Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (28): 4441-4447.doi: 10.12307/2023.523
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Yiqi Tongmai Fang on serum amino acid metabolism of atherosclerotic mice
Wang Shurui1, 2, Zhang Yilei1, 2, Jiao Weijie2, 3, Liu Zhihua3, Zhang Kuiming1, 2, Cui Yinglin2, 3
- 1Second Clinical School, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 3Henan Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-12Accepted:2022-08-27Online:2023-10-08Published:2023-01-29 -
Contact:Cui Yinglin, Master, Chief physician, Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; Henan Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Shurui, MD candidate, Physician, Second Clinical School, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Projects, Nos. 212102311123 (to CYL) and 212102311139 (to LZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shurui, Zhang Yilei, Jiao Weijie, Liu Zhihua, Zhang Kuiming, Cui Yinglin. Effects of Yiqi Tongmai Fang on serum amino acid metabolism of atherosclerotic mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4441-4447.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
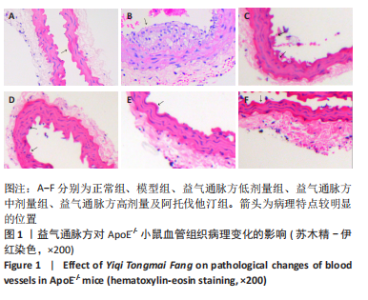
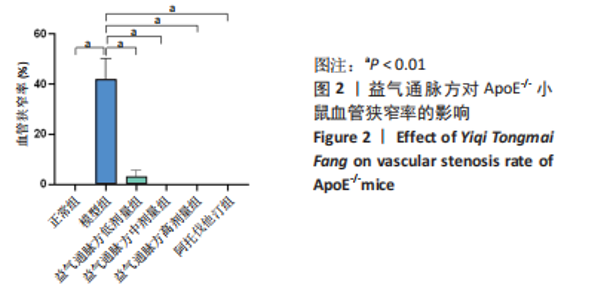
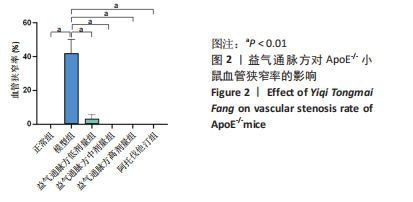
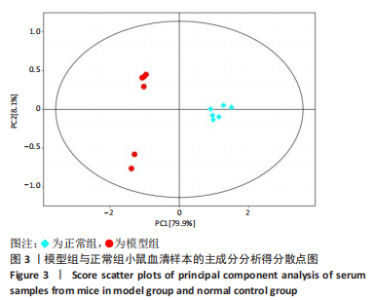
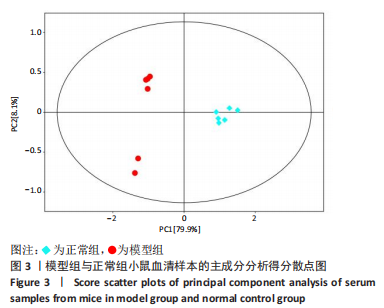
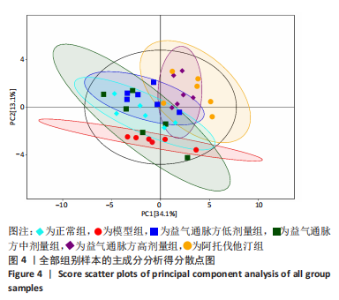
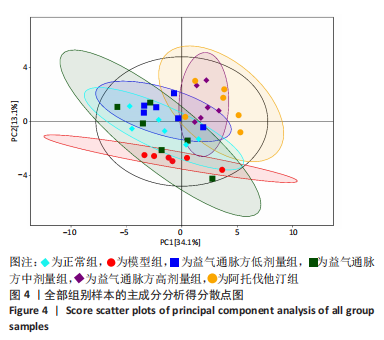
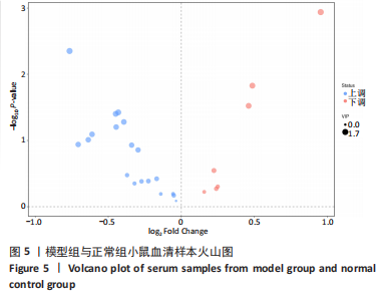
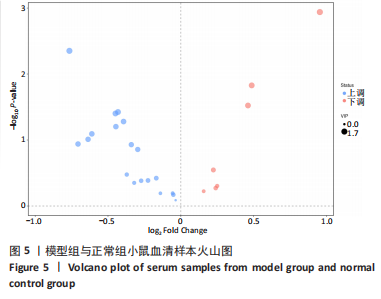
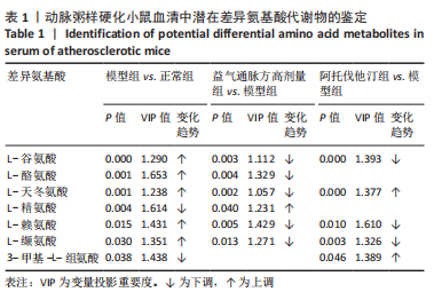
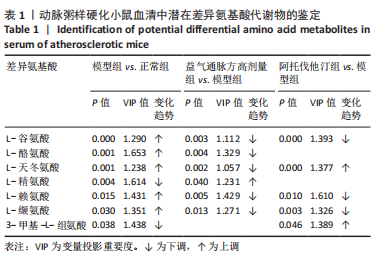
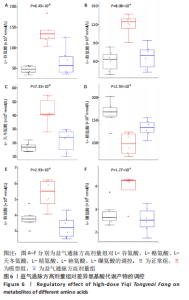
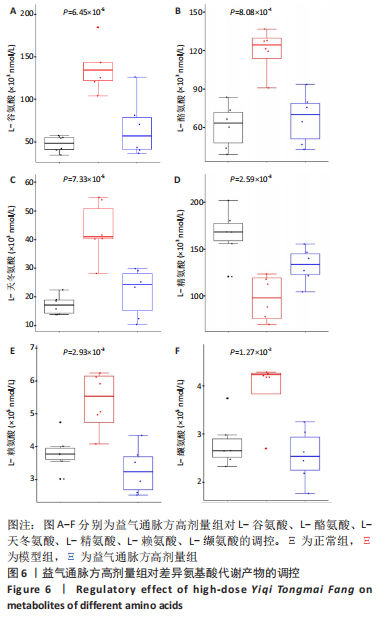
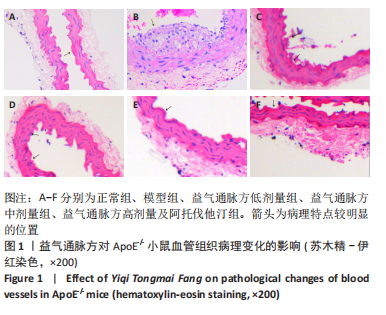
2.1 实验动物数量分析 36只小鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 益气通脉方减轻小鼠血管组织的病理改变 苏木精-伊红染色后观察血管组织,如图1箭头所示。正常组内膜整体光滑完整,平滑肌排列整齐,管腔内无斑块;模型组小鼠主动脉可见明显的斑块形成,结构形态紊乱,内皮连续性损伤,平滑肌细胞增生,斑块内泡沫细胞沉积,管腔狭窄,周围炎性细胞浸润;益气通脉方低剂量组结构较规则,可见内膜增厚,少量泡沫细胞沉积,斑块不明显;益气通脉方中剂量组病变较轻,内皮结构欠规则,平滑肌排列紊乱;益气通脉方高剂量组与阿托伐他汀组主动脉结构较清晰,内膜较平整,结构正常。此次研究结果提示各组主动脉血管壁呈动脉粥样硬化内皮损伤改变,益气通脉方及阿托伐他汀干预后的病理改变较模型组减轻,益气通脉方高剂量组与阿托伐他汀组病理改变程度较轻。"
| [1] PRASHER D, GREENWAY SC, SINGH RB. The impact of epigenetics on cardiovascular disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(1):12-22. [2] RAY S, SAWHNEY JPS, DAS MK, et al. Adaptation of 2016 European Society of Cardiology/ European Atherosclerosis Society guideline for lipid management to Indian patients –A consensus document. Indian Heart J. 2018;70(5):736-744. [3] LI M, WANG X, LI X, et al. Statins for the Primary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4870350. [4] DE JONG HJ, KLUNGEL OH, VAN DIJK L, et al. Use of statins is associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71(5):648-654. [5] PRASHER D, GREENWAY SC, SINGH RB. The impact of epigenetics on cardiovascular disease. