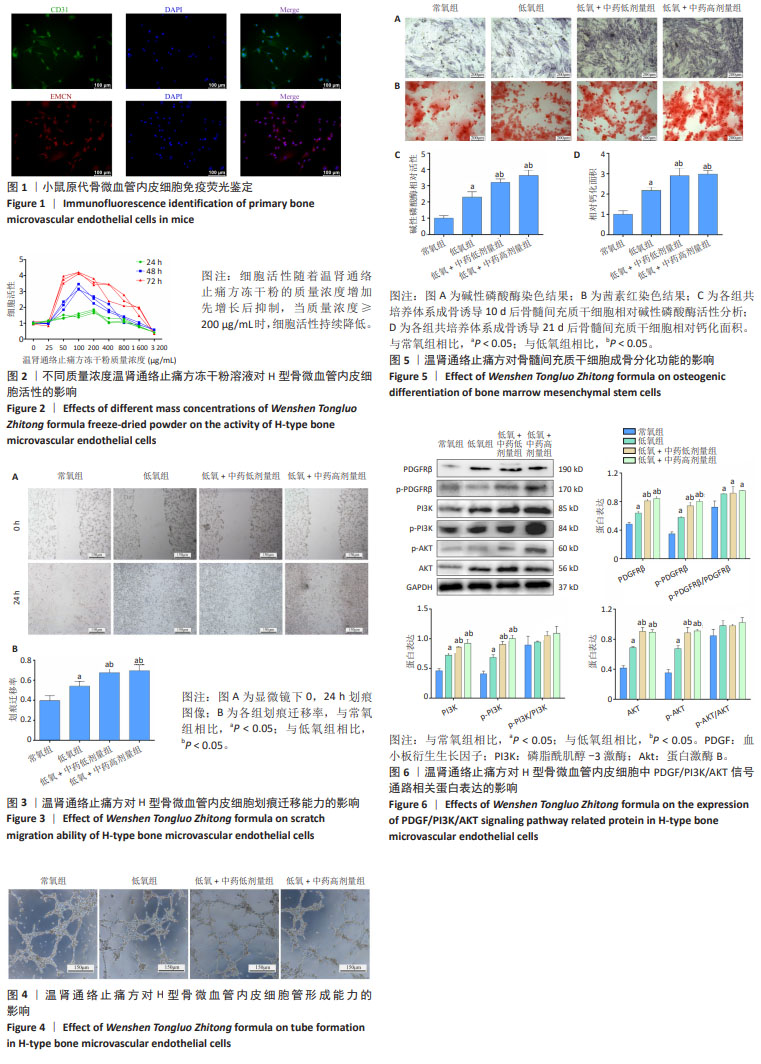
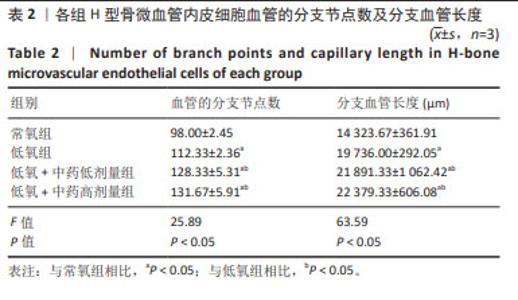
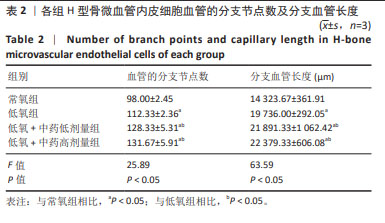
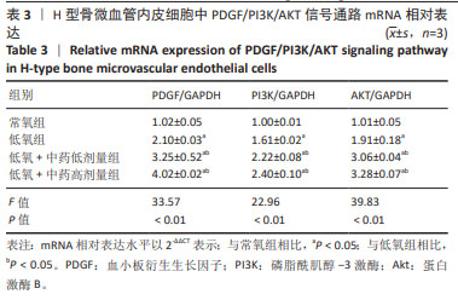
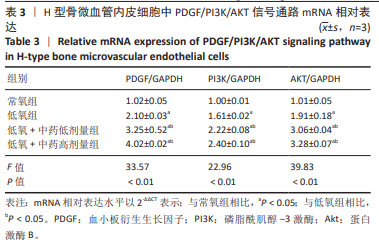
|
[1] AYERS C, KANSAGARA D, LAZUR B, et al. Effecttveness and Safety of
Treatments to Prevent Fractures in People With Low Bone Mass or
Primary Osteoporosis: A Living Systemattc Review and Network Metaanalysis
for the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med.
2023;176(2):182-195.
[2] MÉNDEZ-FERRER S, MICHURINA TV, FERRARO F, et al. Mesenchymal
and haematopoiettc stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche.
Nature. 2010;466(7308):829-834.
[3] SHEN Z, DONG W, CHEN Z, et al. Total ffavonoids of Rhizoma
Drynariae enhances CD31hiEmcnhi vessel formatton and subsequent
bone regeneratton in rat models of distractton osteogenesis by
acttvattng PDGF-BB/VEGF/RUNX2/OSX signaling axis. Int J Mol Med.
2022;50(3):112.
[4] LI J, WEI G, LIU G, et al. Regulattng Type H Vessel Formatton and
Bone Metabolism via Bone-Targettng Oral Micro/Nano-Hydrogel
Microspheres to Prevent Bone Loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(15):
e2207381.
[5] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and
remodeling. Theranosttcs. 2020;10(1):426-436.
[6] SÁ DA BANDEIRA D, CASAMITJANA J, CRISAN M. Pericytes, integral
components of adult hematopoiettc stem cell niches. Pharmacol Ther.
2017;171:104-113.
[7] 王亮 . 骨内特殊亚型血管在骨质疏松症中的作用及临床意义 [D].
