Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (25): 4020-4027.doi: 10.12307/2023.081
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neurotrophic factor 3-chitosan carrier induces neural stem cells to differentiate into neuronal subtypes and their electrophysiological properties
Zhang Boya1, Duan Hongmei1, Bai Tianyu2, Hao Fei3, Hao Peng1, Zhao Wen1, Gao Yudan1, Li Xiaoguang1, Yang Zhaoyang1
- 1Department of Neurobiology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China; 2School of Biological and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China; 3Institute of Medical-Engineering Interdisciplinary Innovation of Beihang University, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Biomedical Engineering, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2022-01-19Accepted:2022-03-03Online:2023-09-08Published:2023-01-17 -
Contact:Yang Zhaoyang, MD, Professor, Department of Neurobiology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China -
About author:Zhang Boya, Master, Department of Neurobiology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31670988, 31971279 (to YZY); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81941011, 31730030 (to LXG); Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, No. 7222004 (to DHM); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31900749 (to HP); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31771053 (to DHM); National Key Research & Development Program, No. 2017YFC1104002 (to YZY); National Key Research & Development Program, No. 2017YFC1104001 (to LXG); Beijing Science and Technology Program, No. Z181100001818007 (to YZY); Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (Youth Program), No. 7214301 (to HF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Boya, Duan Hongmei, Bai Tianyu, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Li Xiaoguang, Yang Zhaoyang. Neurotrophic factor 3-chitosan carrier induces neural stem cells to differentiate into neuronal subtypes and their electrophysiological properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4020-4027.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
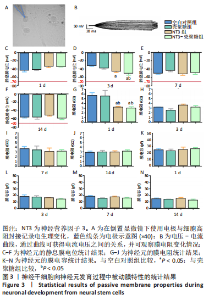
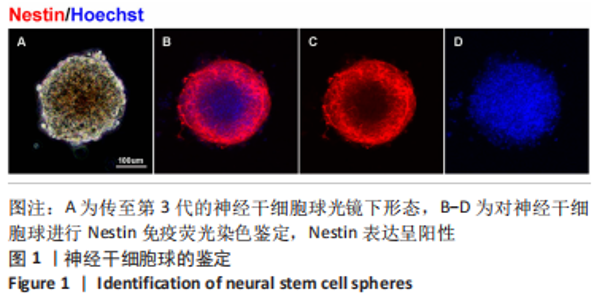
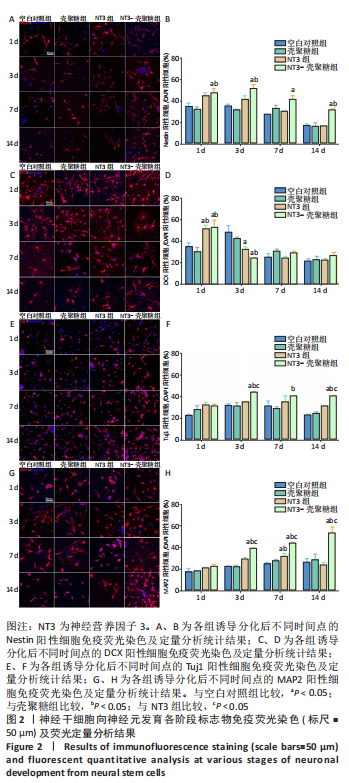
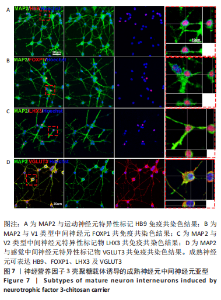
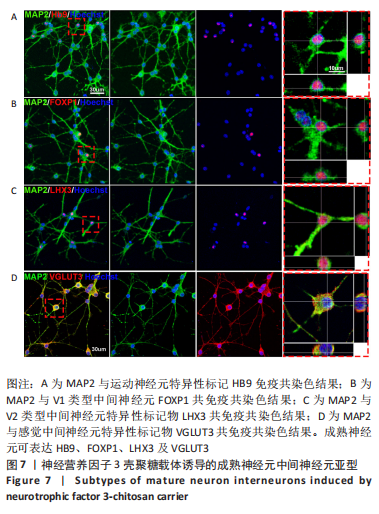
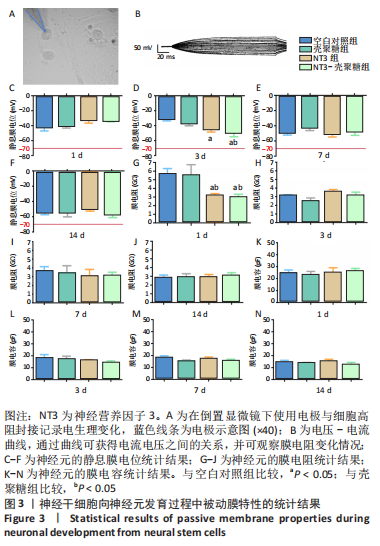