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;98(1):12-22. [6] PAONE S, BAXTER AA, HULETT MD, et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(6):1093-1106. [7] WOLF D, LEY K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2019;124(2):315-327. [8] SAKAKURA K, NAKANO M, OTSUKA F, et al. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis plaque progression. Heart Lung Circ. 2013;22(6):399-411. [9] CHEN X, PANG S, LIN J, et al. Allicin prevents oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cell injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:133. [10] YU XH, ZHANG DW, ZHENG XL, et al. Cholesterol transport system: An integrated cholesterol transport model involved in atherosclerosis. Prog Lipid Res. 2019;73:65-91. [11] BONVALLOT N, TREMBLAY-FRANCO M, CHEVRIER C, et al. Potential input from metabolomics for exploring and understanding the links between environment and health. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2014;17(1):21-44. [12] 张文涛,崔应麟,郑伟锋,等.康益胶囊联合常规治疗对缺血性中风急性期患者的临床疗效[J].中成药,2021,43(6):1676-1679. [13] MEIR KS, LEITERSDORF E. Atherosclerosis in the apolipoprotein-Edefificient mouse: a decade of progress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(6):1006-1014. [14] 魏伟, 吴希美, 李元建. 药理实验方法学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2010. [15] WU M, YANG S, WANG S, et al. Effect of Berberine on Atherosclerosis and Gut Microbiota Modulation and Their Correlation in High-Fat Diet-Fed ApoE-/- Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:223. [16] 李千会,葛卓望,田丁,等. 人参皂苷Rg1对心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤的保护作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(6):1460-1466. [17] 叶劲涛,李锋涛,宋焕瑾,等.人参皂苷Rg1对氧糖剥夺/复氧复糖损伤PC12细胞的保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(7): 1090-1096. [18] 聂忠富,孙小燕,张太平,等.人参皂苷Compound K对动脉粥样硬化大鼠氧化应激、炎症因子和血管活性物质的影响[J].河北中医,2019,41(7):1042-1047. [19] 赵培,李永辉,高伟,等.三七总皂苷通过调节TLR4/SYK信号抑制ApoE 基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化泡沫细胞的形成[J].天然产物研究与开发,2021,33(8):1267-1273. [20] 江小萍,曾凡鹏,刘首明,等.三七总皂苷对动脉粥样硬化患者血管炎症因子及颈动脉内膜中层厚度和斑块的影响[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(10):1753-1754+1779. [21] 陈丽,蔡惠铃,李影雄,等.注射用丹参多酚酸盐对动脉粥样硬化大鼠的作用和机制探讨[J].中医药导报,2021,27(3):4-8. [22] 霍春青.土元提取物对脂多糖诱导血管内皮细胞一氧化氮合酶表达的调节作用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2014. [23] 刘孟楠,任维,罗钢,等.蛭龙活血通瘀胶囊对U937巨噬细胞焦亡的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2020,31(10):2371-2374. [24] 李洋洋,杨乔,胡耀红.水蛭粉对动脉粥样硬化大鼠血管平滑肌细胞的影响[J].中成药,2016,38(4):894-898. [25] 张翔,江兴林,周利玲,等.大黄素对氧化应激所致动脉粥样硬化模型大鼠的干预研究[J].中医药导报,2016,22(21):27-29. [26] 赵剑锋. 大黄素抑制TLR4介导的动脉粥样硬化炎症的分子机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012. [27] WU G. Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids. 2009;37(1):1-17. [28] FU L, DONG SS, XIE YW, et al. Down-regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase at a frequently deleted region 16q22 contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 51(5): 1624-1634. [29] WYPYCH TP, PATTARONI C, PERDIJK O, et al. Microbial metabolism of L-tyrosine protects against allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(3):279-286. [30] 郭天宇,温雨晴,金佰明,等. 