苏州 : 苏州大学 ,2018.
[8] JOHNSON RW, SOWDER ME, GIACCIA AJ. Hypoxia and Bone Metastattc
Disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(4):231-238.
[9] SPENCER JA, FERRARO F, ROUSSAKIS E, et al. Direct measurement of
local oxygen concentratton in the bone marrow of live animals. Nature.
2014;508(7495):269-273.
[10] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch
acttvity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature.
2014;507(7492): 376-380.
[11] RANKIN EB, WU C, KHATRI R, et al. The HIF signaling pathway in
osteoblasts directly modulates erythropoiesis through the productton
of EPO. Cell. 2012;149(1):63-74.
[12] LI C, ZHAO R, YANG H, et al. Constructton of Bone Hypoxic
Microenvironment Based on Bone-on-a-Chip Plattorms. Int J Mol Sci.
2023;24(8):6999.
[13] KASHIWAGI T, TAKAZAWA Y, KAGAWA T, et al. Organizatton of
self-advantageous niche by neural stem/progenitor cells during
development via autocrine VEGF-A under hypoxia. Inffamm Regen.
2023;43(1):8.
[14] ZHANG L, YIN Y, GUO J, et al. Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia
ameliorates osteoporosis affer spinal cord injury through balancing
osteoblast and osteoclast acttvittes in rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
2023;14:1035186.
[15] ZHANG Z, YAO L, YANG J, et al. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in
hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3547-3554.
[16] GUO J, HU Z, YAN F, et al. Angelica dahurica promoted angiogenesis
and accelerated wound healing in db/db mice via the HIF-1α/PDGF-β
signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:447-457.
[17] WANG L, PAN Y, LIU M, et al. Wen-Shen-Tong-Luo-Zhi-Tong Decoctton
regulates bone-fat balance in osteoporosis by adipocyte-derived
exosomes. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):568-580.
[18] 郭杨 , 郑苏阳 , 马勇 , 等 . 温肾通络止痛汤对去卵巢模型大鼠骨
密度与血清生化指标的影响 [J]. 山东中医杂志 ,2017,36(12):1055-
1058+1074.
[19] LIU Y, ZHU S, LIU J, et al. Vitexin Regulates Angiogenesis and
Osteogenesis in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis of Rats via the
VDR/PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(1):
546-556.
20] DIRCKX N, VAN HUL M, MAES C. Osteoblast recruitment to sites
of bone formatton in skeletal development, homeostasis, and
regeneratton. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013;99(3):170-191.
[21] HASSAN S, WANG T, SHI K, et al. Self-oxygenatton of engineered living
ttssues orchestrates osteogenic commitment of mesenchymal stem
cells. Biomaterials. 2023;300:122179.
[22] WICKS EE, SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: cancer progression
and clinical translatton. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(11):e159839.
[23] KROCK BL, SKULI N, SIMON MC. Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: good
and evil. Genes Cancer. 2011;2(12):1117-1133.
[24] CARMELIET P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;
438(7070):932-936.
[25] 马勇 , 汪志芳 , 王培民 . 自拟温肾通络止痛方治疗骨质疏松症 45
例临床研究 [J]. 中医药学报 ,2010,38(1):103-104.
[26] 苑文超 , 马勇 , 闵文 , 等 . 黄桂成运用络病理论治疗骨质疏松症经
验 [J]. 山东中医杂志 ,2018,37(4):310-312.
[27] WANG L, ZHENG S, HUANG G, et al. Osthole-loaded N-octyl-O-sulfonyl
chitosan micelles (NSC-OST) inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis
and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. J Cell Mol Med.
2020;24(7):4105-4117.
[28] WANG W, MAO J, CHEN Y, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenesis
and ameliorates osteoporosis development by targettng JAK2/STAT3
signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;49(1):113-121.
[29] XU H, ZHOU S, QU R, et al. Icariin prevents oestrogen deffciencyinduced
alveolar bone loss through promottng osteogenesis via STAT3.
Cell Prolif. 2020;53(2):e12743.
[30] DONG X, HU H, FANG Z, et al. CTRP6 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferatton and migratton. Biomed Pharmacother.
2018;103:844-850.
[31] SONG C, CAO J, LEI Y, et al. Nuciferine prevents bone loss by disrupttng
multtnucleated osteoclast formatton and promottng type H vessel
formatton. FASEB J. 2020;34(3):4798-4811.
[32] HUANG J, YIN H, RAO SS, et al. Harmine enhances type H vessel
formatton and prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice.
Theranosttcs. 2018;8(9):2435-2446.
[33] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts
induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med.
2014;20(11): 1270-1278.
[34] PAN S, HU Y, HU M, et al. Platelet-derived PDGF promotes the invasion
and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma by upregulattng MMP2/MMP9
expression and inducing EMT via the p38/MAPK signalling pathway.
Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(7):3577-3595.
[35] SONG CY, CHANG SL, LIN CY, et al. Visfattn-Induced Inhibitton of miR1264
Facilitates PDGF-C Synthesis in Chondrosarcoma Cells and
Enhances Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis. Cells. 2022;
11(21):3470.
[36] 任振杰 , 张业 , 李栋梁 , 等 . 基于 PI3K/AKT 通路探讨柴苓汤加味对
阴虚热盛代谢综合征 - 胰岛素抵抗大鼠血管内皮功能的影响 [J].
辽宁中医药大学学报 ,2023,25(9):47-51.
[37] 付尚峰 . 羊膜间充质干细胞源外泌体携 OIP5-AS1 靶向 miR-29a-3p
调控 SIRT1 促进糖尿病创面血管生成的作用与分子机制 [D]. 南昌 :
南昌大学 , 2023.
|