使用Nestin标记神经干细胞,DCX特异性标记神经母细胞,Tuj1标记未成熟神经元,MAP2标记成熟神经元。在整个细胞发育过程中,NT3-壳聚糖组中Nestin阳性神经干细胞数量虽然有所下降,但相较于同一时间节点的其他组来说神经干细胞数量仍旧保持在一个较高的水平。在发育初期(分化后1-3 d)尤其是在分化后1 d,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组的DCX阳性细胞明显高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),并且在分化后3 d时,空白对照组神经母细胞数量才达到较高水平。NT3-壳聚糖组Tuj1阳性细胞在分化后3 d显著升高,高于其他组(P < 0.05)。在分化早期,NT3-壳聚糖组相较于空白对照组和空载体组成熟神经元数量明显增多,并且可将这一优势维持至发育后期(即分化后14 d),说明神经营养因子3-壳聚糖载体具有促进神经元成熟的能力。 2.3 神经营养因子3-壳聚糖载体对神经干细胞发育过程中电生理功能的影响 2.3.1 神经干细胞在发育过程中的被动膜特性变化 见图3。 采用全细胞电流钳和电压钳模式研究神经干细胞向神经元分化过程中各时期神经元的被动膜特性,见图3A、B,结果显示,分化后第3天,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组的静息膜电位相较于另外两组显著增大(P < 0.05),见图3C-F;分化后第1天,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组膜电阻与另外两组相比显著下降(P < 0.05),见图3G-J;神经元各组之间的膜电容并未随着发育时间的延长而变化,见图3K-N。"
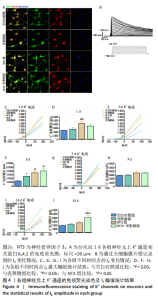
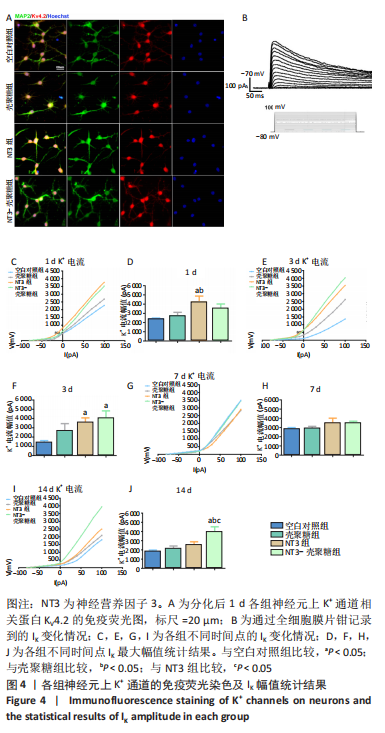
2.3.2 诱导分化的神经干细胞上 K+通道发育情况 见图4。 为了观察细胞膜上K+通道发育情况,首先通过对分化后1 d的细胞进行免疫荧光染色观察, MAP2阳性的神经元上可表达K+通道蛋白KV4.2,见图4A,说明诱导的细胞膜上可以产生K+电流电压的变化,因此可以在接下来的膜片钳实验中,通过记录K电流的变化从功能上反映出 K+通道的发育情况。采用全细胞电压钳模式,钳制电压-70 mV给予细胞去激化步阶刺激,从-80 mV以10 mV的增幅去极化至 +100 mV,记录到全细胞外向K电流(IK),见图4B。对IK的最大幅值进行观察统计分析,见图4C,E,G,I,分化后1 d,NT3组的IK相高于其他3组(P < 0.05),见图4D;分化后3 d,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组IK高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),见图4F;分化后14 d,仅NT3-壳聚糖组IK维持了较高水平,高于其他3组(P < 0.05),见图4J。"
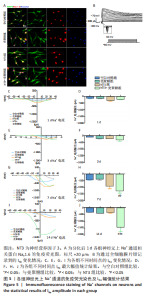
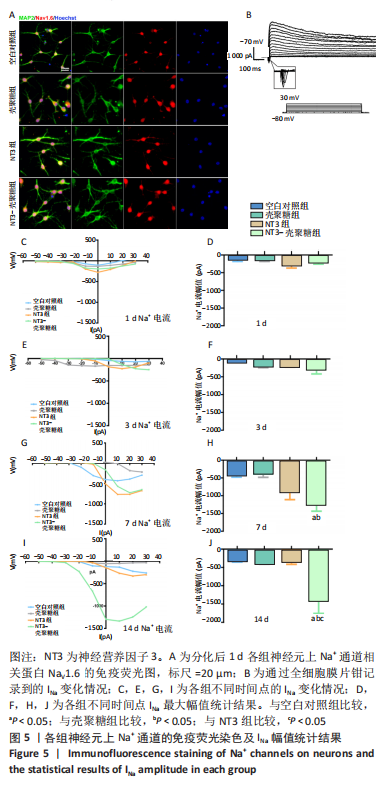
2.3.3 诱导分化的神经干细胞上Na+通道发育情况 见图5。 为了观察细胞膜上Na+通道发育情况,首先对分化后1 d的细胞进行免疫荧光染色观察,MAP2阳性的神经元上可表达Na+通道蛋白NaV1.6,见图5A,说明诱导的细胞膜上可以产生Na+电流电压的变化,因此可以在接下来的膜片钳实验中,通过记录Na电流的变化从功能上反映出Na+通道的发育情况。采用全细胞电压钳模式,钳制电压-70 mV给予细胞去激化步阶刺激,从-50 mV以10 mV的增幅去极化至+30 mV,记录到全细胞内向Na电流(INa),见图5B。对INa的最大幅值进行观察统计分析,见图5C,E,G,I,分化早期,各组之间INa比较无明显差异,见图5D,F;分化后7,14 d,NT3-壳聚糖组INa显著增高,见图5H,J。"
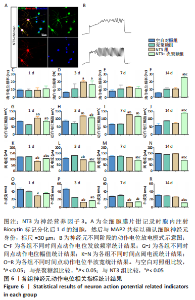
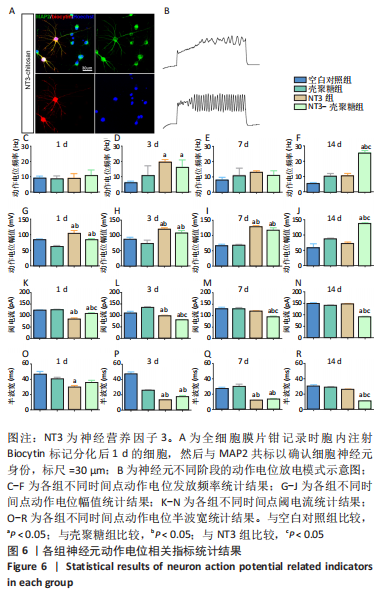
2.3.4 诱导分化的神经干细胞动作电位变化情况 见图6。 为了观察神经干细胞在诱导分化过程中动作电位的变化,采用全细胞电流钳模式,对细胞注入超过基强度的脉冲去极化电流,对于可诱发动作电位的细胞,通过电极胞内注射生物素标记细胞,再与MAP2染色确认细胞神经元身份,见图6A。分化后3 d,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组动作电位频率高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),见图6D;分化后14 d,NT3-壳聚糖组动作电位频率高于其他3组(P < 0.05),见图6F。分化后1 d,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组动作电位幅值显著升高,见图6G;随着神经元的发育,分化后14 d,NT3-壳聚糖组的动作电位幅值依然维持着变大的趋势,高于其他3组(P < 0.05),NT3组的动作电位幅值在经历了第7天的显著升高后,于第14天降低至与空白对照组无明显差异,见图6I-J。在分化后1 d,NT3组和NT3-壳聚糖组阈电流低于其他两组(P < 0.05),见图6K;NT3-壳聚糖组的阈电流在接下来的分化过程中一直维持相对较低的水平,低于其他3组(P < 0.05),见图6L-N。NT3组的动作电位半波宽在分化后1 d显著低于空白对照组(P < 0.05),见图 6O,此时NT3-壳聚糖组的半波宽无明显变化;从分化后3 d开始,NT3-壳聚糖组半波宽持续下降,见图6P-R。"