酪氨酸对小鼠体内氧化应激机制的动态研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2017,38(19):2238-2239. [31] WYPYCH TP, PATTARONI C, PERDIJK O, et al. Microbial metabolism of L-tyrosine protects against allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(3):279-286. [32] WÜRTZ P, RAIKO JR, MAGNUSSEN CG, et al. High-throughput quantification of circulating metabolites improves prediction of subclinical atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(18):2307-2316. [33] BENJAMIN EJ, VIRANI SS, CALLAWAY CW, et al. American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492. [34] DENNINGER JW, MARLETTA MA. Guanylate cyclase and the.NO/cGMP signaling pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1411:334-350. [35] MORRIS SM JR. Enzymes of arginine metabolism. J Nutr. 2004;134(10 Suppl):2743S-2747S; discussion 2765S-2767S. [36] WYSS M, KADDURAH-DAOUK R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2000;80(3):1107-1213. [37] 孟中华,尚莎莎,王建茹,等.巨噬细胞PI3K/Akt通路与动脉粥样硬化的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(1):102-106. [38] YANNI AE, AGROGIANNIS G, NOMIKOS T, et al. Oral supplementation with L-aspartate and L-glutamate inhibits atherogenesis and fatty liver disease in cholesterol-fed rabbit. Amino Acids. 2010;38(5):1323-1331. [39] MARTIN-LORENZO M, GONZALEZ-CALERO L, MAROTO AS, et al. Cytoskeleton deregulation and impairment in amino acids and energy metabolism in early atherosclerosis at aortic tissue with reflection in plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):725-732. [40] TZOULAKI I, CASTAGNÉ R, BOULANGÉ CL, et al. Serum metabolic signatures of coronary and carotid atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(34):2883-2896. [41] YU D, RICHARDSON NE, GREEN CL, et al. The adverse metabolic effects of branched-chain amino acids are mediated by isoleucine and valine. Cell Metab. 2021;33(5):905-922. [42] HE XD, GONG W, ZHANG JN, et al. Sensing and Transmitting Intracellular Amino Acid Signals through Reversible Lysine Aminoacylations. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):151-166. [43] 倪宇昕,章立群,谢安琪,等. L-缬氨酸对巨噬细胞raw264.7的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(24):6069-6073. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Ou Hangjun, Zhao Guangjian, Pan Yujia, Gong Caiwei, Zhao Quanwei, Liu Danan. Construction of a lentiviral vector overexpressing fibronectin type III domain containing 5 to inhibit apoptosis of endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 216-222. |
| [3] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Application and role of exosome-regulated ferroptosis in disease diagnosis and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2443-2452. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiyong, Huang Jingwen, Xie Bingying, Chen Sainan, Xie Lihua, Chen Xuan, Li Shengqiang, Ge Jirong. Anti-osteoporosis effect of Gushukang in ovariectomized rats: a lumbar metabonomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5185-5190. |