| [1] REYNOLDS BA, WEISS S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science (New York, NY). 1992;255(5052):1707-1710. [2] LI L, CLEVERS H. Coexistence of Quiescent and Active Adult Stem Cells in Mammals. Science. 2010;327(5965):542-545. [3] NAIK PP, BIRBRAIR A, BHUTIA SK. Mitophagy-driven metabolic switch reprograms stem cell fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(1):27-43. [4] DUAN H, LI X, WANG C, et al. Functional hyaluronate collagen scaffolds induce NSCs differentiation into functional neurons in repairing the traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:182-195. [5] ZHU Y, UEZONO N, YASUI T, et al. Neural stem cell therapy aiming at better functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Dev Dyn. 2018; 247(1):75-84. [6] LIPPERT T, GELINEAU L, NAPOLI E, et al. Harnessing neural stem cells for treating psychiatric symptoms associated to fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and epilepsy. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017;30(Pt A):10-22. [7] SUZUKI H, AHUJA CS, SALEWSKI RP, et al. Neural stem cell mediated recovery is enhanced by Chondroitinase ABC pretreatment in chronic cervical spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0182339. [8] KOUTSOUDAKI PN, PAPASTEFANAKI F, STAMATAKIS A, et al. Neural stem/progenitor cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes, reduce inflammation, and ameliorate learning deficits after transplantation in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Glia. 2016;64(5):763-779. [9] SHETTY AK. Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: Can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection? Epilepsy Behav. 2014;38:117-124. [10] ZHANG ML, ZHANG XJ, KANG J, et al. Matrine promotes NT3 expression in CNS cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett. 2017;649:100-106. [11] YANG Z, ZHANG A, DUAN H, et al. NT3-chitosan elicits robust endogenous neurogenesis to enable functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(43):13354-13359. [12] YANG Z, DUAN H, MO L, et al. The effect of the dosage of NT-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(18):4846-5448. [13] LI X, YANG Z, ZHANG A. The effect of neurotrophin-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):4978-4985. [14] CALDEIRA V, DOUGHERTY KJ, BORGIUS L, et al. Spinal Hb9::Cre-derived excitatory interneurons contribute to rhythm generation in the mouse. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41369. [15] MORIKAWA Y, KOMORI T, HISAOKA T, et al. Detailed Expression Pattern of Foxp1 and Its Possible Roles in Neurons of the Spinal Cord during Embryogenesis. Dev Neurosci. 2009;31(6):511-522. [16] MORIKAWA Y, HISAOKA T, SENBA E. Characterization of Foxp2-expressing cells in the developing spinal cord. Neuroscience. 2009; 162(4):1150-1162. [17] LEE B, LEE S, AGULNICK AD, et al. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins are required for LIM complexes to induce transcriptionally active chromatin and specify spinal neuronal identities. Development. 2016;143(10):1721-1731. [18] FRANCIUS C, HIDALGO-FIGUEROA M, DEBRULLE S, et al. Vsx1 Transiently Defines an Early Intermediate V2 Interneuron Precursor Compartment in the Mouse Developing Spinal Cord. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016;9:145. [19] SHARMA K, SHENG HZ, LETTIERI K, et al. LIM homeodomain factors Lhx3 and Lhx4 assign subtype identities for motor neurons. Cell. 1998; 95(6):817-828. [20] SAKAI K, SANDERS KM, LIN SH, et al. Low-Threshold Mechanosensitive VGLUT3-Lineage Sensory Neurons Mediate Spinal Inhibition of Itch by Touch. J Neurosci. 2020;40(40):7688-7701. [21] LU H, LI M, SONG T, et al. Retrovirus delivered neurotrophin-3 promotes survival, proliferation and neuronal differentiation of human fetal neural stem cells in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 2008;77(4):158-164. [22] YUAN SH, MARTIN J, ELIA J, et al. Cell-Surface Marker Signatures for the Isolation of Neural Stem Cells, Glia and Neurons Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. PloS One. 2011;6(3):e17540. [23] ZHANG J, JIAO J. Molecular Biomarkers for Embryonic and Adult Neural Stem Cell and Neurogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2015:727542. [24] FRIOCOURT G, KOULAKOFF A, CHAFEY P, et al. Doublecortin Functions at the Extremities of Growing Neuronal Processes. Cerebral Cortex. 2003;13(6):620-626. [25] GUPTE RP, KADUNGANATTIL S, SHEPHERD AJ, et al. Convergent Phosphomodulation of the Major Neuronal Dendritic Potassium Channel Kv4.2 by Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-activating Polypeptide. Neuropharmacology. 2016;101:291-308. [26] KIM DM, NIMIGEAN CM. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels: A Structural Examination of Selectivity and Gating. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a029231. [27] XIAO F, ZHANG X, NI P, et al. Voltage-dependent potassium channel Kv 4.2 alleviates the ischemic stroke impairments through activating neurogenesis. Neurochem Int. 2021;150:105155. [28] O’BRIEN JE, MEISLER MH. Sodium channel SCN8A (Nav1.6): properties and de novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathy and intellectual disability. Front in Genet. 2013;4:213. [29] WANG X, ZHANG XG, ZHOU TT, et al. Elevated Neuronal Excitability Due to Modulation of the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.6 by Aβ1−42. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:94. [30] ZYBURA AS, BAUCUM AJ 2ND, RUSH AM, et al. CaMKII enhances voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.6 activity and neuronal excitability. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(33):11845-11865. [31] BEAN BP. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(6):451-465. [32] KIEHN O. Decoding the organization of spinal circuits that control locomotion. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17(4):224-238. [33] ZHOLUDEVA LV, ABRAIRA VE, SATKUNENDRARAJAH K, et al. Spinal Interneurons as Gatekeepers to Neuroplasticity after Injury or Disease. J Neurosci. 2021;41(5):845-854. [34] KUMAMARU H, LU P, ROSENZWEIG ES, et al. Regenerating Corticospinal Axons Innervate Phenotypically Appropriate Neurons within Neural Stem Cell Grafts. Cell Rep. 2019;26(9):2329-2339.e4. |
| [1] | Sun Jiaqi, Bian Lu, Shi Wentao, Wu Xuechao, Lu Xiaojie. Mechanism of Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 in rat pressure injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1578-1584. |
| [2] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [3] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [4] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [5] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [6] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [7] | He Longcai, Song Wenxue, Ming Jiang, Chen Guangtang, Wang Junhao, Liao Yidong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. An experimental method for simultaneous extraction and culture of primary cortical neurons and microglial cells from SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
| [8] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [9] | Zhang Shuai, Li Zichun, Xu Yihao, Xie Xiaofeng, Guo Zhongsheng, Zhao Qingyang. Effect of transcranial magneto-acousto-electrical stimulation on the plasticity of the prefrontal cortex network in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1108-1117. |
| [10] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [11] | Xu Fei, Yan Jinqiang, Chai Shoudong. Mechanical stress regulates apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1064-1072. |
| [12] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [13] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [14] | Liu Zhaohui, Han Xiaoqian, Duan Xin, Guo Pengda, Zhang Yuntao. Salidroside promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells: an in vitro experiment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 231-237. |
| [15] | Du Zhongqiu, Qi Xiaoyang, Yang Ping, Yu Jianglin, Chen Yixin, Zhang Linjian, Qiu Xusheng. Effects of the prolyl hydroxylase 2 inhibitor cpd17 on mouse osteogenic precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 238-244. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||