| [5] | Wei Gang, Gao Shangyuan, Zhang Ying, Huang Weiyi. Immunostimulation combined with liquid nitrogen freezing to construct a rat model of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5656-5661. |
| [6] | Zhang Wenjiang, Yi Jian, Jia Ping, Chen Bowei, Wang Yong, Liu Baiyan. Genotype identification and model application of apolipoprotein E knockout mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1103-1108. |
| [7] | Cao Jingli, , Marina S. Ferguson, Sun Jie, Zhang Dong, Liu Li, Li Zirui, Wang Yajie, Sui Binbin, Shen Mi, Gao Peiyi, , Thomas S. Hatsukami, Zhao Xihai, Yuan Chun, , . An en bloc paraffin embedding method for serial sectioning of carotid atherosclerotic plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5041-5045. |
| [8] | Sun Zhizhong1, Jiang Yanjun1, Ji Shuliang1, Shi Chushuo1, Zhang Tian1, Zhou Xiaoqi1, Yang Zhihua1, Chen Yuexuan1, Luo Chuanjin2. Role of baicalin in the treatment of mouse models of atherosclerosis and the underlying mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3037-3043. |
| [9] | Chen Yili, Lao Yonghua, Zhang Shaoqun, Wu Baofeng, Li Yikai . Hydrodynamic model of carotid artery atherosclerosis: hemodynamic changes of carotid atherosclerotic plaques under cervical rotatory manipulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2403-2408. |
| [10] | Wang Feng-jiao, Gao Xiang, Yin Hang, Chen Li, Qin Shu-cun, Yang Na-na. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein can affect the function of endothelial progenitor cells: how to increase cell number and function? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(29): 4706-4712. |
| [11] | Chen Ting-ting, Cao Yuan-zhi, Xiong Wei, Dong Shao-hong. Construction of mouse chemerin gene knock-down cell lines mediated by adenovirus vector [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3875-3879. |
| [12] | Wang Xue-mei, Wei Qin, Duan Ming-jun, Zhang Chun, Yang Yi-ning. Effects of recombinant adenovirus-mediated adiponectin on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and the underlying mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(1): 115-121. |
| [13] | Hu Ping, Chen Yi, Sheng Jing. Vascular ultrastructure in atherosclerosis rats after carotid injury under an electron microscope [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7334-7340. |
| [14] | Ji Meng, Wang Wei, Hu Wen-li . Long-term effects of Enterprise self-expanding intracranial stent implantation in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis in patients with ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(34): 5070-5075. |
| [15] | Ma Zhi-gang, Sun Yu-heng, Peng Xiao-xin, Hu Hong-tao. Use of the Smart nitinol stent system for the treatment of severe atherosclerotic carotid stenosis: study protocol for a retrospective non-randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(30): 4554-4560. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||